Aby wyświetlić tę treść, wymagana jest subskrypcja JoVE. Zaloguj się lub rozpocznij bezpłatny okres próbny.
Method Article
The Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy Model of Perinatal Ischemia
W tym Artykule
Podsumowanie
The postnatal rat model for hypoxic-ischemic brain injury is a well-established model of human neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). In this article, we describe the model of HIE in post-natal rat pups.
Streszczenie
Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is the consequence of systemic asphyxia occurring at birth. Twenty five percent of neonates with HIE develop severe and permanent neuropsychological sequelae, including mental retardation, cerebral palsy, and epilepsy. The outcomes of HIE are devastating and permanent, making it critical to identify and develop therapeutic strategies to reduce brain injury in newborns with HIE. To that end, the neonatal rat model for hypoxic-ischemic brain injury has been developed to model this human condition. The HIE model was first validated by Vannucci et al 1 and has since been extensively used to identify mechanisms of brain injury resulting from perinatal hypoxia-ischemia 2 and to test potential therapeutic interventions 3,4. The HIE model is a two step process and involves the ligation of the left common carotid artery followed by exposure to a hypoxic environment. Cerebral blood flow (CBF) in the hemisphere ipsilateral to the ligated carotid artery does not decrease because of the collateral blood flow via the circle of Willis; however with lower oxygen tension, the CBF in the ipsilateral hemisphere decreases significantly and results in unilateral ischemic injury. The use of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) to stain and identify ischemic brain tissue was originally developed for adult models of rodent cerebral ischemia 5, and is used to evaluate the extent of cerebral infarctin at early time points up to 72 hours after the ischemic event 6. In this video, we demonstrate the hypoxic-ischemic injury model in postnatal rat brain and the evaluation of the infarct size using TTC staining.
Protokół
This protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Stanford University and abides by the National Institutes of Health guidelines for the use of experimental animals.
Neonatal Rat HIE model
- Post natal day (PND) 7 Sprague-Dawley rat pups (Charles River Laboratories, Inc., Wilmington, MA) are fully anesthetized with isoflurane (Aerrane, Baxter, Deerfield, IL; 3-4% for induction and 1-2% for maintenance).
- A small incision is made in the neck (Extra Thin Iris Scissors #14088-10, Fine Science Tools Inc, Foster City, CA) to expose the left common carotid artery (CCA).
- The CCA is ligated with a 5-0 silk suture (5-0 silk, Ethicon, Somer, NJ).
- The incision is closed with cyanoacrylate adhesive (Elmers Products Inc, Columbus, OH). The incision is covered with tape and anesthesia is stopped. The pups are returned to their dam and allowed to recuperate for 1-2 hours.
- Pups are then placed in a hypoxic chamber that contains 8% oxygen balanced with 92% nitrogen for 100 minutes at 37°C. 8% oxygen/92% nitrogen gas(Airgas, Sacramento, CA) flow via a tube into the mouse cage outfitted with a plastic cover. The cover is made to fit to the cage and has two holes of 2 cm in diameter, one of which to receive the tube connected to the 8% oxygen gas tank and another allows the gas to flowout. The chamber is placed in a water bath and is warmed up prior to use and a thermometer inside of it must register 37°C before the start of hypoxia.
- At the end of 100 minutes of hypoxia, the pups are returned again to their dam for recovery.
- 24 hours after the end of hypoxia, pups are euthanized by deep anesthesia with isoflurane. Brain tissue is perfused with cold normal saline, followed by a solution of cold 1% TTC in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4 (Sigma Chemical Co, St Louis, MO). TTC must be kept protected from light.
- Brains are removed and cooled for 1-2 minutes on ice, and four coronal sections 3 mm apart (levels 1-4) are cut, beginning rostrally at the level of the opticchiasm and infundibulum, corresponding to the bregma 1.8 ~ 2.0 mm level of the adult mouse brain.
- Brain slices are immersed in TTC solution and incubated at 37°C for 8 minutes, followed by fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde/PBS overnight. Because TTC is light sensitive, keep slices away from light during this time.
- The TTC stained sections are scanned and digitized. Using Image J (NIH, Bethesda, MD), the following are measured for each level: area of infarction (unstained area), the area of the ipsilateral hemisphere, and the area of the contralateral hemisphere. The percent infarcted area per slice is calculated as: (area of infarct/area of ipsilateral hemisphere) or A1, A2, A3, and A4. The percent volume of infarct is calculated as the sum (A1 +A2 + A3+ A4) * 3mm. Areas of cortical or striatal injury can also be separately quantified in a similar manner.
Representative Results
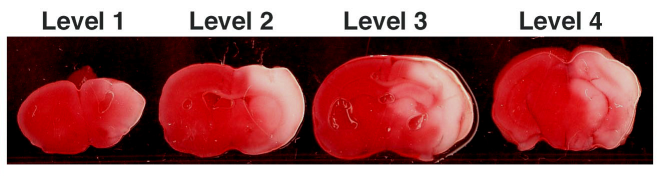
Figure 1. Representative HIE coronal levels 1-4 stained with TTC.
TTC stained coronal sections demonstrate area of infarct (in white).
Dyskusje
The rodent postnatal HIE model is an established model that recapitulates cerebral hypoxia occurring in the peri-natal period in newborns. Extensive histological and immunocytochemical characterization studies have demonstrated that the 7 day old rodent has the analogous brain maturity to model a third trimester human fetus 7. The rodent HIE model has been very informative for understanding mechanisms of brain injury from peri-natal hypoxia 2, where interventions such as hypothermia have been valid...
Podziękowania
Funded by American Heart Association and March of Dimes.
Materiały
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Sprague-Dawley Rat Pups | Animal | Charles River Laboratories | ||
| Isoflurane | Surgery | Baxter Internationl Inc. | ||
| 8% Oxygen/ 92% Nitrogen Gas | Surgery | Airgas | ||
| 2,3,5-triphenyl tetrazolium chloride | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | T8877 | |
| Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 | Reagent | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | ||
| Paraformaldehyde | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | P6148 |
Odniesienia
- Rice, J. E., Vannucci, R. C., Brierley, J. B. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Annals of neurology. 9 (2), 131-141 (1981).
- Vannucci, R. C., Vannucci, S. J. Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage: Evolution of an Animal Model. Dev Neurosci. 27 (2-4), 81-86 (2005).
- Bona, E., Hagberg, H., Loberg, E. M. Protective effects of moderate hypothermia after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: short- and long-term outcome. Pediatric research. 43 (6), 738-738 (1998).
- Trescher, W. H., Ishiwa, S., Johnston, M. V. Effects of hypothermia and hyperthermia on attentional and spatial learning deficits following neonatal hypoxia-ischemic insult in rats. Behavioural brain research. 151 (1-2), 209-209 (2004).
- Mishima, K., Ikeda, T., Yoshikawa, T. Brief post-hypoxic-ischemic hypothermia markedly delays neonatal brain injury. Brain development. 19 (5), 326-326 (1997).
- Young, R. S., Olenginski, T. P., Yagel, S. K. The effect of graded hypothermia on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: a neuropathologic study in the neonatal rat. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 14 (6), 929-929 (1983).
- Bederson, J. B., Pitts, L. H., Germano, S. M., et al. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 17 (6), 1304-1304 (1986).
- Cai, J., Kang, Z., Liu, W. W. Hydrogen therapy reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Neuroscience letters. 441 (2), 167-167 (2008).
- Grow, J., Barks, J. D. Pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in the term infant: current concepts. Clinics in perinatology. 29 (4), 585-585 (2002).
- Aden, U., Halldner, L., Lagercrantz , H., et al. Aggravated brain damage after hypoxic ischemia in immature adenosine A2A knockout mice. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 34 (3), 739-739 (2003).
Przedruki i uprawnienia
Zapytaj o uprawnienia na użycie tekstu lub obrazów z tego artykułu JoVE
Zapytaj o uprawnieniaPrzeglądaj więcej artyków
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone