20.3 : Caminho Entre os Estados Termodinâmicos
Consider the two thermodynamic processes involving an ideal gas that are represented by paths AC and ABC in Figure 1:
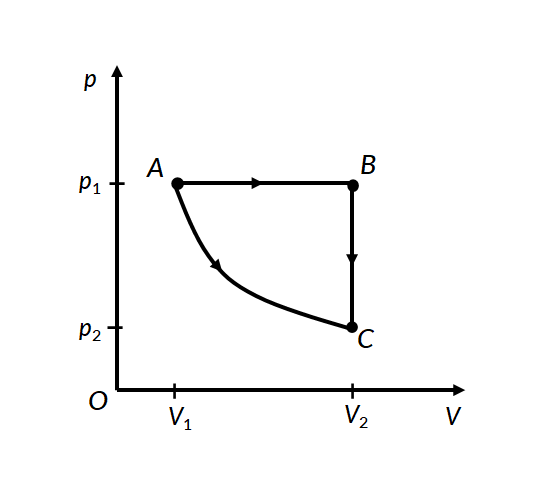
In the first process for path A to C, the gas is kept at constant temperature T. It undergoes an expansion from volume V1 to V2.
The work done by an ideal gas is expressed as
Substituting for pressure as nRT/V from the ideal gas equation and integrating the terms, the work done by an ideal gas at constant temperature is obtained as
In the second process, for path A to B, the ideal gas is first expanded from volume V1 to V2 at constant pressure p1 by applying heat. The gas is then cooled at constant volume V2 along path B to C, such that its pressure drops to p2.
For path A to B, work is done under constant pressure, therefore
For path B to C, since the volume remains constant, no work is done by the gas or on the gas by the surroundings. Therefore the total work done by the gas in this process is the same as the work done for path A to B.
In both processes, the gas expands from volume V1 to volume V2, such that its pressure changes from p1 to p2. However, the work done in both processes is different. This proves that work done by a system is path-dependent.
Do Capítulo 20:

Now Playing
20.3 : Caminho Entre os Estados Termodinâmicos
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
3.0K Visualizações

20.1 : Sistemas Termodinâmicos
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
4.9K Visualizações

20.2 : Trabalho Realizado Durante a Mudança de Volume
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
3.9K Visualizações

20.4 : Calor e Expansão Livre
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
1.7K Visualizações

20.5 : Energia Interna
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
4.5K Visualizações

20.6 : Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
4.1K Visualizações

20.7 : Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica: Resolução de Problemas
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.5K Visualizações

20.8 : Processos Cíclicos e Sistemas Isolados
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.7K Visualizações

20.9 : Processos Isotérmicos
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
3.5K Visualizações

20.10 : Processos Isocóricos e Isobáricos
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
3.3K Visualizações

20.11 : Capacidades Caloríficas de um Gás Ideal I
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.6K Visualizações

20.12 : Capacidades Caloríficas de um Gás Ideal II
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.4K Visualizações

20.13 : Capacidades Caloríficas de um Gás Ideal III
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.1K Visualizações

20.14 : Processos Adiabáticos para um Gás Ideal
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
3.0K Visualizações

20.15 : Pressão e Volume em um Processo Adiabático
A Primeira Lei da Termodinâmica
2.6K Visualizações
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos os direitos reservados