このコンテンツを視聴するには、JoVE 購読が必要です。 サインイン又は無料トライアルを申し込む。
Method Article
アントラーとシカの長命の体の成長の遺伝と環境の相対的な効果の評価のためのプロトコル
要約
人口レベルの遺伝学や栄養物; に関連するシカの集団間の表現型の違い肥えた野生では困難であります。このプロトコルでは、栄養の変化が除去された制御研究の設計方法について説明します。男性オジロジカの表現型変異が遺伝学よりより栄養によって限られたがわかった。
要約
シカの表現型は、2 つのカテゴリのいずれかに配置できる: 効率、贅沢な形態成長、高級、大型武器と体の成長を促進する生存を促進します。同じ種の個体数は、環境条件によって各々 の表現型を表示します。男性オジロジカ (ジューテリウムで子鹿) の枝と体サイズ ミシシッピ州、米国の地形の地域によって異なりますが、栄養的な品質の地域変動と相関が強くがネイティブ株式、返品前の努力からの人口レベルの遺伝学の影響は無視できません。このプロトコルでは、年齢や栄養などの表現型に影響を与えるその他の要因が制御されます制御研究の設計方法について説明します。我々 は、ミシシッピ州、米国ミシシッピ州大学さびたドーキンス記念鹿単位に 3 つの地形領域から 1 歳 6 か月フォーンズ野生で捕獲された妊娠した女性をもたらした。子孫の世代別応答と母性効果を評価することの第二世代を生成する同じ地域から鹿を飼育されました。すべての鹿は、同じ高品質 (20% 粗蛋白質鹿ペレット) ダイエット広告自由を食べた。我々 は一意に各新生児をマークし、体の質量、後ろ足の足と全身の長さを記録しました。各後続の秋はリモート注射を介して個人を鎮静し、同じ津雲プラス大人の鹿の角をサンプリングします。最初から角のサイズ (地域的変動はもはや存在しない) の完全な補償と体重 (地域的変化がいくつかの証拠) 第二世代の明らかの部分的な補償の第二世代のサイズにすべて津雲が増加したことがわかった。表示角サイズの 40% の増加、および野生の収穫された相手に比較すると体の質量の 25% の増加について私たちの最も貧しい品質土壌地域に由来する 2 番目の世代の男性。ワイルド男性オジロジカ ミシシッピ州での表現型変異はより人口レベルの遺伝学より栄養価の違いに関連が示唆されました。
概要
母親の妊娠および授乳期に経験する環境要因は彼女の子孫の表現型は、遺伝子型1,2,3の独立に影響を与えます。質の低い環境に生息する母親が子供を産む効率表現型 (小さな角と体サイズ4) を示すに対し可能性が高い高品質な環境に生息する母親 (大きな枝角と体サイズ4)、高級表現型を示す子孫が生成されます。したがって、高品質の環境で永続化が子孫の生殖機会5,6,7、8に直接影響を与えるし、母の包括適応度に直接な影響を及ぼす可能性のある大規模な表現型特性を持つ男性の子孫を産む母できます。
栄養イチイ (熊の胆、 Ursus arctos9; 全体表現型特性に直接影響がLiasis fuscusI10;都 michahellis11) ミシシッピ州、米国におけるオジロジカの表現型に影響を与える可能性がありますいくつかの要因。角と本体のサイズが12他の人と比較して約 3 分の 1 いくつかの人口のために大きいです。このバリエーションの飼料品質13,14; と相関が強い最も大きい男性は、飼料の最高の品質と地域で発見されます。ただし、ミシシッピ州のオジロジカの歴史的な復興は遺伝的ボトルネックや創始者効果15,16オジロジカの表現型で観測された局所的な値変動のいくつかを説明するかもしれないまた、部分的につながっている可能性があります。
我々 は野生で捕獲されたオジロジカ、男性表現型が遺伝学人口レベルによって制限されているかどうかを評価することができたの栄養の品質管理に使用するプロトコルを提供します。このプロトコルも母性効果を遅れているかどうかを評価することができました私たちの集団に存在していた。私たちの制御設計は栄養制限3,17プロキシとして環境変数の使用に限定されている無料の至るまで人口に調査に優先されます。私たちの制御設計は、潜在的な慢性的なストレス社会に関連する相互作用を似たような住宅と畜産の実践にさらされているすべての個人と一定に保たれるよう、その他の変数もできます。さらに、ため栄養生活史の他の側面に直接影響に至る再生サバイバル18,19栄養の制御により哺乳類の生活史の側面に影響を与える他の変数を評価するために調査官。類似したプロトコルは、(例えば、 20,21) 北アメリカを渡る他の有蹄類の生活史の側面に関連する質問を評価するために記載されています。
プロトコル
Ethics Statement: The Mississippi State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approved all capture, handling, and marking techniques under protocols 04-068, 07-036, 10-033 and 13-034.
1. Establish Capture Sites, Immobilize and Transport wild White-tailed Deer
- Identify public and private properties that are enrolled in the Deer Management Assistance Program22 and establish ≥29 capture sites throughout three source regions in Mississippi, USA.
- Identify several capture locations within each source region to ensure that the range of genetic variation present in the regional population is captured.
- Note: Here, source regions included the Delta, which comprises almost 17% of total land area in Mississippi, USA, and is considered a high-quality soil region with agriculture as the primary land use23,24. All study animals were captured from this region within the distribution of O. v. virginianus25. Other regions included the Thin Loess region (upper and lower Thin Loess combined), which comprises almost 14% of total land area in Mississippi, USA and is considered a medium quality soil region. Agriculture is also a primary land use in the Thin Loess region, though not as prevalent as in the Delta23,24. All study animals were captured from this region within the distribution of O. v. virginianus21. Lastly, the Lower Coastal Plain (LCP) soil region comprises nearly 22% of Mississippi and is classified as a low quality soil region. Primary land uses in the LCP are pine timber production and livestock grazing23,24. The LCP also overlaps the geographical distribution of O. v. osceola; four of the six source populations were within 21 km of this distribution25. This subspecies was described as smaller than O. v. virginianus26.
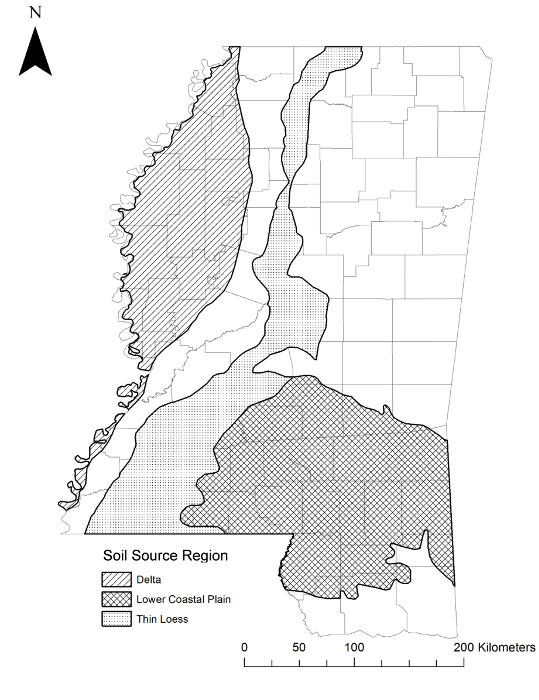
Figure 1: Source Populations. Physiographic regions where pregnant dams and fawns were caught in Mississippi, USA. This figure has been modified from reference31. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Select potential capture sites that meet the following criteria; habitat characteristics conducive to deer movement, proximity to roads for access, and distribution across the study area.
NOTE: Capture sites must allow for concealment of the capture technician.- Bait sites with about 10 kg of shelled corn to entice deer to visit and evaluate use based on bait consumption and deer photographed by motion-sensitive cameras. Relocate to alternate sites if deer do not attend baited sites within 5-7 days.
- During capture events, sit in a concealed "stand."
- Place stand about 20 m downwind from the bait pile, taking the prevailing wind direction into consideration so that deer approaching the bait are less able to smell the capture technician.
NOTE: Elevated stands are strongly preferred, and safety harnesses are required. There are several variations of stands with a variety of commercial sources and use varies by personal preference. For example, a lock-on stand would include seating with a ladder for access attached to a tree with straps. Portable climbing stands can be carried in by the capture technician and allow for increased mobility as the technician can choose a specific tree once they arrive at the capture site. Portable climbing stands are limited to use in straight trees without branches up the chosen height.
- Place stand about 20 m downwind from the bait pile, taking the prevailing wind direction into consideration so that deer approaching the bait are less able to smell the capture technician.
- Use a dart gun coupled with a 3 cc radio-telemetry dart to deliver a mixture of teletamine HCl (4.4 mg/kg) and xylazine HCl (2.2 mg/kg).
- Schedule capture efforts to coincide with the typical crepuscular activity cycle of deer27. Begin each capture attempt 2-3 h prior to sunset.
- Continue capture events for 2-3 h after sunset using night-vision goggles and a red dot laser for shot placement if deer are not captured during daylight hours.
- Take shots at deer when they are broadside and stationary.
NOTE: The hind quarter of the deer is the target because it has significant muscle tissue and is located away from the heart and lungs. - Wait about 15 min for darted target animals (six-month-old fawns of either sex or pregnant adult females) to become fully immobilized before locating it with directional radio-telemetry equipment.
- Confirm individuals are sedated by checking for eye reflexes (blinking). Then apply ophthalmic ointment to the eyes and blindfold deer to reduce stress.
NOTE: Loss of thermoregulation is a consequence of immobilization. - Use a rectal thermometer to assess body temperature after recovery. Warm deer with heated blankets if the animal's temperature is below 37.7 °C. Cool deer with ice packs if the animal's temperature is above 40.0 °C.
- Place deer in a sternal position on a military style gurney and transport deer from the capture location to an enclosed trailer.
- After placing the deer into the trailer, reverse the effects of xylazine HCl with 0.125 mg/kg yohimbine HCl28.
- Transport all captured deer to the desired captive facility (e.g., Mississippi State University Rusty Dawkins Memorial Deer Unit; MSU Deer Unit) and keep them separated by source region.
2. Captive Facilities and General Husbandry Practices of Research Animals
NOTE: The MSU Deer Unit is subdivided into five 0.4 to 0.8 ha pens.
- Cover every side of each pen with shade cloth to act as a visual and physical barrier between pens. Shade cloth helps reduce injuries and provides shade during summer months.
- Place 1-2 elevated box blinds at one end of each pen to facilitate darting events during data collection.
- Place two trough style feeders at separate ends of each pen to reduce competition for food among deer. Also provide a water trough in each pen.
- Provide deer with a high-quality diet (20% crude protein deer pellets) ad libitum.
NOTE: Here, additional available forages within pens included (Trifolium spp) and fescue (Festuca spp) along with volunteer grasses and forbs. - If present, maintain available forages within pens using a mixture of herbicides to control broadleaf weeds and grasses using mixture rates found on respective labels.
NOTE: Using off-campus facilities to house ≥5.5 month old males will likely be needed. These facilities consisted of two 0.7 ha pens on each of three properties with husbandry practices similar to the MSU Deer Unit.
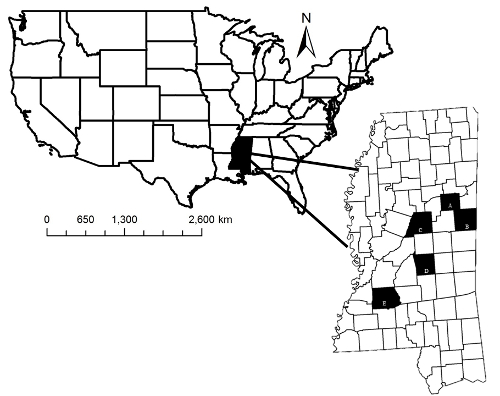
Figure 2: Captive Facility Locations. Study area where satellite facilities and the Mississippi State University (MSU) Deer Unit were located. Shaded areas indicate Oktibbeha (A), Noxubee (B), Attala (C), Scott (D), and Copiah (E), counties, Mississippi, USA.This figure has been modified from reference34. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
3. Parasite and Disease Control
- Monitor research animals for roundworm parasites (Strongyloides spp) using fecal floatation with parasites measured as eggs per gram (EPG).
- If present at high levels, provide parasite control by administering a pelleted wormer (active ingredient fenbendazole) at a rate of about 0.77 kg of pelleted wormer per 22.7 kg of feed during the month of May.
- If parasite levels remain high after initial treatment, use an ivermectin pour-on treatment (5 mg/mL)29, mixed at a rate of 2 mL/0.45 kg and administer to animals at a rate of 0.45 kg of treated feed per 45.4 kg of animal mass.
NOTE: Epizootic hemorrhagic disease is sometimes lethal viral disease spread by a biting midge (Culicoides spp) during summer and fall months. If present, treat the research facility with insecticide (5% ultra-low volume insecticide) 2-3 times per week from July 1 to October 1 to decrease prevalence of the vectors among research animals. Spray this insecticide within each pen and around the perimeter of the facility about 90 min before official sunset via fogger. Preferred methods to control for parasites and diseases are unique to each captive facility. Veterinarians must be consulted during any captive wildlife research to ensure animal health and safety.
4. Data Collection

Figure 3: Data Collection of Newborn Fawns. Measuring hind foot length from a new born fawn at the Mississippi State University Rusty Dawkins Memorial Deer Unit in Oktibbeha County, Mississippi, USA. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Search the captive facility daily for fawns during the parturition season.
- Uniquely mark newborn fawns with medium plastic ear tags using an ear tagger with antibiotic applied to the male end of the tag to prevent potential infection. Place ear tag about the center of the fawn's ear.
- Measure body mass (nearest 0.01 kg) with a digital hanging scale and measure hind foot length and total body length (nearest mm).
- Collect hair samples and send them to a remote site for parentage assignment (see the Table of Materials).
NOTE: Parentage assignment was made using DNA based on a proprietary, non-statistical custom structured query language database. In the pairwise allele comparison, the remote parentage assignment site assigned parentage when they excluded all but one sire and one dam based upon a shared allele from each parent at all loci tested (B. G. Cassidy, personal communication). This method of parentage assignment was also used in previous research conducted on captive white-tailed deer30,31. - Administer 2 cc of Clostridium perfringens types C and D toxoid and Clostridium perfringens types C and D antitoxin subcutaneously and administer 0.3 cc/kg of ivermectin in propylene glycol (Mississippi State University Veterinarian School, Mississippi, USA) orally to each fawn.
- Chemically immobilize adult males (≥1.5 years-old) during October and November for data collection.
- Immobilize penned adults using the same combination of teletamine HCl and xylazine HCl used for capture of wild animals (step 1.4).
- During sedation events, walk the technician who will be darting to the end of the pen where the elevated blinds are located. Have a single technician in each of two blinds.
- Have the individual who walked the technician to the blind walk back to the opposite end of the pen.
NOTE: Deer move away from these technicians and locate themselves in front of the blinds where technicians are in position to take ethical shots on each deer. - Take shots at deer when they are broadside and stationary (section 1.4).
- Wait about 15 min for darted animals to become fully immobilized before approaching it.
- Confirm individuals are sedated by checking for eye reflexes (blinking). Apply ophthalmic ointment to the eyes and blindfold deer to reduce stress.
- After the darters successfully sedate an individual deer, monitor the deer's vital rates.
- Use a rectal thermometer to assess body temperature after recovery. Warm deer with heated blankets if the animal's temperature is below 37.7 °C. Cool deer with ice packs if the animal's temperature is above 40.0 °C.
- Load the deer on a military-style gurney, and transport it via utility task vehicle to a predetermined data collection area.
- Once transported, record the same morphometric measurements recorded at birth (step 4.1).
- Measure body mass (nearest 0.01 kg) with a digital hanging scale and measure hind foot length and total body length (nearest mm).
NOTE: Individual deer react differently to the combination of drugs used during sedation events so administer about 0.1-0.3 cc of the teletamine HCl and xylazine HCl mixture (depending on body mass of an individual deer) if an individual comes out of sedation before data collection is completed.
- Measure body mass (nearest 0.01 kg) with a digital hanging scale and measure hind foot length and total body length (nearest mm).
- Administer size-appropriate amounts of antibiotic, ivermectin, a clostidrial vaccine, and a leptospirosis vaccine to all deer after they are transported to the data collection area (see sections 1 and 3).
- Take three antler measurements from adult males using an antler measuring tape while the animal is sedated.
- Measure the inside spread (widest distance between main beams), basal circumference (smallest diameter located between the burr and G1 tine), and main beam length (distance from antler base to the tip of the main beam) of antlers prior to antler removal.
- Remove antlers about 3 cm above the burr using a reciprocating saw. Do not remove antlers less than 3 cm.

Figure 4: Data Collection of Adult Males. Antler removal via reciprocating saw from a captive adult male white-tailed deer. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- After all data is collected from the sedated individual, place the deer into the appropriate pen and administer either 0.125 mg/kg yohimbine HCl28 or 4.0 mg/kg tolazoline HCl32 to reverse the effects of xylazine HCl. Monitor individuals to ensure they remain in a sternal position until they come out of sedation and are fully alert.
NOTE: If complications occur and animals must be euthanized, then euthanasia by cerebral dislocation via bolt stunner and severing of the jugular vein are ethical means to dispatch the animal. - Bring the antlers to a designated area to finish measuring antler size.
- Measure each individual tine protruding from the main beam (G1, G2, G3, etc.) and additional abnormal points by aid of wire.
NOTE: Points that do not have a matching counterpart on the opposite main beam or are not consistent with the definition of a typical antler set are defined by the Boone and Crockett Club33. - Wrap the wire around where the tine intersects the main beam and mark that point for reference.
- Measure from this reference point to the tip of the tine and repeat for each tine.
- Collect remaining circumference measurements by identifying the smallest point between the G1 and G2 tines (H2 circumference), the G2 and G3 tines (H3 circumference), and the G3 and G4 tine if present (H4 circumference).
- If the G4 tine is not present, measure the distance between the midpoint of the G3 tine and the end of the main beam and measure the H4 circumference at the midway point.
- Measure less than four circumferences when antlers contain less than three tines.
NOTE: For example, a main beam with two typical points include only three circumference measurements. Individuals may use other guidelines (Safari Club International) for calculating antler size; however, consistent methods must be used for each animal for valid comparison. - After making all measurements, calculate an antler score similar to the gross nontypical Boone and Crockett score33.
- Weigh antlers to the nearest 0.1 g using a scientific digital scale and assign a minimal critical antler mass of 1 g for first-year animals with antlers shorter than 3 cm.
- Measure each individual tine protruding from the main beam (G1, G2, G3, etc.) and additional abnormal points by aid of wire.
- Chemically immobilize penned juveniles at approximately 5.5 months of age using the same methods for adults (section 4.2) and mark juveniles with a large plastic ear tag (step 4.1.1).
- Use the same drug mixture rates to immobilize captive adults as used for immobilizing wild deer (section 1).
- Collect the same measurements collected at birth (step 4.1.2) and administer the same prophylactics as adults (section 4.2).
NOTE: After all data is collected, transport each juvenile male to its randomly assigned satellite facility via trailer.
5. Producing First- and Second-generation Offspring
- Classify six-month-old wild-caught fawns and offspring born at the captive facility from wild-caught mothers as first-generation individuals.
- During the breeding season, place two males with 7-16 females for an average breeding sex ratio of one male to eight females.
NOTE: Select breeding males from satellite facilities based on physical appearance, because the healthiest males (largest antlers and body size) are most likely to service females for the entirety of the breeding season without suffering from injury due to the aggressive nature of males during the breeding season.- Only allow deer to breed with other individuals from the same source region (e.g., Delta males breed Delta females, Thin Loess males breed Thin Loess females, and LCP males breed LCP males).
- Classify deer conceived by first-generation parents as second-generation offspring. Raise these individuals in captivity from birth and feed the same high-quality diet as their parents.
NOTE: Females may produce offspring multiple years but typically with different sires each year. Collect the same data on second-generation offspring as collected on first-generation and wild-caught individuals.
結果
個々 の年齢、栄養的な品質、および遺伝学男性オジロジカの表現型に影響を与えます。私たち研究デザインができました栄養鹿の品質を制御するために使用していたし、年クラス内で有効な比較の各鹿の年齢を識別することができました。栄養と私たちの研究デザインと年齢を制御してができますより人口レベルの遺伝学は 2 つの学習集団から男性の表現型が制限さ...
ディスカッション
我々 のプロトコルに関連付けられているいくつかのステップがあります。ただし、このプロトコルの成功を保障するために取られなければならない 4 つの重要なステップがあります。まず、野生の鹿のキャプチャ中に単一のソース領域 (ステップ 1.1.1) 各地キャプチャする必要があります。複数のキャプチャ場所によってソース領域に関連付けられているすべての遺伝の可変性は鹿の間で表?...
開示事項
著者が明らかに何もありません。
謝辞
野生生物復元法 (W-48-61) 連邦政府の援助からの資源を活用した金融支援、ミシシッピ州野生生物部、水産と公園 (MDWFP) に感謝します。我々 はデータ コレクションの MDWFP 生物学者・ w ・ マッキンリー、A. ブレイロック、A. ゲイリー ・ l ・ ウィルフ広範な関与を感謝します。我々 はまた、施設コーディネーターとして s. タッカーと複数の大学院生、技術者データを収集、彼らの助けのために感謝します。この原稿は、ミシシッピ州立大学森林野生動物研究センターの貢献 WFA427 です。
資料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Shelled Corn | |||
| Elevated Stand | |||
| Safety Harness | |||
| Ground Blind | |||
| Model 196 Projector | Pneu-Dart, Pennsylvania, USA | ||
| 3cc Radio-Telemetry Darts | (Pneu-Dart, Pennsylvania, USA) | ||
| Various Sized Darts | (Pneu-Dart, Pennsylvania, USA) | ||
| Teletamine HCl | (Telazol, Fort Dodge Animal Health, Iowa, USA) | ||
| Xylazine HCl | (West Texas Rx Pharmacy, Amarillo, Texas, USA) | ||
| Yhoimbine HCl | |||
| Tolazoline HCl | |||
| Military Style Gurney | |||
| Rectal Thermometer | |||
| Shade Cloth | |||
| 20% Crude Protein Deer Pellets | (Purina AntlerMax Professional High Energy Breeder 59UB, Purina, Missouri, USA) | ||
| Trough Style Feeders | |||
| Commercial Clover | (Durana Clover, Pennington Seed Co., Georgia, USA) | ||
| Commercial Fescue | (Max-Q Fescue, Pennington Seed Co., Georgia, USA) | ||
| Blankets | |||
| Ice Packs | |||
| Broadleaf Weed Control (2, 4-DB Herbacide, Butyrac 200) | |||
| Grass Control | (Poast Herbacide, BASF Co.) | ||
| Pelleted Wormer | Safeguard Co., | active ingredient fenbendazole | |
| Parasite Pour-on Treatment | (Ivomec, Merial Co.) | ||
| Insecticide | Riptide, McLaughlin Gormley King Co.) | ||
| Medium and Large Plastic Ear Tags | (Allflex, Texas, USA) | ||
| Remote site that assigned parentage | DNA Solutions Animal Solutions Manager (DNA Solutions, Oklahoma, USA) | ||
| Digital Hanging Scale | (Moultrie, EBSCO Industries, Inc.) | ||
| Tape Measure | |||
| Clostridium Perfringens Types C and D Toxoid Essential 3 | (Colorado Serum Co.) | ||
| Clostridium Perfringens Types C and D Antitoxin Equine Origin | (Colorado Serum Co.) | ||
| Ivermectin in propylene glycol | |||
| Antibiotic | (Nuflor, Schuering-Plough Animal Health Corp., New Jersey, USA) | ||
| Ivermectin | (Norbrook Labratories, LTD., Down, Northern Ireland, UK) | ||
| Clostidrial vaccine | (Vision 7 with SPUR, Ivesco LLC, Iowa, USA) | ||
| Leptospirosis vaccine | (Leptoferm-5, Pfizer, Inc., New York, USA) | ||
| Trailer for transport | |||
| Reciprocating saw | (DEWALT, Maryland, USA) | ||
| Scientific Digital Scale | (Global Industrail, Global Equipment Company Inc) | ||
| Antler Measuring Tape | |||
| Fogger | |||
| Plastic Ear Tags | (Allflex, Texas, USA) | ||
| Plastic Ear Tagger | (Allflex, Texas, USA) |
参考文献
- Bernardo, J. Maternal effects in animal ecology. Amer Zool. 36 (2), 83-105 (1996).
- Forchhammer, M. C., Clutton-Brock, T. H., Lindstrom, J., Albon, S. D. Climate andpopulation density induce long-term cohort variation in a northern ungulate. J Anim Ecol. 70 (5), 721-729 (2001).
- Freeman, E. D., Larsen, R. T., Clegg, K., McMillan, B. R. Long-lasting effects of maternal condition in free-ranging cervids. PLoS ONE. 8 (3), 5873 (2013).
- Geist, V., Burton, M. N. Environmentally guided phenotype plasticity in mammals and some of its consequences to theoretical and applied biology. Alternative life-history styles of animals. , 153-176 (1989).
- Clutton-Brock, T. H., Guinness, F. E., Albon, S. D. Reproductive success in stags. Red Deer: Behavior and ecology of two sexes. , 151-152 (1982).
- Coltman, D. W., Festa-Bianchet, M., Jorgenson, J. T., Strobeck, C. Age-dependent sexual selection in bighorn rams. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 269 (1487), 165-172 (2002).
- Festa-Bianchet, M. The cost of trying: Weak interspecific correlations among life-history components in male ungulates. Can J Zool. 90 (9), 1072-1085 (2012).
- Kie, J. G., et al. Reproduction in North American elk Cervus elaphus.: Paternity of calves sired by males of mixed age classes. Wildlife Biol. 19 (3), 302-310 (2013).
- Welch, C. A., Keay, J., Kendall, K. C., Robbins, C. T. Constraints on frugivory by bears. Ecology. 78 (4), 1105-1119 (1997).
- Madsen, T., Shine, R. Silver spoons and snake body sizes: Prey availability early in life influences long-term growth rates of free-ranging pythons. J Anim Ecol. 69 (6), 952-958 (2000).
- Saino, N., Romano, M., Rubolini, D., Caprioli, M., Ambrosini, R., Fasola, M. Food supplementation affects egg albumen content and body size asymmetry among yellow-legged gull siblings. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 64 (11), 1813-1821 (2010).
- Strickland, B. K., Demarais, S. Age and regional differences in antlers and mass of white-tailed deer. J Wildl Manage. 64 (4), 903-911 (2000).
- Jones, P. D., Demarais, S., Strickland, B. K., Edwards, S. L. Soil region effects on white-tailed deer forage protein content. Southeast Nat. 7 (4), 595-606 (2008).
- Strickland, B. K., Demarais, S. Influence of landscape composition and structure on antler size of white-tailed deer. J Wildl Manage. 72 (5), 1101-1108 (2008).
- DeYoung, R. W., Demarais, S., Honeycutt, R. L., Rooney, A. P., Gonzales, R. A., Gee, K. L. Genetic consequences of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) restoration in Mississippi. Mol Ecol. 12 (12), 3237-3252 (2003).
- Sumners, J. A., et al. Variable breeding dates among populations of white-tailed deer in the southern United States: The legacy of restocking. J Wildl Manage. 79 (8), 1213-1225 (2015).
- Mech, D. L., Nelson, M. E., McRoberts, R. E. Effects of maternal and grandmaternal nutrition on deer mass and vulnerability to wolf predation. J Mammal. 72 (1), 146-151 (1991).
- Therrien, J. F., Còtê, S., Festa-Bianchet, D. M., Ouellet, J. P. Maternal care in white-tailed deer: trade-off between maintenance and reproduction under food restriction. Anim Behav. 75 (1), 235-243 (2008).
- Parker, K. L., Barboza, P. S., Gillingham, M. P. Nutrition integrates environmental responses of ungulates. Funct Ecol. 23 (1), 57-69 (2009).
- Monteith, K. L., Schmitz, L. E., Jenks, J. A., Delger, J. A., Bowyer, R. T. Growth of male white-tailed deer: consequences of maternal effects. J Mammal. 90 (3), 651-660 (2009).
- Tollefson, T. N., Shipley, L. A., Myers, W. L., Keisler, D. H., Nairanjana, D. Influence of summer and autumn nutrition on body condition and reproduction in lactating mule deer. J Wildl Manage. 74 (5), 974-986 (2010).
- Guynn, D. C., Mott, S. P., Cotton, W. D., Jacobson, H. A. Cooperative management of white-tailed deer on private lands in Mississippi. Wildl Soc Bull. 11 (3), 211-214 (1983).
- Pettry, D. E. Soil resource areas of Mississippi. Mississippi Agricultural and Forestry Experiment Station. , (1977).
- Snipes, C. E., Nichols, S. P., Poston, D. H., Walker, T. W., Evans, L. P., Robinson, H. R. Current agricultural practices of the Mississippi Delta. Office of Agricultural Communications. , (2005).
- Baker, R. H., Halls, L. K. Origin, classification, and distribution of the white-tailed deer. White-tailed deer: ecology and management. , 1-18 (1984).
- Barbour, T., Allen, G. M. The white-tailed deer of eastern United States). J Mammal. 3 (2), 65-80 (1922).
- Rouleau, I., Crête, M., Ouellet, J. P. Contrasting the summer ecology of white-taileddeer inhabiting a forested and an agricultural landscape. Ecoscience. 9 (4), 459-469 (2002).
- Kreeger, T. J. . Handbook of wildlife chemical immobilization. , (1996).
- Pound, J. M., Miller, J. A., Oethler, D. D. Depletion rates of injected and ingested Ivermectin from blood serum of penned white-tailed deer, Odocoileus virginianus (Zimmermann) (Artiodactyla: Cervidae). J Medl Entomol. 41 (1), 65-68 (2004).
- Jones, P. D., Demarais, S., Strickland, B. K., DeYoung, R. W. Inconsistent relation of male body mass with breeding success in captive white-tailed deer. J Mammal. 92 (3), 527-533 (2011).
- Michel, E. S., Flinn, E. B., Demarais, S., Strickland, B. K., Wang, G., Dacus, C. M. Improved nutrition cues switch from efficiency to luxury phenotypes for a long-lived ungulate. Ecol Evol. 6 (20), 7276-7285 (2016).
- Miller, B. F., Muller, L. I., Doherty, T., Osborn, D. A., Miller, K. V., Warren, R. J. Effectiveness of antagonists for tiletamine-zolazepam/xylazine immobilization in female white-tailed deer. J Wildl Dis. 40 (3), 533-537 (2004).
- Nesbitt, W. H., Wright, P. L., Buckner, E. L., Byers, C. R., Reneau, J. . Measuring and scoring North American big game trophies. 3rd edn. , (2009).
- Michel, E. S., Demarais, S., Strickland, B. K., Smith, T., Dacus, C. M. Antler characteristics are highly heritable but influenced by maternal factors. J Wildl Manage. 80 (8), 1420-1426 (2016).
- Severinghaus, C. W. Tooth development and wear as criteria of age in white-tailed deer. J Wildl Manage. 13 (2), 195-216 (1949).
- Gee, K. L., Webb, S. L., Holman, J. H. Accuracy and implications of visually estimating age of male white-tailed deer using physical characteristics from photographs. Wild Soc Bull. 38, 96-102 (2014).
- Storm, D. J., Samuel, M. D., Rolley, R. E., Beissel, T., Richards, B. J., Van Deelen, T. R. Estimating ages of white-tailed deer: Age and sex patterns of error using tooth wear-and-replacement and consistency of cementum annuli. Wild Soc Bull. 38 (1), 849-865 (2014).
- Montero, D., Izquierdo, M. S., Tort, L., Robaina, L., Vergara, J. M. High stocking density produces crowding stress altering some physiological and biochemical parameters in gilthead seabream, Sparus aurata., juveniles. Fish Physiol Biochem. 20 (1), 53-60 (1999).
- Charbonnel, N., et al. Stress demographic decline: a potential effect mediated by impairment of reproduction and immune function in cyclic vole populations. Physiol Biochem Zool. 81 (1), 63-73 (2008).
- Crews, D., Gillette, R., Scarpino, S. V., Manikkam, M., Savenkova, M. I., Skinner, M. K. Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of altered stress responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 109 (23), 9143-9148 (2012).
- Maher, J. M., Werner, E. E., Denver, R. J. Stress hormones mediate predator-induced phenotypic plasticity in amphibian tadpoles. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 280 (1758), 20123075 (2013).
転載および許可
このJoVE論文のテキスト又は図を再利用するための許可を申請します
許可を申請さらに記事を探す
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved