Plasmids are circular, extra chromosomal, DNA molecules and in molecular biology they act as carriers, or vectors, for a specific DNA fragment. Bacteria are used to replicate plasmids, so that your DNA of interest is mass-produced. The process by which researchers obtain plasmids from bacteria is called plasmid purification, which will be explained in this video.
Obviously, plasmid purification involves purifying plasmids, but what does that mean exactly? To purify plasmids, they must be isolated from the bacterial chromosome, proteins, the bacterial membrane, and bacterial ribosomes.
Though many different kits exist for purifying plasmids, the basic principle behind plasmid purification remains the same for all. First, the selected bacterial colony is grown in an appropriate culture media that contains the correct antibiotics. Thanks to an antibiotic resistance gene, encoded by the plasmid, only bacteria containing the plasmid will grow in this media. The bacteria are harvested and lysed under a high pH. The pH is neutralized, salt is added, and then the mixture is spun down to remove debris and genomic DNA.
Neutralized cell lysate is added onto a silica column. Plasmid DNA is believed to adhere to the column via a mechanism called anion exchange, where DNA, a strong anion, binds to the negatively charged column via a cation salt bridge. Other material from the lysate, such as proteins, are washed through the column with high salt buffers. Finally, purified plasmid is released from the column when a low salt buffer is added disrupting the salt bridge.
For this procedure a lab coat, disposable gloves and protective goggles should be worn.
The bacterial cultures, which are transformed with the desired plasmid DNA, should be grown overnight in growth media with appropriate antibiotic in a 37°C shaking incubator.
The next day, the bacteria culture is pelleted by centrifugation and the supernatant is removed. The remaining pellet is resuspended in lysis buffer.
Once resuspended, bacteria can be transferred to a smaller tube where lysis buffer is added. Lysis buffer has a high pH and contains detergents, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate, which disrupt the bacterial membranes, thereby lysing the bacteria. The solution will turn cloudy with the addition of the lysis buffer and after mixing the solution becomes more clear. The mixture should not be vortexed due to the possibility of shearing, or breaking apart, genomic DNA, which could then contaminate plasmid DNA purification.
Then, neutralization buffer is added to neutralize the alkaline conditions and lower the pH. With gentle mixing genomic DNA as well as any proteins bound to it will precipitate, while plasmid DNA will stay in solution. Once again avoid vortexing, so as your plasmids are free of genomic DNA contamination.
The mixture is then centrifuged and the genomic DNA/protein precipitate is pelleted. The supernatant contains the plasmid DNA as well as soluble proteins.
This supernatant is placed onto the column by decanting, a fancy name for pouring it off, or pipetting. The pellet can be discarded.
Next, high salt washing buffer passes through the column while the DNA remains bound to the silica. Repeated washing steps with high salt buffer removes endonucleases, RNA, proteins, dyes, and low-molecular weight impurities. The flow-through of the wash steps should be discarded. After the final washing step make sure the filter is completely dry without any buffer remaining. The plasmid DNA is still located on the filter.
The plasmid DNA is eluted with sterile water or an elution buffer. The DNA is readily available for immediate use in a wide range of applications.
There are a number of ways to verify the purity of plasmids after purification. A spectrometer can be used to compare absorbance at different wavelengths to determine the concentration of plasmid DNA. An agarose gel analysis of the purified plasmid can determine if the plasmid is the correct size and there are no contaminants. This step ensures there is no genomic DNA contamination and the plasmid was not modified in bacteria.
The plasmid purification procedure can be modified to accommodate different plasmid sizes, copy number, culture volume, and can include different equipment for the binding, washing, and elution steps. Yield happens to be one of the most prominent distinctions between plasmid preparations and they are often divided into the minipreparation, or miniprep, the midiprep, a maxiprep, and a megaprep depending on the yield desired.
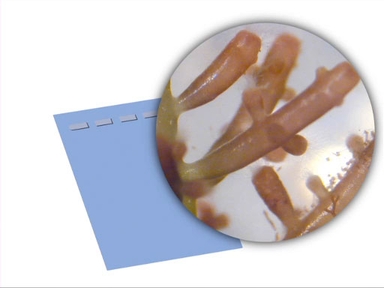
In terms of downstream applications, one procedure that commonly follows plasmid purification is transfection, which involves the introduction of plasmid DNA into eukaryotic cells. Often the goal of a transfection experiment is to visualize the structure of cells and tissues with reporter proteins, such as those labeling the neurons in the images you see here.
Sometimes multiple plasmids purified by several purification preps can be introduced into the same bacteria, thereby reproducing an entire biosynthetic pathway through the production of a number of enzymes encoded by the plasmids. The end result is the manufacturing of a complex compound, like the antibiotic you see here, by the cell.
Purified plasmids may be reintroduced into bacteria, in order generate large amounts of protein encoded by the plasmid. Here you see bacterial cells being homogenized and lysed before a technique called affinity purification can be performed to isolate the target protein. Purified protein is crystallized and its structure then identified.
You’ve just watched JoVE’s introduction to plasmid purification. In this video we discussed the basic principles behind this method, its step by step description, and a handful of applications of your plasmid prep. As always, thanks for watching!