Purificazione del ferrocene per sublimazione
Panoramica
Fonte: Tamara M. Powers, Dipartimento di Chimica, Texas A & M University
La sublimazione, la transizione di fase diretta di un solido in un gas senza prima diventare un liquido, avviene a temperature e pressioni inferiori a quella del punto triplo del composto (Figura 1). Il processo di sublimazione può essere utilizzato per purificare sia i solidi organici che quelli inorganici. Durante la tecnica di purificazione, un solido viene riscaldato direttamente nella fase gassosa. Tutte le impurità non volatili vengono lasciate indietro mentre il composto vaporizzato viene quindi raccolto (deposizione) come solido su una superficie fredda. Qui, useremo la sublimazione per purificare il ferrocene, un solido inorganico con una temperatura a triplo punto di 183 °C.1
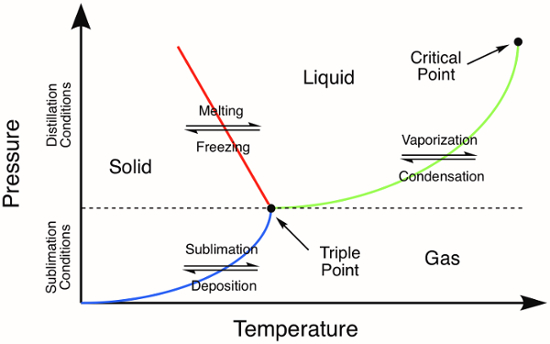
Figura 1. Diagramma di fase generico. Le linee colorate rappresentano i requisiti di pressione e temperatura per le transizioni di fase. La distillazione di un solido avverrà a pressioni e temperature superiori al punto triplo, rappresentato dalla linea verde nel diagramma di fase. La linea blu rappresenta le condizioni di temperatura e pressione in cui si verifica la sublimazione.
Procedura
1. Configurazione della linea Schlenk
Per una procedura più dettagliata, consultare i video "Schlenk Lines Transfer of Solvent" e "Degassing Liquids" nella serie Essentials of Organic Chemistry. La sicurezza della linea Schlenk deve essere rivista prima di condurre questo esperimento. La vetreria deve essere ispezionata per le crepe delle stelle prima dell'uso. Prestare attenzione per assicurarsi che O2 non sia condensato nella trappola della linea di Schlenk se si utilizza N
Risultati
Ferrocene (99%) è stato acquistato da Alfa Aesar. La sublimazione di 500 mg come descritto ha dato adito a 493 mg di prodotto isolato. Il ferrocene purificato è stato analizzato mediante 1H NMR. 1 H NMR (cloroformio-d, 300 MHz, δ, ppm): 4.17 (s).
Applicazione e Riepilogo
La sublimazione è una tecnica utilizzata nella purificazione dei solidi. I solidi che sublimano a bassa pressione e temperatura sono buoni candidati per la purificazione per sublimazione. Qui, abbiamo dimostrato come utilizzare una camera di sublimazione per sublimare il ferrocene sotto vuoto statico a 80 °C.
In un ambiente di laboratorio, la sublimazione è una tecnica utile che può essere applicata alla purificazione dei solidi in una varietà di situazioni, compresa la purificazione di m...
Riferimenti
- Kaplan, L., Kester, W. L., Katz, J. J. Some properties of iron biscyclopentadienyl. J Am Chem Soc. 74, 5531-5532 (1952).
Vai a...
Video da questa raccolta:

Now Playing
Purificazione del ferrocene per sublimazione
Inorganic Chemistry
54.3K Visualizzazioni

Sintesi di un Ti(III) metallocene utilizzando la tecnica della linea Schlenk
Inorganic Chemistry
31.5K Visualizzazioni

Scatola a guanti (Glove Box) e sensori di impurezze
Inorganic Chemistry
18.6K Visualizzazioni

Il metodo di Evans
Inorganic Chemistry
68.0K Visualizzazioni

Diffrazione a raggi X su cristallo singolo e su polveri
Inorganic Chemistry
104.0K Visualizzazioni

Spettroscopia di risonanza paramagnetica elettronica (EPR)
Inorganic Chemistry
25.4K Visualizzazioni

Spettroscopia Mössbauer
Inorganic Chemistry
21.9K Visualizzazioni

Interazione acido-base di Lewis in Ph3P-BH3
Inorganic Chemistry
38.7K Visualizzazioni

Struttura del ferrocene
Inorganic Chemistry
79.1K Visualizzazioni

Applicazione della teoria dei gruppi nella spettroscopia infrarossa
Inorganic Chemistry
45.0K Visualizzazioni

Teoria degli orbitali molecolari
Inorganic Chemistry
35.1K Visualizzazioni

Paddlewheel a quadruplo legame metallo-metallo
Inorganic Chemistry
15.3K Visualizzazioni

Celle di Grätzel (Dye-sensitized Solar Cells)
Inorganic Chemistry
15.7K Visualizzazioni

Sintesi di un complesso di cobalto (II) legato ad ossigeno
Inorganic Chemistry
51.5K Visualizzazioni

Inizio fotochimico di una reazione di polimerizzazione radicalica
Inorganic Chemistry
16.7K Visualizzazioni