A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Facile Preparation of 4-Substituted Quinazoline Derivatives
In This Article
Summary
A protocol for facile preparation of 4-substituted quinazoline derivatives from 2-aminobenzophenones, thiourea and dimethyl sulfoxide is presented.
Abstract
Reported in this paper is a very simple method for direct preparation of 4-substituted quinazoline derivatives from a reaction between substituted 2-aminobenzophenones and thiourea in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). This is a unique complementary reaction system in which thiourea undergoes thermal decomposition to form carbodiimide and hydrogen sulfide, where the former reacts with 2-aminobenzophenone to form 4-phenylquinazolin-2(1H)-imine intermediate, whilst hydrogen sulfide reacts with DMSO to give methanethiol or other sulfur-containing molecule which then functions as a complementary reducing agent to reduce 4-phenylquinazolin-2(1H)-imine intermediate into 4-phenyl-1,2-dihydroquinazolin-2-amine. Subsequently, the elimination of ammonia from 4-phenyl-1,2-dihydroquinazolin-2-amine affords substituted quinazoline derivative. This reaction usually gives quinazoline derivative as a single product arising from 2-aminobenzophenone as monitored by GC/MS analysis, along with small amount of sulfur-containing molecules such as dimethyl disulfide, dimethyl trisulfide, etc. The reaction usually completes in 4-6 hr at 160 ºC in small scale but may last over 24 hr when carried out in large scale. The reaction product can be easily purified by means of washing off DMSO with water followed by column chromatography or thin layer chromatography.
Introduction
Substituted quinazolines, as a unique type of heterocycles, have been known for a variety of biological activities, including antibiotic,1 antidepressant,2 anti-inflammatory,3,4 anti-hypertensive,3 antimalarial,5 and anti-tumoral,6 among others. What is more, 4-substituted quinazolines, e.g., 4-aryl-quinazolines, with anti-plasmodial activity7 have been recognized as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors,8 CNS depressants,9 and antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis.10 Because of its wide spectrum of biological activities, synthetic methods for substituted quinazolines have been largely explored. As an example, more than 25 synthetic methods have already been reported for the preparation of 4-phenylquinazolines.11 Representative methods include the formation of 4-phenylquinazolines from 2-aminobenzophenones and formamide in the presence of boron trifluoride etherate (BF3·Et2O)12 or formic acid,13 or from the reaction of 2-aminobenzophenones with urotropine and ethyl bromoacetate,14 or the reaction with aldehyde and ammonium acetate in the presence of an oxidizing agent.15
Different from the above reactions using moisture sensitive reagent (e.g., BF3·Et2O) or expensive reagent (e.g., urotropine and ethyl bromoacetate), a facile method that can easily convert 2-aminobenzophenones into corresponding 4-phenylquinazolines in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in the presence of thiourea has been explored. Extensively mechanistic studies on this reaction indicate that it is a complementary reaction in which thiourea undergoes thermal decomposition to form carbodiimide and hydrogen sulfide, where carbodiimide reacts with 2-aminobenzophenone to form 4-phenylquinazolin-2(1H)-imine intermediate, whilst DMSO is used not only as a solvent, but also the reagent to generate sulfur-containing reducing reagent when it reacts with hydrogen sulfide (also arising from thiourea). Then, the sulfur-containing reducing agents reduce the 4-phenylquinazolin-2(1H)-imine intermediate to form 4-phenyl-1,2-dihydroquinazolin-2-amine that undergoes elimination of ammonia to form 4-phenylquinazoline. This reaction is usually carried out at temperature from 135-160 °C, and can be easily performed by means of traditional oil bath heating on hotplate or under microwave irradiation. This reaction is generally illustrated in Figure 1 below.
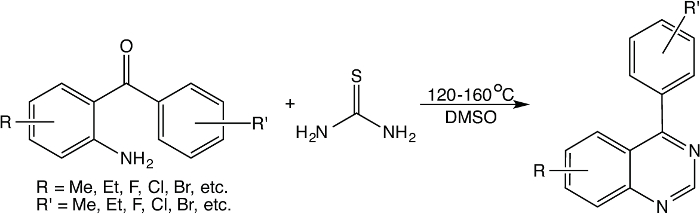
Figure 1: A general reaction between 2-aminobenzophenone and thiourea in DMSO. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Protocol
Caution: Please consult all relevant material safety data sheets (MSDS) before use. Whilst 2-aminobenzophenones are odorless, some sulfur-containing molecules are generated in this reaction. Therefore, good condition of ventilation should always be used. Please use all appropriate safety practice when performing the reactions at temperature higher than 140 °C, as pressure may go above 5 bars as recorded under microwave irradiation. When the temperature is set at 160 °C, the highest pressure recorded is 21 bars, which is almost the upper limit the microwave reactor can handle. Although pressure is not an issue when the reaction is carried out in oil bath under refluxing, good ventilation should always be used.
1. Preparation of 4-Phenylquinazoline in Small Scale Under Microwave Irradiation
- Preparation of Reaction Mixture
- Add a compatible magnetic stir bar to a 2-5 ml microwave reaction tube.
- Use analytical balance and weigh 0.0866 g of 2-aminobenzophenone (yellow powder), 0.0988 g of thiourea (white crystal, 3 equivalents) into the above reaction tube.
Note: The optimal ratio between 2-aminobenzophenone and thiourea is 1:3. - Transfer 5 ml of DMSO to the reaction tube.
Note: The amount of DMSO is quite flexible, 5 ml of DMSO is just about enough to meet the minimal requirement of volume for correct absorption of microwave according to manufacturer's guide. However, under thermal condition, much less solvent is needed for reaction of this scale. - Seal the reaction tube with a compatible aluminum cap containing rubber septum inlet.
- Vigorously shake the tube on a vortexer for 1-2 min to dissolve the reactants.
Note: Thiourea may not completely dissolve in DMSO at room temperature, but it will fully dissolve when heat is applied. - Use a micro-syringe to withdraw 5 μl of reaction mixture to a 2 ml glass sampling tube containing 0.35 ml of ethyl acetate (EtOAc) for gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy (GC/MS) analysis before the reaction starts.
- Formation of 4-phenylquinazoline Under Microwave Irradiation
- Turn on microwave reactor, put the microwave reaction tube in one of the eight tube holders.
- Setup reaction parameters through touch screen, such as the location of tube (e.g., from well 1 to 8), type of tube (e.g., 2-5 ml), reaction temperature (at 150 °C), pre-stirring duration (1 min), microwave absorption level (high), stirring speed (600 rpm), and reaction time (5 hr).
- Once all parameters are setup correctly, click "run" button, the robot will automatically pick up the reaction tube from the tube holder (or well) and put it inside the heating hole. Then, the microwave reactor will run the reaction according to the parameters set up previously.
- When microwave irradiation completes, wait until temperature drops to close to 30 ºC, the robot will pick up the reaction tube and put it back to the original holder.
- Use micro-syringe to withdraw 5 μl of reaction mixture (clear yellow solution, no insoluble substance observed) and add it to another 2 ml glass sampling tube containing 0.35 ml of EtOAc for GC/MS analysis.
- As GC/MS analysis indicates that the reaction is only half completed, set up the microwave reaction of the same tube for another 5 hr at the same temperature.
Note: Reaction time varies depending on the amount of starting material used, the concentration of reaction solution, the substituting groups on 2-aminobenzophenones, and more importantly, the reaction temperature. For example, a reaction of 0.3 g 2-aminobenzophenone in 3 ml of DMSO will complete in 6 hr at 160 °C, but lasts more than 14 hr at 140 °C under both microwave irradiation and hotplate heating. It is also recommended to monitor the reaction periodically with GC or GC/MS analysis. People without access to GC or GC/MS should then use thin layer chromatography (TLC) to monitor the reaction, although it is not the best tool.
- GC/MS Analysis of Reaction Mixture
- Make sure GC/MS is setup properly according to manufacturer's protocol.
- Put the glass sampling tubes on auto-sampler tray.
- Click "GCMS_3" shortcut on the monitor to initiate the data acquisition program that controls and coordinates the functions of injector, GC and mass spectrometer. Load a proper method by clicking the "Method" on the drop down menu and highlighting "Load Method." The selected method contains all necessary parameters for both GC and quadruple mass spectrometer to analyze the target samples. If there is no such method, create a necessary method.
- For a new sample, if modify some of the GC parameters to suit a particular sample, highlight the "Edit Entire Method" by clicking "Method" from the drop down menu and change the relevant parameters accordingly. The GC parameters that are often changed are the initial temperature and the duration to hold that temperature, the rate of increasing temperature, the final temperature and the duration to maintain the temperature, the injection amount, the times to wash the injection needle before and after the injection, the equilibration time and post run time, and the post run temperature.
- For this experiment, set the initial GC temperature at 70 °C (1 min), with an increasing rate of temperature at 20 °C/min, and the final temperature at 250 °C (5 min). Use a total running time of 15 min. Use an injection volume of 2 μl, with 4 pre-wash and 4 after-washes of needle. Use pure helium as the carrier gas used under this condition.
Note: A method for GC/MS analysis contains the pre-set parameters to run both GC and MS instruments. The parameters for GC include the initial temperature of oven to heat the GC column and the number of minutes to retain that temperature, the rate to raise the temperature of oven, the final temperature of the oven and the number of minutes to retain the final temperature before the GC analysis completes; the amount of sample injected; the split rate of the carrier gas; the number of times to wash the needle before sample is injected; and the number of times to wash the needle after the sample is injected; etc. The choice of initial and final temperatures as well as the rate of raising temperature depends on the nature of analyzed sample. In general, non-polar molecules of low boiling points are analyzed at relatively low initial temperature.
- Tune the Mass Spectrometer According to Manufacturer's Protocol.
- Once a running method is selected, click "Instrument" on top of the drop down menu, and highlight "Tune MSD." Then another window appears in front of the data acquisition window. One can select either "Tune MSD" or "QuickTune", and click "OK" button to start the tuning process of mass spectrometer. The "QuickTune" option takes about 3 min to complete, whereas the "Tune MSD" option runs about 10 min. Under normal circumstance, "QuickTune" option is good enough to calibrate the mass spectrometer with accuracy up to 0.1 Dalton. The tuning process will measure the relative abundance of peak 69, 219 and 502 of perfluorotributylamine (PFTBA) as well as the amount of N2, O2, H2O, CO2, etc.
Note: The mass spectrometer must be calibrated every other day in order to have an accurate measurement of mass. The tuning is to adjust the parameters for the mass spectrometer to work properly, such as the voltage of quadruple, vacuum of mass detector, the background noise, the standard peaks to gauge the mass spectrometer, etc. One can choose either autotune or manual tune mode to calibrate the mass spectrometer, i.e., by selecting "QuickTune" or "Tune MSD" option.
- Once a running method is selected, click "Instrument" on top of the drop down menu, and highlight "Tune MSD." Then another window appears in front of the data acquisition window. One can select either "Tune MSD" or "QuickTune", and click "OK" button to start the tuning process of mass spectrometer. The "QuickTune" option takes about 3 min to complete, whereas the "Tune MSD" option runs about 10 min. Under normal circumstance, "QuickTune" option is good enough to calibrate the mass spectrometer with accuracy up to 0.1 Dalton. The tuning process will measure the relative abundance of peak 69, 219 and 502 of perfluorotributylamine (PFTBA) as well as the amount of N2, O2, H2O, CO2, etc.
- Acquire the GC/MS Data
- Edit data acquisition sequence. Click the "Sequence" on top of the drop down menu to highlight "Edit Sequence", and a new window pops up, in which the information about samples should be input, such as the type of sample (sample, blank, calibration, QC, etc.), the location of sample vial (from 1 to 100), sample name, data file name, comments of sample, etc. When all sample information has been input, click "OK" button. Then click the "Sequence" on top of the drop down menu to highlight "Save Sequence As.." and input the sequence name in a proper folder.
- Acquire the GC/MS data. Click the "Sequence" on top of the drop down menu to highlight "Run Sequence", choose a proper "Data File Directory" to save the acquired data, and then click the "Run Sequence" button to start the data acquisition process.
- Analyze the GC/MS Results
Note: Molecules can be characterized by the minutes they are eluted from the GC column, so-called the retention time. Under the same GC condition (i.e., the above mentioned GC parameters), the retention time of a particular molecule is very reproducible. The compound can be further confirmed by its mass spectrum. One can easily identify a compound in terms of retention time and mass spectrum, and check the purity of a compound as well.- Double click the "GCMS_3 Data Analysis" shortcut on the monitor to bring up the software that deliberately processes the acquired data from the GC/MS machine.
- During the data acquisition process, to see the instant result of the analyzed sample, click "File" from the drop down menu and highlight "Take Snapshot" to get the synchronized GC spectrum of sample. Often, people will process the data after the acquisition process completes. In this case, click "File" from the drop down menu to highlight "Load Data File" and select the correct data file, or browse the data directory and double click the data file, to show the whole GC spectrum of the sample. A vertical line appears at the position where mouse is pointed to inside the window of GC spectrum.
- Move mouse to the center of a peak where the vertical line hits the highest point of the peak, and double click the right button of mouse to bring up the mass spectrum of the sample in a new window below the window of GC spectrum. One can zoom the mass spectrum by holding the left button and select the region to zoom for the detail of mass spectrum.
- Identify the compounds by double clicking the right button of mouse inside the mass spectrum window to obtain two new windows. The small front window with a name of "PBM Search Results: C:\Database\W8N08.L" brings up 20 molecules from the database that most likely match the analyzed mass spectrum, and ranks the 20 molecules in order of their similarities. The large back window contains two panels, of which the top panel displays the original mass spectrum of the analyzed peak inside the GC spectrum, and the bottom panel displays the mass spectrum of the selected molecule from the list of small front window. Often, common organic compounds can be confirmed by comparing its mass spectrum with the standard mass spectrum collected in the database. Although new compounds or molecules not collected in the database cannot be directly confirmed, their identities can be obtained through the matching of expected molecular weight and possible fragments with their structures.
- Identify the same compound in different samples by comparing its retention time on the GC spectrum. Under the same condition of data acquisition, the same compound should appear with the same retention time on the GC spectrum.
- Analyze the purity of sample by clicking the "Chromatogram" on the drop down menu, highlighting either "Integrate" or "AutoIntegrate", and selecting "Percent Report".
- Print both GC spectrum and mass spectra corresponding to the peaks inside the GC spectrum in either portrait or landscape format by selecting "Printer Setup" when one click "File" on the drop down menu. Also, print the spectra directly into pdf format by selecting a pdf converter.
- Extraction of Reaction Mixture
Note: The isolation process has been carried out in fume hood, as small amount of sulfur-containing molecules with unpleasant smell are generated in this reaction.- Open the microwave reaction tube with manufacturer provided plier, and transfer the reaction mixture into a 125 ml separating funnel. Add 20 ml of EtOAc to this funnel followed by 10 ml of water.
Note: If the reaction solution is left at room temperature over one day, long needle shape crystals may appear in the solution depending on the concentration of solution. Thus, it is wise to leave the large-scale reaction mixture at room temperature to form crystal and isolate the product of crystal directly if time is not a factor. - Shake the separating funnel vigorously, and drain the bottom aqueous layer. Then add another 10 ml of water to the separating funnel, and repeat this process.
- Concentrate the remaining EtOAc solution down to about 1 ml by rotatory evaporation.
- Open the microwave reaction tube with manufacturer provided plier, and transfer the reaction mixture into a 125 ml separating funnel. Add 20 ml of EtOAc to this funnel followed by 10 ml of water.
- Purification of 4-phenylquinazoline by Preparative TLC
- Transfer the concentrated EtOAc solution with Pasteur pipette to a 20 cm x 20 cm preparative TLC plate in such a way that the stripe of sample on the TLC plate is less than 1 cm wide and is about 1 cm from the edge. Dip this plate to a glass chamber containing 150 ml of hexane and EtOAc (2:1). Watch the movement of solvent frontier approaching the top of the TLC plate, and take out the plate when solvent frontier is about 1 cm from the top edge.
- Draw two straight lines on the TLC plate with pencil to mark the place before sample is loaded. Also, dip the TLC plate in glass chamber in such a way that the stripe of sample is at the bottom but still about 2 mm above the solvent level.
- Under ultra-violet (UV) light, use a pencil to mark the band with green fluorescence, and scratch off the marked band on the TLC plate to a weighing paper (with a relative mobility of Rf = 0.68, Hexane/EtOAc = 2:1).
Note: Due to high sensitivity of UV absorption, one may observe multiple weak bands on the plate. However, the very top bands often correspond to sulfur-containing molecules, such as dimethyl disulfide, dimethyl trisulfide; others bands below 4-phenylquinazoline are visible but their amount are too little to be isolated and characterized. - To a glass pipette filled with glass wool, transfer the scratched silica gel powder to the pipette by folding the weighing paper diagonally to allow the powder of silica gel falls into the pipette, and tap the pipette against a hard surface to pack the silica gel tight. Wash the pipette with acetone (8-15 ml) into a 2-drum scintillation vial.
- Transfer 0.35 ml of the eluted acetone solution to another 2 ml glass sampling tube for GC/MS analysis, and directly dry the remaining acetone solution on a rotatory evaporator. Put the whole scintillation vial containing the purified compound in vacuum desiccator for further drying.
Note: Up to this step, the product is purified and can be used for further characterization (e.g., nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy) or additional transformations.
- Transfer the concentrated EtOAc solution with Pasteur pipette to a 20 cm x 20 cm preparative TLC plate in such a way that the stripe of sample on the TLC plate is less than 1 cm wide and is about 1 cm from the edge. Dip this plate to a glass chamber containing 150 ml of hexane and EtOAc (2:1). Watch the movement of solvent frontier approaching the top of the TLC plate, and take out the plate when solvent frontier is about 1 cm from the top edge.
2. Preparation of 4-Phenylquinazoline in Small Scale via Hotplate Heating
Note: The procedures for the GC/MS analysis of reaction mixture, extraction of reaction mixture, and purification of reaction product are very similar to the ones described in section 1 (1.1.1-1.3.4, 1.4.1-1.4.3, and 1.5.1-1.5.5, respectively), so that most of these steps will be omitted below.
- Preparation of reaction mixture for hotplate heating
- Weigh 0.0240 g of 2-aminobenzophenone and 0.0280 g of thiourea into a 2 ml glass vial, then transfer 0.5 ml of DMSO to the same vial, and close the vial with a screw cap.
Note: The amount of DMSO used under this condition is much less than the one under microwave irradiation. Due to small scale of this reaction, magnetic stirring is not needed anymore, so for the vortex stirring of the solution to dissolve the reactants. However, in a relative large reaction scale, for example, in 2-drum scintillation vial or round-bottomed flask, magnetic stirring is still needed.
- Weigh 0.0240 g of 2-aminobenzophenone and 0.0280 g of thiourea into a 2 ml glass vial, then transfer 0.5 ml of DMSO to the same vial, and close the vial with a screw cap.
- Preparation of 4-phenylquinazoline via Hotplate Heating
- Inside fume hood, put a heating block on top of hotplate, and set temperature to 160 °C.
- When temperature reaches 160 °C, insert the glass vial into one of the wells in heating block. With about half an hour interval, take out of the vial and hand shake it for 2-3 sec, and put it back to the well again. After 6 hr, take out of the vial and leave it inside the fume hood to cool down.
- Transfer 5 μl of the reaction mixture to another 2 ml glass sampling tube containing 0.35 ml of EtOAc, and submit the sample for GC/MS analysis.
- Once the reaction completes, work out the product as described in section 1. See the details in section 1.1.1-1.3.4, 1.4.1-1.4.3, and 1.5.1-1.5.5 for GC/MS analysis, extraction of reaction mixture, and purification of product, respectively.
Results
The GC analysis of reaction mixture before the reaction, 5 hr after reaction under microwave irradiation, and 10 hr after reaction under microwave irradiation at 150 °C are presented in Figure 2, which clearly illustrates the process of this neat reaction. The mass spectra of 2-aminobenzophenone and 4-phenylquinazoline are presented in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively. An apparent mechanism for the reaction between 2-aminobenzophe...
Discussion
This clean reaction (as shown in Figure 2) appears very intriguing at beginning as molecular weight of the product is only increased by 9 with respect to that of starting material (as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4). This sounds impossible because the atomic weight of carbon is 12. Very likely, introduction of one carbon atom into a molecule will increase the molecular weight by at least 12 if the accompanying hydrogen atom(s) were not included. Therefore, the reaction h...
Disclosures
Except for the contents described in patent (pending), the authors have nothing else to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the National Science Foundation (NSF, grant number 0958901), the Robert Welch Foundation (Welch departmental grant BC-0022 and the Principal Investigator grant BC-1586), and the University of Houston-Clear Lake (FRSF grant) are greatly appreciated.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2-Aminobenzophenone | Alfa Aesar | A12580 | 98% purity, with tiny impurity as seen on Figure 1(A) in the manuscript. |
| Thiourea | Acros | 138910010 | 1 kg package, 99%, extra pure |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Acros | 326880010 | Methyl sulfoxide, 99.7+%, Extra Dry, AcroSeal® |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | Acros | 348430010 | N,N-Dimethylformamide, 99.8%, Extra Dry over Molecular Sieve, AcroSeal® |
| Ethyl Acetate | Acros | 610170040 | Ethyl acetate, used as solvent for GC/MS analysis |
| Preparative TLC plate | Sigma-Aldrich | Z740216 SIGMA | PTLC (Preparative TLC) Glass Plates from EMD/Merck KGaA |
| Rotavapor | Buchi | Rotavapor R-205 | Use to dry solvent |
| Microwave Reactor | Biotage | Initiator+ | Use to carry out chemical reaction under microwave irradiation |
| Hotplate | IKA | RCT basic | use to carry out thermal chemical reaction |
References
- Kamal, A., Reddy, K. L., Devaiah, V., Shankaraiah, N., Rao, M. V. Recent Advances in the Solid-Phase Combinatorial Synthetic Strategies for the Quinoxaline, Quinazoline and Benzimidazole Based Privileged Structures. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 6 (1), 71-89 (2006).
- Spirkova, K., Stankovsky, S. Some Tricyclic Annelated Quinazolines. Khim. Geterotsikl. Soedin. (10), 1388-1389 (1995).
- Connolly, D. J., Cusack, D., O'Sullivan, T. P., Guiry, P. J. Synthesis of Quinazolinones and Quinazolines. Tetrahedron. 61 (43), 10153-10202 (2005).
- Baba, A., et al. Studies on Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: Synthesis of Novel Quinoline and Quinazoline Derivatives and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effect. J. Med. Chem. 39 (26), 5176-5182 (1996).
- Gama, Y., Shibuya, I., Simizu, M. Novel and Efficient Synthesis of 4-Dimethylamino-2-Glycosylaminoquinazolines by Cyclodesulfurization of Glycosyl Thioureas with Dimethylcyanamide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 50 (11), 1517-1519 (2002).
- Wakeling, A. E., et al. Specific Inhibition of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase by 4-Anilinoquinazolines. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 38 (1), 67-73 (1996).
- Verhaeghe, P., et al. Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of New 4-Aryl-2-Trichloromethylquinazolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18 (1), 396-401 (2008).
- Kitano, Y., Suzuki, T., Kawahara, E., Yamazaki, T. Synthesis and Inhibitory Activity of 4-Alkynyl and 4-Alkenylquinazolines: Identification of New Scaffolds for Potent Egfr Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17 (21), 5863-5867 (2007).
- Goel, R. K., Kumar, V., Mahajan, M. P. Quinazolines Revisited: Search for Novel Anxiolytic and Gabaergic Agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15 (8), 2145-2148 (2005).
- Parhi, A. K., et al. Antibacterial Activity of Quinoxalines, Quinazolines, and 1,5-Naphthyridines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 23 (17), 4968-4974 (2013).
- Brown, D. J. . Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds, Volume 55: Quinazolines, Supplement I. , (1996).
- Yang, C. -. H., et al. Color Tuning of Iridium Complexes for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: The Electronegative Effect and -Conjugation Effect. J. Organomet. Chem. 691 (12), 2767-2773 (2006).
- Byford, A., Goadby, P., Hooper, M., Kamath, H. V., Kulkarni, S. N. O-Aminophenyl Alkyl/Aralkyl Ketones and Their Derivatives. Part V. An Efficient Synthetic Route to Some Biologically Active 4-Substituted Quinazolines. Ind. J. Chem. B. 27 (4), 396-397 (1988).
- Blazevic, N., Oklobdzija, M., Sunjic, V., Kajfez, F., Kolbah, D. New Ring Closures of Quinazoline Derivatives by Hexamine. Acta Pharmaceut. Jugo. 25 (4), 223-230 (1975).
- Panja, S. K., Saha, S. Recyclable, Magnetic Ionic Liquid Bmim[Fecl4]-Catalyzed, Multicomponent, Solvent-Free, Green Synthesis of Quinazolines. RSC Adv. 3 (34), 14495-14500 (2013).
- Wang, Z. D., Eilander, J., Yoshida, M., Wang, T. Mechanistic Study of a Complementary Reaction System That Easily Affords Quinazoline and Perimidine Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. (34), 7664-7674 (2014).
- Wang, D. Z., Yoshida, M., George, B. Theoretical Study on the Thermal Decomposition of Thiourea. Comput. Theoret. Chem. 1017, 91-98 (2013).
- Zhang, P., et al. Inhibitory Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on Ozone-Induced Airway Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 52 (1), 129-137 (2015).
- Yan, J., et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Cdxzn1-Xs-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites with Improved Photoelectrochemical Performance for Selective Determination of Cu2+. RSC Adv. 3 (34), 14451-14457 (2013).
- Keith, J. D., Pacey, G. E., Cotruvo, J. A., Gordon, G. Experimental Results from the Reaction of Bromate Ion with Synthetic and Real Gastric Juices. Toxicology. 221 (2-3), 225-228 (2006).
- Timchenko, V. P., Novozhilov, A. L., Slepysheva, O. A. Kinetics of Thermal Decomposition of Thiourea. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 74 (7), 1046-1050 (2004).
- Wang, S., Gao, Q., Wang, J. Thermodynamic Analysis of Decomposition of Thiourea and Thiourea Oxides. J. Phys. Chem. B. 109 (36), 17281-17289 (2005).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved