Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
The Trier Social Stress Test Protocol for Inducing Psychological Stress
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
This article describes a protocol for inducing psychological stress in participants, which enables researchers to measure psychological, physiological and neuroendocrine responses to stress within single participants or between groups.
Streszczenie
This article demonstrates a psychological stress protocol for use in a laboratory setting. Protocols that allow researchers to study the biological pathways of the stress response in health and disease are fundamental to the progress of research in stress and anxiety.1 Although numerous protocols exist for inducing stress response in the laboratory, many neglect to provide a naturalistic context or to incorporate aspects of social and psychological stress. Of psychological stress protocols, meta-analysis suggests that the Trier Social Stress Test (TSST) is the most useful and appropriate standardized protocol for studies of stress hormone reactivity.2 In the original description of the TSST, researchers sought to design and evaluate a procedure capable of inducing a reliable stress response in the majority of healthy volunteers.3 These researchers found elevations in heart rate, blood pressure and several endocrine stress markers in response to the TSST (a psychological stressor) compared to a saline injection (a physical stressor).3 Although the TSST has been modified to meet the needs of various research groups, it generally consists of a waiting period upon arrival, anticipatory speech preparation, speech performance, and verbal arithmetic performance periods, followed by one or more recovery periods. The TSST requires participants to prepare and deliver a speech, and verbally respond to a challenging arithmetic problem in the presence of a socially evaluative audience.3 Social evaluation and uncontrollability have been identified as key components of stress induction by the TSST.4 In use for over a decade, the goal of the TSST is to systematically induce a stress response in order to measure differences in reactivity, anxiety and activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) or sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) axis during the task.1 Researchers generally assess changes in self-reported anxiety, physiological measures (e.g. heart rate), and/or neuroendocrine indices (e.g. the stress hormone cortisol) in response to the TSST. Many investigators have adopted salivary sampling for stress markers such as cortisol and alpha-amylase (a marker of autonomic nervous system activation) as an alternative to blood sampling to reduce the confounding stress of blood-collection techniques. In addition to changes experienced by an individual completing the TSST, researchers can compare changes between different treatment groups (e.g. clinical versus healthy control samples) or the effectiveness of stress-reducing interventions.1
Protokół
1. Set Up
- All research should be approved by the appropriate Institutional Review Board or human subjects review committee prior to data collection.
- Ideally, two rooms should be available to conduct the TSST. A comfortable waiting room should be available to participants prior to beginning the TSST and during recovery periods. A separate interview room should be used during the speech preparation, speech performance and math portions of the TSST to introduce novelty and uncontrolability.
- Arrange the interview room so that the participant will be facing confederate interviewers and position video or audio recording equipment in the visual field of the participant. Lab coats should be available for interviewers to wear during the TSST to increase stress during the TSST. Instruct interviewers to maintain eye contact with participants and refrain from making emotional facial expressions during the TSST.
- Carefully consider the research question(s) when selecting dependent measurements. Guidelines for the analysis and publication of various measurements of stress response are provided by several sources (guidelines for the publication and analysis of psychophysiological measures are provided by the Society for Psychophysiological Research: http://www.sprweb.org/journal/index.cfm#guidelines).5 Consultation of these resources during the design of experiments is recommended.
- Set up all equipment needed to record physiological, psychological or endocrine responses to the TSST. This equipment may include (but is not limited to) electrodes and electronic equipment and/or software to record heart rate, cardiovascular reactivity, skin conductance or response, eye blink, muscle contraction/tone, respiratory rate; paper and pencil or electronic versions of psychological instruments such as the State Trait Anxiety Inventory;6 tubes and other collection materials for urine, blood or saliva samples; or video recording equipment. For this demonstration, we will be using three-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) electrodes to measure heart rate during the TSST, and repeated administration of the State Trait Anxiety Inventory to measure psychological response before and after the stressor. We will utilize a basic recording system designed to measure physiological responses (BioPac MP36 system) to record heart rate.
- If blood samples (rather than saliva) will be collected during the experiment, efforts to minimize pain and distress during collection should be made. Blood collection procedures can introduce additional physical or psychological stress, confounding response to the TSST.
- When the participant arrives, welcome them to the lab. Obtain informed consent and seat the participant comfortably.
- Collect demographic information, screening information or additional arrival measures that are required by your experiment. Verify that the participant has not consumed food or beverage (other than water) in the past hour if collecting cortisol measurements. A short period of fasting is recommended if you will be collecting saliva samples for analysis. Changes in pH associated with acidic food or drink or visible contamination can interfere with accurate measurement of salivary markers. Urine toxicology screening may be required if measures of interest may be contaminated by medication or other metabolites. Information about factors that may affect stress response (e.g. medications, illness, sleep, recent stressful events, social phobia) should also be considered when screening participants.
2. Pre-stress Measurements
- Instruct the participant to wait comfortably for 45 minutes in the waiting room. You may choose to provide the participant with reading material, such as magazines containing emotionally-neutral content, or another emotionally-neutral activity during this period.
- After the 45-minute waiting period, administer the State Trait Anxiety Inventory to assess pre-stress anxiety.6 Alternatively, other instruments that are designed to evaluate state changes in stress, anxiety or relaxation may be administered (e.g. visual analogue scales).
- Collect a "pre-stress" saliva sample. Instruct the participant to rinse their mouth with water. Give the participant a 5-10 cm section of drinking straw and a clean, disposable 2.0 ml polypropylene vial. Instruct the participant to tilt their head forward to allow saliva to pool on the floor of the mouth then pass the saliva through the straw into the vial. Collect approximately 1.5-2.0 ml of saliva from the participant. Alternatively, saliva can be collected by using absorbent dental wick (or similar material) and instructing the participant to chew or saturate the material with saliva. If possible, leave the room to provide the participant with privacy. Label and store all saliva samples at -20° C as soon as possible.
- Record 5 minutes of pre-stress physiological measurements.
3. The TSST
- If you will be using a separate interview room (to increase the stress effects of the TSST), bring the participant from the waiting room into the interview room.
- To begin the TSST speech preparation period, read the following script to the participant: "This is the speech preparation portion of the task; you are to mentally prepare a five-minute speech describing why you would be a good candidate for your ideal job. Your speech will be videotaped and reviewed by a panel of judges trained in public speaking. You have ten minutes to prepare and your time begins now."
- Record physiological measurements during the 10-minute speech preparation period. Set a digital timer for 10 minutes and leave the room.
- After 10 minutes, return to the room wearing a lab coat. Read the following script to the participant: "This is the speech portion of the task. You are to deliver a speech describing why you would be a good candidate for your ideal job. You should speak for the entire the five-minute time period. Your time begins now." The prop video camera should be turned on now, to increase evaluative/performance stress.
- Record physiological measurements during the 5-minute speech performance period. If the participant stops talking during the speech, allow him or her to remain silent for 20 seconds. If he or she does not resume speaking, prompt the participant to continue speaking by instructing them: "You still have time remaining."
- At the end of the 5-minute speech performance period, read the following script to the participant: "During the final five-minute math portion of this task you will be asked to sequentially subtract the number 13 from 1,022. You will verbally report your answers aloud, and be asked to start over from 1,022 if a mistake is made. Your time begins now." If the participant makes a mistake, prompt them with: "That is incorrect, please start over from 1,022." Set a digital timer for 5 minutes.
- Record physiological measurements during the 5-minute math performance period.
- At the end of the math performance period of the TSST, collect a "post-stress" saliva sample.
- Administer post-stress State Trait Anxiety Inventory.
4. Post-stress Recovery Measurements
- Return participants to the original waiting room. During the first recovery period, instruct the participant to wait comfortably for 20 minutes. Set a digital timer for 20 minutes and leave the room.
- Return to the waiting room after 20 minutes and collect a "recovery 1" saliva sample.
- During the second recovery period, instruct the participant to again wait comfortably for 20 minutes. Set a digital timer for 20 minutes and leave the room.
- Return to the waiting room after 20 minutes and collect a "recovery 2" saliva sample.
- Instruct the participant to complete the "recovery" State Trait Anxiety Inventory.
- Debrief the participant as to the true nature of the experiment. Inform the participant that their performance was not recorded and that no analysis of their speech or math performance will be conducted. Explain to the participant that the tasks with which they were presented were unreasonably difficult and do not reflect upon the participant's aptitude or ability.
5. Data Analysis
- To analyze psychological measures, score each State Trait Anxiety Inventory from the pre-stress, post-stress and recovery time points.6
- To analyze physiological measures, compute a mean heart rate score for each of the 5-minute "pre stress," "speech preparation," "speech performance" and "math" periods of the TSST. Alternatively, compute mean scores for each minute of the TSST or measure heart rate at discrete time points during the TSST.
- To analyze neuroendocrine measures, assay salivary samples for hormone concentration using commercially available EIA kits.
6. Optional: Additional Salivary Cortisol Assay Protocol Information (reproduced from Salimetrics salivary cortisol assay kit insert)
- Bring all salivary assay kit reagents to room temperature.
- Prepare wash buffer according to kit instructions.
- Determine plate layout and pipette 25 μL of standards and controls into appropriate wells in duplicate.
- Thaw saliva samples, vortex and centrifuge at 1,500 X G (@3,000 RPM) for 15 minutes.
- Pipette 25 μL of clear liquid from centrifuged samples into appropriate wells in plate (in duplicate).
- Prepare enzyme conjugate and pipette 200 μL into all wells.
- Mix plate for 5 minutes at 500 rpm and incubate for an additional 55 minutes.
- Wash and blot the plate 4 times with wash buffer.
- Add 200 μL tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) solution to each well using a multichannel pipette.
- Mix the plate for 5 minutes at 500 rpm and incubate in the dark for an additional 25 minutes.
- Add 50 μL stop solution to each well and mix for 3 minutes at 500 rpm to stop the reactions.
- Wipe the plate bottom clean and read the plate in a plate reader at 450 nm within 10 minutes of adding stop solution.
- To calculate cortisol concentration, compute the average optical density for all duplicate wells. Subtract the average optical density of the non-specific binding wells from the average optical density of the zero, standard, control and sample wells.
- Calculate the percent bound (B/Bo) for each standard, control and sample by dividing the average optical density of these wells (B) by the average optical density of the zero wells (Bo). Determine the concentration of the controls and samples by interpolation using software capable of logistics.
7. Representative Results:
The representative data presented here is compiled from a review of the literature and two studies that were conducted in our lab during the afternoon with healthy adult male participants. These data are intended to approximately represent the results that might be found using the protocol presented in this article.
This TSST protocol (Figure 1) induces increases in self-reported anxiety (as measured by the State Trait Anxiety Inventory; Figure 2), heart rate (Figure 3), and salivary cortisol concentrations (Figure 4). The experimental protocol illustrated in Figure 1 is meant to provide one example of how various measurements might be made during a data collection session with the TSST. The timing of measurements and the inclusion of different measures will be dictated by the specific research question. If using an intervention that is intended to reduce anxiety and/or stress response, blunted or attenuated increases in these measures are predicted.
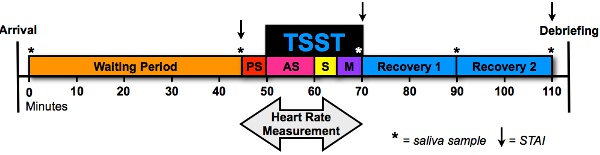
Figure 1. Experimental protocol. Note: Trier Social Stress Test (TSST); State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI); 5-minute Pre Stress period (PS); 10-minute Anticipatory Stress period (speech preparation) (AS); 5-minute Speech period (S); 5-minute Math period (M).

Figure 2. Representative state anxiety scores. Note: State Anxiety score calculated from 20-iten state anxiety measure of State Trait Anxiety inventory (STAI). Representative scores reflect data collected in our lab and published in literature.
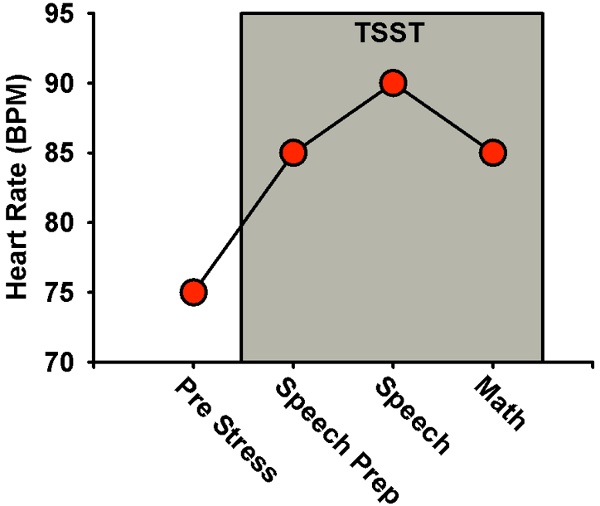
Figure 3. Representative heart rate data. Note: Heart rate in beats per minute (BPM). Representative values reflect data collected in our lab and published in literature.
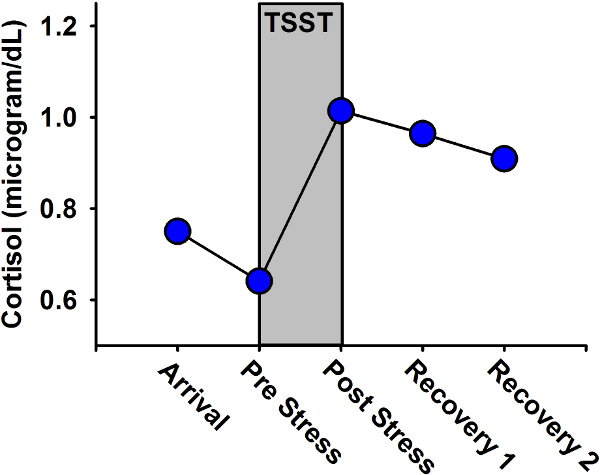
Figure 4. Representative salivary cortisol data. Note: Cortisol concentration in uL/dL. Representative values reflect data collected in our lab and published in literature.
Dyskusje
In this article, we demonstrated how to conduct the Trier Social Stress Test in a healthy volunteer. The TSST is a standardized laboratory social stressor that induces robust and reliable increases in psychological, physiological and neuroendocrine measures. The TSST is a useful alternative to physical stressors such at the cold presser test or treadmill walking, and reproduces the more naturalistic psychological stress of performance in the presence of an evaluative audience.
Many aspects ...
Ujawnienia
No conflicts of interest declared.
Podziękowania
Thank you to Jessica Ottmar for protocol suggestions and contributions to the representative data. Special thanks to Sabrina Blackledge, Lauren Kohoutek and Kerisa Shelton for demonstrating this protocol.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Name of the equipment/Supply | Company | Catalogue number | |
| BSL Psychophysiology System, Mac OSIncluding MP36 Data Acquisition Unit and three lead electrocardiogram electrodes | Biopac Systems, Inc. | BSLPSY-M | |
| State Trait Anxiety Inventory | Mind Garden, Inc. | STAID-B | |
| Salivary Cortisol Enzyme Immuno Assay Kit | Salimetrics | 1-3002 | |
| 2.0 ml polypropylene vials | Fisher Scientific | 05 40B 146 | |
| BioRad Microplate Reader, Model 680, with Microplate Manager software | Bio-Rad | Plate Reader: 168 1000Software: 1706800 |
Odniesienia
- Kudielka, B. M., Hellhammer, D. H., Kirschbaum, C., Harmon-Jones, E., Winkielman, P. Ten years of research with the Trier Social Stress Test - Revisited. Social Neuroscience: Integrating Biological and Psychological Explanations. , (2007).
- Dickerson, S. S., Kemeny, M. E. Acute stressors and cortisol responses: A theoretical integration and synthesis of laboratory research. Psychol. Bull. 130, 355-391 (2004).
- Kirschbaum, C., Pirke, K., Hellhammer, D. H. The "Trier social stress test" - a tool for investigating psychobiological stress response in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology. 28, 76-81 (1993).
- Gruenewald, T. L., Kemeny, M. E., Aziz, N., Fahey, J. L. Acute threat to the social self: shame, social self-esteem, and cortisol activity. Psychosom. Med. 66, 915-924 (2004).
- Mendes, W. B., Harmon-Jones, E., Beer, J. S. Assessing autonomic nervous system activity. Methods in Social Neuroscience. , 118-147 (2009).
- Spielberger, C. D., Gorsuch, R. L., Lushene, P. R., Vagg, P. R., Jacobs, A. G. . Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (Form Y). , (1983).
- Dawans, B. v. o. n., Kirschbaum, C., Heinrichs, M. The Trier Social Stress Test for groups (TSST-G): A new research tool for controlled simultaneous social stress exposure in a group format. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 36, 514-522 (2011).
- Pace, T. W. W., Negi, L. T., Adame, D. D., Cole, S. P., Sivilli, T. I., Brown, T. D., Issa, M. J., Raison, C. L. Effect of compassion meditation on neuroendocrine, innate immune and behavioral responses to psychosocial stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34, 87-98 (2010).
- Kirschbaum, C., Würst, S., Hellhammer, D. Consistent sex differences in cortisol responses to psychological stress. Psychosom. Med. 54, 648-657 (1992).
- Therrien, F., Drapeau, V., Lalonde, J., Lupien, S. J., Beaulieu, S., Dore, J., Tremblay, A., Richard, D. Cortisol response to the Trier Social Stress Test in obese and reduced obese individuals. Biol. Psychol. 84, 325-329 (2010).
- Wüst, S., Entringer, S., Federenko, I. S., Schlotz, W., Hellhammer, D. H. Birth weight is associated with salivary cortisol responses to psychosocial stress in adult life. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 30, 591-598 (2005).
- Simeon, D., Yehuda, R., Cunill, R., Knutelska, M., Putnam, F. W., Smith, L. M. Factors associated with resilience in healthy adults. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32, 1149-1152 (2007).
- Quirin, M., Pruessner, J. C., Kuhl, J. HPA system regulation and adult attachment anxiety: Individual differences in reactive and awakening cortisol. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 33, 581-590 (2009).
- Pierrehumbert, B., Torrisi, R., Glatz, N., Dimitrova, N., Heinrichs, M., Halfon, O. The influence of attachment on perceived stress and cortisol response to acute stress in women sexually abused in childhood or adolescence. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34, 924-938 (2009).
- Fiocco, A. J., Joober, R., Lupien, S. J. Education modulates cortisol reactivity to the Trier Social Stress Test in middle-aged adults. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 32, 1158-1163 (2007).
- Oswald, L. M., Zandi, P., Nestadt, G., Potash, J. B., Kalaydjian, A. E., Wand, G. S. Relationship between cortisol responses to stress and personality. Neuropsychopharmacology. 31, 1583-1591 (2006).
- Fries, E., Hellhammer, D. H., Hellhammer, J. Attenuation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity to the Trier Social Stress Test by the benzodiazepine alprazolam. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 31, 1278-1288 (2006).
- Kudielka, B. M., Fischer, J. E., Metzenthin, P., Helfricht, S., Preckel, D., von Känel, R. No effect of 5-day treatment with acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) or the beta-blocker propranolol (Inderal) on free cortisol responses to acute psychosocial stress: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neuropsychobiology. 56, 159-166 (2007).
- Gaab, J., Blättler, N., Menzl, T., Pabst, B., Stoyer, S., Ehlert, U. Randomized controlled evaluation of the effects of cognitive-behavioral stress management on cortisol responses to acute stress in healthy subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 28, 767-779 (2003).
- Khalfa, S., Bella, S. D., Roy, M., Peretz, I., Lupien, S. J. Effects of relaxing music on salivary cortisol level after psychological stress. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 999, 374-376 (2003).
- Balodis, I. M., Wynne-Edwards, K. E., Olmstead, M. C. The other side of the curve: Examining the relationship between pre-stressor physiological responses and stress reactivity. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 35, 1363-1373 (2010).
- Shultheiss, O. C., Stanton, S. J., Harmon-Jones, E., Beer, J. S. Assessment of salivary hormones. Methods in Social Neuroscience. , 17-44 (2009).
- Kudielka, B. M., Hellhammer, D. H., Wüst, S. Why do we respond so differently? Reviewing determinants of human salivary cortisol responses to challenge. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 34, 2-18 (2009).
- Buske-Kirschbaum, A., Jobst, S., Wustmans, A., Kirschbaum, C., Rauh, W., Hellhammer, D. Attenuated free cortisol response to psychosocial stress in children with atopic dermatitis. Psychosom. Med. 59, 419-426 (1997).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone