Method Article
2 - 광자 현미경을 사용하여 마우스 Thymus의 Intravital 영상
요약
We have developed novel laboratory tools and protocols for intravital imaging acquisition of the thymus. Our technique should help in the identification of “niches” within the thymus where T cell development occurs.
초록
두 광자 현미경 (TPM)은 조직과 장기 깊숙한 지역에서 이미지 수집을 제공합니다. 새로운 stereotactic 도구 및 수술 절차의 개발과 함께, TPM은 장기 내부의 '틈새 시장'을 파악하고, 살아있는 동물의 세포 "행동"을 문서화하는 강력한 기술이됩니다. intravital 이미징이 가장 장기 내부의 실제 세포 동작과 유사한 정보를 제공하고 있지만, 더 힘드는 및 기술적 대안 전직 생체내 이미징 인수보다 필요한 장비 / 절차의 측면에서 까다로운 둘 수 있습니다. 따라서, 우리는 수술과 우리가 thymus 내에서 Foxp3의 움직임 + 세포를 수행하실 수 있습니다 소설 "stereotactic"장기 보유자에 대해 설명합니다.
Foxp3은 규제 T 세포 (Tregs)의 생성에 대한 마스터 조절기입니다. 예 : 또한, 이러한 세포들은 원산지에 따라 분류하실 수 있습니다. thymus - 차별화된 Tregs는 O로 "자연 - 발생 Tregs"(nTregs)를 부릅니다peripherally - 변환 Tregs (pTregs)에 pposed. 연구의 상당 금액이 T 세포의 표현형 및 생리학에 관한 문헌에서보고되었습니다 있지만, 거의 자신의 다른 세포와 생체내 상호 작용에 대한 알려져있다. 이 결핍은 관찰을 허용 것이 기술의 부재로 인해 수 있습니다. 이 문서에서 설명하는 프로토콜은 이러한 상황에 대한 구제 수단을 제공합니다.
우리 프로토콜들은 thymic 상피 세포 등 일부 상피 세포의 차별을 떨어뜨리고 DNA 순서에 엄격 돌연변이 때문에 내생 thymus 부족 누드 마우스를 사용하여 구성되어 있습니다. 누드 마우스는 감마 조사되었으며 Foxp3 - KI GFP / GFP 마우스에서 뼈 marrows (BM)와 재구성. BM 복구 (6 주) 후, 각각의 동물은 신장 캡슐 내부의 배아 thymus 이식을 받았습니다. thymus 수용 (6 주) 후, 동물 anesthetized 있었다, 신장을 포함하는이식 thymus는 노출의 장기 보유자에 고정하고, TPM에 의해 생체내 이미징에 대한 생리적 조건 하에서 보관되었습니다. 우리는 규제 T 세포의 생성에 약물의 영향을 연구하기 위해이 방법을 사용하고 있습니다.
프로토콜
1. 동물 준비
중요 사항 : BM 세포 정지와 thymic transplantations는 무균 조건에서 수행되었다. thymic 이식은 우리의 동물 시설 내에있는 수술 방에서 수행하는 동안 BM 정지는, 우리의 세포 배양 실의 후드 안쪽 준비했다. 이러한 무균 조건을 유지하고 보장하기 위해, 우리는이 장소에서 우리의 동영상을 녹화할 수 없습니다되었습니다. 그러나 모든 수술 자료는 autoclaved되었으며 수술 벤치는 이전에 다음 ID로 Virkon (Pharmacal 연구소 연구소 주식 회사)와 70 % 에탄올로 세척했다. 모든 절차는 기관 동물 케어에 의해 승인위원회 (IACUC)를 사용하여 그들은 유럽의 실험실 동물 과학 협회 (FELASA) 지시어의 연맹과 계약에있었습니다. 승인 ID 번호는 AO10/2010입니다. 모든 이미지 실험은 터미널 성형 수술과 동물은 이미지의 끝에 바로 다음 euthanized되었습니다인수.
다음과 같은 세부적인 절차는 다음과 같습니다
- 비추다 (γ - irradiator 포함) 뼈 marrows (BM) 내부의 내생 조혈 엽 성의 전구 물질을 파괴 900 래드와 8주 오래된 누드 마우스. 당신은 정맥 주사를 더욱 BM reconstitution에 대한 기증자 BM 세포를 준비하기 전까지 조사 후, 자신의 새장에 동물을 반환합니다. 이 BM 전송은 조사 후 1 H을 수행했다.
- BM 기증자 동물을 분리합니다. 한 동물의 뒷다리 사지 Tibias과 대퇴골은 일반적으로 최대 3받는 동물 reconstitute 충분히 있습니다. CO 2와 안락사 후, 두 다리를 제거한 후 뼈가에서 피부와 근육을 제거하십시오.
- 각 뼈의 폐쇄 끝을 잘라하고 BM을 제거하기 위해 PBS (또는 RPMI) 2 ML과 유봉을 사용하여, PBS (또는 RPMI)로 플러시 또는 절구에 모두를 부술.
- 활발한 흡인 usi의 반복에 의한 단일 셀 중단에 BM 구조를 방해NG P1000의 피펫. 또는, 당신은 또한 21G 주사 바늘을 통해 여러 번 BM을 전달할 수 있습니다. 원심 분리기 (400g, 5 분, RT)은 PBS로 세포를 다시 중지, 그리고 누드 - 조사받는 사람으로 정맥 주입. 우리의 실험에서 우리는 규제 T 세포 (Tregs)는 GFP 1 표현됩니다 Foxp3 - KI GFP / GFP 마우스에서 BM 사용됩니다.
- 비 BM - 재구성 동물들이 이상 십사일 면할 수 없다는 이후 기증자 BM의 수락, 이전 후 첫 일 이내에 발생합니다. 그러나, 하나는 모두 BM 구획의 완전 회복을 허용하도록 4~6주 기다려야한다. Bactrim은 (Roche는) 세균 감염의 위험을 감소하기 위해 조사 후 첫 주 동안 물 (2 MG / ML)에 추가되었습니다.
- 배아 thymus 이식은 이미 2 설명했다. 간단히, isogenic 생쥐의 쌍을 사육 시작하고 매일 (성교의 증거) 연결해 있는지 확인합니다. 별도의 연결의 여자와 공동 pregn 하루에 15을 2 - 안락사ancy (플러그의 관찰은 임신 1 일입니다.) 배아와 thymuses을 제거합니다. 이전까지 차가운 PBS에서 배아 thymuses를 놓습니다.
- thymuses 이식, ketamin (120 마우스 중량 μg / g) / xylazine (마우스 중량의 16 μg / g)과 마취 BM -받는 누드 마우스를 수행하고 그들이 얻을 ° C까지 37 가열 패드 위에 그들을 유지하려면 무의식.
- 수술 thymuses의 이식을 수행할 수있는 신장을 노출. 먼저 ChloraPrep (Carefusion 주식 회사)와 70 % 에탄올로 피부를 씻어. 그런 다음 백 측면 바디 동물의 부분 2mm 우는 지난 흉부 리브의 피부에 상처 1cm합니다.
- 복막 구멍을 잘라 이런 곳에의 신장을 가져옵니다. 메스 블레이드와 신장 캡슐의 작은 피상적인 상처를 확인합니다. 매우 얇은 팁을와 집게를 사용하면받는 마우스의 신장 캡슐 밑에 주머니를 만들고이 주머니에 4 thymic 엽 (叶)까지 추가할 수 있습니다.
- 신장 B를 넣고 그 장소에 ACK, 하나 또는 두 개의 바늘로 복막 구멍을 봉합하고 같은 치료 방법을 사용하여 마우스 피부를 닫습니다. 또는 봉합 수술은 접착제를 사용하여 수행할 수 있습니다.
- subcutaneously 바로 동물의 고통을 피할들이 마취에서 회복하기 위해 시작 때까지 가열 패드에있는 동물을 유지하기 위해 수술을 마친 후 (5 밀리그램 / kg에서 Butorphanol) 진통제 주사. 생쥐는 실밥을 제거 케이지 짝을을 방지하기 위해 이식 후 처음 3 일 동안 개별적으로 갇힌 수 있습니다. 일주 후 바늘을 제거합니다.
- 누드 마우스는 T 세포를 필요가 없습니다. 따라서 혈액에 CD4 + CD8 + T 또는 세포의 비율을 모니터링하여 thymus 그래프트 동의 평가할 수 있습니다. 일단 주당, 이주 thymus 이식 후 동물 피가 및 안티 - CD4와 CD8 단클론 항 항체 (MAbs)로 혈액을 얼룩. CD4시 : CD8 비율이 약 2시 1분이며, 이식 thymus는 (그림 1) 완벽하게 작동합니다.
미리 필요로하고 그들을 버려 것입니다 모든 재료를 준비합니다.
- 37 ketamin / xylazine (항목 1.5에서 설명한 동일한 복용)와 동물 마취 및 난방 패드의 상단에 넣어 ° C. 혈액 흐름이 미래의 시각화를 허용 자에게 Rhodamine B isothiocyanate - Dextran (PBS에서 20 밀리그램 / ML) 100 μl를 주입.
- 이전 항목 1.6에서 설명하는 프로토콜에 따라 이식 thymus를 포함하는 신장을 폭로.
- 원래 위치로 복귀에서 신장을 방지하기 위해, 바늘로 피부 절개의 측면 측면을 닫습니다.
- 그것이 촉촉한 유지하는 기관의 상단에 PBS - 절어 코튼 조각을 넣으십시오.
- 동물 홀더 단계 (그림 2A)의 상단에있는 가열 패드를 넣어.
- 동물 홀더, 장기 접속 (그림 2B)에서 가열 패드의 상단에있는 동물을 넣어.
- 클램프 m로 양쪽에서 오르간을 핀치얇은 알루미늄 호일의 ADE (그림 2C).
- 동물 홀더를 닫고 가까이 가능한 귀하의 조직 (그림 2D) 가기 히터 프로브를 놓습니다. 이 히터 프로브는 지속적으로 장기 온도를 측정하고 37 ° C.에 보관, 전기 전류를 조정하는 히터에이 정보를 전송
- PBS - 절어 목화를 제거하고 ° C 귀하의 준비 위에 30 낮은 용융 아가로 오스를 (PBS 2 %) 추가합니다.
- 상단 히터 (그림 2E)로 전체 준비를 커버. 이 히터의 조리개에서 목표 (그림 2 층)에서 아가로 오스를 분리 coverglass있다. 마우스 마취를 모니터링하고 반 선량 부스트마다 40 분을 주입. 이미지 수집 후, CO 2와 함께 동물을 안락사.
참고 : 알루미늄 호일 클립 및 상단 히터의 사진은 그림 3에서 제공됩니다.
3. 두 광자 영상 획득
우리는 직립 "프레리 울티마 XY"두 광자 현미경을 사용. 우리 시스템은 티를 갖춘 : 사파이어 레이저, 동시 최대 4 채널 인수를위한 네 부류의 일급 PMTs 및 20x 물 침지 목표.
- 티 켜고 : 사파이어 레이저와 전체 현미경 시스템.
- 원하는 파장에 따라 이색성 거울과 필터 세트를 추가합니다. 우리의 경우 우리는 565 nm의 이색성 거울을 포함하는 올림푸스 - BX2 채도 홀더, 하나 50분의 525 nm의 필터 (Foxp3 - GFP 신호에 대해) 한 50분의 595 nm의 필터 (혈관 안에서 Dextran - Rhodamine - B 신호에 사용 ). 사용되는 레이저 파장 범위는 880-900 nm의 사이되었습니다.
- , 현미경으로 동물 홀더를 추가 연결하여 물로, 상단 히터 구멍에 물을 추가, 모든 히터에 조심스럽게 낮은 목표를 설정하고, 선박 또는 일부 GFP - Tregs에 중점을두고 있습니다.
- 현미경의 X와 Y, Z 외부 컨트롤은 빠르게 영역을 찾을 수있는 조직을 조사 관심.
- 색상 분리를 최적화하고 배경을 통해 충분한 신호를 달성하는 데 필요한 레이저의 양을 최소화하기 위해 PMTs에 게인을 조정합니다. 당신의 조직 사진 손상을 방지하려면 레이저의 최소 금액을 사용해보십시오.
- 관심의 영역이있는되면, 시간이 경과 이미징을 시작합니다. 우리의 경우 전형적인 5D에서 (X, Y, Z, T, 색상) 수집 프로토콜은 4.0 μm의 Z - 단계, X와 140 μm의의 Y 길이로 나누어 50 μm의 깊이있는 조직 볼륨의 연속 이미지를 인수로 구성되어 있습니다 각. 각 볼륨은 약 30 초이 취득 걸립니다. 따라서, 60 인수는 이미지 수집 중 약 30 분을 수행합니다.
- 기관 서버로 데이터를 전송 및 다중 차원 렌더링과 셀 추적을 수행하는 ImageJ, Imaris 또는 Volocity 소프트웨어를 사용합니다.
4. 대표 결과
g1.jpg "/>
그림 1. . 배아 thymus 접수 및 기능 BM 복구 후, 배아 thymuses는 BM 재구성 동물 이식했고, 이주 thymus 이식 후,이 생쥐는 안티 - CD4 또는 방지 CD8와 얼룩에 의한 T 세포 subtypes의 비율을 모니터 한 번 주당 출혈이 있었다 MAbs. 우리는 thymus가 성공적으로 CD4와 동물의 수락으로 간주 : 1.5-2.0:1 주변 CD8 비율 (A). 그 기능을 확인하려면, 우리는 몇 가지 thymus - 이식 동물을 희생하고 WT 생쥐 (B)와 다른 thymocyte subpopulations의 비율을 비교했다. subpopulations (안티 CD25 및 안티 CD44 MAbs와 얼룩에 의해), 이중 긍정적인 (DP; CD4 + CD8 + thymocytes), (- - CD8 thymocytes CD4 DN)과 단일 긍정적인 (SP) CD4 이중 부정의 비율 + 나 CD8 + thymocytes이 동물 사이에 유사한했다.
ig2.jpg "/>
그림 2. 동물 홀더 어셈블리가. 깊게 anesthetized 후, 동물 가열 패드 위에 넣고, 이전에 동물 홀더 단계의 상단 (A)에 장착. 이식 thymus를 포함하는 신장은 (B)까지 직면하고 있습니다. 알루미늄 호일 클램프는 정교한 그 자리에 유지하기 위해 전체 신장 (C)를 pinches. 그림. 1C 삽입 상세 클램프를 보여줍니다. 동물 소유자의 상단 부분은 장소 (D)에 들어가게된다. PBS - 절어 목화는 따뜻한 낮은 용융 아가로 오스로 교체 기관의 최상위에서 제거하고, 상단 히터는 (E) 추가됩니다. 마지막으로, 온 회중은 여기 현미경으로 전송 목적 (F)으로 표시됩니다.
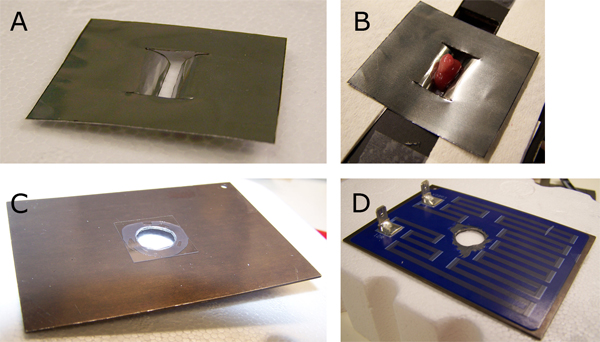
그림 3. 홀더 부분의 세부 사항.이 사진은 알루미늄 호일 클램프를 (A)는 신장 (B)를 개최 보여줍니다. 이식 thymus가있는 지역도 있습니다. 이것은 약 영역을 나타냅니다thymus 캡슐을 잘라 배아 thymus 넣어 주머니를 만들 수 있습니다. 상단 히터 coverglass (C)는 자사의 하단 부분 (D)에 실리콘 접착제로 고정되었습니다.
영화 1. 산소 및 온도의 생리 수준 (37 ° C)이 전체 과정 동안 유지되었습니다 thymus 내부 Foxp3 - GFP + thymocytes의 Intravital 이미징. Tregs의 혈액 흐름과 움직임을합니다. 이러한 속도는 측정 및 게시된 데이터와 비교할 수 있습니다. 동영상을 보려면 여기를 누르십시오.
영화 2. 이미지가 30 취득했다 thymus 내부 Tregs의 Intravital 이미징 ° C. 혈액 흐름의 유지에도 불구하고 움직임과 세포의 둥근 모양의 부재가. 참고 동영상을 보려면 여기를 누르십시오.
토론
In this paper we demonstrated the procedures for two-photon imaging of thymocytes inside a living animal. We also described some parameters that one should carefully control, such as the continuation of blood flow and the maintenance of organ temperature during the imaging procedures. Nonetheless, despite careful efforts to keep the organ stable, motion artifacts such as "organ drifting" can occur. Posterior image correction can be performed by the development of algorithms specifically designed for this purpose. Further image analysis could also be the source of new protocols development which seeks to minimize errors.
The thymus is the organ where all T cells are produced and, therefore, it is the organ where immunologists interested in understanding the generation of γδ, CD4, or CD8 T cells will focus their attention. Most studies concerning T cells are based upon differences in the numbers and/or stability of these cells after different in vitro/in vivo manipulations. However, only after the in vivo visualization we could observe the interaction between cells of the immune system involved in maintaining homeostasis3-7. Therefore, the in vivo observation of thymocytes is probably one of the most important missing information to better understand T cell biology. Intravital TPM provides a detailed picture of T cell movements and interactions and we demonstrate here how it can be used for detailed thymocyte studies. However, every technique has its limitations. While intravital imaging acquisition is the most accurate system for reflecting cells behavior inside the body, it is also true that explanted image acquisition of organs is less laborious and has been used to collect important information about the immune system8,9. Moreover, one cannot deny intravital imaging methods require surgery to expose tissues and blood vessels in anesthetized animals, which per se could cause an alteration in the whole organ physiology10. Nevertheless, there are non-invasively methods that abolish the artifacts caused by the surgical procedure11 and new methods are being developed that better prepare in advance the animals to be used12. Therefore, new surgical procedures and tolls will minimize or bypass actual limitations of intravital imaging acquisition and become more and more accessible to the scientific community.
We have demonstrated that the method we have described is feasible and it reports all in vivo systemic manipulations, such drug administration, that we have used. Thus, we suggest the use of this method together with ex vivo techniques already available in order to complement and strengthen further studies concerning thymocytes development.
공개
우리는 공개 아무것도 없어.
감사의 말
We would like to thank Dr. David Olivieri for critical review of this manuscript, Dr. Nuno Moreno for the logistic help to build our animal holder and heating pads and Dr. Vijay K. Kuchroo for the kind donation of Foxp3-KIgfp/gfp mice. This work is supported by "Fundação para Ciência e Tecnologia" (FCT, Portugal), grant # PTDC/EBB-BIO/115514/2009.
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Rhodamine B ishothiocyanate-Dextran | Sigma-Aldrich | R9379 | prepare stock at 20 mg/ml | |
| Two-photon microscope | Prairie Technologies Inc. | Prairie Ultima X-Y | ||
| Ti:Sapphire laser | Coherent, Inc. | Chameleon Ultra Family | ||
| 20x/1.00 NA immersion objective | Olympus Inc. | XLUMPLFLN 20XW | ||
| Holder (Filters/Dichroic) | Chroma Technology Corp. | 91018 BX2 (U-MF2) | ||
| 525 nm/50 filter | Chroma Technology Corp. | ET525/50m | ||
| 595 nm/50 filter | Chroma Technology Corp. | ET595/50m | ||
| 565 nm dichroic | Chroma Technology Corp. | 565dcxr | ||
| Imaris software | Bitplane AG Inc. | Imaris | ||
| Volocity | PerkinElmer Inc. | Volocity | ||
| ImageJ | NIH, USA | ImageJ |
참고문헌
- Bettelli, E. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441, 235-238 (2006).
- Ramsdell, F., Zúñiga-Pflücker, J. C., Takahama, Y. In vitro systems for the study of T cell development: fetal thymus organ culture and OP9-DL1 cell coculture. Current protocols in immunology. Coligan, J. E. , (2006).
- Tadokoro, C. E. Regulatory T cells inhibit stable contacts between CD4+ T cells and dendritic cells in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 203, 505-511 (2006).
- Mempel, T. R., Henrickson, S. E., Von Andrian, U. H. T-cell priming by dendritic cells in lymph nodes occurs in three distinct phases. Nature. 427, 154-159 (2004).
- Miller, M. J. Imaging the single cell dynamics of CD4+ T cell activation by dendritic cells in lymph nodes. J. Exp. Med. 200, 847-856 (2004).
- Shakhar, G. Stable T cell-dendritic cell interactions precede the development of both tolerance and immunity in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 6, 707-714 (2005).
- Hugues, S. Distinct T cell dynamics in lymph nodes during the induction of tolerance and immunity. 5, 1235-1242 (2004).
- Tang, Q. Visualizing regulatory T cell control of autoimmune responses in nonobese diabetic mice. Nat. Immunol. 7, 83-92 (2006).
- Le Borgne, M. The impact of negative selection on thymocyte migration in the medulla. Nature immunology. 10, 823-830 (2009).
- Baez, S. An open cremaster muscle preparation for the study of blood vessels by in vivo microscopy. Microvascular research. 5, 384-394 (1973).
- Wang, B., Zinselmeyer, B. H., McDole, J. R., Gieselman, P. A., Miller, M. J. Non-invasive Imaging of Leukocyte Homing and Migration in vivo. J. Vis. Exp. (46), e2062-e2062 (2010).
- Barretto, R. P. J. Time-lapse imaging of disease progression in deep brain areas using fluorescence microendoscopy. Nature medicine. 17, 223-228 (2011).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기더 많은 기사 탐색
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유