Method Article
Electroeluting DNA Fragments
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This procedure allows the purification of DNA fragments with high yield.
Streszczenie
Purified DNA fragments are used for different purposes in Molecular Biology and they can be prepared by several procedures. Most of them require a previous electrophoresis of the DNA fragments in order to separate the band of interest. Then, this band is excised out from an agarose or acrylamide gel and purified by using either: binding and elution from glass or silica particles, DEAE-cellulose membranes, "crush and soak method", electroelution or very often expensive commercial purification kits. Thus, selecting a method will depend mostly of what is available in the laboratory. The electroelution procedure allows one to purify very clean DNA to be used in a large number of applications (sequencing, radiolabeling, enzymatic restriction, enzymatic modification, cloning etc). This procedure consists in placing DNA band-containing agarose or acrylamide slices into sample wells of the electroeluter, then applying current will make the DNA fragment to leave the agarose and thus be trapped in a cushion salt to be recovered later by ethanol precipitation.
Protokół
- In order to select DNA fragments of interest to be purified, these should be resolved in agarose or acrylamide gels gel stained with ethidium bromide by electrophoresis using 0.5X TBE buffer (Tris borate, EDTA) at 120 volts for 1 hour. For this, ~ 700 ng of plasmid pProEx-GdMre11S (6000-bp) previously digested with NdeI and HindIII was used to release a 900-bp fragment (560 ng of plasmid and 84 ng of fragment).
- The electroeluter tank (Figure 1) should be filled with 0.5X TBE equally distributed in each side of the mid plateau taking care of not spill it onto the mid plateau.
- The selected band (or bands) is cut out of the gel, and placed in sample chamber as close as possible to the V channel (one slice per well). Running buffer should be added to each chamber; just enough to cover the gel slice.
- Each V channel used must be flushed with a Pasteur pipette to eliminate any air bubble trapped.
- Then 100 ul of 10 M NH4 acetate (to facilitate visualization a small amount of bromophenol blue is added, just enough to color it) are gently added inside the V channel.
- The lid should be closed gently to prevent any resuspension of the high salt cushion.
- Electroelution is begun at 100 volts for 25 minutes.
- When electrolution is completed, 400 ul are removed from V-channel, and placed in a microfuge tube to be precipitated with 2 volumes of cold ethanol and glycogen (recommended to improve DNA recovery) at 4 ° C for 1 hour or overnight.
- Centrifuge for 20 minutes, remove supernatant and wash with 70% ethanol.
- Dry tube and quantify DNA at OD 260 nm.
- The recovery obtained was 75% (63 ng recovered when 84 ng were placed on the V-channel).
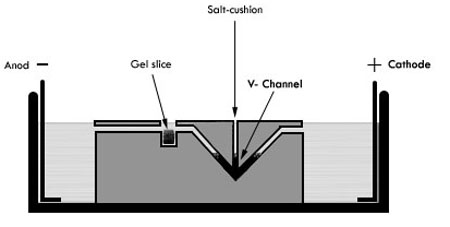
Figure 1. Electroeluter diagram. Anod an cathode are indicated on each side of tank, DNA contained in gel sliced (illustrated as a black square) will migrate towards cathode due to its negative charge. Then it will be trapped in the salt cushion (represented as an inverted black triangle) located in the V-channel.
Dyskusje
The duration of the run will depend highly on the size of the fragments, normally for fragments up to 20 kb 50 minutes to 1 hour is enough, while for small fragments UV light monitoring every 10 minutes is required to prevent the fragment to go through the salt cushion and consequently to the anodal buffer chamber decreasing recovery. It is important to make sure that when you set your power supply at 100 volts, there is a current at least of 10 mAmp. The DNA band can be monitored by using a UV-hand lamp and detect when this abandons the gel slice. The cushion salt can also be made with 3 M Na acetate.
This procedure allows the purification of DNA or RNA fragments of different sizes with good recovery (~80%) to be radiolabeled, digested by restriction enzymes, processed by modifying enzymes, etc.
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
Work in Dr. Bermudez laboratory was funded by Conacyt (Grant # 82622) .We thank Gabriela Gutierrez-Sosa, Eliuth Reyes-Martinez and Ximena Rodriguez-Torres for video recording the electroleution procedure.
Materiały
| Material Name | Type | Company | Catalogue Number | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| NdeI | New England Biolabs | R0111L | ||
| HindIII | New England Biolabs | R0104L | ||
| NH4 acetate | JTBaker | 0596 | ||
| agarose | Invitrogen | 15510-027 | ||
| Biophotometer | Eppendorf | 6131 000 020 | ||
| Electroeluter | IBI | UEA CAT 46000 |
Odniesienia
- Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., Maniatis, T. . Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. , (1989).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone