When a substance—isolated from its environment—is subjected to heat changes, corresponding changes in temperature and phase of the substance is observed; this is graphically represented by heating and cooling curves.
For instance, the addition of heat raises the temperature of a solid; the amount of heat absorbed depends on the heat capacity of the solid (q = mcsolidΔT). According to thermochemistry, the relation between the amount of heat absorbed or released by a substance, q, and its accompanying temperature change, ΔT, is:
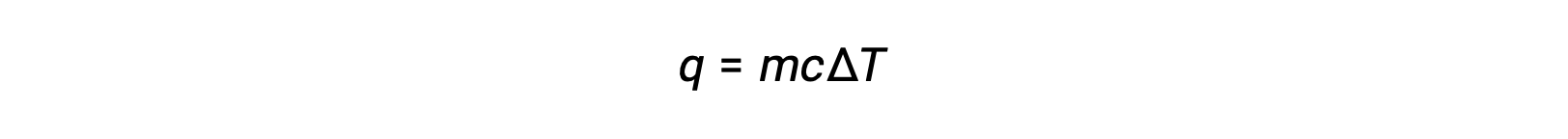
where m is the mass of the substance, and c is its specific heat. The relation applies to matter being heated or cooled, but not changing state.
When the temperature is high enough, the solid begins to melt (Figure 1, point A). The heat absorbed depends on the solid’s heat capacity (q = mcsolidΔT), and a plateau is observed at its melting point. The plateau indicates a change of state from solid to liquid, during which the temperature does not rise due to the heat of fusion (q = mΔHfusion). In other words, further heat gain is a result of diminishing intermolecular attractions, instead of increasing molecular kinetic energies. Consequently, while a substance is changing state, its temperature remains constant.
Once the solid has completely melted (Figure 1, point B), the liquid starts warming and experiences a rise in temperature. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity (q = mcliquidΔT). When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to vaporize (Figure 1, point C) and the temperature remains constant despite the continued input of heat. Another plateau (constant temperature) is observed at the liquid's boiling point during the liquid to gas transition due to the heat of vaporization (q = mΔHvap). This same temperature is maintained by the liquid as long as it is boiling. If heat is provided at a greater rate, the liquid's temperature does not rise, but instead, the boiling becomes more vigorous (rapid). After all the liquid has vaporized (Figure 1, point D), the temperature of the gas increases.
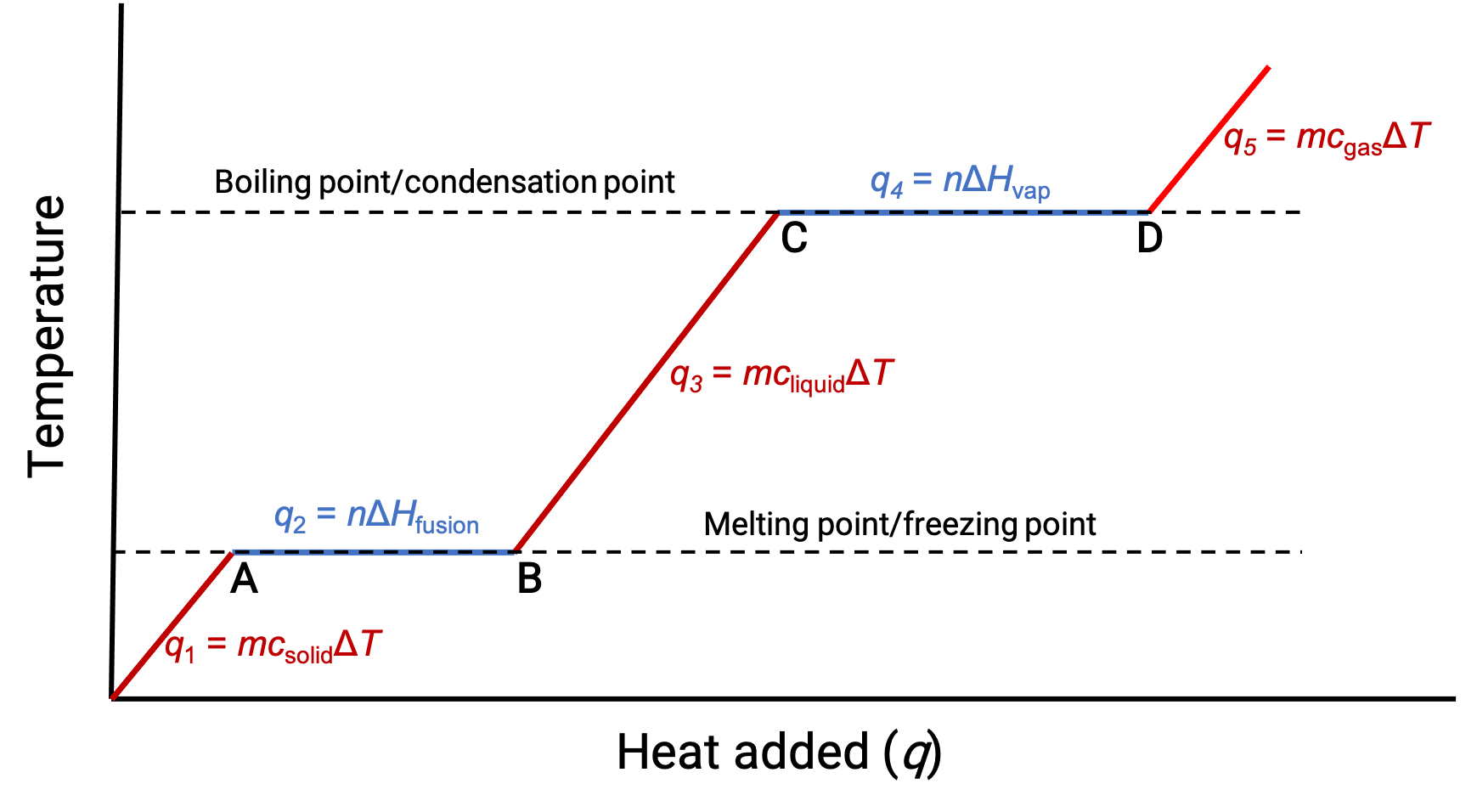
Figure 1. The representative heating curve for a substance depicts changes in temperature that result as the substance absorbs increasing amounts of heat. Plateaus in the curve (regions of constant temperature) are exhibited when the substance undergoes phase transitions.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 10.3: Phase Transitions.
From Chapter 11:

Now Playing
11.12 : Heating and Cooling Curves
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
22.1K Views

11.1 : Molecular Comparison of Gases, Liquids, and Solids
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
40.0K Views

11.2 : Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
84.1K Views

11.3 : Intermolecular Forces
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
55.4K Views

11.4 : Comparing Intermolecular Forces: Melting Point, Boiling Point, and Miscibility
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
43.4K Views

11.5 : Surface Tension, Capillary Action, and Viscosity
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
27.2K Views

11.6 : Phase Transitions
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
18.5K Views

11.7 : Phase Transitions: Vaporization and Condensation
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.9K Views

11.8 : Vapor Pressure
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
33.9K Views

11.9 : Clausius-Clapeyron Equation
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
54.9K Views

11.10 : Phase Transitions: Melting and Freezing
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
12.1K Views

11.11 : Phase Transitions: Sublimation and Deposition
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.5K Views

11.13 : Phase Diagrams
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
38.6K Views

11.14 : Structures of Solids
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
13.5K Views

11.15 : Molecular and Ionic Solids
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces
16.5K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved