ניתוח זרבובית: וריאציות במספר ה-Mach ובלחץ לאורך התכנסות וזרבובית מתפצלת
Overview
מקור: שרייאס נרסיספור, הנדסת מכונות וחלל, אוניברסיטת צפון קרוליינה סטייט, ראלי, NC
זרבובית היא התקן המשמש בדרך כלל להאצת הזרימה או להאטה מכוח חתך הרוחב השונה שלה. חרירים נמצאים בשימוש נרחב במערכות הנעה בחלל. ברקטות, דלק הנפלט מהתא מואץ דרך זרבובית כדי ליצור כוח תגובה המניע את המערכת. במנועי סילון, זרבובית משמשת להפיכת אנרגיה ממקור בלחץ גבוה לאנרגיה קינטית של הפליטה כדי לייצר דחף. המודל האיסנטרופי לאורך הזרבובית מספיק לניתוח מסדר ראשון שכן הזרימה בזרבובית מהירה מאוד (ולכן אדיאבטית לקירוב ראשון) עם מעט מאוד חיכוכים מפסידים (מכיוון שהזרימה כמעט חד ממדית עם שיפוע לחץ חיובי, אלא אם צורת גלי הלם וחרידים קצרים יחסית).
בניסוי זה, שני סוגים של חרירים מותקנים על אסדת בדיקת זרבובית, וזרימת לחץ נוצרת באמצעות מקור אוויר דחוס. החריקות מנוהלות עבור הגדרות לחץ אחורי שונות כדי לנתח את הזרימה הפנימית בזרבוביות בתנאי זרימה משתנים, לזהות את משטרי הזרימה השונים ולהשוות את הנתונים לתחזיות תיאורטיות.
Principles
זרבובית מתחילה בנקודה שבה קוטר התא מתחיל לרדת. ישנם שני סוגים עיקריים של חרירים: הזרבובית המתכנסת והזרבובית המתפצלת. אחד מהיחסים האיסנטרופיים השולטים בין מספר Mach (M), אזורזרבובית (A) ומהירות (u) מיוצג על-ידי המשוואה הבאה:
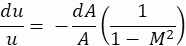 (1)
(1)
כאשר u הוא המהירות, A הוא אזור הזרבובית, ו- M הוא מספר האך. בהתבסס על משוואה 2,
- ב- M = 0, הזרימה היא סטטית, כלומר, מצב ללא זרימה קיים
- ב 0 < M < 1, כמו האזור פוחת, עלייה פרופורציונלית במהירות הזרימה הוא ציין
- ב M ≥ 1, כל עלייה באזור תיצור עלייה יחסית במהירות
חרירים מתכנסים, כפי שמוצג באיור 1, הם צינורות עם אזור שיורד מכניסת הזרבובית ליציאה (או לגרון) של הזרבובית. ככל שאזור הזרבובית פוחת, מהירות הזרימה גדלה, כאשר מהירות הזרימה המרבית מתרחשת בגרון הזרבובית. ככל שמהירות זרימת המפרצון גדלה, מהירות הזרימה בגרון הזרבובית ממשיכה לגדול עד שהיא מגיעה לאך 1. בשלב זה, הזרימה בגרון נחנקת, כלומר כל עלייה נוספת של מהירות זרימת המפרצון לא תגדיל את מהירות הזרימה בגרון. מסיבה זו, חרירי התכנסות משמשים להאצת נוזלים במשטר הזרימה התת-קולי בלבד וניתן למצוא אותם בדרך כלל בכל המטוסים המסחריים (למעט הקונקורד) כשהם נעים במהירויות תת-קוליות.

איור 1. סכמטי של זרבובית מתכנסת. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
עבור כלי רכב כמו רקטות ומטוסים צבאיים, שחייבים לנסוע במהירות הקול ומעליה, נעשה שימוש בזרבובית מתפצלת, כפי שמודגם באיור 2. בזרבובית מתפצלת, החלק המתכנס מלווה בקטע זרבובית מתפצלת והוא מעוצב באופן כזה שהזרימה נחנקת בגרון של קטע המתכנס, ובכך מתקנת את קצב זרימת המסה במערכת. לאחר מכן הזרימה מתרחבת באופן טרופי כדי להגיע למספרי מאק על-קוליים במקטע המתפצל. מהירויות הזרימה העל-קוליות שנקבעו במקטע המתפצל הן פונקציה של יחסי אזור הזרבובית לאחר הגרון. בהתבסס על העיצוב של הזרבובית המתפצלת, מהירות הזרימה לאחר הזרבובית יכולה: (i) להקטין למהירויות תת-קוליות, (ii) להפוך לעל-קוליות, לגרום להלם רגיל ולאחר מכן להקטין למהירויות תת-קוליות ביציאת הזרבובית, או (iii) להישאר על-קולית לאורך כל מקטע ההתפצלות. כמות הדחף המיוצר על ידי הזרבובית תלויה במהירות היציאה ובלחץ ובקצב זרימת המסה דרך הזרבובית.
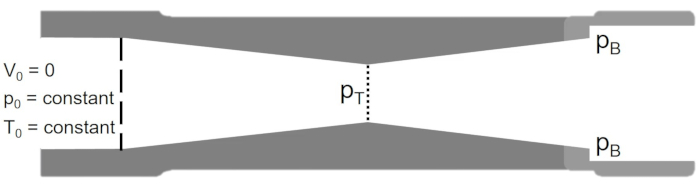
איור 2. סכמטי של זרבובית מתכנסת. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
הלחץ האחורי (pB) הוא הגורם המניע הקובע את מצב הזרימה בזרבובית. כאשר לחץ הקיפאון, pO = pB, אין זרימה דרך הזרבובית. כאשר pB מצטמצם, מספר המך בגרון (pT) גדל עד הזרימה נחנקת (MT = 1). המצב שבו מתרחשת זרימה חנוקה באמצעות הקשר isentropic:
 (2)
(2)
כאשר γ הוא יחס החום הספציפי של הנוזל. החלפת γ = 1.4 (יחס חום ספציפי לאוויר יבש) במשוואה 2, אנו מקבלים יחס לחץ אחורי של:
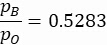 (3)
(3)
משוואה 3 מגדירה את הגבול בין משטרי הזרימה הלא חנוקים והחנוקים. כאשר הזרימה נחנקת, מספר ה- Mach אינו גדל עוד והוא מוגבל ב- M = 1.
במקרה של זרבובית מתכנסת, יציאת הזרבובית תואמת את גרון הזרבובית (כפי שניתן לראות באיור 1); לכן, מספר מאך ממש ביציאה אינו עולה על 1, כלומר, הזרימה לעולם לא עוברת על-קולית. ברגע שהזרימה יוצאת מהזרבובית, היא עוברת התרחבות, בשל הגידול הפתאומי באזור שעלול להוביל למהירויות זרימה על-קוליות (בלתי מבוקרות).
בהתבסס על איור 3, להלן תנאי הזרימה שניתן לצפות בהם בזרבובית מתכנסת:
- אין מצב זרימה, שבו לחץ הגב שווה ללחץ הכולל.
- זרימה תת-קולית, שבה הזרימה מאיצה ככל שהאזור פוחת, והלחץ יורד.
- זרימה תת-קולית, שם יש תאוצה גבוהה משמעותית והלחץ יורד.
- זרימה חנוקה, שבה כל ירידה בלחץ אינה מאיצה את הזרימה.
- זרימה חנוקה, שם הזרימה מתרחבת לאחר יציאת הזרבובית (נחשבת לא-איסנטרופית).

איור 3. תנאי זרימה ומשטרים בזרבובית מתכנסת (תחזיות תיאורטיות). אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
הפרמטר זרימת המסה (MFP) הוא משתנה הקובע את הקצב שבו המסה זורמת דרך הזרבובית וניתנת על-ידי המשוואה:
 (4)
(4)
כאן, 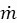 הוא קצב זרימת המסה דרך הזרבובית, T O הוא טמפרטורת הקיפאון, ו- AT הוא אזור הגרון, אשר, במקרה של זרבובית מתכנסת, שווה לאזור ביציאת הזרבובית, AE. כפי שנצפה באיור 3, עד לזרימה חנוקה, ה- MFP ממשיך לעלות. לאחר הזרימה נחנקת, קצב זרימת המסה קבוע, ו- MFP נשאר קבוע להפחתת יחסי לחץ הגב.
הוא קצב זרימת המסה דרך הזרבובית, T O הוא טמפרטורת הקיפאון, ו- AT הוא אזור הגרון, אשר, במקרה של זרבובית מתכנסת, שווה לאזור ביציאת הזרבובית, AE. כפי שנצפה באיור 3, עד לזרימה חנוקה, ה- MFP ממשיך לעלות. לאחר הזרימה נחנקת, קצב זרימת המסה קבוע, ו- MFP נשאר קבוע להפחתת יחסי לחץ הגב.
כדי להשיג זרמים על-קוליים מבוקרים בזרבובית, יש להציג קטע מתפצל לאחר גרונה של זרבובית מתכנסת, כפי שמודגם באיור 2. ברגע שהזרימה נחנקת בגרון של זרבובית מתכנסת (המבוססת על משוואה 3), שלושה תנאי זרימה אפשריים יכולים להתרחש: זרימה איסנטרופית תת-קולית (הזרימה מואטת לאחר המצב החנוק), זרימה על-קולית לא-איסנטרופית (שבה הזרימה מאיצה באופן סופר-אוני, יוצרת גל הלם - אזור דק של מולקולות מגובשות היוצר נורמלי לנקודה מסוימת על הזרבובית וגורם לשינוי פתאומי בתנאי הזרימה, המכונה בדרך כלל הלם רגיל - ומאט באופן תת-תאי לאחר ההלם), או זרימה איסנטרופית על-קולית (שם הזרימה מאיצה באופן סופר-סוני לאחר המצב החנוק). איור 4 מציג את שבעת הפרופילים הבאים בעלילת יחס המיקום לעומת הלחץ. שים לב שהקו המקווקו האנכי הראשון משמאל ל- p/pO לעומת המרחק לאורך התוויית הזרבובית הוא מיקום הגרון, הקו המקווקו האנכי השני הוא מיקום יציאת הזרבובית, והקו המקווקו האופקי מסמן את המצב החנוק.
- זרימה תת-קולית שלעולם לא מגיעה למצב חנוק.
- זרימה תת-קולית המגיעה למצב חנוק אך אינה משיגה מהירויות על-קוליות (נחשבות איסנטרופיות).
- זרימה תת-קולית המגיעה למצב חנוק, כאשר הזרימה העל-קולית שנוצרת ויוצרת הלם רגיל, אשר חווה אז האטה תת-קולית. כאן, ההלם הרגיל גורם לירידה פתאומית במהירות ולעלייה בלחץ הגב, כפי שמעיד העלייה הפתאומית ב- p / pO.
- זרימה תת-קולית המגיעה למצב חנוק, כאשר הזרימה העל-קולית שנוצרת ויוצרת הלם רגיל לאחר הזרבובית (הנחשבת לאיסנטרופית בזרבובית).
- זרימה מורחבת יתר על המידה – הלחץ ביציאת הזרבובית נמוך יותר מלחץ הסביבה, מה שגורם למטוס היוצא מהזרבובית להיות מאוד לא יציב עם שינויים עצומים בלחץ ובמהירות כשהוא נע במורד הזרם.
- זרימה לאחר המצב החנוק הוא על קולי דרך הזרבובית, ולא נוצר הלם.
- זרימה לא מורחבת – הלחץ ביציאת הזרבובית גבוה יותר מלחץ הסביבה ומביא להשפעות דומות לזרימה מורחבת יתר על המידה.

איור 4. תנאי זרימה ומשטרים בזרבובית מתפצלת (תחזיות תיאורטיות). אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
Procedure
בהדגמה זו נעשה שימוש באסדת בדיקת זרבובית, שהורכבה ממקור אוויר דחוס המתעל אוויר בלחץ גבוה דרך הזרבוביות הנבדקות, כפי שמוצג באיור 5. לחץ הזרימה נע בין 0 - 120 פסאיי והוא נשלט באמצעות שסתום מכני. בעוד הלחצים נמדדים באמצעות חיישן חיצוני, קצבי זרימת המסה בזרבובית נמדדים על ידי זוג רוטהמטרים שהוצבו ממש לפני הפליטה של אסדת בדיקת הזרבובית.

איור 5. אסדת בדיקת זרבובית. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
1. מדידת לחץ צירי בזרבוביות מתכנסות ומתכנסות
- עלו על הזרבובית המתכנסת במרכז אסדת בדיקת הזרבובית, כפי שמוצג באיור 5. המקטע הדו-ממדי לזרבובית המתכנסת עם תוויות עבור הקשות הלחץ מוצג באיור 6.
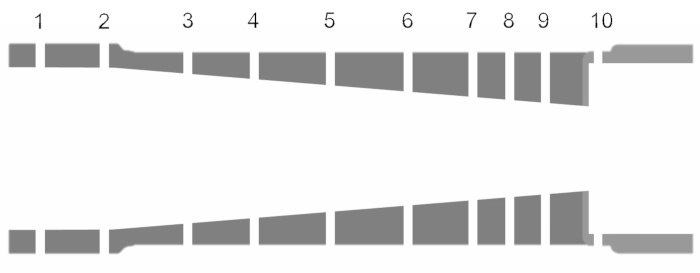
איור 6. גיאומטריה של זרבובית התכנסות. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
- חבר את 10 יציאות הלחץ הסטטי ואת יציאת לחץ הקיפאון למערכת מדידת הלחץ באמצעות צינורות PVC גמישים בלחץ גבוה.
- חבר את מערכת מדידת הלחץ לממשק התוכנה הגרפית לקריאת נתוני לחץ בזמן אמת.
- קח את קריאת מצב האפס/ללא זרימה.
- פתח את שסתום בקרת הזרימה המכני כדי להתחיל את זרימת האוויר.
- סובב את השסתום כדי להתאים את קצב הזרימה כדי לקבל יחס לחץ אחורי (pB/ pO) של 0.9. שים לב שהלחץ האחורי הן עבור חריני ההתכנסות והן עבור חריצי ההתכנסות-מתפצלים תואמים לקריאת נתוני הלחץ מיציאה 10.
- הקלט את הנתונים המתאימים לטבלה 1.
- הקטן את יחס הלחץ האחורי בשלבים של 0.1 עד pB/pO = 0.1 שלב 7 חוזר עבור כל הגדרה. בנוסף, חזור על שלב 7 עבור pB/pO = 0.5283 כדי ללכוד נתוני זרימה במצב הזרימה החנוק התיאורטית.
- החלף את הזרבובית המתכנסת בזרבובית המתפצלת וחזר על שלבים 1.2 - 1.8. המקטע הדו-ממדי לזרבובית המתכנסת עם תוויות עבור הקשות הלחץ מוצג באיור 7.
- עם השלמת הבדיקות, נתק את כל המערכות ופרק את אסדת בדיקת הזרבובית.
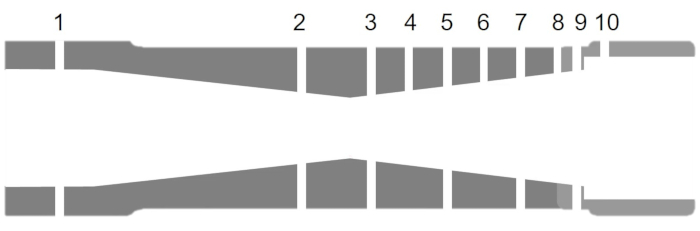
איור 7. גיאומטריה של זרבובית מתפצלת. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
טבלה 1. נתונים שנאספו לניסוי הזרבובית.
| הקש על מספר | מיקום צירי של הקשה (ב) | יחס שטח זרבובית (A/A) |
Pסטטי (פסאיי) |
Po (פסאיי) |
מסה קצב זרימה (שבלולים/שני) |
Patm (פסאיי) |
To (°F) |
| איור 6/7 | טבלה 2 | טבלה 2 | לחץ מד | מד לחץ |
רוטמטר | לחץ מד | חיישן טמפרטורה |
טבלה 2. נתוני גיאומטריה זרבובית.
| הקש על מספר | זרבובית מתכנסת | זרבובית מתכנסת-מתפצלת | ||
| מיקום צירי של הקשה (ב) | יחס שטח זרבובית (A/A) | מיקום צירי של הקשה (ב) | יחס שטח זרבובית (A/A) | |
| 1 | 0 | 60.14 | 0 | 60.14 |
| 2 | 1 | 51.379 | 4.5 | 6.093 |
| 3 | 2 | 35.914 | 6.5 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 23.218 | 6.9075 | 1.053 |
| 5 | 4 | 13.275 | 7.3795 | 1.222 |
| 6 | 5 | 6.094 | 7.8515 | 1.403 |
| 7 | 5.5 | 3.54 | 8.3235 | 1.595 |
| 8 | 6 | 1.672 | 8.7955 | 1.802 |
| 9 | 6.5 | 1 | 9.2675 | 2.02 |
| 10 | 7 | 60.041 | 9.5 | 60.041 |
Results
הקבועים הבאים שימשו בניתוח: חום ספציפי של אוויר יבש, γ: 1.4; אזור זרבובית ייחוס, Ai = 0.0491ב- 2, ולחץ אטמוספרי סטנדרטי, Patm = 14.1 פסאיי. איורים 8 ו-9 מראים את השונות ביחס הלחץ ובמספר ה-Mach לאורך הזרבובית (מנורמלת בהתבסס על אורך הזרבובית הכוללת) עבור הגדרות שונות של לחץ גב עבור חרירים מתכנסים ומתפצלים, בהתאמה. פרמטר זרימת המסה לעומת יחס הלחץ האחורי הוא גם שרטט ונחקר עבור שני החרירים.
מאיור 8אנו מבחינים שככל שיחס ה-p B/pO יורד(עד 0.5283), הזרימה בכל חלק בזרבובית היא תת-קולית ומתגברת עם הירידה בשטח. ב- p/pO ומתחתיו = 0.5283, מספר המאך בגרון (מרחק זרבובית מנורמל = 0.93) אינו עולה על אחד. זה ממחיש בבירור כי הזרימה נחנקת בגרון. מעבר ליציאת הגרון/זרבובית, יש התרחבות בלתי מבוקרת של הזרימה, מה שמוביל למספרי מאך על-קוליים. המגמות הכוללות בהתפלגות ה-p/pO תואמות למגמות תיאורטיות מאיור 3. המגמות ב- MFP עוקבות אחר התוצאות התיאורטיות עד pB/pO = 0.6 אך מתחילות לרדת במקום לרמה לערכים נמוכים יותר של יחסי לחץ אחורי. בהתחשב בכך שהזרימה נחנקת, ה- MFP צריך להיות קבוע. עם זאת, בהתבסס על מיקום הברז המודד את לחץ הגרון (הקש 9, איור 6), אנו רואים שהמדידות נלקחות מעט לפני גרון הזרבובית האמיתי שמוביל למדידה שגויה של ה- MFP.
עבור הזרבובית המתפצלת(איור 9), נצפתה זרימהתת-קולית עד ש-p/p O בגרון (מרחק זרבובית מנורמל = 0.68) שווה ל- 0.5283 (מצב זרימה חנוק). הפחתה נוספת של pB/ pO מראה שלושה דפוסים נפרדים:
a. תבנית 1 - הזרימה מגיעה למצב חנוק בגרון ומאטה באופן תת-סאנדי בסעיף המתפצל (0.8 < pB/pO < 0.7).
b. תבנית 2 - הזרימה מאיצה באופן על-סנוני מעבר לגרון, יוצרת הלם בקטע המתפצל ומאטה (במקרים מסוימים למהירויות תת-קוליות) עבור 0.7 < pB/pO < 0.3.
ג. תבנית 3 - הזרימה ממשיכה להאיץ באופן על-סוני למשך כל מקטע ההתפצלות עבור ערכי pB/pO הנמוכים מ- 0.3.
ה- MFP עולה עם ירידה ביחסי הלחץ האחורי, מגיע לשיאו ב- pB/ pO = 0.5, ומתחיל לרדת במקום להישאר קבוע כצפוי על ידי התיאוריה.
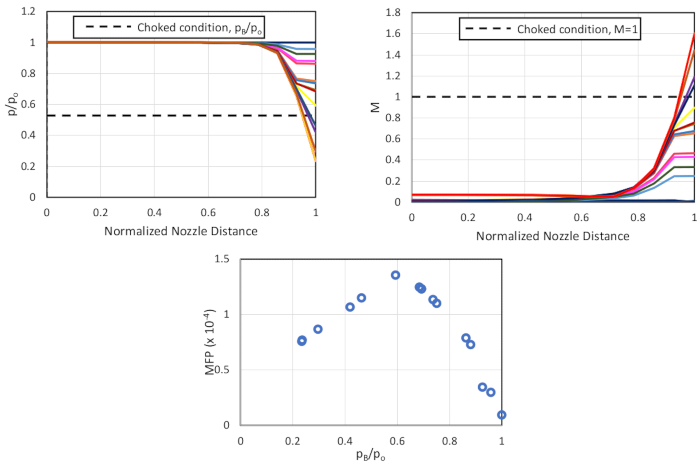
איור 8. תוצאות עבור זרבובית מתכנסת (מימין למעלה, כיוון השעון) יחס לחץ על פני הזרבובית; וריאציה במספר Mach על-פני הזרבובית; וריאציה בפרמטר מחריש המוני עם יחס לחץ אחורי. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
Application and Summary
חרירים משמשים בדרך כלל במערכות הנעה של מטוסים ורקטות מכיוון שהם מציעים שיטה פשוטה ויעילה להאצת הזרימה במרחקים מוגבלים. על מנת לתכנן חרירים שיתאימו ליישום נתון, הבנה של התנהגות הזרימה וגורמים המשפיעים על ההתנהגות האמורה עבור מגוון תנאי זרימה חיונית לתכנון מערכות הנעה יעילות. בהדגמה זו, חריני ההסתה וההתכנסות - שניים מסוגי הזרבובית הנפוצים ביותר המשמשים ביישומי תעופה וחלל - נבדקו באמצעות אסדת בדיקת זרבובית. וריאציות הלחץ ומספר המך על פני שתי החרירים נחקרו עבור מגוון רחב של תנאי זרימה.
תוצאות בדיקות הזרבובית המתכנסות הראו כי המגבלה המרבית עד אשר ניתן להאיץ את הזרימה היא M = 1, ובשלב זה הזרימה בגרון הזרבובית נחנקת. ברגע שהזרימה נחנקת, כל עלייה במהירות זרימת המפרצון לא הגדילה את מהירות הזרימה בגרון/יציאה למהירויות על-קוליות. ניתוח הזרבובית המתפצלת מספק תובנה כיצד ניתן להשיג מהירויות זרימה על-קוליות ברגע שהזרימה נחנקת בגרון. ראינו גם שלושה סוגים של זרימות שניתן להשיג לאחר הגרון החנוק בהתאם ליחס הלחץ האחורי של הזרימה. השוואה בין מגמות הלחץ שהושגו הן עבור חרירים מסוג התכנסות והן עבור חרירים מתפצלים עם תוצאות תיאורטיות הייתה מצוינת. עם זאת, תוצאות הניסוי הראו שפרמטר זרימת המסה יורד לערכים נמוכים יותר של יחס לחץ אחורי במקום לרמה ברגע שהערך המרבי הושג, כפי שחזו התיאוריה.
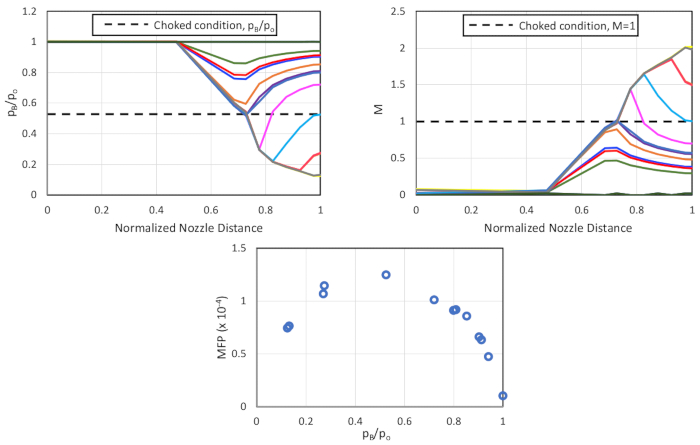
איור 9. תוצאות עבור זרבובית מתפצלת (מימין למעלה, בכיוון השעון) וריאציה ביחס הלחץ על פני הזרבובית; וריאציה במספר Mach על-פני הזרבובית; וריאציה בפרמטר מחריש המוני עם יחס לחץ אחורי. אנא לחץ כאן כדי להציג גירסה גדולה יותר של איור זה.
Tags
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
ניתוח זרבובית: וריאציות במספר ה-Mach ובלחץ לאורך התכנסות וזרבובית מתפצלת
Aeronautical Engineering
38.0K Views

ביצועים אווירודינמיים של דגם מטוס: DC-6B
Aeronautical Engineering
8.3K Views

אפיון מדחף: שינויים ב-גובה, בקוטר ובמספר הלהב בביצועים
Aeronautical Engineering
26.5K Views

התנהגות חיל האוויר: התפלגות לחץ על כנף קלארק Y-14
Aeronautical Engineering
21.2K Views

ביצועי כנף קלארק Y-14: פריסה של התקנים בעלי הרמה גבוהה (מדפים ולוחות)
Aeronautical Engineering
13.4K Views

שיטת כדור מערבולת: הערכת איכות זרימת מנהרת הרוח
Aeronautical Engineering
8.7K Views

זרימה גלילית צולבת: מדידת התפלגות לחץ והערכת מקדמי גרירה
Aeronautical Engineering
16.2K Views

שלירן הדמיה: טכניקה לדמיין תכונות זרימה על קולית
Aeronautical Engineering
11.7K Views

הדמיה של זרימה במנהרת מים: התבוננות במערבולת המובילה מעל כנף דלתא
Aeronautical Engineering
8.2K Views

הדמיה של זרימת צבע פני השטח: שיטה איכותית להתבוננות בדפוסי סטריקלין בזרימה על-קולית
Aeronautical Engineering
4.9K Views

צינור פיטו-סטטי: מכשיר למדידת מהירות זרימת האוויר
Aeronautical Engineering
49.2K Views

אנמומטריית טמפרטורה קבועה: כלי לחקר זרימת שכבת גבול סוערת
Aeronautical Engineering
7.3K Views

מתמר לחץ: כיול באמצעות צינור פיטו-סטטי
Aeronautical Engineering
8.5K Views

בקרת טיסה בזמן אמת: כיול חיישנים משובצים ורכישת נתונים
Aeronautical Engineering
10.3K Views

אווירודינמיקה רב-תכליתית: אפיון דחף על הקסאקופטר
Aeronautical Engineering
9.2K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved