A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Methods to Assess Beta Cell Death Mediated by Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
In This Article
Summary
Cell-mediated lymphocytotoxicity (CML) assays can be used to test autoreactive responses and study mechanisms of cell death in vitro. However, using live-cell confocal microscopic imaging techniques with fluorescent dyes, the type and kinetics of cell death as well as the pathways utilized can be studied in greater detail.
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a T cell mediated autoimmune disease. During the pathogenesis, patients become progressively more insulinopenic as insulin production is lost, presumably this results from the destruction of pancreatic beta cells by T cells. Understanding the mechanisms of beta cell death during the development of T1D will provide insights to generate an effective cure for this disease. Cell-mediated lymphocytotoxicity (CML) assays have historically used the radionuclide Chromium 51 (51Cr) to label target cells. These targets are then exposed to effector cells and the release of 51Cr from target cells is read as an indication of lymphocyte-mediated cell death. Inhibitors of cell death result in decreased release of 51Cr.
As effector cells, we used an activated autoreactive clonal population of CD8+ Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) isolated from a mouse stock transgenic for both the alpha and beta chains of the AI4 T cell receptor (TCR). Activated AI4 T cells were co-cultured with 51Cr labeled target NIT cells for 16 hours, release of 51Cr was recorded to calculate specific lysis
Mitochondria participate in many important physiological events, such as energy production, regulation of signaling transduction, and apoptosis. The study of beta cell mitochondrial functional changes during the development of T1D is a novel area of research. Using the mitochondrial membrane potential dye Tetramethyl Rhodamine Methyl Ester (TMRM) and confocal microscopic live cell imaging, we monitored mitochondrial membrane potential over time in the beta cell line NIT-1. For imaging studies, effector AI4 T cells were labeled with the fluorescent nuclear staining dye Picogreen. NIT-1 cells and T cells were co-cultured in chambered coverglass and mounted on the microscope stage equipped with a live cell chamber, controlled at 37°C, with 5% CO2, and humidified. During these experiments images were taken of each cluster every 3 minutes for 400 minutes.
Over a course of 400 minutes, we observed the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential in NIT-1 cell clusters where AI4 T cells were attached. In the simultaneous control experiment where NIT-1 cells were co-cultured with MHC mis-matched human lymphocyte Jurkat cells, mitochondrial membrane potential remained intact. This technique can be used to observe real-time changes in mitochondrial membrane potential in cells under attack of cytotoxic lymphocytes, cytokines, or other cytotoxic reagents.
Protocol
1. Preparation of cells
- Target cell culture: Culture of the mouse beta cell lines, NIT-1 and NIT-4, was a previously described1,2 in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 0.02%BSA, Non-essential Amino Acid, 15mM HEPES, 16.5mM Glocose and Penicillin/Streptomycin. For 51Cr labeling, seed cells in a flat-bottom 96-well culture plate at 5X104 cells/well in 200 μl culture medium. For microscopy experiments, seed cells in a 8-well Lab-Tak II chambered coverglass at 5x104 per chamber in 500 μl culture medium, and allow to grow for 48 hours prior to using in the cytotoxicity experiments.
- Control T cell line culture: Use the Jurkat cell line (ATCC, CD3+ human lymphocyte cell line) as a negative control. Culture Jurkat cells in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1.5 g/L sodium bicarbonate, 10 mM HEPES and 1.0 mM sodium pyruvate.
2. Collection and activation of effector autoreactive CD8+ T cells
NOD.Cg-Rag1tm1MomTg(TcraAI4)1Dvs/DvsJ [NOD-AI4a] and NOD.Cg-Rag1tm1MomTg(TcrbAI4)1Dvs/DvsJ [NOD-AI4b] were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) and bred in our mouse facility. F1 hybrid progeny from matings of NOD-AI4a with NOD-AI4b [NOD-AI4a/b] develop diabetes at 3-5 weeks of age. All mice were housed in specific pathogen-free facilities and approved by the relevant institution’s Animal Care and Use Committee.
- Euthanize 3-4 week old NOD-AI4a/b mice using CO2.
- Collect spleens from mice. Euthanized mice are prepared with ethanol spray and opened under surgical hood. Spleens are removed and put in ice-cold HBSS buffer immediately.
- Collect spleen cells using a 7 mL glass homogenizer. Two to three spleens each are put in 5 mL of cold HBSS and homogenized with a 7 mL glass homogenizer. Homogenate is collected and centrifuged at 1200rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C using a Sorvall RT7+ centrifuge. Cell pellets are collected.
- Remove red blood cells using hypotonic solution treatment. Pellets are treated with 5 mL hypotonic solution/spleen on ice for 5 minutes, then neutralized by adding an equal volume of HBSS. Collect cells by centrifugation, as above, and resuspend in 50 mL HBSS. Pass the suspended cells through cell strainer and count using a hemocytometer with TrypanBlue staining.
- Activate cells. Resuspend cells at 5x106/mL and activate using a 3 day culture with 0.1 μM AI4 mimotope (amino acid sequence YFIENYLEL) and 25 U/mL IL-2 in RPMI1640 supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1.5 g/L sodium bicarbonate, 10 mM HEPES and 1.0 mM sodium pyruvate.
3. 51Cr release assay to examine CML
- Label target cells: Add 51Cr to target cells at 1 μCi/well and culture for 3 hours, and wash 3 times with culture medium.
- Suspend effector cells in RPMI 1640 medium as mentioned in step 2.5 so that the final volume added to each well is 200 μl.
- After the final wash of labeled target cells, add activated effector cells to the target cell cultures at desired effector to target (E:T) ratios. We usually use E:T ratios at 0.4:1, 1:1, 2:1, 5:1, 10:1, 20:1 and 50:1.
- Add fresh modified RPMI 1640 medium (see step 2.5) to 6 wells of target cells to act as a spontaneous lysis control.
- Co-culture effector and target cells for 16 hours.
- Collect supernatant in 6x50 mm Lime Glass tubes
- Lyse cells by adding 100μl 2% SDS and pipetting several times gently.
- Collect cell lysate in another set of 6x50 mm Lime Glass tubes.
- Wash wells once with clean H2O and add the wash to the cell lysate tubes.
- Count the supernatants and cell lysates using a gamma counter.
- Calculate specific lysis as follows:
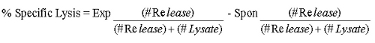
4. Staining of cells for live cell imaging
Among most commonly used mitochondrial membrane potential dyes, TMRM exhibits the least mitochondrial toxicity.3 Therefore, we choose TMRM for these live cell imaging studies.
- Prepare a 40 mM stock TMRM solution in DMSO and store at -20°C. Make a [25 nM] fresh working solution in phenol red-free DMEM with all the supplements for NIT-1 cell culture 1.
- Stain target NIT-1 cells with TMRM 25 nM for 30 min at 37°C.
- Replace the media with fresh media containing 5 nM TMRM to maintain the equilibrium distribution of the dye4.
- Count activated effector AI4 T cells using a hematocytometer.
- Stain activated effector AI4 T cells with 1 μl/mL Picogreen for 5 minutes at room temperature and wash with phenol red-free culture medium 3 times.
5. Assessing T lymphocyte-mediated beta cell death using live cell imaging
- Mount the chambered coverglass with stained NIT cells on the stage of a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal microscope. Remove the tab with a dremmel and gas sterilize the chambered glass with etheline oxide. The stage is equipped with a live-cell imaging chamber that has temperature controlled at 37°C and 5% CO2 with moisture.
- Add activated and stained T cells to designated chambers at different E:T ratios.
- Added same number of stained Jurkat cells to the control chambers.
6. Obtaining live cell images
The microscope is equipped with a motorized stage that allowed us to repeatedly acquire images at different locations from the same or different chambers automatically over the time course of the experiment.
- Using a 63x oil objective lens, take images at an interval of every 3 minutes for a total of 300 frames per location.
- Detect TMRM staining using an excitation wave length of 543 nm and filter set for emission 565-619 nm
- Detect Picogreen staining using an excitation 488 nm and a filter set for emission 500-630 nm. The video was created using Zeiss LSM software.
7. Video conversion for publication
- Using the Zeiss LSM software, create an uncompressed movie file in an AVI format.
- To convert the video into the published format, import the video into the software package FIJI (http://pacific.mpi-cbg.de/wiki/index.php/Fiji), an ImageJ (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/) distribution, using the Bioformats plugin from LOCI (http://www.loci.wisc.edu/software/bio-formats).
- Adjust the brightness and contrast settings to balance the green and red signals and the frame rate was set to 2 frames/second using the animation options menu.
- Crop the video to 512 x 512 pixels and export as an uncompressed AVI file.
- Open this AVI file in the software Quicktime 7 (Apple computer, Cupertino, CA) and compress and export in the open video file format H264/MPEG-4 at 1200 kbs/second.
8. Representative Results:
- A representative result of 51Cr CML assay. Figure 1 shows a representative result of a CML assay where percent specific lysis (Y axis) increases as the Effector:Target ratio (X axis) increases. Target cells are primary islets isolated from immunodeficient NOD.Rag1-/- mice and labeled with 51Cr. Splenocytes from NOD.AI4α/β transgenic mice are isolated and activated as described in step 2 above. Targets and effectors were co-cultured for 16 hours. Percent specific lysis is calculated as described in step 3.11 above.
- Two representative (positive and negative) results of a T cell-mediated beta cell mitochondrial membrane potential dissipation are presented. Cells are stained and reactions are recorded as described in steps 4, 5 and 6 above, video files are created as in step 7. Video 1: The mouse beta cell line NIT-1 was stained the mitochondrial membrane potential dye TMRM (Red). Activated, autoreactive CD8+ T cell AI4 (Stained green with Picogreen) were co-cultured with these NIT-1 cells at an E:T ratio of 50:1. NIT-1 mitochondrial membrane potential dissipated gradually during a 400-minute duration, but only in the clusters that were interacting with AI4 T cells. Video 2: As a control experiment, NIT-1 cells were stained with TMRM and co-cultured with Picogreen stained Jurkat cells at an E:T ratio of 50:1. Jurkat cells are a human T cell line that is MHC mismatched. NIT-1 cells maintained mitochondrial membrane potential throughout the entire duration of the 400 minutes co-incubation period. Jurkat cells did not interact with NIT-1 clusters and therefore, do not induce killing.
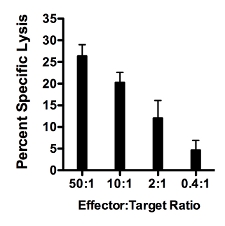
Figure 1. Representative result of CML using as target cells primary islets isolated from immunodeficient NOD.Rag1-/- mice and splenocytes from NOD.AI4α/β transgenic mice. Targets and effectors were co-cultured for 16 hours. Percent specific lysis increases as the Effector:Target ratio increases.
Video 1. Mouse beta cell line NIT-1 was stained the mitochondrial membrane potential dye TMRM (Red). Activated autoreactive CD8+ T cell AI4 (Stained green with Picogreen) were co-cultured with these NIT-1 cells at E:T ratio of 50:1. NIT-1 mitochondrial membrane potential dissipated gradually during a 400-minute duration, but only in the clusters that were interacting with green AI4 T cells. Click here to watch video.
Video 2. NIT-1 cells were stained same as described in Video 1 and co-cultured with Picogreen stained human T cell line Jurkat. NIT-1 cells were able to maintain mitochondrial membrane potential throught out the duration of 400 minutes. Jurkat cells did not interact with NIT-1 clusters and therefore do not induce killing. Click here to watch video.
Discussion
Cytotoxic T cell mediated beta cell death is the main pathophysiology of T1D 5. CML assays using 51Cr release allow us to study the degree of effector-target response 6. However, the detailed process and pathways of T cell-mediated beta cell death is still not fully understood. Since mitochondria are critical for beta cell function and death7, we focused on mitochondrial changes during the visual CML. Mitochondrial membrane potential dissipation is an early and irreversible...
Disclosures
Experiments on animals were performed in accordance with the guidelines and regulations set forth by University of Florida Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health DK074656 and AI56374 (CEM), as well as the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Cr-51 | PerkinElmer, Inc. | NEZ030500IMC | |
| PBS | Cellgro | 21-040-60 | |
| Tetramethyl Rhodamine Methyl Ester (TMRM) | Invitrogen | T668 | |
| Picogreen | Invitrogen | P7581 | |
| AI4 mimotope | mimotopes.com | amino acid sequence: YFIENYLEL | |
| IL-2 | R&D Systems | 485-MI | |
| DMEM | Invitrogen | 11885 | |
| FBS | Hyclone | SH30071.03 | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma-Aldrich | A8412 | |
| HEPES | Cellgro | 25-060-Cl | |
| MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids | GIBCO, by Life Technologies | 11140 | |
| Penicillin/Streptomycin | Gemini Bio Products | 400-109 | |
| Phenol red-free DMEM | Sigma-Aldrich | D5303 | |
| CO2 Incubator | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | HeraCell 150i | Kept sterile for cell culture |
| Biological safety cabinet | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | Forma 1440 | |
| Disposable culture tubes, 6x50 mm Lime Glass | Fisher Scientific | 14-958-A | |
| Gamma Counter | PerkinElmer, Inc. | Wizard 1470 Automatic Gamma Counter | |
| Confocal microscope | Carl Zeiss, Inc. | LSM 510 Meta Confocal | With motorized stage and live cell chamber |
| Pipette (1ml, 200μl, 20μl,10μl, 2μl) | Eppendorf | ||
| Tubes (Amber) | Fisher Scientific | 50819772 | |
| Centrifuge | Sorvall, Thermo Scientific | 75004377 | |
| Hemacytometer | Fisher Scientific | 267110 | |
| Upright Microscope | Carl Zeiss, Inc. | Axioskop40 | |
| NOD.Cg-Rag1tm1Mom Tg(TcraAI4)1Dvs/DvsJ Mice | Jackson Laboratory | 004347 | |
| NOD.Cg-Rag1tm1Mom Tg(TcrbAI4)1Dvs/DvsJ Mice | Jackson Laboratory | 004348 | |
| NOD-AI4α/ β F1 mice | N/A | N/A | Bred in UF animal facility |
References
- Hamaguchi, K., Gaskins, H. R., Leiter, E. H. NIT-1, a pancreatic beta-cell line established from a transgenic NOD/Lt mouse. Diabetes. 40, 842-849 (1991).
- Chen, J., Gusdon, A. M., Piganelli, J., Leiter, E. H., Mathews, C. E. mt-Nd2a modifies resistance against autoimmune Type 1 diabetes in NOD mice at the level of the pancreatic beta cell. Diabetes. , (2010).
- Scaduto, R. C., Grotyohann, L. W. Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys J. 76, 469-477 (1999).
- Lemasters, J. J., Ramshesh, V. K. Imaging of mitochondrial polarization and depolarization with cationic fluorophores. Methods Cell Biol. 80, 283-295 (2007).
- Abel, M., Krokowski, M. Pathophysiology of immune-mediated (type 1) diabetes mellitus: potential for immunotherapy. BioDrugs. 15, 291-301 (2001).
- Mathews, C. E., Graser, R. T., Savinov, A., Serreze, D. V., Leiter, E. H. Unusual resistance of ALR/Lt mouse beta cells to autoimmune destruction: role for beta cell-expressed resistance determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. , 235-240 (2001).
- Szabadkai, G., Duchen, M. R. Mitochondria mediated cell death in diabetes. Apoptosis. 14, 1405-1423 (2009).
- Ly, J. D., Grubb, D. R., Lawen, A. The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis. 8, 115-128 (2003).
- Dudek, N. L. Cytotoxic T-cells from T-cell receptor transgenic NOD8.3 mice destroy beta-cells via the perforin and Fas pathways. Diabetes. 55, 2412-2418 (2006).
- Pakala, S. V., Chivetta, M., Kelly, C. B., Katz, J. D. In autoimmune diabetes the transition from benign to pernicious insulitis requires an islet cell response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 189, 1053-1062 (1999).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved