For a chemical reaction (the system) carried out at constant pressure – with the only work done caused by expansion or contraction – the enthalpy of reaction (also called the heat of reaction, ΔHrxn) is equal to the heat exchanged with the surroundings (qp).
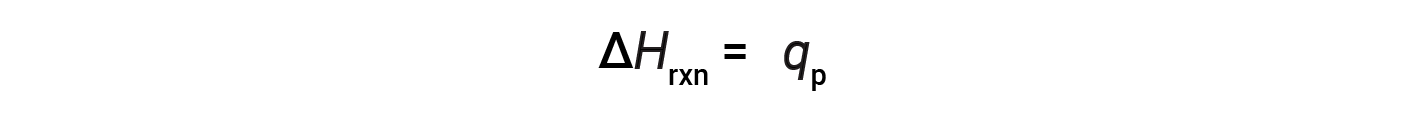
The change in enthalpy is an extensive property, and it depends on the amounts of the reactants participating in the reaction (or the number of moles of reactants). The change in enthalpy is specific to the reaction, and the physical states of the reactant and product species are important. An exothermic reaction is characterized by a −ΔHrxn value, while an endothermic reaction has a +ΔHrxn value.
Because the amount of heat released or absorbed by a reaction corresponds to the amount of each substance consumed or produced by the reaction, it is convenient to use a thermochemical equation to represent the changes in both matter and energy. In a thermochemical equation, the change in enthalpy of a reaction is shown as ΔHrxn, and it is generally provided following the equation for the reaction. The magnitude of ΔHrxn indicates the amount of heat associated with the reaction shown in the chemical equation. The sign of ΔHrxn indicates if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic, as written. In the following equation, 1 mole of hydrogen gas and 1/2 mole of oxygen gas (at some temperature and pressure) react to form 1 mole of liquid water (at the same temperature and pressure).
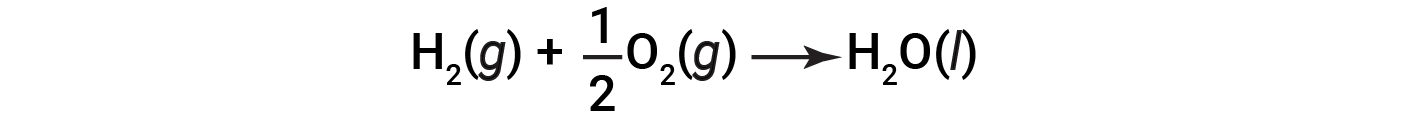
This equation indicates that 286 kJ of heat is released to the surroundings. In other words, 286 kJ of heat is released (reaction is exothermic) for every mole of hydrogen that is consumed or for every mole of water that is produced. Therefore, the enthalpy of reaction is a conversion factor that can be used to calculate the amount of heat that is released or absorbed during reactions involving specific amounts of reactants and products.
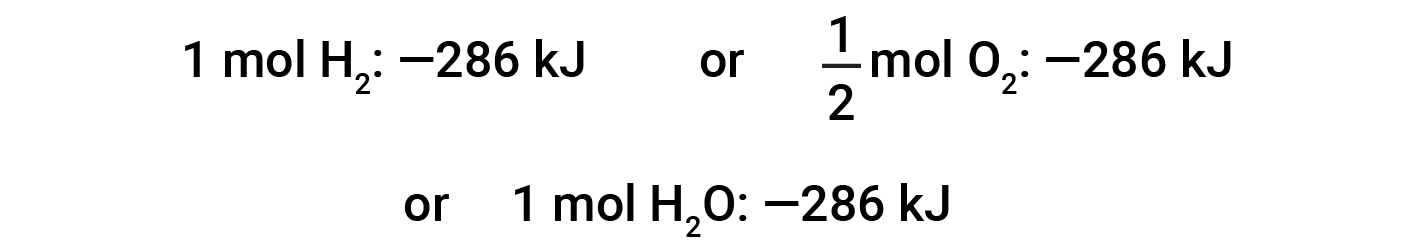
If the coefficients of the chemical equation are multiplied by some factor (i.e., if the amount of a substance is changed), the change in enthalpy must be multiplied by that same factor.
(two-fold increase in amounts)
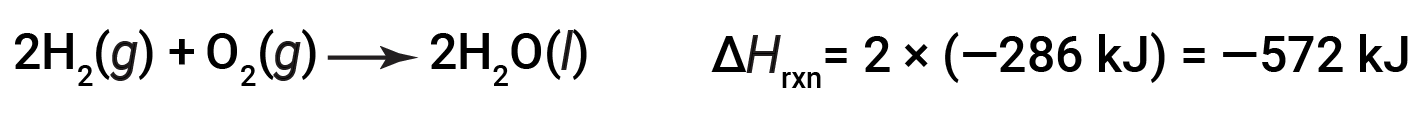
(two-fold decrease in amounts)
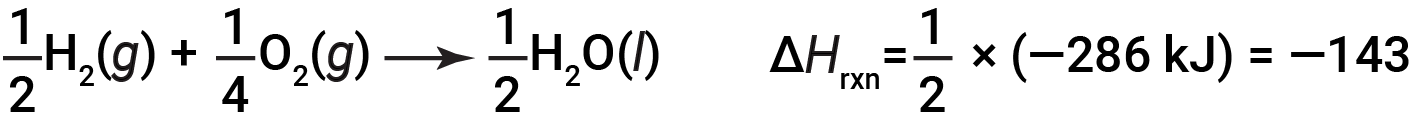
To illustrate that the enthalpy change of a reaction depends on the physical states of the reactants and products, consider the formation of gaseous water (or water vapor). When 1 mole of hydrogen gas and ½ mole of oxygen gas react to form 1 mole of gaseous water, only 242 kJ of heat are released, as opposed to 286 kJ of heat, which is released when liquid water forms.
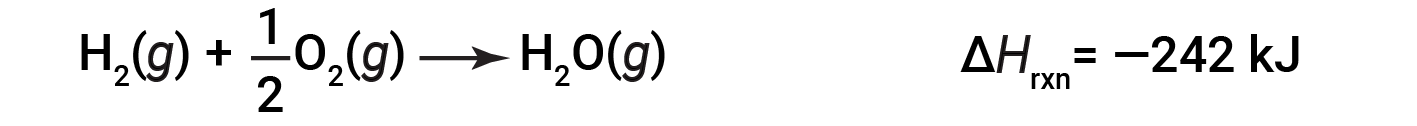
Aus Kapitel 6:

Now Playing
6.7 : Thermochemische Gleichungen
Thermochemie
27.8K Ansichten

6.1 : Energiegrundlagen
Thermochemie
36.3K Ansichten

6.2 : Erster Hauptsatz der Thermodynamik
Thermochemie
30.4K Ansichten

6.3 : Innere Energie
Thermochemie
28.2K Ansichten

6.4 : Quantifizierung von Wärme
Thermochemie
52.7K Ansichten

6.5 : Quantifizierung von Arbeit
Thermochemie
18.7K Ansichten

6.6 : Enthalpie
Thermochemie
34.3K Ansichten

6.8 : Konstantdruck-Kalorimetrie
Thermochemie
83.4K Ansichten

6.9 : Kalorimetrie bei konstantem Volumen
Thermochemie
26.6K Ansichten

6.10 : Hessscher Wärmesatz
Thermochemie
43.7K Ansichten

6.11 : Standardbildungsenthalpie
Thermochemie
40.4K Ansichten

6.12 : Reaktionsenthalpie
Thermochemie
31.2K Ansichten
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten