A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
The Evolution of Silica Nanoparticle-polyester Coatings on Surfaces Exposed to Sunlight
In This Article
Summary
Two types of surfaces, polyester-coated steel and polyester coated with a layer of silica nanoparticles, were studied. Both surfaces were exposed to sunlight, which was found to cause substantial changes in the chemistry and nanoscale topography of the surface.
Abstract
Corrosion of metallic surfaces is prevalent in the environment and is of great concern in many areas, including the military, transport, aviation, building and food industries, amongst others. Polyester and coatings containing both polyester and silica nanoparticles (SiO2NPs) have been widely used to protect steel substrata from corrosion. In this study, we utilized X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, attenuated total reflection infrared micro-spectroscopy, water contact angle measurements, optical profiling and atomic force microscopy to provide an insight into how exposure to sunlight can cause changes in the micro- and nanoscale integrity of the coatings. No significant change in surface micro-topography was detected using optical profilometry, however, statistically significant nanoscale changes to the surface were detected using atomic force microscopy. Analysis of the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and attenuated total reflection infrared micro-spectroscopy data revealed that degradation of the ester groups had occurred through exposure to ultraviolet light to form COO·, -H2C·, -O·, -CO· radicals. During the degradation process, CO and CO2 were also produced.
Introduction
Environmental corrosion of metals in the environment is both prevalent and costly1-3. A recent study conducted by the Australasian Corrosion Association (ACA) reported that corrosion of metals resulted in a yearly cost of $982 million, which was directly associated with the degradation of assets and infrastructure through metallic corrosion within the water industry4. From an international perspective, the World Corrosion Organization estimated that metallic corrosion was responsible for a direct cost of $3.3 trillion, over 3% of the world's GDP5. The process of galvanizing as a corrosion preventative method has been widely used to increase the lifespan of steel material6. In humid and subtropical climates, however, water tends to condense into small pockets or grooves within the surface of the galvanized steel, leading to the acceleration of corrosion rates through pit corrosion7,8. Thermosetting polymer coatings based on polyesters have been developed to coat the galvanized steel substrata increasing their ability to withstand humid weathering conditions for items such as satellite dishes, garden furniture, air-conditioning units or agricultural construction equipment9-11. Unfortunately polymer coatings on steel surfaces have been found to be considerably adversely affected by the presence of high levels of ultraviolet (uv) radiation12-14. Coatings comprised of silica nanoparticles (SiO2) spread over a polymer layer have been widely used with a view to increasing their corrosion-, wear-, tear- and degradation-resistance15,16. The tendency of the protective polymeric coatings to form pores and cracks can be reduced by incorporating nanoparticles (NPs), which contribute to the passive obstruction of corrosion initiation17,18. Also, the mechanical stability of the protective polymeric layer can be improved by NPs inclusion. However, these coatings act as passive physical barriers and, in comparison to the galvanization approach, cannot inhibit corrosion propagation actively.
An in-depth understanding of the effect that high-levels of ultraviolet light exposure under humid conditions upon these metal coatings is yet to be obtained. In this paper, a wide range of surface analytical techniques, including X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), attenuated total reflection infrared micro-spectroscopy (ATR IR), contact angle goniometry, optical profiling and atomic force microscopy (AFM) will be employed to examine the changes in the surface of steel coatings prepared from polyester- and silica nanoparticle-coated polyester (silica nanoparticles/polyester) after exposure to sunlight. Furthermore, the aim of this work is to give a concise, practical overview of the overall characterization techniques to examine weathered samples.
Protocol
1. Steel Samples
- Obtain steel samples of 1 mm thickness from a commercial supplier.
NOTE: Samples were coated with either polyester or polyester coated with silica nanoparticles. - Expose samples to sunlight at Rockhampton, Queensland, Australia: collect samples after one-year and five-year intervals over a total 5-year period. Cut sample panels into round discs of 1 cm diameter using hole puncher.
- Prior to surface characterization, rinse samples with double-distilled water, and then dry using nitrogen gas (99.99%). Keep all samples in air-tight containers to prevent any air contaminants adsorbing to the surface (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Preparation of metal discs with polyester-based coating. Samples were stored in containers until required. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
2. Chemical and Physicochemical Characterization of Surfaces
- Analyze surface chemistry using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
- Perform X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS) using a monochromatic X-ray source (Al Kα, hν = 1486.6 eV) operating at 150 W.
NOTE: Spot size of utilized X-ray beam is 400 µm in diameter. - Load samples on the sample plate. Place the sample plate into vacuum chamber of XPS then pump the chamber. Wait for the vacuum in the chamber to reach ~1 × 10-9 mbar.
- In the photoelectron spectroscopy software, press the option of "Flood Gun" to flood the samples with low-energy electrons to counteract surface charging.
- Press "Insert">"Point">"Point" to insert an analysis point.
NOTE: This will be a location at which analysis is performed. Enable the auto height function to obtain the best height for acquisition. - Press "Insert">"Spectrum">"Multi Spectrum" to add scans to this point.
NOTE: This will open a window with a periodic table; select an element by clicking on it to highlight it. - After setting up the experiments, press the "Play" command to proceed the scans.
- Press "Peak Fit" command then press "Add Peak" and "Fit All Level" commands to resolve the chemically distinct species in the high-resolution spectra.
NOTE: This step will acquire the Shirley algorithm to remove the background and Gaussian-Lorentzian fitting to deconvolute the spectra19. - Select all high-resolution and survey spectra. Press "Charge Shift" option to correct spectra using the hydrocarbon component of the C 1s peak (binding energy 285.0 eV) as a reference.
- After charge correction, press "Export" option to generate the data table of the relative atomic concentration of elements on the basis of the peak area.
- Perform X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS) using a monochromatic X-ray source (Al Kα, hν = 1486.6 eV) operating at 150 W.
- Surface chemistry
NOTE: Analyze surface chemistry using attenuated total reflection infrared micro-spectroscopy (ATR-IR) on the infrared (IR) spectroscopy beamline at the Australian Synchrotron as following:- Load samples on the stage of microscope. Open a "Start Video Assisted Measurement" or "Start Measurement without 3D" option. Turn "VIS" mode on. Use the objective to focus on sample surface. Press "Snapshot/Overview" to take desired images.
NOTE: 0.5 mm thick CaF2plate can be used as the background. - Change the ATR objective to the sample. Carefully move the stage to place a 45° multi-reflection germanium crystal (refractive index of 4) 1-2 mm above surfaces. Right-click on the Live Video window. Press "Start Measurement">"Change Measurement Parameters". Choose the option "Never use existing BG for all positions".
NOTE: This will choose not to take background spectra for every measurement point. - Draw a map on video screen to choose the area of interest. Press a red aperture square and choose "Aperture">"Change Aperture". Change the actual "Knife Edge Aperture" settings to X = 20 µm and Y = 20 µm.
- Right-click on the newly sized aperture square and go to "Aperture"> "Set all Apertures to selected Apertures". Press "Measurement" icon to start the scans. Save the data.
NOTE: The refractive index of Ge crystal is 4, so an aperture of 20 µm × 20 µm will define the spot size of 5 µm × 5 µm. This step will allow setting up FTIR mapping with an aperture of 20 by 20 µm, which corresponds to a 5 µm by 5 µm spot through the crystal across a maximum wavenumber range of 4,000-850 cm-1. - Open master file using spectroscopy software. Choose the peak of interest on IR spectra. Right-click on the peak of interest. Choose "Integration">"Integration". It will allow creating 2D false color maps
- Load samples on the stage of microscope. Open a "Start Video Assisted Measurement" or "Start Measurement without 3D" option. Turn "VIS" mode on. Use the objective to focus on sample surface. Press "Snapshot/Overview" to take desired images.
- Surface wettability measurements
NOTE: Perform wettability measurement using a contact angle goniometer equipped with a nanodispenser19.- Place the sample on the stage. Adjust the position of the microsyringe assembly so that the bottom of the needle appears about a fourth of a way down in the Live video window screen.
- Raise the sample using z-axis until distance between the sample and surface is about 5 mm. Move the syringe down until a droplet of double distilled water touches the surface. Move the syringe up to its original position.
- Press the "Run" command to record the water droplet impacting on the surface for a 20 sec period using a monochrome CCD Camera which is integrated with hardware.
- Press the "Stop" command to acquire the series of images.
- Press "Contact Angle" command to measure contact angles from acquired images. Repeat the contact angle measurements at three random locations for each sample.
3. Visualization of the Surface Topography
- Optical profiling measurement.
NOTE: The instrument is operated under the white light vertical scanning interferometry mode.- Place samples on the stage of the microscope.
NOTE: Ensure there is a sufficient gap (e.g., >15 mm) between objective lens and the stage. - Focus on surface using the 5× objectives by controlling z-axis until the fringes appear on the screen. Press "Auto" command to optimize the intensity. Press "Measurement" command to initiate the scanning. Save the master files.
- Repeat the step 3.1.2 for 20× and 50× objectives.
- Prior to statistical roughness analyses, press "Remove Tilt" option to remove the surface waviness. Press "Contour" option to analyze the roughness parameters. Click on "3Di" option to generate three-dimensional images of optical profiling files using compatible software20.
- Place samples on the stage of the microscope.
- Atomic force microscopy
- Place samples on steel discs. Insert the steel discs into magnetic holder.
- Perform AFM scans in tapping mode21. Mechanically load phosphorus doped silicon probes with a spring constant of 0.9 N/m, tip curvature with radius of 8 nm and a resonance frequency of ∼20 kHz for surface imaging.
- Manually adjust the laser reflection on the cantilever. Choose "Auto Tune" command then press "Tune" command to tune the AFM cantilever to reach the optimum resonance frequency reported by the manufacturer.
- Focus on the surface. Move the tips close to sample surface. Click on Engage command to engage AFM tips on surfaces.
- Type "1 Hz" into scanning speed box. Choose the scanning areas. Press "Run" command to perform scan. Repeat the scanning at least for ten areas of each of five samples of each condition.
- Choose the leveling option to process the resulting topographical data. Save the master files.
- Open the compatible AFM software. Load the AFM master file. Press "Leveling" command to remove the tilting of surfaces. Press "Smoothen" command to remove the background.
- Press "Statistical Parameters Analysis" to generate the statistical roughness 21.
4. Statistical Analysis
- Express the results in terms of mean value and its standard deviation. Perform statistical data processing using paired Student's two-tailed t-tests to evaluate the consistency of results. Set p-value at <0.05 indicating level of statistical significance.
Results
The coated steel samples that had been subjected to exposure to the sunlight for either one or five years were collected, and water contact angle measurements were carried out to determine whether the exposure had resulted in a change in the surface hydrophobicity of the surface (Figure 2).
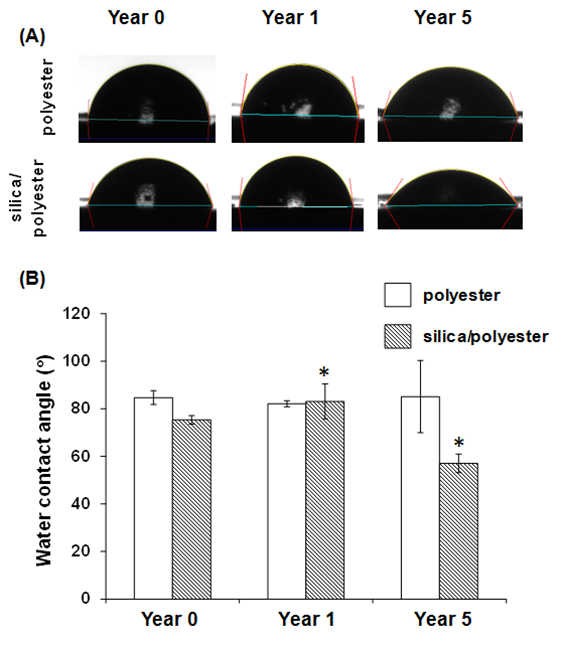
Figure 2. Wettability variation of surfaces with polyester or silica nanopa...
Discussion
Polyester coatings have been widely used to protect steel substrata from the corrosion that would occur on an uncoated surface due to the accumulation of moisture and pollutants. The application of polyester coatings can protect the steel from corrosion; however the longer-term effectiveness of these coatings is compromised if they are exposed to high levels of ultraviolet light under humid conditions, as occurs in tropical climates. Silica nanoparticles can be applied to the surface of the polyester to improve the robus...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
Funding from the Australian Research Council Industrial Transformation Research Hubs Scheme (Project Number IH130100017) is gratefully acknowledged. Authors gratefully acknowledge the RMIT Microscopy and Microanalysis Facility (RMMF) for providing access to the characterisation instruments. This research was also undertaken on the Infrared Microscopectroscopy beamline at the Australian Synchrotron, Victoria, Australia.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| polyester-coated steel silica nanoparticle-polyester coated steel substrata | BlueScope Steel | Samples provided by company | |
| Millipore PetriSlideTM | Fisher Scientific | PDMA04700 | Storing samples |
| Thermo ScientificTM K-alpha X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometer | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | IQLAADGAAFFACVMAHV | Acquire XPS spectra |
| Avantage Data System | Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | IQLAADGACKFAKRMAVI | Analyse XPS spectra |
| A Bruker Hyperion 2000 microscope | Bruker Corporation | Synchrotron integrated instrument | |
| Bruker Opus v. 7.2 | Bruker Corporation | ATR-IR analysis software | |
| Contact angle goniometer, FTA1000c | First Ten Ångstroms Inc., VA, USA | Measuring the wettability of surfaces | |
| FTA v. 2.0 | First Ten Ångstroms Inc., VA, USA | Anaylyzing water contact angle | |
| Optical profiler, Wyko NT1100 | Bruker Corporation | Measure surface topography | |
| Innova atomic force microscope | Bruker Corporation | Measure surface topography | |
| Phosphorus doped silicon probes, MPP-31120-10 | Bruker Corporation | AFM probes | |
| Gwyddion software | http://gwyddion.net/ | Software used to measure optical profiling and AFM data |
References
- Fathima Sabirneeza, A. A., Geethanjali, R., Subhashini, S. Polymeric corrosion inhibitors for iron and its alloys: A review. Chem. Eng. Commun. 202 (2), 232-244 (2015).
- Gupta, R. K., Birbilis, N. The influence of nanocrystalline structure and processing route on corrosion of stainless steel: A review. Corros. Sci. 92, 1-15 (2015).
- Lee, H. S., Ismail, M. A., Choe, H. B. Arc thermal metal spray for the protection of steel structures: An overview. Corros. Rev. 33 (1-2), 31-61 (2015).
- Moore, G. . Corrosion challenges - urban water industry. , (2010).
- Hays, G. F. . World Corrosion Organization. , (2013).
- Koch, G. H., Brongers, M. P. H., Thompson, N. G., Virmani, P. Y., Payer, J. H. Corrosion cost and preventive strategies in the United States. CC Technologies Laboratories, Incorporated; NACE International; Federal Highway Administration, NACE International. , (2002).
- Pojtanabuntoeng, T., Singer, M., Nesic, S. . Corrosion 2011. , (2011).
- Jas̈niok, T., Jas̈niok, M., Tracz, T., Hager, I. . 7th Scientific-Technical Conference on Material Problems in Civil Engineering, MATBUD 2015. , 316-323 (2015).
- Cambier, S. M., Posner, R., Frankel, G. S. Coating and interface degradation of coated steel, Part 1: Field exposure. Electrochim. Acta. 133, 30-39 (2014).
- Barletta, M., Gisario, A., Puopolo, M., Vesco, S. Scratch, wear and corrosion resistant organic inorganic hybrid materials for metals protection and barrier. Mater. Des. 69, 130-140 (2015).
- Fu, J., et al. Experimental and theoretical study on the inhibition performances of quinoxaline and its derivatives for the corrosion of mild steel in hydrochloric acid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 51 (18), 6377-6386 (2012).
- Hattori, M., Nishikata, A., Tsuru, T. EIS study on degradation of polymer-coated steel under ultraviolet radiation. Corros. Sci. 52 (6), 2080-2087 (2010).
- Yang, X. F., et al. Weathering degradation of a polyurethane coating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 74 (2), 341-351 (2001).
- Armstrong, R. D., Jenkins, A. T. A., Johnson, B. W. An investigation into the uv breakdown of thermoset polyester coatings using impedance spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 37 (10), 1615-1625 (1995).
- Zhou, W., Liu, M., Chen, N., Sun, X. Corrosion properties of sol-gel silica coatings on phosphated carbon steel in sodium chloride solution. J. Sol. Gel. Sci. Technol. 76 (2), 358-371 (2015).
- Hollamby, M. J., et al. Hybrid polyester coating incorporating functionalized mesoporous carriers for the holistic protection of steel surfaces. Adv. Mater. 23 (11), 1361-1365 (2011).
- Borisova, D., Möhwald, H., Shchukin, D. G. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for active corrosion protection. ACS Nano. 5 (3), 1939-1946 (2011).
- Wang, M., Liu, M., Fu, J. An intelligent anticorrosion coating based on pH-responsive smart nanocontainers fabricated via a facile method for protection of carbon steel. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3 (12), 6423-6431 (2015).
- Truong, V. K., et al. The influence of nano-scale surface roughness on bacterial adhesion to ultrafine-grained titanium. Biomaterials. 31 (13), 3674-3683 (2010).
- Nečas, D., Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An open-source software for SPM data analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 10 (1), 181-188 (2012).
- Crawford, R. J., Webb, H. K., Truong, V. K., Hasan, J., Ivanova, E. P. Surface topographical factors influencing bacterial attachment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 179-182, 142-149 (2012).
- Allen, N. S., Edge, M., Mohammadian, M., Jones, K. Physicochemical aspects of the environmental degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 43 (2), 229-237 (1994).
- Newman, C. R., Forciniti, D. Modeling the ultraviolet photodegradation of rigid polyurethane foams. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40 (15), 3346-3352 (2001).
- Ivanova, E. P., et al. Vibrio fischeri and Escherichia coli adhesion tendencies towards photolithographically modified nanosmooth poly (tert-butyl methacrylate) polymer surfaces. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 1, 33-44 (2008).
- Biggs, S., Lukey, C. A., Spinks, G. M., Yau, S. T. An atomic force microscopy study of weathering of polyester/melamine paint surfaces. Prog. Org. Coat. 42 (1-2), 49-58 (2001).
- Signor, A. W., VanLandingham, M. R., Chin, J. W. Effects of ultraviolet radiation exposure on vinyl ester resins: Characterization of chemical, physical and mechanical damage. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 79 (2), 359-368 (2003).
- Wang, H., et al. Corrosion-resistance, robust and wear-durable highly amphiphobic polymer based composite coating via a simple spraying approach. Prog. Org. Coat. 82, 74-80 (2015).
- Liszka, B. M., Lenferink, A. T. M., Witkamp, G. J., Otto, C. Raman micro-spectroscopy for quantitative thickness measurement of nanometer thin polymer films. J. Raman Spectrosc. 46 (12), 1230-1234 (2015).
- Alghunaim, A., Kirdponpattara, S., Newby, B. M. Z. Techniques for determining contact angle and wettability of powders. Powder Technol. 287, 201-215 (2016).
- Treviño, M., et al. Erosive wear of plasma electrolytic oxidation layers on aluminium alloy 6061. Wear. 301 (1-2), 434-441 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved