Method Article
염색질 레귤레이터 및 미국에서의 게놈 전체의 스냅 샷
요약
방법 염색질 규제 및 염색질 상태의 문제는 생체 내에서 유전자가 세포 운명 결정이 배아에서 어떻게 만들어 지는지 초기에 대한 우리의 이해의 열쇠입니다 영향을 미칩니다. 칩 서열 번호 - 글로벌 수준입니다 Xenopus의 배아 여기 설명에서 크로 마틴의 기능을 조사하기 가장 인기있는 방법.
초록
The recruitment of chromatin regulators and the assignment of chromatin states to specific genomic loci are pivotal to cell fate decisions and tissue and organ formation during development. Determining the locations and levels of such chromatin features in vivo will provide valuable information about the spatio-temporal regulation of genomic elements, and will support aspirations to mimic embryonic tissue development in vitro. The most commonly used method for genome-wide and high-resolution profiling is chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-Seq). This protocol outlines how yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus can be processed for ChIP-Seq experiments, and it offers simple command lines for post-sequencing analysis. Because of the high efficiency with which the protocol extracts nuclei from formaldehyde-fixed tissue, the method allows easy upscaling to obtain enough ChIP material for genome-wide profiling. Our protocol has been used successfully to map various DNA-binding proteins such as transcription factors, signaling mediators, components of the transcription machinery, chromatin modifiers and post-translational histone modifications, and for this to be done at various stages of embryogenesis. Lastly, this protocol should be widely applicable to other model and non-model organisms as more and more genome assemblies become available.
서문
The first attempts to characterize protein-DNA interactions in vivo were reported about 30 years ago in an effort to understand RNA polymerase-mediated gene transcription in bacteria and in the fruit fly1,2. Since then, the use of immunoprecipitation to enrich distinct chromatin features (ChIP) has been widely adopted to capture binding events and chromatin states with high efficiency3. Subsequently, with the emergence of powerful microarray technologies, this method led to the characterization of genome-wide chromatin landscapes4. More recently, chromatin profiling has become even more comprehensive and high-resolution, because millions of co-immunoprecipitated DNA templates can now be sequenced in parallel and mapped to the genome (ChIP-Seq)5. As increasing numbers of genome assemblies are available, ChIP-Seq is an attractive approach to learn more about the genome regulation that underlies biological processes.
Here we provide a protocol to perform ChIP-Seq on yolk-rich embryos such as those of the frog Xenopus. Drafts of the genomes of both widely used Xenopus species—X. tropicalis and X. laevis—have now been released by the International Xenopus Genome Consortium6. The embryos of Xenopus species share many desirable features that facilitate and allow the interpretation of genome-wide chromatin studies, including the production of large numbers of high-quality embryos, the large size of the embryos themselves, and their external development. In addition, the embryos are amenable to classic and novel manipulations like cell lineage tracing, whole-mount in situ hybridisation, RNA overexpression, and TALEN/CRISPR-mediated knockout technology.
The following protocol builds on the work of Lee et al., Blythe et al. and Gentsch et al.7-9. Briefly, Xenopus embryos are formaldehyde-fixed at the developmental stage of interest to covalently bind (cross-link) proteins to their associated genomic DNA. After nuclear extraction, cross-linked chromatin is fragmented to focus subsequent sequencing on specific genomic binding or modification sites, and to minimize the contributions of flanking DNA sequences. Subsequently, the chromatin fragments are immunoprecipitated with a ChIP-grade antibody to enrich those containing the protein of interest. The co-immunoprecipitated DNA is stripped from the protein and purified before creating an indexed (paired-end) library for next-generation sequencing (NGS). At the end, simple command lines are offered for the post-sequencing analysis of ChIP-Seq data.
프로토콜
참고 : 모든 Xenopus의 작품은 영국의 동물 (과학적인 절차) 의료 연구를위한 MRC 국립 연구소에 의해 구현 된 법 1986의 표준을 만족합니다.
1. 준비
- 칩 실험 (설명 참조)에 필요한 배아의 개수를 추정한다.
- 다음 RT에 저장된 용액 준비 : 7.5로 조정하고 오토 클레이브에 의해 멸균 EDTA, pH가없는 배 마크 개변 링거 (MMR)의 500 ㎖에 (1 M의 NaCl, 20 mM의 KCl을 20 mM의 CaCl2를, 10mM의 황산, 의 50 mM HEPES pH를 7.5) (10), 1 % SDS)과 1 5X DNA 로딩 완충액 (0.2 % 오렌지 G, 30 % 글리세롤 ㎖, 60 SDS 용출 완충액 (50 mM Tris-HCl pH를 8.0, 1 mM의 EDTA, ml의 mM의 EDTA의 pH 8.0).
- 4 ° C에 저장되어있는 다음과 같은 솔루션을 준비 : 50 HEG 버퍼 (50 mM의 HEPES-KOH pH가 7.5, 1 mM의 EDTA의 pH 8.0, 20 % 글리세롤), 추출 버퍼 E1 (50 mM의 HEPES-KOH pH를 500 ml의 ml의 7.5, 150 mM의 염화나트륨, 1 mM의 EDTA. 10 % 글리세롤, 0.5 %의 Igepal CA-630, 0.25 % 트리톤 X-100), E2 (10 mM의 pH를 8.0 트리스 -HCl, 150 mM의 염화나트륨, 1 mM의 EDTA, 0.5 mM의 EGTA) 및 E3 (10 mM 트리스 - 염산 하여 pH 8.0, 150 mM의 염화나트륨, 1 mM의 EDTA, 1 %의 Igepal CA-630, 0.25 % Na- 데 옥시 콜레이트, 0.1 % SDS), RIPA 완충액 (50 mM의 HEPES-KOH pH가 7.5, 500 mM의의 LiCl, 1 mM의 EDTA 500㎖의 1 %의 Igepal CA-630, 0.7 % 나트륨 데 옥시 콜레이트 -)하고 TEN 완충액 (10 mM 트리스 - 염산 pH를 8.0, 1 mM의 EDTA, 150 mM의 염화나트륨)의 50 ㎖.
- 점수와 7 ml의 시점에서 15 ml의에게 원뿔 폴리스티렌 튜브 클립. 초음파를 겪고 핵 추출물을 포함하는이 튜브를 사용합니다.
- 후 염기 서열 분석을 위해, 최소 8 기가 바이트 RAM과 500기가바이트 디스크 여유 공간이 멀티 코어 유닉스 스타일의 운영 시스템을 사용합니다. 로컬에있는 대부분의 명령 줄에서 사용되는 다음과 같은 소프트웨어를 설치 FastQC, 일루미나 CASAVA 1.8 품질 필터, 나비 넥타이 (11), SAMtools (12), 호머 (13), MACS2 (14), IGV 15, 16, Cluster3 (17), 자바 트 리뷰, BLAST + 18 및 b2g4pipe 19. 컴파일러 및 타사 소프트웨어에 대한 설치 지침과 요구 사항을 확인하십시오.
- 짧은 NGS는 Xenopus의 게놈을 읽고 정렬을위한 나비 넥타이 인덱스를 구축 할 수 있습니다. 예는 X 용 여기에 표시됩니다 Xenbase FTP 서버 (/ 주점 / 유전체학 / JGI)에서 FASTA 파일 (genome.fa)로 다운로드 할 수 있습니다 tropicalis 게놈 V7.1 (헤세이 23 년 11 월). 나비 넥타이의 인덱스 하위 디렉토리에 FASTA 파일을 이동합니다.
- xenTro7 인덱스 파일을 생성 (> 프롬프트 문자 다음에 여기에) 다음 명령 줄을 사용합니다 :
> 나비 넥타이 빌드 /path/to/bowtie/index/genome.fa의 xenTro7
> 수출 BOWTIE_INDEXES = / 경로 /에 / 나비 넥타이 / 색인 /
- xenTro7 인덱스 파일을 생성 (> 프롬프트 문자 다음에 여기에) 다음 명령 줄을 사용합니다 :
- UCSC 게놈 브라우저 또는 도구 / 표 브라우저를 통해 최신 게놈 버전 (genomes.nimr.mrc.ac.uk)에 대한 국립 기상 연구소 서버의 미러 사이트에서 유전자 주석 파일 (GTF)을 다운로드합니다. 게놈 FASTA 파일 및 H를 사용자 정의 할 수있는 GTF 파일을 사용하여아프리카 발톱 개구리에 대한 메르 (예를 들어, X. tropicalis 게놈 7.1 - xenTro7 이름).
- 또한, Xenopus의 게놈의 일부 이전 버전의 사전 구축 된 호머 패키지를 사용합니다.
> loadGenome.pl -name xenTro7 -org 널 -fasta /path/to/genome.fa -gtf에 / 대한 / 경로 genes.gtf
- 또한, Xenopus의 게놈의 일부 이전 버전의 사전 구축 된 호머 패키지를 사용합니다.
- 그리고 주석 파일 (genes.gtf) (같은 폴더에 genome.fa.fai 파일로 genome.fa) 인덱스 FASTA 파일을 업로드하여 게놈 브라우저 IGV에 대한 게놈 트랙 (.genome 파일)을 만듭니다. 다음과 같이 Xenopus의 게놈에 대한 게놈 발판 지수 (genome.fa.fai)를 만듭니다 :
> samtools faidx /path/to/genome.fa - 다음과 같이 Xenopus의 유전자 상에 여러 모델 종 (인간, 마우스, 제브라 피쉬, 초파리 및 효모)에서 유전자 온톨로지 (GO) 조건을 통과 BLAST +를 사용하여
- 도구를 통해 UCSC 게놈 브라우저에서 하나의 FASTA 파일 (cds.fa) 모든 코딩 서열 (CDS)를 다운로드/ 테이블 브라우저 및 비 중복 단백질 (NR)의 미리 포맷 BLAST 데이터베이스와 업데이트 BLAST + :
> update_blastdb.pl NR - 인간 (txid9606)를 검색, 마우스 (txid10090), 제브라 피쉬 (txid7955), 과일 파리 (txid7227) 및 효모 (txid4932)의 고급 검색 기능을 통해 NCBI 사이트에서 단백질 (HTTP : //www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 모양의 정부 / 단백질 / 고급) 과 컴퓨터에 결과 GI (시퀀스 식별자) 목록 (sequence.gi.txt)를 보낼 수 있습니다.
- 특정 기대 (E) 값 컷오프 (여기에 10 -20)으로 BLASTX을 실행하여 GI 목록에서 가장 유사한 단백질 Xenopus의 유전자를 할당합니다. 확인 출력 형식은 XML 확인하십시오 (-outfmt 5 -out blastx_results.xml). 사용 가능한 컴퓨터 코어의 개수와 상관 관계가 시간 절약 스레드 (-num_threads) 사용한다.
> BLASTX -db / 경로 /로 / NR -gilist /path/to/sequence.gi.txt - 쿼리 / 경로 / tO / cds.fa -evalue 1E-20
-outfmt 5 -out /path/to/blastx_results.xml -num_threads [# 스레드] - 텍스트 편집기를 사용하여 b2g4pipe 폴더의 b2gPipe.properties 파일을 열고 Dbacces.dbname = b2go_sep13 및 Dbacces.dbhost = publicdb.blast2go.com에 데이터베이스 속성을 업데이트합니다. 설치 폴더에서 실행 b2g4pipe.
> 자바 Xmx1000m -cp * : 내선 / * : es.blast2go.prog.B2GAnnotPipe -in /path/to/blastx_results.xml
-out 결과 / xenTro7 프로 프 b2gPipe.properties -v -annot
참고 :이 프로그램 추출물 명중 각 BLAST에 대한 조건을 가서 해당 Xenopus의 유전자 (xenTro7.annot)에 할당합니다. 가장 최근에 업데이트 된 데이터베이스 설정 도구에서 찾을 수 있습니다 / 일반 설정 / Blast2GO 자바 웹 스타트 응용 프로그램의 DATAACCESS 설정 (9.11.1 참조).
- 도구를 통해 UCSC 게놈 브라우저에서 하나의 FASTA 파일 (cds.fa) 모든 코딩 서열 (CDS)를 다운로드/ 테이블 브라우저 및 비 중복 단백질 (NR)의 미리 포맷 BLAST 데이터베이스와 업데이트 BLAST + :
2. 염색질 상호 연결
- 아프리카 발톱 개구리 계란, 드 젤리와 문화 안에 기름지게bryos 표준 프로토콜 (20)에있어서.
- 캡 8 ㎖의 유리 샘플 유리 병에 관심있는 발달 단계에서 dejellied 배아 (최대 2,500 X를 laevis의 10,000 X. tropicalis)를 전송하고 0.01x의 MMR 짧게 한 번 씻어.
- 실온에서 40 분에 15 (예를 들어, 8 ml의 0.01x의 MMR에 36.5-38 % 포름 알데히드 225 μl를 추가) 0.01x MMR 1 %의 포름 알데히드와 배아를 수정 (고정 시간과 필요한 배아의 수에 대한 설명을 참조하십시오 ) 칩 실험 당.
참고 : 포름 알데히드는 부식성 및 독성이 강한 것입니다. 그것은 눈과 피부 접촉, 소화 불량, 및 흡입의 위험합니다. 유리 병에 포름 알데히드를 추가 할 때 흄 후드를 사용합니다. - 잠시 차가운 0.01x의 MMR과 배아를 세 번 세척하여 고정을 중지합니다. 표면 장력이 그들을 파열의 원인 때문에 엠브리 운영 체제가 액체 표면과 접촉하게하지 마십시오.
- 얼음에 2 ml의 마이크로 원심 튜브에 배아를 나누어지는약 250 μL (X를 tropicalis) 또는 부화하기 전에 600 μL (X를 laevis의)의 볼륨을 차지 튜브 당 250 배아의 최대.
- 가능한 한 피펫 거리만큼 0.01x의 MMR. 당신이 제 3 항에 따라 즉시 계속하면 다음 단계를 건너 뛰십시오.
- 차가운 HEG 버퍼의 250 μL의 배아를 평형. 배아는 튜브의 바닥에 정착 한 후에는 가능한 한 많은 액체를 제거하고 스냅인 동결을 액체 질소에. -80 ° C에서 보관하십시오.
3. 염색질 추출
참고 : Xenopus의 배아에서 가교 염색질의 다음 추출 단계 2.3 50-80 X에서 표시된 고정 시간으로 가장 효율적으로 작동 40 X.에 tropicalis 25 추출 완충액 E1, E2 및 E3 1 ㎖ 당 laevis의 배아. 버퍼 배 부피 계산이 필요하다는 것을 각각의 추출 단계가 반복된다. 업 스케일링은 여러 2 ML의 microcentri를 사용fuge 튜브 또는 50 ㎖ 원심 분리기 튜브. 염색질 추출하는 동안 얼음에 샘플 버퍼를 유지합니다.
- 버퍼 E1, E2, 1 mM의 DTT와 E3 및 프로테아제 억제제 정제의 적절한 볼륨을 보충합니다. 포스 특이 항체, 5 mM의 NaF가 2 mM의 나 3 VO 4 더 보충 버퍼와 칩을 수행합니다.
- 피펫 팅 아래로 E1과 고정 된 배아를 균질. 2 분 동안 1,000 XG에 냉장 원심 분리기 (4 ° C)에서 원심 분리기 균질 (또는 5 분 50 ml의 튜브를 사용하는 경우). 뜨는 벽에 부착 된 지질을 대기음.
- E1에 펠렛을 재현 탁. 10 분 동안 얼음에 샘플을 유지합니다. 단계 3.2에서와 같이 원심 분리기 및 폐기 상층 액.
- E2에서 펠렛을 재현 탁. 단계 3.2에서와 같이 원심 분리기 및 폐기 상층 액.
- 단계를 반복 3.4하지만, 원심 분리 전에 10 분 동안 얼음에 샘플을 유지.
- E3에서 펠렛을 재현 탁. 적어도 10 분 동안 얼음에 샘플을 유지합니다. 원심 분리기 및 폐기 스와단계 3.2에서와 같이 pernatants.
참고 :이 단계에서, resuspensions 상당히 투명하게해야한다. E3에서 음이온 세제 용해 남은 노른자 혈소판의 대부분을 렌더링함으로써 가교 핵을 추출합니다. - 가교 핵 재현 탁하고 풀 펠릿 E3 1 ㎖의 총 부피 (통상적으로 불용 색소 과립으로부터 갈색으로). 매우 점성이 나타나고 피펫 어려운 경우, 2 또는 3 ㎖ E3에 샘플을 희석. 얼음에 보관 또는 4 ° C에서 동일하거나 다음날의 4 단계를 진행합니다. 나중에 사용하기 위해 -80 ° C에서 액체 질소와 저장소에 스냅 동결.
4. 염색질 조각화
참고 : 초음파 처리 용해하고, 가교 염색질을 전단을 모두 사용됩니다. 다음은 1/16 인치 테이퍼 마이크로 팁과 사운드 인클로저 장착 Misonix 초음파기 3000을 실행하는 매개 변수입니다. 다른 sonicators를 사용하는 경우, 제조업체의 권장 전단에 따라가교 염색질 또는 총 4 내지 8 분 동안 12 W 6을 사용한다.
- 초음파 (단계 1.4)에 대한 맞춤형 튜브로 단계 3.7에서 핵 샘플을 전송합니다. 짧은 온도계 클램프를 통해 얼음 물이 가득 800 ml의 플라스틱 비커에 연결된 튜브를함으로써 초음파 동안 냉각 샘플을 보관하십시오.
- 실험실 잭 비커를 놓습니다. 초음파기의 마이크로 팁이 튜브 벽을 건드리지 않고 볼륨 깊이의 약 3 분의 2에 샘플에 잠겨과 중앙에 오도록 잭을 조정합니다.
- 총 7 분에 대한 샘플 초음파 처리, 1 분 일시 정지로 매 30 초를 중단. 1.0 전원을 설정합니다. 초음파 처리를 시작하고 바로 샘플 거품되기 시작하면 즉시 W. 일시 9~12의 판독에 도달하도록 (일반적으로 2 내지 4) 전력 설정을 증가시킨다. 튜브를 옮기고 거품이 완전히 사라질 때 다시 시작합니다.
- 15,0> (최고 속도로 미리 냉장 1.5 ml의 마이크로 원심 튜브와 스핀에 전단 염색질로 이동4 ℃에서 5 분 00 XG).
- 1.5 ml의 마이크로 원심 튜브에 미리 냉장 뜨는을 전송합니다. 염색질 조각 (5 장)의 정도를 시각화 (이상적으로 약 40 만 이상의 핵의 크로 마틴을 포함) 상층 액의 50 μl를 수집합니다. 온칩 (6 절)의 상층 액의 나머지 부분을 사용합니다.
- 최대 하루 동안 4 ° C에서 보관 샘플. 분취 같은 스냅 동결 샘플 -80 ° C에서 장기 보관 용 액체 질소 (칩 실험 당 하나).
5. 이미징 염색질 조각화
- SDS 용출 버퍼의 50 μL, 5 M의 NaCl 4 μL와 단계 4.6에서 뜨는의 50 μL에 단백질 분해 효소 K (20 ㎍ / μL) 1 μl를 추가합니다.
- 오븐 65 ° C로 설정 하이브리드에 6-15 시간 (O / N)에 대해 품어.
- 상업용 PCR 정제 키트를 사용하여 DNA를 정제. 필요한 경우, 제조자가 권장하여 pH를 조정할 아세트산 나트륨 (PH 5.2)의 3 M을 사용한다. 용출DNA 회 용출 완충액 11 μL (10 mM 트리스 - 염산 pH를 8.5)와.
- 100 BP와 함께 전체 시료와 전기로 1.4 % 아가로 오스 겔에 1킬로바이트의 DNA 사다리를 실행하기 전에의 RNase의 0.4 μL (20 ㎍ / μL) 및 5 배 DNA 로딩 버퍼의 5 μl를 추가합니다. 전기 영동 후 안전한 핵산 염색 액으로 최적의 결과, 얼룩 젤하십시오.
6. 염색질 면역 침전
참고 :이 섹션에서는 4 ℃에서 5 분 동안 자기 구슬을 씻어 낮은 유지 1.5 ml의 마이크로 원심 튜브와 튜브 당 지정된 버퍼의 최소 1 ml에 사용합니다. 구슬에서 버퍼를 제거하기 전에 20 때마다 30 초 또는 솔루션이 깨끗해질 때까지의 자기 랙에 튜브를 둡니다.
- 새로운 튜브 단계 4.6에서 뜨는 (전단 염색질)의 30 μL로 전송 (10)는 칩 사용 총 염색질의 약 1 %에 해당하는 입력 샘플로 나중에 사용할 수 있습니다. 4에서 보관칩 샘플 크로스 링크를 취소하기위한 준비가 될 때까지 C를 °.
- 새로운 튜브에 남아있는 염색질을 전송합니다. 항체 제어를 필요로하는 칩 qPCR의 실험의 경우, 두 개의 튜브로 염색질의 동일한 볼륨을 배포 할 수 있습니다.
- 염색질로 칩 등급 항체 (또는 해당 항체 제어)를 추가한다. 대략적인 기준으로 약 1 μg의 관심의 에피토프를 표현 백만 셀 당 항체를 사용합니다.
- 더 정확하게 항체의 다양한 양의와 동일한 칩을 실행 (예를 들어, 0.25 μg의 1 μg의 2.5 μg의)를 칩 실험 당 필요한 항체의 양을 추정 및 칩 qPCR에 의해 부정과 양성 대조군 유전자 좌에서 수율을 비교하려면 (참조 (10)). 항체 대조군으로서, 항체와 같은 아이소 타입 및 숙주 동물 종의 정상 혈청을 사용한다.
- 4 ° C에서 / 회전 (10 회전) O에 N을 품어.
- 5 분 위해 E3로 한번 항체 호환 자성 비드의 적당량을 씻으t 4 ° C에서. 확인 구슬의 항체 결합력에 대한 제조업체의 사양 (구슬의 보통 5-20 μl의 IgG 항체의 1 μg의 결합).
- 항체 사전 배양 염색질에 씻어 구슬을 추가합니다. 또한 4 시간 동안 회전 (10 회전)에 품어.
- 워시 사전 냉장 TEN 버퍼에 한 번 네 번 (칩 qPCR에) 또는 사전 냉장 RIPA 버퍼와 열 번 (칩 서열 번호) 및 비즈.
- 칩-SEQ 실험을 수행하는 경우에만이 단계를 수행한다.
- 재현 탁 튜브 당 TEN 버퍼의 50 μL에 구슬을 세척 하였다. 하나의 새로운 튜브로 전송하여 단일 칩 실험에서 풀 모든 구슬. 튜브의 하단에 구슬을 수집하기 위해 1,000 XG에서 자기 랙 및 냉장 (4 ℃로) 원심 분리를 사용합니다. 구슬의 펠렛을 방해하지 않고 많은 액체 가능한 폐기하십시오.
- SDS 용출 버퍼와 vort의 50 ~ 100 μL에 구슬을 재현 탁하여 구슬 없애기 칩 재료65 ° C에서 15 분 동안 써모 (1000 RPM)와 함께 그들을 계속 exing. 30 초 동안 최대 속도 (> 15,000 XG)에서 그 원심 분리 후. 새로운 튜브에 뜨는 (칩 용출액)를 전송합니다.
- 마지막 단계를 반복하고 칩 용출액을 결합한다.
7. 염색질 역 간 연결 및 DNA 정화
- 100-200 μL (단계 6.10) 인 칩 샘플의 부피에 도달하는 입력 샘플 (단계 6.1)로 충분히 SDS의 용출 완충제를 추가한다. 5 M의 NaCl 1/20 볼륨 모두 칩과 입력 샘플을 보충합니다. 하이브리드 오븐에서 65 ° C에서 6-15 시간 (O / N)에 대한 샘플을 품어.
- 200 ㎍ / ㎖의에서 TE 버퍼와의 RNase의 1 볼륨을 추가합니다. 37 ° C에서 1 시간 동안 품어.
- 200 ㎍ / ㎖의에서 단백질 분해 효소 K를 추가합니다. 55 ° C에서 2 시간 4 알을 품다.
- 페놀에 의해 DNA를 정제하여 클로로포름 : 에탄올 침전에 이어 이소 아밀 알코올 추출 이전에 설명 된대로 9. 칩 서열 번호의 경우, (32)를 추가용출 완충액 (10 mM의 트리스 -HCl pH 8.5)의 μl의 DNA 펠렛을 용해. 30 분은 DNA가 완전히 용해 될 수 있도록 얼음에 샘플을 남겨주세요.
주 : 상용 PCR 정제 키트 저급 DNA 복구를 갖지만 더 편리하고, 칩 샘플 qPCR에 사용될 수있다. - 칩은 SEQ, 형광 측정 기반의 방법을 이용하여 DNA 칩과 입력 1 μL의 농도를 결정한다. 제조업체의 지침에 따라 DNA의 농도는 형광의 안정적인 감지 범위 내에 있는지 확인하십시오.
8. 칩 서열 번호 라이브러리 생성 및 검증
참고 : DNA 라이브러리 준비를위한 현재의 방법은 1 ~ 2 NG에 NGS 높은 복잡성 라이브러리를 건설 할 수 있습니다. 일부 복잡성의 비용으로, 라이브러리는 DNA의 적은 50 페이지 (특정 재료 / 장비의 표 참조)에서 할 수있다. 칩과 입력 DNA 라이브러리 모두의 동일한 양을 사용한다. 간단히, MAK하기전자 인덱스 칩 서열 번호 라이브러리, 칩과 입력 DNA가 최종 수리해야 (쌍 엔드)는, (특정 재료 / 장비의 표 참조) 특수 어댑터에 결찰, 크기 선택과 PCR 증폭.
- 칩 서열 번호 라이브러리를 만들기 위해 제조업체의 지침을 따르십시오. 추가 권장 사항에 대한 설명을 참조하십시오.
- 용출 완충제 12 ㎕를 각 라이브러리를 용출하고 형광을 이용하여 각각의 칩 입력 라이브러리 1 μL의 농도를 결정한다. 5-25 NG / μL의 농도를 기대합니다. 농도보다 높은 25 NG / μL 인 경우 PCR 사이클 (18 사이클보다 적게)의 수를 감소 고려한다.
참고 : 정확한 정량 최적의 NGS 결과를 달성하는 데 매우 중요한 역할을합니다. 18 PCR주기 후 1 NG / μL의 낮은 농도 라이브러리는 서열,하지만 자주 덜 복잡하다 할 수 있습니다. - 단편 크기 분포를 결정하는 라이브러리의 1 μl를 사용하여 C에 의한 어댑터 이량 체 오염 (밴드 약 120 BP)를 확인하기 위해엉덩이 기반 모세관 전기. 1 : 1의 비드 간 샘플 비율로 고체상 가역적 고정화 정제를 반복 (대신에 1.6 : 1) 라이브러리 어댑터 다이머를 포함하는 경우.
- 비슷한 DNA 농축 동향 전과 라이브러리 준비 후 관찰 여부를 확인하기 위해 검증 양성 및 음성 제어 유전자 좌 (10 항을 참조)에 qPCR을 수행합니다. 시퀀싱 품질 관리 승인 라이브러리를 제출합니다.
9. 후 염기 서열 분석 및 데이터 시각화
참고 : 요즘, NGS는 종종 사내 또는 상업적 시퀀싱 시설 (일부 NGS 가이드 라인에 대한 설명을 참조)에 의해 수행된다. 표준 출력은 시퀀싱 읽기의 수백만을 저장하는 하나 또는 여러 개의 gzip으로 압축 FASTQ 파일 (* .fastq.gz)입니다. 일반적으로, 멀티 플렉스는 인덱스에 따라 이미 분리되어 각각의 판독 및 판독 각 BAS하는 시퀀스 식별자 및 품질 관리 점수 (Illumina 사 용 Phred 33 + 1.8)를 포함전자 콜. 이러한 접근은 여기 NGS 데이터를 분석하는 많은 방법 중 단지 하나이다. 독자는 다음 명령 줄의이 필드를 빠르게 진행되고 업데이트가 정기적으로 발생하는로 변경할 필요가 있는지 여부를 확인하도록 권장된다.
- GZIP 압축 FASTQ 파일을 연결하고 FastQC 스크립트를 사용하여 시퀀싱 데이터의 품질을 확인. 이 작업을 실행하고 모두 칩과 입력 시퀀싱 데이터에 대한 다음과 같은 대부분의 명령 터미널에서 (예 칩 표시) :
> 고양이 /path/to/*.fastq.gz> ChIP.fastq.gz
> fastqc ChIP.fastq.gz
참고 : 높은 복잡성 칩-SEQ 라이브러리의 성공적인 시퀀싱에서 원시 데이터가 대부분의 시험을 통과해야합니다. 실패는 가난한 순서 실행 및 바이어스 PCR 증폭 또는 어댑터 오염 등의 실험 유물에서 주로 발생. 중복이 선의의 DNA 농축을 나타낼 수 읽는 중복 (중복)의 어느 정도 예상됩니다 21. 5 '말단 또는 판독 - - 단, 나중에 판독 한 태그를 제한 할 수있는 하나에 기재 쌍당의 중복 (단계 9.4) 21 피크의 검출 감도에 영향을주지 않고 제거 판독. - 사전 프로세스 시퀀싱 데이터 (homerTools 트림 -3 <어댑터 순서>) 허용 한 불일치 (-mis 1) 어댑터 오염을 제거합니다. 결찰시 관심있는 DNA 단편에 기단 ( '3'5) (인덱스) 어댑터의 처음 20 염기를 사용하여 (특정 재료 / 장비의 표에 도시 된 어댑터).
>을 gzip -cd ChIP.fastq.gz | fastq_illumina_filter -vn> ChIP.fastq
> homerTools 트림 -3 GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCT는 하나라는 우수한 성능을 나타내었다 (36) ChIP.fastq을 -mis
참고 : 필터의 제거는 (-N)가 만 일루미나 1.8에 의해 생성 FASTQ 파일에서 기본적으로 필요합니다 읽습니다. fastq_illumina_filter 명령을 생략 (예. '| fastq_illumina_filter -vn')1.8보다 이전 버전의 시퀀스 식별자를 생성합니다. - 맞 춥니 사전 처리는 나비 넥타이를 사용하여 참조 게놈 (xenTro7)로 읽습니다. 만 유일하게 매핑 계속 읽기 (-m 1) (-S) 제 28 기지와 SAM 형식으로 최대 70 보고서 정렬의 읽기 당 모든 불일치 총 Phred + (33) 품질 평가 점수에 기본 즉 설정, 최대 두 불일치를 사용하여 . 청크 메모리가 고갈되면 스레드 당 메가 바이트 (--chunkmbs)의 수를 증가 :
> 나비 넥타이 -m (1) -S -p [# 스레드] --chunkmbs [예 : 200] xenTro7 ChIP.fastq.trimmed> ChIP.sam
주 : 나비 넥타이는 기본적으로 Phred + (33) 품질 평가 점수를 기대하고있다. 옵션을 포함 - phred64-quals을 FASTQ 파일이 1.8보다 오래된 일루미나 (Illumina)에 의해 Phred + (64) 품질 평가 점수로 생성 된 경우. - 중요 인물 파일 (.bw)로 정렬 (SAM) 파일을 변환하는 두 개의 홈런 명령을 사용하여
> makeTagDirectory에 칩 / 단수 -tbp 1 ChIP.sam
> makeUCSCfile에 칩 /ChIP.bw -o -bigWig / 경로 /로는 / genome.fa.fai -fsize 1E20 -norm 1E7
참고 : 변환 참조 게놈 (단계 1.8)의 발판 지수 (genome.fa.fai)가 필요합니다. 다음은 프로파일 (-norm 1E7)은 천만 염기쌍 (-tbp 1) 정규화 당 하나의 태그에 대한 읽기 제한됩니다. 중요 인물은 동적으로 IGV (단계 9.12)와 같은 게놈 브라우저 염색질 프로파일을 시각화하는 기본 형식 중 하나입니다. - (예를 들어, +/- 25 bp의 쓰레기통과 10킬로바이트 -si '제 20000 -hist 25) 등의 전사 시작 (TSS, 예를 들어 여기에 표시) 및 종료 등 (게놈 유적지에서 태그의 분포 (-d 칩 /) 결정 TTS) 사이트. 아프리카 발톱 개구리 주석 xenTro7 (단계 1.7)와 호머 펄 스크립트 annotatePeaks.pl을 실행
> annotatePeaks.pl TSS xenTro7 - 크기 20000 -hist 25 -d에 칩 /> ChIP_tagDensity.tss - 에 칩 사이의 DNA 농축의 중요한 피크 찾기(ChIP.sam -t)와 X의 입력 (-c Input.sam) tropicalis 게놈 모델 구축 200 BP (--bw = 200)의 (0.01 -q) 1 % FDR 차단하고 (초음파 후) DNA 조각으로 MACS2를 사용. 이러한 히스톤 마크 또는 RNA 중합 효소로 관심의 염색질 기능의 폭 넓은 분포를 기대하는 경우이 명령 줄 플래그 --broad를 추가합니다.
> macs2 callpeak -t ChIP.sam -c Input.sam -f SAM -n에 칩 -g 1.4376e9 -q 0.01 --bw = 200
참고 : X의 유효 크기 tropicalis 게놈 조립 7.1은 약 1,437,600,000 BP (-g 1.4376e9)입니다. MACS2 자신의 게놈 위치에 피크를 입대 BED 파일 (ChIP_peaks.bed)를 생성한다. - 클러스터 히트 맵의 형태로 여러 염색질 프로파일을 비교 :
- 관심의 태그 밀도 디렉토리에서 태그 배포 매트릭스를 작성 (-d에 칩 / other_ChIP /) MACS2 피크 (에서 예를 들어, 25 bp의 쓰레기통, -size 2000 -hist 2 +/- 1킬로바이트5 -ghist) :
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 - 크기 2000 -hist 25 -ghist -d에 칩 / other_ChIP /> ChIP.matrix - ChIP.matrix 파일을 업로드하고 계층 적으로 가장 가까운 중심에 최소 유클리드 거리에 따라 이러한 태그 밀도를 클러스터링 Cluster3의 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스를 사용합니다. 클러스터링을 시각화하기 위해 자바 트 리뷰에서 생성 된 CTD 파일을 엽니 다.
- 관심의 태그 밀도 디렉토리에서 태그 배포 매트릭스를 작성 (-d에 칩 / other_ChIP /) MACS2 피크 (에서 예를 들어, 25 bp의 쓰레기통, -size 2000 -hist 2 +/- 1킬로바이트5 -ghist) :
- 피크 정상 회담에 충실 소설 이전에 알려진 바인딩 모티브, +/- 100 혈압 (200 -size) 찾습니다. 모티브 발생을지도하고 주제 밀도를 플롯 annotatePeaks.pl을 사용하여
> findMotifsGenome.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 ChIP_motifs / -size (200) -p [# 스레드]
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif> ChIP_peaks.motif1
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 -m motif1.motif - 크기 800 -hist 25> motif1.density
참고 : findMotifsGenome.pl 스크립트 infeRS 비교에서 농축 임의로 유전자 중심 배경 시퀀스를 선택한다. 가장 풍부한 새로운 모티브 위치 가중치 행렬의 형식으로 motif1.motif으로 저장됩니다. 독자는 이러한 cisFinder 22 MEME (23)와 같은 다른 드 노보 모티브 검색 방법과 결과를 입증 것이 좋습니다. - 가장 가까운 유전자의 거리를 계산하여 400 bp의 창 (400 -size) 내에서의 표준화 된 읽기 수를 결정하여 피크 주석 :
> annotatePeaks.pl ChIP_peaks.bed xenTro7 400 -d에 칩 / 입력 /> ChIP_peaks.genes을 -size - 수 (N), 위치 및 개별 (R)의 표준화 된 읽기 수와 가장 가까운 (대상) 유전자에 따른 모든 (LR) 피크를 나열하려면 다음 awk 명령을 사용하여 출력을 요약한다.
> AWK '{의 t'7달러> = -5000 && 7달러 <= 1000 FS의 =} BEGIN '을
{N [$ 8] + = 1; R [$ 8] + = 9달러; LR [$ 8], 'LR [$ 8] =# 39; 7달러 '('$ 9 ')'} END {용 (I N)에
{인쇄 내가 't'N [I] ' t'R [I] ' t'SUBSTR (LR [I], 2)}} 'ChIP_peaks.genes> ChIP_peaks.summary
주 : $ 후의 수가 이전 단계에서 생성 ChIP_peaks.genes 파일 맞게 수정해야 할 수도 열 번호를 의미한다. 이 스크립트의 모범이 5킬로바이트 상류와 TSS의 다운 스트림 1킬로바이트 넘어 피크를 필터링합니다. 7달러 $ 8 9달러 TSS, 각각의 유전자 식별자와 피크 당 정규화 읽기 카운트까지의 거리 정보를 참고하십시오. - 다음과 같이 표적 유전자 중에서 농축 GO 용어의 분석을 수행 :
- 자바 웹 스타트 (의 Javaws) (19)를 통해 명령 줄에서 Blast2GO의 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스를 시작합니다.
>의 Javaws http://blast2go.com/webstart/blast2go1000.jnlp - 주석을 업로드하는 개발자의 지침에 따라아프리카 발톱 개구리 1.9.4에서 생성 된 유전자 (xenTro7.annot) 및 식별 된 표적 유전자의 플랫 파일에 대한 파일. 동일한 유전자 식별자가 두 파일에 사용되어 있는지 확인합니다.
- 자바 웹 스타트 (의 Javaws) (19)를 통해 명령 줄에서 Blast2GO의 그래픽 사용자 인터페이스를 시작합니다.
- 트랙으로 IGV에 중요 인물 (ChIP.bw, Input.bw)와 BED 파일 (ChIP_peaks.bed)을 추가하여 염색질 프로필을 시각화. RNA-SEQ와 보완 자료 개발의 동일한 단계에 대한 가능한 경우 추적합니다. 세션 등의 결과를 저장합니다.
- 프로그래밍 플랫폼 R 사용 (www.r-project.org) 상기 생성 된 추가 데이터를 조작하고 시각화 또는 MATLAB을. 또한, 엑셀 작은 데이터 세트를 플롯.
(10) 칩 qPCR에 테스트 칩 및 확인 칩 서열 번호
- 긍정적 인 (피크 별) 및 음성 대조군 유전자 좌 모두 60 ° C (T의 m)에서 약 100 염기쌍의 DNA를 둘러싼 프라이머를 설계하는 온라인 플랫폼 Primer3를 사용합니다. 프라이머 특이 사용 확인에 실리 PCR 검색은 UCSC 게놈 브라우저에 구현했습니다.
- 약 1 %의 입력에서 시작하여 3 배 희석 8 점 표준 곡선을 만들거나 2를 사용 - DNA 농축의 정량 ΔΔC (T) 방법 8,24를.
- 필요하다면, 표준 곡선 샘플을 모든 샘플, 즉, 칩 제어 기술 3 회 반복 실시간 PCR을 실행합니다.
- 입력 DNA의 백분율 또는 양성 및 음성 대조군 유전자좌 모두 대조군 샘플에 비해 칩의 비율로서 플롯 DNA 엔리치.
결과
프로토콜은 잘 실행되는 경우 여기 제시된 동등한 결과가 예상되는 사용 및 항체 칩 품질 등급 (설명 참조)이다. 이 프로토콜은 포름 알데히드 고정 아프리카 발톱 개구리의 배아에서 핵의 추출 및 초음파에 의한 염색질의 효율적인 전단 (그림 1A-C)를 할 수 있습니다. 전단 염색질은 주로 100 내지 1000 염기쌍의 범위 및 BP (도 1C) 300 내지 500 피킹 DNA 단편의 비대칭 분포를 나타낸다. 면역 DNA의 최소 50 페이지가 성공적으로 비슷한 크기의 DNA를 삽입 (그림 2A)와 인덱스 쌍 엔드 칩-SEQ 라이브러리를 만들기 위해 필요합니다. 도서관은 약 120 bp의 electropherogram에서 볼 수 있습니다 어댑터 이량 체의 크게 결여해야한다.
시퀀싱 합성에 의한시 읽기 사전 처리는 게놈 (그림 2B, C)에 매핑됩니다. 성공적인 실험과에서 X. tropicalis 배아는 하나의 엔드의 일반적 50-70%는 최대한 두 불일치와 7.1의 게놈 어셈블리에 고유하게 매핑 할 수 있습니다 (40) 혈압 읽습니다. 입력 게놈에 걸쳐 매우 균일하게 정렬 읽는 동안, 칩의 정렬은 관심 염색질 기능의 측면 가닥 별 부화에 결과를 읽습니다. 조각을 모두 5 '말단 (그림 2C) 25 서열 때문입니다. 평균 단편 크기에 방향을 읽는 정렬을 확장하는 것은 같은 전사 인자 바인딩 이벤트와 같은 하나의 크로 마틴 기능에 대한 정확한 프로파일을 생성합니다. IGV 또는 기타 호환 게놈 브라우저 시각화 할 때 이러한 DNA의 점유는 피크로 나타납니다. MACS 등 피크 발신자는 이들 피크 (도 3a)의 위치를 결정하기 위해 사용된다. 수십 결합 부위의 수천이 방법은 X에서 결정되었습니다 tropicalis 게놈 같은 VegT (26) T-상자 전사 인자에 대한. 칩 qPCR에의 체험관사항 칩-SEQ (그림 3B)에 의해 발견 된 지역 농축을 확인해야합니다.
칩 서열 번호 실험 염색질 기능의 게놈 전체의 특성을 탐구 할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 전사 개시 및 종결 부위로 게놈 요소를 판독 분포를 산출하는 임의의 유전자 주위 공간 결합 선호도 (도 3c)를 강조 할 수있다. 마찬가지로, 피크 위치에서 읽기 분포의 히트 맵은 게놈 전체 규모 (그림 3D)에서 다른 염색질 기능을 비교하는 데 사용됩니다. 특정 전사 인자는 잠재적 인 공동 요인 (그림 3E)의 공동 풍부한 주제를 포함하여 이러한 종류의 정보를 검색 할 수 있습니다 게놈 DNA 기본 피크의 DNA 서열 특히. 드 노보 모티브 분석을 결합한다. 표적 유전자의 대다수는 DNA의 하부에 점유보다는 더 높은 레벨 (도 3f)를 도시한다. 이 규모없는 기능은 그럴 사이에서 매우 일반적인 것 같다anscription 인자와 표적 유전자의 작은 부분을 직접 생물학적 관련성 27,28으로 조절되는 것을 제시한다. 이러한 추가 Xenopus의 배아 (그림 3G)에서 염색질 기능의 생물학적 기능에 대한 통찰력을 공개 할 수있다 표적 유전자의 발현 차이 등 풍부한 GO의 조건이나 다른 속성의 분석.
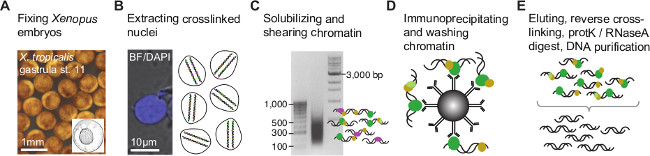
아프리카 발톱 개구리의 배아 1. 염색질 면역 침전 과정을 그림. (A) 배아 포름 알데히드 고정 공유 바인드 (가교)에 관심 게놈 DNA와 관련된 단백질의 발달 단계에있다. 핵 추출 (B)시, 가교 염색질 바인딩 게놈 DNA 또는 측면에서는 DN을 최소화하여 염색질 변형 사이트를 좁힐 조각난시퀀스 (C). 그 후, 염색질 조각은이자 (D)의 에피토프를 포함하는 사람들을 풍요롭게 칩 수준의 항체와 면역 있습니다. 공동 면역 DNA가 단백질을 제거하고 NGS (그림 2)의 칩 조각 라이브러리를 작성하기 전에 (E)를 정제한다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.

그림 2. 칩 서열 번호 라이브러리 준비, 시퀀싱 합성에 의한, 매핑 및 피크를 호출합니다. (A) electropherogram는 250 bp의 450의 DNA 템플릿과 좋은 칩 서열 번호 라이브러리를 표시합니다. 이러한 템플릿은 보편적 (58 BP)에 의해 형벌 관심의 DNA 삽입 및 인덱스 (63 BP) 어댑터를 수반한다. (B) 수백만, 가역, 독특한 형광과 동일한 종료 속성을 가진 네 개의 뉴클레오티드의 존재에 기초하여 시퀀스 기본이다. 형광 이미지 읽기에 궁극적으로 조립 해당 기지를, 전화를 실시간으로 처리됩니다. (C)는 만 유일하게 아프리카 발톱 개구리의 게놈지도가 유지되는 것을 읽습니다. 모든 단편은 5 '말단으로부터 순서가되기 때문에, 칩의 매핑은 관심 염색질 기능의 측면 가닥 특정 피크의 결과를 판독한다. 이에 따라, 피크 호출자가 정확하게 크로 마틴 기능을 현지화 평균 조각 길이로 읽어 면역에서 유래하고 확장 농축을 감지합니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.

그림 3. 접합체의 T-상자 전사 인자 VegT (zVegT). 모두 여기에 표시된 수가 10 만명 정규화 읽어 고유 매핑과 비 중복이 읽습니다. (A) 발췌에 의한 후 염기 서열 분석 및 데이터 시각화의 예 zVegT의 게놈 전체 프로필 X에서 바인딩 (Nieuwkoop 및 페이버 (29) 후 12.5로 무대 11) tropicalis 낭배 배아. 각 피크, 확장 된 읽기의 더미 업, 하나의 결합 부위를 나타냅니다. 이들 피크는 1 % 미만의 오류 발견 레이트 (FDR)와 MACS2 의해 호출된다. 각 mesp 유전자 바인딩 매우 인접 상류 zVegT를 보여줍니다,하지만 mespa 및 mespb는 그 단계 (RNA-SEQ 데이터 30)에 의해 표현된다. (B) zVegT의 DNA 점유율 수준 여러 유전자 좌에서 칩 qPCR에 의해 결정 (비 포함 KB 상류 β 액틴의 -bound 지역 0.5) 확인 합니칩 서열 번호에 의해 발견 된 특정 농축을 RM은. (A)에서 (빨간색 막대)라고 피크 mespa에 대한 결과를 비교한다. DNA 점유 레벨은 모두 입력의 비율, VegT 항체 (IgG의 이소 타입의 토끼 폴리 클로 날) 및 항체 제어 (정상 토끼의 IgG)와 칩 (Chip) 칩으로 보여집니다. 오차 막대는 두 개의 생물학적 반복 실험의 표준 편차를 반영한다. (C) Metagene 분석 주위에 다른 게놈 영역 및 유전자 기관 내 프로모터 상대에 바인딩 우선 zVegT을 (태그 25 bp의 이상 비닝)를 보여줍니다. (D)는 히트 맵은 K-평균을 보여줍니다 클러스터 (K = 5) DNA 점유율 수준 낭배 단계에서 모든 zVegT 바인딩 지역에 zVegT과 된 Smad2 /의 Smad3 (칩 서열 번호 데이터 31) 상대의 (태그는 25 bp의 이상 비닝). 히트 맵은 드 노보 모티브 분석 zVegT-의 38 %에 결합 모티프 정식 T-상자 전사 인자를 발견 2 기반 BP 당 5 태그를 중심으로. (E) 로그입니다기본 모티브 스코어 배경 서열에서 5 %의 비율로 발견 정규화 경우 결합 영역. 정식 된 Smad2 / Smad3이 결합 모티프가 거의 농축되지 않은 반면, 밀도지도, zVegT 결합 부위의 중앙에 T-상자 모티브 가장 높은 농축을 보여줍니다. (F) 히스토그램은 각 표적 유전자에 대해 계산된다 zVegT의 DNA 점유율 수준을 보여줍니다 [-] 모든 피크 (+/- 200 BP) 5킬로바이트 상류 사이에서. 전사 시작 사이트를 대응하고 1킬로바이트 하류 [+] (G) 가장 높은 DNA 점유율 내 -5 킬로바이트 수준과 1킬로바이트 아르와 최고 300 유전자 초기 배아 발달의 생물학적 과정에 대한 풍부. 이 용어가 zVegT의 추정 함수와 함께 줄에 이동합니다. FDR은 양측 피셔의 정확한 테스트를 기반으로 여러 테스트를 위해 수정됩니다. 이 그림의 더 큰 버전을 보려면 여기를 클릭하십시오.
토론
우리의 프로토콜은하고 아프리카 발톱 개구리의 배아에서 게놈 전체 염색질 프로파일을 분석하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다. 그것은 실리에 풍부한 게놈 사이트를 나타내는 읽기의 수백만을 처리하는 생체 내에서 내인성 유전자 좌에 가교 단백질에서 모든 단계를 다루고 있습니다. 게놈 초안의 증가 번호를 사용할 수 있기 때문에,이 프로토콜은 다른 모델과 비 모델 생물에 적용해야합니다. 이전의 연구 8,31,33,34에서 떨어져이 프로토콜을 설정하는 가장 중요한 실험 부분은, 가교 핵을 추출 후 고정 절차입니다. 그것은 효율적인 염색질 용해 화 및 전단 쉽게 업 스케일링을 용이하게한다. 함께 도서관 준비의 개선 된 효율성이 프로토콜은 반에서 관심있는 염색질 관련 항원을 발현하는 이백만 세포에 높은 복잡성 칩-SEQ 도서관의 건축을 할 수 있습니다. 칩 qPCR의 실험의 경우, 이들 세포의 몇 만 정상적으로 충분아마도 여섯 별개의 게놈 유전자 좌에서 DNA 농축을 확인합니다. 이러한 숫자는 보수적이지만, 단백질 발현 수준, 항체의 품질에 따라 효율, 에피토프의 접근성을 가교 달라질 수있다. 가이드로, 단일 Xenopus의 배아 중반 포배 단계 (Nieuwkoop 및 페이버 (29) 후 8.5)에서 약 4,000 세포를 포함, 후반 낭배 단계 (12)에서 40,000 세포와 초기 tailbud 단계 (20)에서 10 만 셀.
효율적인 면역에 대한 정확한 고정 시간은 칩 qPCR에 (10 항)에 의해 경험적으로 결정해야합니다. 실험이 X를 포함하는 경우 일반적으로 더 이상 고정 시간이 필요합니다 배아, 초기 발달 단계, 약한 (또는 간접) DNA 결합 특성을 laevis의. 그러나, 염색질 전단 효율성이 떨어질대로, 40 분보다 긴 아프리카 발톱 개구리 배아를 고정, 또는 표시 (섹션 3)보다 더 많은 배아를 처리하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 그것은 중요하지매우 어려운 노른자 풍부한 배아에서 핵 추출을 할 수 포름 알데히드를 담금질이 일반적인 단계로 고정 후 어떤 글리신를 사용합니다. 현재, 그 이유는 알려져 있지 않다. 또한 포름 알데히드 부가 물 상기 글리신 아미노 기 또는 아르기닌 잔기 35 N 말단과 반응하여 생각할 수있다.
항체는 칩 실험의 핵심입니다 충분한 컨트롤 (Landt 등. (36) 가이드 라인을 참조) 관심의 항원에 대한 특이성을 보여주기 위해 수행 될 필요가있다. 더 칩 등급 항체가없는 경우이 단백질이 차지하는 결합 부위 내인성 수 37, 에피토프 태그 융합 단백질 대응 소개 합법적 대안이 될 수있다. 이 경우, uninjected 배아는 음성 대조군보다는 비특이적 혈 칩으로 사용하는 것이 최선이다. 관심의 단백질이 enri의 가난한 복구의 결과로 낮은 수준에서 표현되는 경우,이 전략은 적용 할 수있다CHED DNA.
왜냐하면 사용중인 DNA의 소량 칩-SEQ 라이브러리 제조용으로서,이 세정 공정 수를 줄이고 최소한 DNA의 손실을 유지하는 반응을 조합하는 방법을 선택하는 것을 권장한다. 어댑터와 프라이머 (특정 재료 / 장비의 표 참조) 멀티 플렉스 시퀀싱 및 NGS 플랫폼과 호환 될 수 있도록해야합니다. (긴 단일 가닥 무기를 포함) Y-어댑터를 사용하는 경우, 그것은 크기 선택 DNA 삽입하기 전에 PCR의 3-5 라운드 사전 증폭 라이브러리에 중요하다 (예., 100 내지 300 bp) 겔 전기 영동에 의해. 단일 가닥 말단 DNA 단편이 균질하게 이동. 시험은 PCR 사이클의 총 수를 결정하도록 권장 입력 DNA (예를 들면, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20 NG)의 다양한 양으로 실행 (이하 또는 18 사이클 같음) 크기를 만드는 데 필요한 100-200 NG의 - 선정 된 라이브러리입니다. PCR 사이클의 수를 줄이면 redu의 시퀀싱을 렌더링ndant은 덜 읽습니다. 고상 가역적 고정화 비즈 효율적으로 관심있는 DNA를 복구하고 안정적으로 결찰 및 PCR 반응이없는 임의의 어댑터 및 이량 체를 제거하는 시약을 정리 좋다.
수, 유형 및 길이의 측면에서 약 20-30000000 단일 엔드 36 bp의 충분한 깊이와 전체 Xenopus의 게놈을 커버하는 대부분의 칩 서열 번호 실험에 충분하다의 읽기, 읽기의. 가장 널리 NGS 기계는 이러한 기준을 충족 일상적으로 할 수있다. 그러나, 판독의 광범위한 분포가 예상되는 경우의 판독 샤프한 피크보다 오히려, 히스톤 변형 관찰로, 수를 늘리는 것이 유리할 수있다. 다수의 칩 - 서열 번호 실험을 위해, 4-5 다르게 인덱싱 라이브러리 풀링 할 수 있고, 고성능 NGS 기계를 사용하여 하나 이상의 유동 세포 차선 서열화. 때때로 mappability w을 증가 판독 길이 및 서열 DNA 템플릿의 양단 (페어링 엔드)를 연장하는 것이 바람직하다반복적 인 게놈 영역 내에서 염색질 암탉 분석입니다.
이 프로토콜은 전사 인자 시그널링 매개체 번역 후 변형으로 히스톤 염색질 다양한 기능에 성공적으로 적용되었다. 그들이 개발하고 염색질 프로파일을 해석하기 어렵게 될 그러나, 배아 세포 이질성의 증가 학위를 취득. 유망 단계는 세포 유형 특정 핵 (38, 39)를 추출하여 조직 특별히 프로필 염색질 풍경에 애기 장대와 초파리되었습니다. 우리의 프로토콜은 다른 배아 조직 특이 칩 서열 번호에 대한 방법을 포장 할 수있는 핵 추출 단계를 포함한다.
공개
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
감사의 말
We thank Chris Benner for implementing the X. tropicalis genome (xenTro2, xenTro2r) into HOMER and the Gilchrist lab for discussions on post-sequencing analysis. I.P. assisted the GO term analysis. G.E.G and J.C.S. were supported by the Wellcome Trust and are now supported by the Medical Research Council (program number U117597140).
자료
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1/16 inch tapered microtip | Qsonica | 4417 | This microtip is compatible with Sonicator 3000 from Misonix and Q500/700 from Qsonica. |
| 8 ml glass sample vial with cap | Wheaton | 224884 | 8 ml clear glass sample vials for aqueous samples with 15-425 size phenolic rubber-lined screw caps. |
| Adaptor | e.g., IDT or Sigma | NA | TruSeq universal adaptor,
AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAG ATCTACACTCTTTCCCTACAC GACGCTCTTCCGATC*T. TruSeq indexed adaptor, P-GATCGGAAGAGCACACGTC TGAACTCCAGTCAC ‐NNNNNN‐ ATCTCGTATGCCGTCT TCTGCTT*G. *, phosphorothioate bondphosphate group at 5' end. NNNNNN, index (see TruSeq ChIP Sample Preparation Guide for DNA sequence). Order adaptors HPLC purified. Adaptors can be prepared by combining equimolar amounts (each 100 µM) of the universal and the indexed adaptor and cooling them down slowly from 95 °C to room temperature. Use 1.5 pmol per ng of input DNA. Store at -20 °C. |
| b2g4pipe (software) | Blast2GO | non-commercial | http://www.blast2go.com/data/blast2go/b2g4pipe_v2.5.zip |
| BLAST+ (software) | Camacho et al. | non-commercial | http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE_TYPE=BlastDocs& DOC_TYPE=Download |
| Bowtie (software) | Langmead et al. | non-commercial | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml |
| cisFinder (software) | Sharov et al. | non-commercial | http://lgsun.grc.nia.nih.gov/CisFinder/ |
| Chip for capillary electrophoresis | Agilent Technologies | 5067-1504 | Load this chip with 1 µl DNA for library quality control. Store at 4 °C. |
| Chip-based capillary electrophoresis system | Agilent Technologies | G2940CA | The Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer is used to check the quality of ChIP-Seq libraries. Keep reagents at 4 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (KAPA Hyper Prep Kit) | Kapa Biosystems | KK8504 | Kit contains KAPA end repair and A-tailing enzyme mix, end Repair and A-tailing buffer, DNA ligase, ligation buffer, KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (2X), and KAPA library amplification primer mix (10X) (see also PCR primers). Adaptors are not included. Store at -20 °C. |
| ChIP-Seq library preparation kit (alternative, ThruPLEX-FD Prep Kit) | Rubicon Genomics | R40048 | Kit uses their own stem-loop adaptors and primers. This kit eliminates intermediate purification steps and is as sensitive as the KAPA Hyper Prep Kit. Store at -20 °C. |
| Cluster3 (software) | de Hoon et al. | non-commercial | http://bonsai.hgc.jp/~mdehoon/software/cluster |
| FastQC (software) | Simon Andrews | non-commercial | http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc |
| Fluorometer | life technologies | Q32866 | Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer |
| Fluorometer reagents | life technologies | Q32851 | The kit provides concentrated assay reagent, dilution buffer, and pre-diluted DNA standards for the Qubit fluorometer. Store DNA standards at 4 °C, buffer and dye at room temperature. |
| Formaldehyde | Sigma | F8775-4X25ML | Formaldehyde solution, for molecular biology, 36.5-38% in H2O, stabilised with 10-15% methanol. Store at room temperature. CAUTION: Formaldehyde is corrosive and highly toxic. |
| Gel (E-Gel EX agarose , 2%) | life technologies | G4010 | Pre-cast gel with 11 wells, openable format. Leave one lane between ladder and library empty to avoid cross-contamination. Store gels at room temperature. |
| Gel electrophoresis system | life technologies | G6465 | E-Gel iBase and E-Gel Safe Imager combo kit for size-selecting ChIP-Seq libraries. |
| Gel extraction kit | Qiagen | 28706 | Store all reagents at room temperature. Use 500 µl of QG buffer per 100 mg of 2% agarose gel slice to extract DNA. Use MinElute columns (from MinElute PCR purification kit) to elute DNA twice. |
| HOMER (software) | Chris Benner | non-commercial | http://homer.salk.edu/homer/index.html |
| Hybridization oven | Techne | FHB1D | Hybridizer HB-1D |
| IGV (software) | Robinson et al. | non-commercial | http://www.broadinstitute.org/igv/home |
| Illumina CASAVA-1.8 quality filter (software) | Assaf Gordon | non-commercial | http://cancan.cshl.edu/labmembers/gordon/fastq_illumina_filter |
| Java TreeView (software) | Alok Saldanha | non-commercial | http://jtreeview.sourceforge.net |
| Laboratory jack | Edu-Lab | CH0642 | This jack is used to elevate sample in sound enclosure for sonication. |
| Ladder, 100 bp | New England BioLabs | N3231 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Ladder, 1 kb | New England BioLabs | N3232 | Keep 1x solution at room temperature. Store stock at -20 °C. |
| Low-retention 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes | life technologies | AM12450 | nonstick, RNase-free microfuge tubes, 1.5 ml |
| MACS2 (software) | Tao Liu | non-commercial | https://github.com/taoliu/MACS |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11201D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-mouse IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 11203D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with affinity purified polyclonal sheep anti-rabbit IgG covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10001D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein A covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic beads | life technologies | 10003D | These Dynabeads are superparamagnetic beads with recombinant protein G covalently bound to the bead surface. Store at 4 °C. |
| Magnetic rack | life technologies | 12321D | DynaMag-2 magnet |
| MEME | Bailey et al. | non-commercial | http://meme.nbcr.net/meme/ |
| Na3VO4 | New England BioLabs | P0758 | Sodium orthovanadate (100 mM) is a commonly used general inhibitor for protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NaF | New England BioLabs | P0759 | Sodium fluoride (500 mM) is commonly used as general inhibitor of phosphoseryl and phosphothreonyl phosphatases. Store at -20 °C. |
| NGS machine | Illumina | SY-301-1301 | Genome Analyzer IIx |
| NGS machine (high performance) | Illumina | SY-401-2501 | HiSeq |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2028 | Use as control for goat polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2025 | Use as control for mouse polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Normal serum (antibody control) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-2027 | Use as control for rabbit polyclonal IgG antibodies in ChIP-qPCR experiments. Store at 4 °C. |
| Nucleic acid staining solution | iNtRON | 21141 | Use RedSafe nucleic acid staining solution at 1:50,000. Store at room temperature. |
| Orange G | Sigma | O3756-25G | 1-Phenylazo-2-naphthol-6,8-disulfonic acid disodium salt. Store at 4 °C. |
| PCR primers | e.g., IDT or Sigma | Primers to enrich adaptor-ligated DNA fragments by PCR: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGA*G and CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGA*G, phosphorothioate bond. Primers designed by Ethan Ford. Combine primers at 5 µM each. Use 5 µl in a 50 µl PCR reaction. Store at -20 °C. | |
| MinElute PCR purification kit | Qiagen | 28006 | for purification of ChIP-qPCR and shearing test samples. Store MinElute spin columns at 4 °C, all other buffers and collection tubes at room temperature. |
| Phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1, pH 7.9) | life technologies | AM9730 | Phenol:Chloroform:IAA (25:24:1) is premixed and supplied at pH 6.6. Use provided Tris alkaline buffer to raise pH to 7.9. Store at 4 °C. CAUTION: phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol is corrosive, highly toxic and combustible. |
| Primer3 (software) | Steve Rozen & Helen Skaletsky | non-commercial | http://biotools.umassmed.edu/bioapps/primer3_www.cgi |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11836170001 | cOmplete, Mini, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 10 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Protease inhibitor tablets | Roche | 11873580001 | cOmplete, EDTA-free. Use 1 tablet per 50 ml. Store at 4 °C. |
| Proteinase K | life technologies | AM2548 | proteinase K solution (20 µg/µl). Store at -20 °C. |
| RNase A | life technologies | 12091-039 | RNase A (20 µg/µl). Store at room temperature. |
| Rotator | Stuart | SB3 | Rotator SB3 |
| SAMtools (software) | Li et al. | non-commercial | http://samtools.sourceforge.neta |
| Solid phase reversible immobilisation beads | Beckman Coulter | A63882 | The Agencourt AMPure XP beads are used to minimise adaptor dimer contamination in ChIP-Seq libraries. Store at 4 °C. |
| Sonicator 3000 | Misonix/Qsonica | Newer models are now available. Q125, Q500 or Q700 are all suitable for shearing crosslinked chromatin. | |
| Sound enclosure | Misonix/Qsonica | optional: follow the manufacturer's recommendation to obtain the correct sound enclosure. | |
| Thermomixer | eppendorf | 22670000 | Thermomixer for 24 x 1.5 mL tubes. Precise temperature control from 4 °C above room temperature to 99 °C. |
참고문헌
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. Detecting protein-DNA interactions in vivo: distribution of RNA polymerase on specific bacterial genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 81 (14), 4275-4279 (1984).
- Gilmour, D. S., Lis, J. T. In vivo interactions of RNA polymerase II with genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 5 (8), 2009-2018 (1985).
- Solomon, M. J., Larsen, P. L., Varshavsky, A. Mapping protein-DNA interactions in vivo with formaldehyde: evidence that histone H4 is retained on a highly transcribed gene. Cell. 53 (6), 937-947 (1988).
- Ren, B., et al. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science. 290 (5500), 2306-2309 (2000).
- Johnson, D., Mortazavi, A., Myers, R., Wold, B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 316 (5830), 1497-1502 (2007).
- Hellsten, U., et al. The genome of the Western clawed frog Xenopus tropicalis. Science. 328 (5978), 633-636 (2010).
- Lee, T. I., Johnstone, S. E., Young, R. A. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nature Protocols. 1 (2), 729-748 (2006).
- Blythe, S. A., Reid, C. D., Kessler, D. S., Klein, P. S. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in early Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Dyn. 238 (6), 1422-1432 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., Smith, J. C. Investigating physical chromatin associations across the Xenopus genome by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014 (5), (2014).
- Ubbels, G. A., Hara, K., Koster, C. H., Kirschner, M. W. Evidence for a functional role of the cytoskeleton in determination of the dorsoventral axis in Xenopus laevis eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 77, 15-37 (1983).
- Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., Salzberg, S. L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10 (3), R25 (2009).
- Li, H., et al. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25 (16), 2078-2079 (2009).
- Heinz, S., et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell. 38 (4), 576-589 (2010).
- Zhang, Y., et al. Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 9 (9), R137 (2008).
- Robinson, J. T., et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29 (1), 24-26 (2011).
- Thorvaldsdottir, H., Robinson, J. T., Mesirov, J. P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform. 14 (2), 178-192 (2013).
- Imoto, S., Nolan, J., Bioinformatics Miyano, S. . 20 (9), 1453-1454 (2004).
- Camacho, C., et al. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics. 10, 421 (2009).
- Conesa, A., et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 21 (18), 3674-3676 (2005).
- Sive, H., Grainger, R., Harland, R. . Early development of Xenopus laevis: A laboratory manual. , (2000).
- Chen, Y., et al. Systematic evaluation of factors influencing ChIP-seq fidelity. Nat Methods. 9 (6), 609-614 (2012).
- Sharov, A. A., Ko, M. S. H. Exhaustive search for over-represented DNA sequence motifs with CisFinder. DNA Res. 16 (5), 261-273 (2009).
- Bailey, T. L., et al. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucl Acids Res. 37 (2), W202-W208 (2009).
- Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25 (4), 402-408 (2001).
- Park, P. J. ChIP-seq: advantages and challenges of a maturing technology. Nat Rev Genet. 10 (10), 669-680 (2009).
- Gentsch, G. E., et al. In vivo T-box transcription factor profiling reveals joint regulation of embryonic neuromesodermal bipotency. Cell Rep. 4 (6), 1185-1196 (2013).
- Barabasi, A. L., Oltvai, Z. N. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev Genet. 5 (2), 101-113 (2004).
- Biggin, M. D. Animal transcription networks as highly connected, quantitative continua. Dev Cell. 21 (4), 611-626 (2011).
- Nieuwkoop, P. D., Faber, J. . Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin): a systematical and chronological survey of the development from the fertilized egg till the end of metamorphosis. , (1994).
- Akkers, R. C., et al. A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos. Dev Cell. 17 (3), 425-434 (2009).
- Yoon, S. J., Wills, A. E., Chuong, E., Gupta, R., Baker, J. C. . HEB and E2A function as SMAD/FOXH1 cofactors. Genes Dev. 25 (15), 1654-1661 (2011).
- Jallow, Z., Jacobi, U. G., Weeks, D. L., Dawid, I. B., Veenstra, G. J. Specialized and redundant roles of TBP and a vertebrate-specific TBP paralog in embryonic gene regulation in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101 (37), 13525 (2004).
- Buchholz, D. R., Paul, B. D., Shi, Y. -. B. Gene-specific changes in promoter occupancy by thyroid hormone receptor during frog metamorphosis. Implications for developmental gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 280 (50), 41222-41228 (2005).
- Wills, A. E., Guptaa, R., Chuonga, E., Baker, J. C. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and deep sequencing in Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis. Methods. 66 (3), 410-421 (2014).
- Metz, B., et al. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins: reactions with model peptides. J Biol Chem. 279 (8), 6235-6243 (2004).
- Landt, S. G., et al. ChIP-seq guidelines and practices of the ENCODE and modENCODE consortia. Genome Res. 22 (9), 1813-1831 (2012).
- Mazzoni, E. O., et al. Embryonic stem cell-based mapping of developmental transcriptional programs. Nat Methods. 8 (12), 1056-1058 (2011).
- Deal, R. B., Henikoff, S. A simple method for gene expression and chromatin profiling of individual cell types within a tissue. Dev Cell. 18 (6), 1030-1040 (2010).
- Bonn, S., et al. Tissue-specific analysis of chromatin state identifies temporal signatures of enhancer activity during embryonic development. Nat Genet. 44 (2), 148-156 (2012).
재인쇄 및 허가
JoVE'article의 텍스트 или 그림을 다시 사용하시려면 허가 살펴보기
허가 살펴보기This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유