Method Article
Extraction and Analysis of Microbial Phospholipid Fatty Acids in Soils
In This Article
Summary
Phospholipid fatty acids provide information about the structure of soil microbial communities. We present methods for extraction from soil samples with a single-phase chloroform mixture, fractionation of extracted lipids using solid phase extraction columns, and methanolysis to produce fatty acid methyl esters, which are analyzed by capillary gas chromatography.
Abstract
Phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) are key components of microbial cell membranes. The analysis of PLFAs extracted from soils can provide information about the overall structure of terrestrial microbial communities. PLFA profiling has been extensively used in a range of ecosystems as a biological index of overall soil quality, and as a quantitative indicator of soil response to land management and other environmental stressors.
The standard method presented here outlines four key steps: 1. lipid extraction from soil samples with a single-phase chloroform mixture, 2. fractionation using solid phase extraction columns to isolate phospholipids from other extracted lipids, 3. methanolysis of phospholipids to produce fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs), and 4. FAME analysis by capillary gas chromatography using a flame ionization detector (GC-FID). Two standards are used, including 1,2-dinonadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PC(19:0/19:0)) to assess the overall recovery of the extraction method, and methyl decanoate (MeC10:0) as an internal standard (ISTD) for the GC analysis.
Introduction
Phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) are part of microbial cellular membranes from the domains Bacteria and Eukarya. Microorganisms produce PLFAs of different chain lengths and composition as a means to maintain cell-membrane integrity and cellular function in response to their immediate environmental conditions; hence it can be argued that microbial communities that are separated geographically but are subjected to similar soil conditions will express similar PLFAs. Soil PLFAs with a chain length between 14 and 20 C atoms are typically considered to be of predominantly bacterial and fungal origin1. In mixed cultures, PLFA analysis cannot be used to identify individual microbial species, but it can provide an overall fingerprint of the microbial communities found in soils. In addition, since PLFAs are rapidly degraded upon cell death, they can be considered to be representative of the viable soil microbial community2. This technique has been extensively used to characterize the structural composition of microbial communities found in a wide range of environments, ranging from forests3-4 to prairies5-6 and agricultural fields7. It has been successfully applied in characterizing soil response to land management changes, including forest clear-cutting8, liming9, reclamation10-12, as well as disturbances such as fire13, contamination by metals14 and hydrocarbons15, and insect outbreak16.
The contemporary PLFA analytical method evolved during the last six decades through several key advancements by a number of research groups. In 1958, a significant improvement arose from adjusting the chloroform:methanol:water ratio in the extraction solution to shift the mixture from a monophasic to a diphasic system17. This optimized lipid extraction and the revised isolation protocol became known as the Bligh and Dyer method. The protocol was adopted by many laboratories over the next few decades and, during this time, White and colleagues contributed significant advancements to the method; for instance, they improved the extraction step by exchanging a phosphate buffer for water, and they optimized the analysis by gas chromatography (GC) through enhanced peak identification and quantification. Perhaps of more relevance to soil science, they determined in 1979 that the extracted lipids could be used as an index of microbial structure when they examined the microbial biomass of marine sediments18.
Further developments occurred in the 1980s as the method became more widely utilized in soil science, specifically in relation to the rhizosphere19. At that time, the method included methyl nonadecanoate (MeC19:0) as an internal standard19 and the use of a silicic acid column for lipid fractionation21. Following his work with White19,21, Tunlid returned to Sweden and started collaborative research with Bååth and Frostegård. By examining the efficiency of different extraction buffers for a suite of soils varying in organic matter content, the group showed that the citrate buffer increased the amount of lipid phosphate extracted compared to the phosphate buffer22. Further, their 1993 publication23 on the influence of liming on soil microbial communities went on to become a citation classic in Soil Biology & Biochemistry24. The researchers utilized principal component analysis in their data processing. PLFA analysis, as the method is now called, generates large data sets and the use of multivariate statistical procedures to process these data was highly innovative for the time and inspirational to many. Concurrent to the work being done in Sweden, modifications to the PLFA procedure were being investigated in Germany by Zelles and colleagues25-26. Their version of the procedure was notable for its use of a solid-phase extraction (SPE) column instead of the silicic acid column but, overall, was more laboratory intensive.
Frostegård's paper23, along with the detailed methodology by White & Ringelberg27, provided the foundation for an explosion in the use of the PLFA technique to investigate fundamental questions in soil science. Since then, further refinements of the method by Firestone and colleagues have included adding an internal GC standard (C10:0) and C19:0 as a surrogate standard to improve quantification28, and replacing the use of separatory funnels for round bottom vials to simplify extraction29. More recently, Chowdhury and Dick30 investigated the methylation step and reported that of the two methylation procedures used in the soil science literature the KOH/MeOH method identified a larger range of fatty acids.
The presented method is largely based on the original method developed by Bligh and Dyer, and incorporates the modifications mentioned above, such as the use of methanolic KOH for the methylation step. Two standards are used for each sample: a surrogate standard of 1,2-dinonadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PC(19:0/19:0)), which is added to the soil sample prior to the first extraction to assess efficiency and recovery of the entire protocol, and an instrument standard of methyl decanoate (MeC10:0), which is added prior to identification and quantification by GC.
We acknowledge that the PLFA method is commonly used by many microbial ecology laboratories worldwide, and has been documented many times, including by the International Organization for Standardization2. The objective of this paper is to present an easy to follow and robust protocol that can be useful to soil scientists who are trying to learn the PLFA technique.
Protocol
NOTE: Always ensure that proper personal protective equipment (PPE) is worn throughout the protocol. Glassware should not be touched with bare hands. Lipids from fingers, hair, grease, oils and hydrocarbons are all potential contaminants. Always wear nitrile gloves and rinse gloves with 70% alcohol when handling clean glassware.
1. Preparation of Glassware for Analysis
- Disposable glassware (e.g., centrifuge tubes)
- Wrap in aluminum foil and heat in muffle furnace for four and a half hours at 450 ºC.
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-lined caps
- Soak caps for one hour in phosphate detergent, and then wash with scrub brush in hot water and phosphate detergent. Rinse off soap with tap water.
- Place in acid bath (5% HCl) for one hour only (do not leave longer as the liners may fall out of the caps if they are soaked for too long. Rinse three times in tap water. Rinse three times in distilled water. Dry in oven at 40 ºC.
- Reusable glassware (e.g., 10 ml, 15 ml, 45 ml vials/jars)
- Wash with scrub brush in hot water and phosphate detergent. Rinse off soap with tap water and place in acid bath (5% HCl) overnight. Rinse three times in tap water, then rinse three times in distilled water and then dry in oven at 40 ºC.
- Wrap in clean aluminum foil (50 ml jars are wrapped individually and other glassware is wrapped in sample batches, e.g., 20) and heat in muffle furnace for four and a half hours at 450 ºC.
- Volumetric glassware (e.g., volumetric flask)
- Wash with scrub brush in hot water and phosphate detergent. Rinse off soap with tap water and place in acid bath (5% HCl) overnight. Rinse three times in tap water, rinse three times in distilled water, and then dry in oven at 40 ºC.
- Prior to use rinse 3 times with a small amount of solvent (e.g., methanol) — do NOT put volumetric glassware in the muffle furnace.
2. Collection and Processing of Soil Samples Prior to PLFA Analysis
- Collect soil samples into sterile bags, and unless these can be analyzed immediately, freeze them as soon as possible. Store samples in freezer (-80 ºC) until ready to proceed with freeze drying of samples. Freeze dry batches of samples following the instructions of the freeze dryer.
- Transfer each freeze-dried sample to new-labeled sterile bag. Weigh out sample from freeze-dried material in bag into pre-labeled muffled centrifuge tube for PLFA extraction.
NOTE: A general guideline is to use 0.5 g for organic materials (carbon content > 17% wt) and up to 3.0 g for mineral soil samples. Record sample weight for each sample. - For every 10 samples, also weigh out an additional duplicate for analysis, and for every 20 samples include a blank (i.e., a centrifuge tube that does not have any sample in it — used as a control to identify any potential contamination during the PLFA extraction process). Process batches of sample tubes at the same time.
NOTE: A set of 20 samples will correspond to a batch of 23 sample tubes (samples 1 to 10, one duplicate of sample 10, samples 12 to 22, one duplicate of sample 22, and one blank = batch of 23 sample tubes).
NOTE: Conduct extraction, then separation, then methylation in batches of samples before preparing them for GC analysis and running them all together. This helps to identify where mistakes have happened if anything goes wrong, and may help lower the number of necessary repeat extractions.
3. PLFA Technique (steps are for individual sample but complete one entire batch at a time)
NOTE: All steps of the PLFA technique described in Steps 1-3 below should be conducted in a fume hood using appropriate PPE and following lab safety guidelines.
- Extraction (Step 1):
- Prepare 5.0 M KOH by dissolving 14 g of KOH in 50 ml distilled, deionized water (dH2O).
- Prepare 0.15 M citrate buffer by dissolving 31.52 g citric acid monohydrate in 400 ml of dH2O. Adjust to pH 4.00 ± 0.02 by adding 5.0 M KOH; approximately 45-50 ml of 5.0 M KOH will be required to adjust the pH to 4.00. When the pH is adjusted, dilute citrate buffer to 1,000 ml using a volumetric flask. Store citrate buffer in the refrigerator when not in use (for up to one month).
- Prepare daily the PC(19:0/19:0) nonadecanoate surrogate standard by diluting 250 μl of the stock solution (10 mg/ml) in 25 ml chloroform (this provides enough surrogate standard for a batch of 23 samples). Add 0.5 ml of PC(19:0/19:0) surrogate standard solution to the sample centrifuge tube.
- Add the Bligh and Dyer extractant to the soil sample in the following order: i) 2.0 ml citrate buffer, ii) 2.5 ml chloroform, and iii) 5.0 ml methanol. Cap sample with a PTFE-lined cap and vortex for 30 sec; place in end-over-end shaker for 2 hr.
- Centrifuge at 226 x g for 15 min with cap on. Draw supernatant off with a Pasteur pipette and transfer to a labeled 45 ml glass vial.
- Add a second round of Bligh and Dyer extractant to each sample, and repeat steps 4 and 5 above. Draw supernatant off with a Pasteur pipette and transfer to the same labeled 45 ml glass vial.
- Add to labeled 45 ml glass vial containing supernatant: i) 5.0 ml chloroform, and ii) 5.0 ml citrate buffer. Cap with white PTFE-lined cap and vortex glass vial for 30 sec. Let it sit overnight at room temperature in the dark (to avoid oxidation).
- Carefully vacuum off the upper aqueous phase of the 45 ml vial (if no vacuum is available, the pipette should be lowered through the aqueous phase very carefully as to not collect any in the pipette when pipetting the organic phase). Pipette lower organic phase into labeled 15 ml vial.
- Place batch of 15 ml vials under compressed N2 (to avoid oxidation) at room temperature. Evaporate chloroform off slowly, setting the N2 flow to ruffle the surface of the liquid in the vial but not climb the sides of the vial.
- Screw on PTFE-lined cap and store samples in the freezer at -20 ºC wrapped in aluminum foil (wrap in batches rather than individually) until ready to proceed with Step 2.
- Lipid fractionation (Step 2)
- Place SPE column holder with spigots on the glass tank. Insert new SPE columns (silica, 500 mg, 6 ml) into spigots. Label columns as necessary (recommended to avoid mixing up samples).
- Condition each column by adding 5 ml of acetone and letting it drain through, and then add two additions of 5 ml chloroform (total volume = 10 ml). Allow second chloroform wash to flow out until ~ 1 mm above the frit and then close the spigot.
- Re-dissolve sample (stored in 15 ml vial at end of Step 1) by adding 0.5 ml chloroform to vial and vortex gently. Transfer re-dissolved sample to the SPE column using a Pasteur pipette; repeat for a total of 2 transfers (total transfer volume of 1 ml chloroform per sample).
- Lay lipid sample directly into center of the column and allow solvent to drain completely into tank.
- Elute neutral lipids by adding 5 ml of chloroform to each column. Allow solvent to drain completely into tank.
- Elute glycolipids by adding 5 ml of acetone to each column. Allow solvent to drain completely into the collection tank.
- Remove column stand from tank and drain tank with vacuum apparatus. Insert rack with clean and labeled centrifuge tubes into the tank. Replace column stand on tank; labeled column above should line up with labeled centrifuge tube below.
- Elute phospholipids into centrifuge tubes by adding 5 ml of methanol to each column. Wait for SPE columns to dry out in fume hood before disposing of them. Dry down phospholipid fractions at room temperature under compressed N2.
- Purge tubes with N2. Screw on PTFE-lined cap and store samples in the freezer at -20 ºC wrapped in aluminum foil (wrap in batches rather than individually) until ready to proceed to Step 3.
- Lipid methylation (Step 3).
- Turn on the hot water bath set to 37 ºC. Prepare 1M acetic acid (if not already made) by dissolving 57.1 ml glacial acetic acid in 1,000 ml dH2O using a 1,000 ml volumetric flask. This solution can be stored at room temperature for up to three months. .
- Prepare batch of methanolic KOH. Prepare 0.2 M KOH solution by dissolving 0.45 g KOH in 40 ml methanol. Adjust volume of KOH and methanol according to anticipated batch size in Step 3. Prepare this solution daily; do not store for longer periods.
- Remove samples (in centrifuge tubes stored after Step 2) from freezer and allow samples to come to room temperature. Add 0.5 ml chloroform and 0.5 ml methanol to each sample, followed by 1.0 ml methanolic KOH. Cap tubes tightly with PTFE-lined cap. Swirl to mix.
- Place sealed samples in 37 ºC bath for 30 min. Ensure that the water level is a minimum of 1-2 mm above the level of the sample liquid. Remove and allow samples to cool. While samples are in water bath, label small glass vials with sample IDs (10 ml glass vial with PTFE-lined cap).
- Add 2.0 ml hexane to each sample and swirl. Then add 0.2 ml of 1.0 M acetic acid to each sample and swirl to mix again; phase separation should become visible.
- Add 2.0 ml of dH2O to each sample to break phase. Vortex samples for 30 sec. Then centrifuge samples at 226 x g for 2 min.
- Using short Pasteur pipette, transfer the top phase to clean labeled 10 ml vials. Be careful not to transfer any of the lower (aqueous) phase.
- Add 2.0 ml hexane to each sample centrifuge tube and swirl. Vortex samples for 30 sec. Then centrifuge samples at 226 x g for 2 min.
- Using short Pasteur pipette, again add the top phase to the labeled 10 ml glass vial.
- Evaporate solvent in labeled-10 ml glass vial at room temperature under N2. Screw on PTFE-lined cap and store samples in the freezer at -20 ºC wrapped in aluminum foil (wrap in batches rather than individually) until ready to proceed with GC analysis. Be sure to label all samples.
- Gas chromatograph (GC) analysis
NOTE: Identification and quantification of the individual PLFAs is accomplished using a GC connected to either a FID or a MS detector. While the instructions below are for GC-FID, the sample preparation would be valid for GC-MS as well. An example set-up for a GC-FID system would include a 25 m × 0.2 mm × 0.33 μm (5%-phenyl)-methylpolysiloxane column with the following temperature protocol: initial temperature 190 ºC, ramp 10 ºC/min to 285 ºC, hold 9.5 min, ramp 60 ºC/min to 310 ºC, hold 0.42 min31.- Prepare the GC internal standard (ISTD) by adding one drop of MeC10:0 (methyl decanoate) to 100 ml hexane (record added weight to 0.1 mg). Turn on gases to GC and then turn on the GC. Make sure that H2, N2 and air cylinders are open and that there is sufficient gas to run the analysis (H2 should never get below 500 psi).
- Check that conditions of a good calibration are met by running calibration standards containing a mix of fatty acids, followed by a hexane blank. Identity of individual fatty acids can be manually assigned based on comparisons with retention times obtained for standards, or this can be automatically assigned using commercially available softwares31. In all cases, unequivocal identification can be achieved using a MS detector2.
NOTE: Additional signs of a good calibration include a flat baseline and no contamination in the hexane rinse. - Dissolve each PLFA sample residue (contained in 10 ml glass vial from lipid methylation Step 3) in 150 µl of the ISTD solution and transfer into GC vial (alternatively use 50 to 75 μl if sample response is anticipated to be weak, such as in very sandy soils).
- Set the sample injection volume to 2 µl. Set the FID temperature to 300 ºC. Run the samples using an inlet temperature of 250 ºC, with H2 as the carrier gas (flow rate 1.3 ml/min) and a split ratio of 30:1.
Results
Fatty acids are designated as X:YωZ, where X represents the number of carbon atoms, Y represents the number of double bonds, and Z indicates the position of the first double bond from the aliphatic (ω) end of the molecule. The suffixes 'c' and 't' indicate cis and trans geometric isomers. The prefixes and suffixes 'a' and 'i' refer to anteiso and iso branching and Me and OH specify methyl groups and hydroxyl groups, respectively.
Post-GC run, check that samples received adequate ISTD by looking at the 10:0 peak. Also check the response of the GC standards, i.e., the vials containing hexane with added ISTD solution; these should have no other peaks. Internal standard response should be similar throughout all runs.
Figure 1 presents a representative sample run. The large hexane solvent peak characteristically appears at a retention time (RT) around 1.8 min. The ISTD standard peak (C10:0) appears at a RT of 3.4 min, while C19:0 has a RT of 16.2 min. The GC analysis separates the PLFAs based on their chain length, with longer chains eluting more slowly; for instance, C18:0 elutes at 14.4 min while C16:0 elutes at 10.8 min. In addition, this analytical protocol can separate PLFAs based on their degree of unsaturation and the position of their double bond; for example, C18:0 elutes at 14.4 min, while C18:1 9c, and C18:1 7c elute at 14.0 and 14.1 min, respectively (Figure 1). Lastly, PLFAs of similar chain length and saturation but different branching configuration (anteiso versus iso) can be separated; for example, C15:0i and C15:0a elute at 8.6 and 8.7 min, respectively (Figure 1).
The areas of the different GC peaks can be imported into a spreadsheet to further process the gas chromatogram information. Each identified PLFA is quantified (nmol g-1 of dry soil) using the following equation:
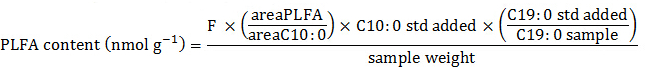
where F is an adjustment factor that takes into account FID selectivity and the molarity differences between fatty acids32, areaPLFA is the peak area for each identified PLFA, areaC10:0 is the peak area for the ISTD (MeC10:0), C10:0 std added is the amount of ISTD (nmol) added to each sample prior to the GC run, the ratio (C19:0 std added / C19:0 sample) corresponds to the recovery of the PC (C19:0/C19:O) surrogate standard, and the sample weight is the amount of oven-dried soil (g) added to the original sample centrifuge tube and used to extract PLFAs.
NOTE: The areas under the different peaks are expressed as peak areas, response or %response depending on the GC system. Within the range relevant to soil PLFA characterization, areas can be assumed to be linearly proportional to the weights of fatty acids; alternatively, small correction factors can be applied to account for FID selectivity32. In addition, because results are initially expressed on a weight percent basis, they need to be normalized to yield molar amounts. Adjusting for molarity differences is achieved by taking into account molecular weights of the individual fatty acids; published tables32 and commercial software31 are also available to help when normalizing for molarity.
The amount of ISTD (nmol) added to each sample can be further calculated as:
C10:0std added = [ISTD] × V(STD added)
where [ISTD] is the concentration (nmol l-1) of the MeC10:0 (methyl decanoate) dissolved in hexane (see Step 3.4.1), and V(STD added) is the volume (L) of prepared ISTD solution added to each sample prior to the GC run (i.e., 150 µl according to Step 3.4.4).
The amount of C19:0 (nmol) present in each sample during GC analysis corresponds to:
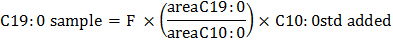
where areaC19:0 is the peak area for C19:O, while the corresponding amount of C19:0 (nmol) added to each sample at the beginning of the PLFA extraction method (cf. Step 3.1.3) is:
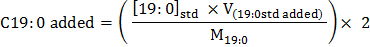
where [19:0]Std (mg L-1) is the concentration of the C19:0 nonadecanoate surrogate standard dissolved in chloroform (Step 3.1.3), V(19:0 std added) is the volume of prepared surrogate standard added to each sample at the beginning of the PLFA extraction method (cf. Step 3.1.3), M19:0 is the molecular weight of 1,2-dinonadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PC(19:0/19:0)).
NOTE: One mole of C19:0 nonadecanoate surrogate standard yields two moles of C19:0 following the methylation step, while the C10:0 standard is added after methylation.
The following PLFAs are typically excluded from analysis of soil microbial communities: i) PLFAs that are <14 C and >20 C in length, and ii) PLFAs with less than 0.5% of total in peak area. Once these PLFAs have been excluded, the responses from all of the remaining PLFAs can be summed to obtain the total PLFA biomass (nmol g-1 of dry soil). Univariate analysis of PLFA data (e.g., ANOVA, following data transformation as appropriate to meet the assumptions of the test being performed) can be used to compare total PLFA biomass and/or PLFA biomass of selected groups among sample groups/treatments. For instance, Figure 2 presents results for the relative distribution of different PLFA groups, such as straight-chained saturated PLFAs, saturated PLFAs with either mid-chain (10-methyl) or terminal branching, and mono- or polyunsaturated PLFAs, as well as the sum of total PLFAs (nmol g-1 of dry soil). In this particular example, the age of the trees (which decreases from Site 1 to Site 3) is seen to influence both total PLFAs and the relative distribution of the different PLFA groups.
To evaluate overall patterns in PLFA composition among samples, multivariate analysis of all PLFAs can be conducted33. The PLFA data need to be transformed as necessary prior to the selected multivariate analysis to meet the assumptions of the statistical test and the research question being addressed, e.g., a Hellinger transformation is often used to relativize the data. Figure 3 shows results from a non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of the same data that were used in Figure 2; NMDS is a non-parametric, multivariate technique that produces 2- or 3-dimensional positioning of data points based on the similarity of ranking scores between samples.
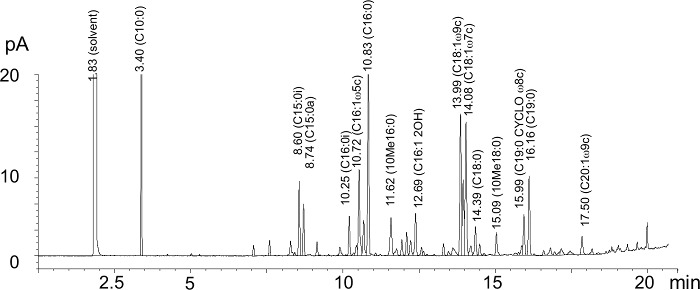
Figure 1. Representative GC-FID chromatogram. A sample obtained from a cultivated Brown Chernozemic soil was used for this analysis. Retention times and corresponding PLFAs (in parentheses) and their peak area (pA) are indicated on the figure for representative peaks. For clarity, not all peaks are indicated on the figure, although this particular sample yielded 33 identified PLFAs. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
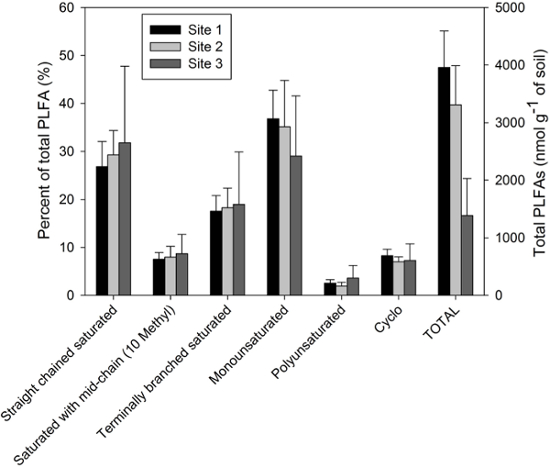
Figure 2. Relative abundance of six different classes of PLFAs (% of total PLFAs), and total PLFA biomass (nmol g-1 of dry soil). Samples from forested Luvisolic soils were used for this analysis. Results indicate greater total PLFAs for the soil at Site 1, which is located under older trees (> 50 years), followed by the intermediate-aged (25 years) trees (Site 2), and lastly the youngest (10 years) trees (Site 3). Relatively more saturated PLFAs are present at the youngest site, while more unsaturated PLFAs are present at the oldest site. Error bars represent standard deviations. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
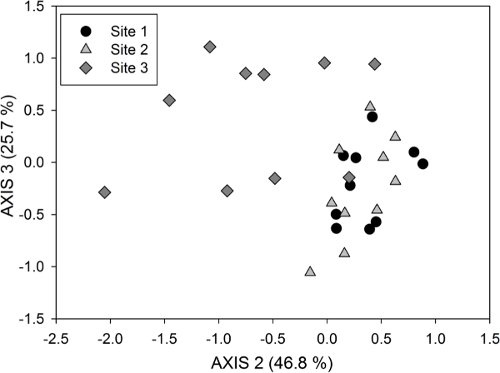
Figure 3. Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of PLFAs (using % of total PLFAs data) for axes 2 and 3 of a 3-dimensional solution. This ordination was computed using the same data as those used for Figure 2. The youngest site (Site 3) separates very clearly from the older two sites (Sites 2 and 3), which show overlap in their PLFA microbial community composition. The amount of variation in the PLFA community data explained by each axis is included in parentheses; 72.5% of the variation is explained by these two axes for a 3-dimensional NMDS solution. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
To minimize and avoid misinterpretation of PLFA data, careful data screening must be done because some PLFAs that are found in the soil microbial community are also present in single and multicellular eukaryotic organisms, such as plant roots, algae, and soil animals. In addition, Archaea do not contain PLFAs; instead, archaeal membranes are comprised of phospholipid ether lipids (PLELs). Consequently, the PLFA protocol cannot be used to characterize archaeal communities in soil.
Associating individual PLFAs to specific microbial groups should be exercised with caution (see the 2011 publication by Frostegård and colleagues34 for an excellent discussion of some of the limitations of the PLFA method). Instead, it may be more appropriate, as was done in Figure 2, to group PLFAs based on their chemical structure, e.g., i) straight-chained saturated PLFAs, ii) saturated PLFAs with mid-chain (10-methyl) branching, iii) terminally-branched saturated fatty acids, iv) monounsaturated PLFAs, v) polyunsaturated PLFAs, and vi) hydroxy fatty acids.
Sample weight may need to be adjusted based on the quantity of extractable PLFAs contained in a given soil sample. By not adjusting the amount of soil extracted in less microbially active soils, users are at risk of not obtaining a sufficient number of PLFA responses (peaks) to accurately represent the overall microbial community. In highly microbially active soils with high concentrations of PLFAs, users are at risk of overloading the GC column, thereby preventing accurate quantification of PLFAs. In both cases, soil samples must be re-analyzed for PLFAs. A good starting point is to add 0.5 g for organic soil samples (such as forest floors), and about 3 g for mineral soil samples. Since the quantity of extractable PLFAs is typically correlated to the amount of organic carbon contained in a soil, sample weight can be adjusted based on soil carbon content; e.g., 1 g of mineral soil sample may be sufficient to obtain a good PLFA quantification when carbon content is 10-15%, while >5 g may be necessary if the carbon content is ≤ 0.5%. It is always a good idea to do a trial run with a few samples to optimize sample weight before the entire set is run.
Common troubleshooting strategies for the PLFA protocol and GC analysis are as follows. If the GC chromatogram baseline is too high, the H2 gas cylinder should be changed. If the solvent or ISTD peaks are missing from the chromatogram, there might be a problem with sample injection (e.g., plugged syringe, problem with autosampler, empty or missing vial, error with vial positioning). If more than three peaks are detected in the method/sample blank, there is contamination of the blank, and there is a high probability that the same contaminant(s) will be present in the sample GC chromatograms. Find the source of contamination (usually aqueous media), or at the very least, ensure that the peaks corresponding to the contaminant are removed from the sample chromatograms and that these peaks are not included in any statistical analysis of the PLFA data. Also, it is a good idea to run hexane rinses between samples when carry-over is suspected. Additional peaks in the hexane rinse will indicate carry-over (i.e., heavier components eluting from previous run).
Lipids are particularly susceptible to oxidation, and particular care needs to be exercised throughout the protocol to protect samples from air and light exposure, such as storing them in the dark and keeping them under nitrogen. All samples and blanks must have sufficient C19:0 surrogate standard. A missing C19:0 peak, in either samples or blanks, indicates a poor recovery or a complete loss of analytes. A response of C19:0 in the samples that is considerably lower than the method/sample blanks indicates a loss of analytes at some point in the PLFA methodology. When faced with poor C19:0 recovery, all aspects of the procedure have to be carefully considered and examined including the initial extraction, all stages of sample transfer, SPE extraction, fatty acid methylation, drying, storage and sample manipulation in order to isolate the stage or stages where analytes are lost. On the other hand, it may be that the extraction of some soil samples may yield C19:0, in which case recovery of the surrogate standard may be overestimated. While using two standards ((PC(19:0/19:0) and MeC10:0) is not an absolute requirement, we have found this to be very useful when needing to troubleshoot. As long as the MeC10:0 response is adequate, troubleshooting can focus on the steps prior to GC analysis.
As previously noted, caution must be used when interpreting ecological significance and ecosystem relationships based solely on biomarkers derived from PLFA data, because pure culture studies reveal that isolated bacterial strains will contain different categories of PLFAs. Instead, biomarker PLFAs should be viewed as a useful addition in a suite of evidence when making broader ecological inferences. In the literature, individual PLFAs have been proposed and utilized as biomarkers for different microbial groups. Saturated PLFAs are typically used to represent gram-positive bacteria and monounsaturated PLFA are used for gram-negative bacteria. Recognized biomarkers for gram-negative bacteria include monounsaturated fatty acids with the unsaturation at the ω5 or ω7 position, such as C16:1ω7, C18:1ω7, and C18:1ω5. In addition, cyclopropyl fatty acids may also be representative of gram-negative bacteria35. Hence, PLFAs from gram-negative bacteria can be calculated as equal to the sum of A:1ω5 + A:1ω7 + A:0cyclo. Recognized biomarkers for gram-positive bacteria are terminally branched saturated fatty acids, iso-branched such as C15:0i, C16:0i, C17:0i; or anteiso-branched, such as C15:0a and C17:0a. Saturated PLFAs with mid-chain (10-methyl) branching, such as 10Me16:0 and 10Me18:0 are characteristically present in actinomycetes36. Thus, PLFAs from gram-positive bacteria can be calculated as equal to the sum of A:0(ISO, ANTEISO, 10-methyl).
Many biomarkers associated with fungal PLFA are often polyunsaturated, but some fungal biomarkers are monounsaturated. For instance, in terms of fungal monounsaturated biomarkers, C16:1ω5 has been identified as an indicator of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF)37, C18:1ω9 is common in saprophytic fungi, and ectomycorrhizae typically contain C16:1ω9. The presence of di-unsaturated C18:2ω6,9 often occurs in conjunction with C18:1ω9 and also correlates well with the fungal sterol ergosterol, which indicates that C18:2ω6,9 can adequately represent ectomycorrhizae and saprophytic fungi38. The tri-unsaturated C18:3ω 6,9,12 has also been used as a biomarker for fungi10; however, C18:3ω6c can be found in other eukaryotic organisms including plants and algae, although it is typically not found in bacteria. In term of soil protists, C20:4ω6c has been recognized as a protist biomarker39, although, other work failed to detect C20:4ω6c even when viable protist populations were confirmed visually using light microscopy40.
Many studies address ecological questions related to the overall soil microbial community by utilizing multivariate ordination techniques as a PLFA data analysis tool. When using this approach, some authors have chosen to exclude rare PLFAs from the dataset by removing PLFAs that are present in less than 5% of the samples4. The normal saturates C16:0 and C18:0 are abundant in all soil microorganisms, including prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Hence, some researchers choose to remove these PLFAs prior to statistical analysis on the basis that they may not be sensitive indicators of the composition of the soil microbial community — although C16:0 and C18:0 are still to be included when summing all PLFAs for an index of microbial biomass. In term of statistical analyses, many researchers choose to conduct a non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination as this technique is well suited to data that may not be normally distributed33. Additional analyses related to categorical variables can include indicator species analysis, which can relate the occurrence of specific PLFAs to categorical groupings and multi response permutation procedures (MRPP), which can help determine similarities or differences among microbial communities assigned to categorical groups. Additionally, multivariate regression trees (MRT) can be particularly useful when the influence of multiple experimental variables or treatments needs to be assessed as potential explanatory variables5 (e.g., soil texture, moisture, reclamation age).
Once established, the PLFA protocol is a relatively simple analytical method that can be very useful when quantifying soil microbial response to environmental changes and anthropogenic disturbance. While molecular techniques such as genetic fingerprinting are better suited to the detailed characterization of microbial communities, the PLFA method presents the advantage of providing quantitative information on total microbial biomass34. In our research laboratory, one person can comfortably process a set of 20 samples over 4 days, and we have found the protocol presented here to be a robust and reproducible technique to assess soil biological quality.
The power of the PLFA method can be greatly extended by coupling it to stable isotope analysis41, 42. Specifically, addition of 13C-labelled substrates to soils allows for the quantification of substrate incorporation into soil microorganisms though isotopic analysis of individual PLFAs41. In addition, this method appears to be a very promising tool to elucidate trophic links in soil food webs42.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada. The authors acknowledge Jela Burkus, Donna Macey, and Jennifer Lloyd for their technical expertise and their contribution to the optimization of this method.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Pierce Reacti-Vap III-evaporator gassing manifold with 27 ports | Used in Steps 1-3 | ||
| Compressed Nitrogen | Praxair | Ni-T | Dangerous: Use only after training and minimize contact and use; Used in Steps 1-3 |
| Disposable centrifuge tube and Teflon-lined cap | Fisher Scientific | 05-569-3 | Used for Step 1 (1 per sample) and Step 2 (1 per sample) |
| Disposable glass long-necked Pasteur pipettes | Fisher Scientific | 13-678-20D | Used for Step 1 (2 per sample) |
| Disposable glass short-necked Pasteur pipettes | Fisher Scientific | 13-678-4 | Used for Step 2 (1 per sample), Step 3 (1 per sample), GC analysis (1 per sample), and one for each type of solution dispensed during PLFA methods (~10 per batch of samples) |
| Elastic band | Grand & Toy | 42199 | 1 per sample for freeze drying |
| Freeze Dryer-Labconco 7806002 and 7753000 | Used for preparing samples for PLFA analysis - use whatever model your lab has | ||
| Freezer (-20 °C, -80 °C) | Revco | ULT2586-5-A36 | Minus 80 °C is used for freezing freshly collected soil samples, -20 °C is used for storing samples at end of each of 3 steps of PLFA analysis |
| Gas chromatograph - Agilent 6890 Series capillary gas chromatograph (GC; Wilmington, DE) equipped with a 50 m Ultra 2 (5%-phenyl)-methylpolysiloxane column | Agilent Technologies | Used for GC analysis, other models of GC could also be used (1 needed) | |
| Analytical column | Agilent Technologies | 19091B-105 | |
| Gas chromatograph insert | Agilent Technologies | 5183-4692 | Used for GC analysis (1 per sample) |
| Gas chromatograph vial and lid | Agilent Technologies | 5188-6592 | Used for GC analysis (1 per sample) |
| Hexanes | Fisher Scientific | H292-4 | Hazardous: use only in fume hood, Read MSDS, minimize use and wear appropriate PPE; Total volume per sample = 4 ml (2.0 ml + 2.0 ml (step 3)) |
| Hot water bath -Isotemp 220 | Fisher Scientific | Used for Step 3 (1 per batch of samples) | |
| Kimwipe | Fisher Scientific | 06-666-2 | Used for freeze drying samples |
| KOH, ACS grade | Fisher Scientific | P250-500 | Hazardous: Use only in fume hood, Read MSDS, minimize use and wear appropriate PPE; Used for making citrate buffer (used in Step 1) and methanolic KOH (step 3) |
| Lab quake end-over-end shaker for centrifuge tubes | Barnstead/Thermolyne | 3,625,485 | Used for Step 1 (1 per batch of samples of appropriate holding capacity) |
| MeC10:0 methyl decanoate internal standard | Sigma-Aldrich | 299030-2.5G | Used for GC analysis |
| Methanol | Fisher Scientific | A454-4 | Hazardous: Use only in fume hood, Read MSDS, minimize use and wear appropriate PPE; Total volume per sample = 15.5 ml (5 ml + 5 ml (step 1) + 5 ml (step 2) + 0.5 ml (step 3)) |
| MIDI Peak Identification Software | MIDI, Inc., Newark, DE | Used for interpreting GC analysis output | |
| MIDI Calibration Standard Mix for Microbial Identification System | Lab Sphere Inc | 1200-A | Used as a Calibration mix for TSBA 40 |
| Nitrile gloves | Fisher Scientific | 27-058-52 | Used always when conducting PLFA lab work |
| pH Meter - Accumet XL200 | Fisher Scientific | Used for making citrate buffer | |
| Pipette (0.2 - 2 ml) - Socorex - Calibra Digital 832 Macropipette | Socorex | 832.02 | Used throughout Steps (1 per sample) |
| 250 µl gastight syringe | Hamilton | 1725 | Used for GC analysis (1 per sample) |
| silver shield gloves | Sigma-Aldrich | Z529575 | For use when handling chloroform |
| solid phase extraction (SPE) column | Agilent Technologies | 5982-2265 | Used for Step 2 (1 per sample) |
| SPE glass column holder with spigots and vacuum apparatus attached | Sigma-Aldrich | Used for Step 2 (1 per batch of samples) | |
| Vortex - Barnstead International Maxi Mix II- M37615 | Barnstead International | M37615 | Used in Steps 1-3 |
| Water - ultra-pure and Chromosolv HPLC grade | Sigma-Aldrich | 270733-4L | Used throughout analysis |
| Whirl-Pak® bags | Fisher Scientific | 01-812-120 | Used in sample collection - 2 bags required per sample collected |
References
- Zelles, L. Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: a review. Biol. Fert. Soils. 29, 111-129 (1999).
- ISO/TS 29843-1: 2010-Soil quality-determination of soil microbial diversity. , ISO/TC. Geneva, Switzerland. Available from: http://www.iso.org/iso/home.htm (2010).
- Swallow, M. J. B., Quideau, S. A. Moisture effects on microbial communities in boreal forest floors are stand-dependent. Appl. Soil Ecol. 63, 120-126 (2012).
- McIntosh, A. C. S., Macdonald, S. E., Quideau, S. A. Linkages between the forest floor microbial community and resource heterogeneity within mature lodgepole pine forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 63, 61-72 (2013).
- Card, S. M., Quideau, S. A. Microbial community structure in restored riparian soils of the Canadian prairie pothole region. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42, 1463-1471 (2010).
- McKinley, V. L., Peacock, A. D., White, D. C. Microbial community PLFA and PHB responses to ecosystem restoration in tallgrass prairie soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 37, 1946-1958 (2005).
- Bossio, D. A., Scow, K. M., Gunapala, N., Graham, K. J. Determinants of soil microbial communities: effects of agricultural management, season, and soil type on phospholipid fatty acid profiles. Microbial Ecol. 36, 1-12 (1998).
- Hannam, K. D., Quideau, S. A., Kishchuk, B. E. Forest floor microbial communities in relation to stand composition and timber harvesting in northern Alberta. Soil Biol. Biochem. 38, 2565-2575 (2006).
- Pettersson, M., Bååth, E. The rate of change of a soil bacterial community after liming as a function of temperature. Microbial Ecol. 46, 177-186 (2003).
- Degrood, S. H., Claassen, V. P., Scow, K. M. Microbial community composition on native and drastically disturbed serpentine soils. Soil Bio.l Biochem. 37, 1427-1435 (2005).
- Quideau, S. A., Swallow, M. J. B., Prescott, C. E., Grayston, S. J., Oh, S. -W. Comparing soil biogeochemical processes in novel and natural boreal forest ecosystems. Biogeosciences. 10, 5651-5661 (2013).
- Hahn, A. S., Quideau, S. A. Long-term effects of organic amendments on the recovery of plant and soil microbial communities following disturbance in the Canadian boreal forest. Plant Soil. 363, 331-334 (2013).
- Swallow, M., Quideau, S. A., MacKenzie, M. D., Kishchuk, B. E. Microbial community structure and function: The effect of silvicultural burning and topographic variability in northern Alberta. Soil Biol. Biochem. 41, 770-777 (2009).
- Pennanen, T. Microbial communities in boreal coniferous forest humus exposed to heavy metals and changes in soil pH-a summary of the use of phospholipid fatty acids. Biolog (R) and H-3-thymidine incorporation methods in field studies. Geoderma. 100, 91-126 (2001).
- Margasin, R., Hämmerle, M., Tscherko, D. Microbial activity and community composition during bioremediation of diesel-oil-contaminated soil: effects of hydrocarbon concentration, fertilizers, and incubation time. Microbial Ecol. 53, 259-269 (2007).
- Štursová, M., Šnajdr, J., Cajthaml, T., Bárta, J., Šantrůčková, H., Baldrian, P. When the forest dies: the response of forest soil fungi to a bark beetle-induced tree dieback. ISME J. 8, 1920-1931 (2014).
- Bligh, E. G., Dyer, W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction. Can. J. Biochem. Phys. 37, 911-917 (1959).
- White, D. C., Davis, W. M., Nickels, J. S., King, J. D., Bobbie, R. J. Determination of the sedimentary microbial biomass by extractible lipid phosphate. Oecologia. 40, 51-62 (1979).
- Tunlid, A., Hoitink, H. A. J., Low, C., White, D. C. Characterization of bacteria that suppress Rhizoctonia damping-off in bark compost media by analysis of fatty acid biomarkers. Appl. Environ. Microb. 55, 1368-1374 (1989).
- Bobbier, J., White, D. C. Characterization of benthic microbial community structure by high resolution gas chromatography of fatty acid methyl esters. Appl. Environ. Microb. 39, 1212-1222 (1980).
- Tunlid, A., et al. Determination of phospholipid ester-linked fatty acids and poly P-hydroxybutyrate for the estimation of bacterial biomass and activity in the rhizosphere of the rape plant Brassica napus (L.). Can. J. Microbiol. 31, 1113-1119 (1985).
- Frostegård, A., Tunlid, A., Bååth, E. Microbial biomass measured as total lipid phosphate in soils of different organic content. J. Microbiol. Meth. 14, 151-163 (1991).
- Frostegård, Å, Bååth, E., Tunlid, A. Shifts in the structure of soil microbial communities in limed forests as revealed by phospholipid fatty acid analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 723-730 (1993).
- Burns, R. G. Soil Biology and Biology Citation Classic X. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 1619-1620 (2011).
- Zelles, L., Bai, Q. Y., Beck, T., Beese, F. Signature fatty acids in phospholipid and lipopolysaccharides as indicators of microbial biomass and community structure in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 317-323 (1992).
- Zelles, L., Bai, Q. Y. Fractionation of fatty acids derived from soil lipids by solid phase extraction and their quantitative analysis by GC-MS. Soil Biol. Biochem. 25, 495-507 (1993).
- White, D. C., Ringelberg, D. B. Signature lipid biomarker analysis. Techniques in Microbial Ecology. Burlage, R. S., Atlas, R., Stahl, D., Geesey, G., Sayler, G. , Oxford University Press. New York. 255-272 (1998).
- Bird, J. A., Herman, D. J., Firestone, M. K. Rhizosphere priming of soil organic matter by bacterial groups in a grassland soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 718-725 (2011).
- Waldrop, M. P., Firestone, M. K. Microbial community utilization of recalcitrant and simple carbon compounds: impact of oak-woodland plant communities. Oecologia. 138, 275-284 (2004).
- Chowdhury, T. R., Dick, R. P. Standardizing methylation method during phospholipid fatty acid analysis to profile soil microbial communities. J. Microbiol. Meth. 88, 285-291 (2012).
- Buyer, J. S., Sasser, M. High throughput phospholipid fatty acid analysis of soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 61, 127-130 (2012).
- Christie, W. W., Han, X. Gas chromatographic analysis of fatty acid derivatives. Lipid analysis, isolation, separation, identification, and lipidomic analysis. , Woodhead Publishing Ltd. Cambridge, UK. 159-180 (2010).
- McCune, B., Grace, J. B. Analysis of ecological communities. , MjM Software Design. Oregon. 300(2002).
- Frostegård, A., Tunlid, A., Bååth, E. Use and misuse of PLFA measurements in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 1621-1625 (2011).
- Högberg, M. N., Högberg, P., Myrold, D. D. Is microbial community composition in boreal forest soils determined by pH, C-to-N ratio, the trees, or all three. Oecologia. 150, 590-601 (2007).
- Brennan, P. Mycobacterium and other actinomycetes. Microbial Lipids. Ratledge, C., Wilkinson, S. , Academic Press. London. 203-298 (1988).
- Olsson, P. A. Signature fatty acids provide tools for determination of the distribution and interactions of mycorrhizal fungi in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 29, 303-310 (1999).
- Frostegård, Å, Bååth, E. The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol. Fert. Soils. 22, 59-65 (1996).
- Myers, R. T., Zak, D. R., White, D. C., Peacock, A. Landscape-level patterns of microbial community composition and substrate use in upland forest ecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 65, 359-367 (2001).
- Swallow, M. J. B., Quideau, S. A., Norris, C. E. Ciliate dependent production of microbial anthranilic acid occurring within aspen litter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 60, 113-121 (2013).
- Norris, C. E., Quideau, S. A., Macey, D. E. Processing of 13C glucose in mineral soil from aspen, spruce, and novel ecosystems in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Appl. Soil Ecol. 71, 24-32 (2013).
- Ruess, L., Chamberlain, P. M. The fat that matters: Soil food web analysis using fatty acids and their carbon stable isotope signature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42, 1898-1910 (2010).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved