A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Human Fetal Blood Flow Quantification with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Motion Compensation
In This Article
Summary
Here we present a protocol for measuring fetal blood flow rapidly with MRI and retrospectively performing motion correction and cardiac gating.
Abstract
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an important tool for the clinical assessment of cardiovascular morphology and heart function. It is also the recognized standard-of-care for blood flow quantification based on phase contrast MRI. While such measurement of blood flow has been possible in adults for decades, methods to extend this capability to fetal blood flow have only recently been developed.
Fetal blood flow quantification in major vessels is important for monitoring fetal pathologies such as congenital heart disease (CHD) and fetal growth restriction (FGR). CHD causes alterations in the cardiac structure and vasculature that change the course of blood in the fetus. In FGR, the path of blood flow is altered through the dilation of shunts such that the oxygenated blood supply to the brain is increased. Blood flow quantification enables assessment of the severity of the fetal pathology, which in turn allows for suitable in utero patient management and planning for postnatal care.
The primary challenges of applying phase contrast MRI to the human fetus include small blood vessel size, high fetal heart rate, potential MRI data corruption due to maternal respiration, unpredictable fetal movements, and lack of conventional cardiac gating methods to synchronize data acquisition. Here, we describe recent technical developments from our lab that have enabled the quantification of fetal blood flow using phase contrast MRI, including advances in accelerated imaging, motion compensation, and cardiac gating.
Introduction
Comprehensive assessment of the fetal circulation is necessary for monitoring fetal pathologies such as fetal growth restriction (FGR) and congenital heart disease (CHD)1,2,3. In utero, patient management and planning for postnatal care depend on the severity of the fetal pathology4,5,6,7. Feasibility of fetal blood flow quantification with MRI and its applications in assessing fetal pathologies have recently been demonstrated3,8,9. The imaging method, however, faces challenges, such as increased imaging times to achieve high spatiotemporal resolution, lack of cardiac synchronization methods, and unpredictable fetal motion10.
Fetal vasculature comprises small structures (~5 mm diameter for major blood vessels that comprise the descending aorta, ductus arteriosus, ascending aorta, main pulmonary artery, and superior vena cava11,12,13).To resolve these structures and to quantify flow, imaging at high spatial resolution is required. Moreover, the fetal heart rate is about twice that of an adult. A high temporal resolution is thus also required to resolve dynamic cardiac motion and blood flow across the fetal cardiac cycle. Conventional imaging at this high spatiotemporal resolution requires relatively long acquisition times. To address this issue, accelerated fetal MRI14,15,16 has been introduced. Briefly, these acceleration techniques involve undersampling in the frequency domain during data acquisition and retrospective high-fidelity reconstruction using iterative techniques. One such approach is compressed sensing (CS) reconstruction, which allows reconstruction of images from heavily undersampled data when the reconstructed image is sparse in a known domain and undersampling artifacts are incoherent17.
Motion in fetal imaging presents a major challenge. Motion corruption can arise from maternal respiratory motion, maternal bulk motion or gross fetal movement. Maternal respiration leads to periodic translations of the fetus, whereas fetal movements are more complex. Fetal movements can be classified as localized or gross10,18. Localized movements involve motion of only segments of the body. They typically last for about 10-14 s and their frequency increases with gestation (~90 per hour at term)10. These movements generally cause small corruptions and do not affect the imaging area of interest. However, gross fetal movements can lead to severe image corruption with through plane motion components. These movements are whole body movements mediated by the spine and last for 60-90 s.
To avoid artifacts from fetal motion, steps are first taken to minimize maternal motions. Pregnant women are made more relaxed using supportive pillows on the scanner bed and dressed in comfortable gowns and may have their partners present beside the scanner to reduce claustrophobia19,20. To mitigate effects of maternal respiratory motion, studies have performed fetal MR exams under maternal breath-hold21,22,23. However, such acquisitions must be short (~15 s) given the reduced breath-hold tolerance of pregnant subjects. Recently, retrospective motion correction methods have been introduced for fetal MRI14,15,16. These methods track fetal motion using registration toolkits and correct for motion or discard uncorrectable portions of acquired data.
Finally, postnatal cardiac MR images are conventionally acquired using electrocardiogram (ECG) gating to synchronize data acquisition to the cardiac cycle. Without gating, cardiac motion and pulsatile flow from throughout the cardiac cycle are combined, producing artifacts. Unfortunately, the fetal ECG signal suffers from interference from the maternal ECG signal24 and distortions from the magnetic field25. Hence, alternative non-invasive approaches to fetal cardiac gating have been proposed, including self-gating, metric optimized gating (MOG) and doppler ultrasound gating21,26,27,28.
As described in the following sections, our MRI approach to quantify fetal blood flow leverages a novel gating method, MOG, developed in our laboratory and combined with motion correction and iterative reconstruction of accelerated MRI acquisitions. The approach is based on a pipeline in a previously published study14 and is composed of the following five stages: (1) fetal blood flow acquisition, (2) real-time reconstructions, (3) motion correction, (4) cardiac gating, and (5) gated reconstructions.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
All MRI scans were performed with informed consent from volunteers as part of a study approved by our institutional research ethics board.
NOTE: The methods described below have been used on a 3T MRI system. The acquisition is performed using a radial phase contrast MRI sequence. This sequence was prepared by modifying the readout trajectory (to achieve a stellate pattern) of the manufacturer's Cartesian phase contrast MRI. The sequence and sample protocols are available upon request through our C2P exchange platform. All reconstructions in this work were performed on a standard desktop computer with the following specifications: 32 GB memory, 3.40 GHz processor with 8 cores, and 2GB graphic card with 1024 compute unified device architecture (CUDA) cores. Image reconstruction was performed on MATLAB. Nonuniform fast Fourier transform (NUFFT)29 was performed on the graphics processing unit (GPU). Motion correction parameters were calculated using elastix30. Figure 1 depicts the protocol in a chronological order, tracking how the acquired velocity encodes (color coded in Figure 1) are processed with representative images at each stage of reconstruction. The reconstruction code is available at https://github.com/datta-g/Fetal_PC_MRI. While we provide the steps in the protocol here, most of these algorithm steps are automated in our pipeline.
1. Subject positioning and localizer exams
- Assist the mother in positioning herself on the MRI table in her preferred comfortable position, usually supine or lateral decubitus positions, for the MRI exam.
- Place the cardiac coil over the abdominal region of the mother.
- Load the MRI table in the magnet bore and notify the mother that the scan is about to start.
- Run a localizer exam to locate the fetal body (resolution: 0.9 x 0.9 x 10 mm3, TE/TR: 5.0/15.0 ms, FOV: 450 x 450 mm2, slices: 6).
- Run a refined localizer exam to locate the fetal vasculature with the slice group centered on the fetal heart (resolution 1.1 x 1.1 x 6.0 mm3, TE/TR: 2.69/1335.4 ms, FOV: 350 x 350 mm2, slices: 10, orientation: axial to fetus).
- Repeat the refined localizers with sagittal and coronal orientations for a clearer view of the fetal vessels.
- Repeat the refined localizers in cases of gross fetal motion.
2. Acquisition of fetal blood flow data
- Locate fetal vessels using the localizer exams. For example, the descending aorta is a long straight vessel near the spine in the sagittal planes. The ascending aorta and main pulmonary arteries can be identified as vessels leaving the left and right ventricles, respectively. The ductus arteriosus can be tracked as a downstream segment of the main pulmonary artery proximal to the descending aorta. The superior vena cava can be identified from axial planes near the base of the fetal heart as the vessel adjacent to the ascending aorta.
- Prescribe a slice perpendicular to the axis of the fetal vessel of interest. Rotate and move the slice guideline on the MRI console computer such that it intersects the target vessel perpendicularly.
- Set the scan parameters (acquisition type: radial phase contrast MRI, resolution: 1.3 x 1.3 x 5.0 mm3, echo time (TE)/ repetition time (TR): 3.25/5.75 ms, field-of-view (FOV): 240 x 240 mm2, slice: 1, velocity encoding: 100-150 cm/s depending on vessel of interest, velocity encoding direction: through plane, radial views: 1500 per encode, free breathing).
- Run the scan and verify the prescription based on the initial time-averaged reconstruction performed and displayed on the MRI console computer. Repeat the localizer and phase contrast scans if the target vessel is absent or unidentifiable from the initial reconstruction. Acquired raw data is represented in the schematic in Figure 1A with the velocity compensated and through plane acquisitions color coded as red and blue, respectively.
- Repeat the fetal blood flow data acquisition for each target blood vessel.
NOTE: The acquired raw data (format: DAT files) must be transferred for offline reconstruction. For example, on Siemens scanners, this can be performed by running 'twix'. The acquired raw data is right clicked from the list acquisitions and "copy total raid file" is chosen.
3. Motion correction of fetal measurements
- Reconstruct real-time series (temporal resolution: 370 ms, radial views: 64) from the acquired data using CS with 15 iterations of a conjugate gradient descent optimization exploiting spatial total variation (STV, weight: 0.008) and temporal total variation (TTV, weight: 0.08) regularization as represented by the schematic in Figure 1B.
- Select a region of interest (ROI) encompassing the vessel of interest from this first real-time reconstruction using a graphic user interface developed in MATLAB. In this step, the user must draw a contour that encloses the fetal anatomy, such as the target great vessels or the fetal heart.
- Perform rigid-body motion tracking with elastix30 (based on normalized mutual information with empirically optimized parameters: 4 pyramid levels, 300 iterations and translational transforms).
- Reject tracked real-time frames that share low mutual information (MI) with all other frames (whereby MI is less than 1.5x the interquartile range from the mean MI). These frames are deemed to be represented through plane motion or gross fetal motion.
- Use the MRI data corresponding to the longest series of continuous real-time frames (without gaps) from the remaining frames as the quiescent period used for further reconstruction.
- Interpolate translational motion correction parameters from the temporal resolution of the real-time series (370 ms) to the TR of the quiescent acquisition (5.75 ms).
- Apply interpolated parameters to the defined quiescent period of the MRI data by modulating the phase as in:
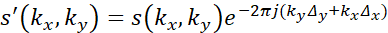
where s' is the motion corrected data, kx and ky are the coordinates in k-space, s is the acquired uncorrected data, Δx and Δy are the tracked displacements in space, and j represents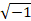 .
.
NOTE: All numerical values of regularization coefficients in this work were optimized in earlier experiments. This was accomplished using a brute-force grid search to find the regularization coefficients that minimized the error between reconstructions of a highly sampled fetal reference dataset and retrospectively undersampled cases from the same dataset.
4. Solving for fetal heart rate
- Reconstruct a second real-time image series at a higher temporal resolution (temporal resolution: 46 ms, radial views: 8) using the acquired data using CS, again with 15 iterations of a conjugate gradient descent optimization with STV (weight: 0.008) and TTV (weight: 0.08) regularization as represented by the schematic in Figure 1C.
- Re-select an ROI encompassing the fetal vessel of interest.
- Run multiparameter MOG on the real-time series to derive the time-dependent fetal heart rate.
- Bin motion corrected MRI data into 15 cardiac phases using the derived heart rate waveform. In this step, the temporal boundaries of the cardiac phases are computed using the heart rate from the previous step. For instance, the boundaries for the ith phase in the kth heartbeat are given by:
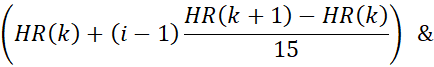
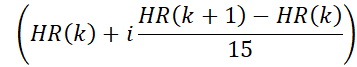
where HR(K) is the time at which the kth heartbeat occurs. The timestamp of the nth radial acquisition is given by (n x TR). Data with timestamps falling within the boundaries of a cardiac phase are assigned to that phase.
NOTE: MOG is a gating technique26 that comprises iterative binning of the acquired data based on a multi-parameter fetal heart rate model to create CINE images that optimize an image metric over a region of interest.
5. Reconstruction of fetal CINEs
- Reconstruct fetal flow CINEs using the binned motion corrected MRI data and CS with 10 iterations of a conjugate gradient descent optimization with STV (weight: 0.025) and TTV (weight: 0.01) regularization. Two CINEs are produced at this step: one for the flow compensated acquisition, CFC, and one with the flow encoded data, CFE, as represented in the schematic in Figure 1D.
- Compute the velocity image given by the phase of the elementwise product of CFE and the complex conjugate of CFC.
- Apply background phase correction31 to correct for eddy current effects. Briefly, in this automatic step, a plane is fitted to the phase of static fetal and maternal tissues. The correction is performed by subtracting the plane from the velocity sensitive phase computed in 4.2.
- Write reconstructed data into DICOM files.
- Load DICOMs into flow analysis software, such as Segment v2.232.
- Draw an ROI encompassing the lumen of the blood vessel of interest using the anatomical and velocity sensitive images.
- Propagate the ROI to all cardiac phases and correct for changes in the vessel's diameter.
- Record flow measurements.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
In general, phase MRI examinations of flow target six major fetal vessels: the descending aorta, ascending aorta, main pulmonary artery, ductus arteriosus, superior vena cava, and umbilical vein. These vessels are of interest to the clinician as they are often implicated in CHD and FGR, influencing the distribution of blood throughout the fetus9. A typical scan duration with the radial phase contrast MRI is 17 s per vessel such that the scans are short while also allowing time for enough data acqu...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
This method enables the non-invasive measurement of blood flow in human fetal great vessels and allows for retrospective motion correction and cardiac gating by making use of iterative reconstruction techniques. Fetal blood flow quantification has been performed with MRI in the past1,3,8,9. These studies had a prospective approach to mitigate motion corruption w...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
None.
Acknowledgements
None.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| elastix | Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht | Image registration software | |
| Geforce GTX 960 | Nvidia | 04G-P4-3967-KR | |
| gpuNUFFT | CAI²R | Non-uniform fast Fourier transform | |
| MAGNETOM Prisma | Siemens | 10849583 | |
| MATLAB | MathWorks | ||
| Radial Phase Contrast MRI sequence | Trajectory modification of manufacturer's Cartesian Phase Contrast sequence | ||
| Segment | Medvisio | Data analysis | |
| VENGEANCE | Corsair | LPX DDR4-2666 |
References
- Zhu, M. Y., et al. The hemodynamics of late-onset intrauterine growth restriction by MRI. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 214 (3), 1-17 (2016).
- Zhu, M. Y., Jaeggi, E., Roy, C. W., Macgowan, C. K., Seed, M. Reduced combined ventricular output and increased oxygen extraction fraction in a fetus with complete heart block demonstrated by MRI. HeartRhythm Case Reports. 2 (2), 164-168 (2016).
- Sun, L., et al. Reduced Fetal Cerebral Oxygen Consumption is Associated With Smaller Brain Size in Fetuses With Congenital Heart Disease. Circulation. 131 (15), 1313-1323 (2015).
- Freud, L. R., et al. Fetal aortic valvuloplasty for evolving hypoplastic left heart syndrome: postnatal outcomes of the first 100 patients. Circulation. 130 (8), 638-645 (2014).
- Peleg, D., Kennedy, C. M., Hunter, S. K. Intrauterine growth restriction: identification and management. American Family Physician. 58 (2), 453-467 (1998).
- Krishna, U., Bhalerao, S. Placental Insufficiency and Fetal Growth Restriction. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of India. 61 (5), 505-511 (2011).
- Seravalli, V., Miller, J. L., Block-Abraham, D., Baschat, A. A. Ductus venosus Doppler in the assessment of fetal cardiovascular health: an updated practical approach. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 95 (6), 635-644 (2016).
- Seed, M., et al. Feasibility of quantification of the distribution of blood flow in the normal human fetal circulation using CMR: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 14 (1), 79(2012).
- Prsa, M., et al. Reference ranges of blood flow in the major vessels of the normal human fetal circulation at term by phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation. Cardiovascular Imaging. 7 (4), 663-670 (2014).
- Piontelli, A. Development of Normal Fetal Movements: The Last 15 Weeks of Gestation. , Springer-Verlag. Mailand. (2015).
- Cartier, M., et al. The normal diameter of the fetal aorta and pulmonary artery: echocardiographic evaluation in utero. American Journal of Roentgenology. 149 (5), 1003-1007 (1987).
- Ruano, R., de Fátima Yukie Maeda, M., Niigaki, J. I., Zugaib, M. Pulmonary artery diameters in healthy fetuses from 19 to 40 weeks' gestation. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 26 (3), 309-316 (2007).
- Nowak, D., Kozłowska, H., Żurada, A., Gielecki, J. Diameter of the ductus arteriosus as a predictor of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). Central European Journal of Medicine. 6 (4), 418-424 (2011).
- Goolaub, D. S., et al. Multidimensional fetal flow imaging with cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a feasibility study. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 20 (1), 77(2018).
- Roy, C. W., Seed, M., Kingdom, J. C., Macgowan, C. K. Motion compensated cine CMR of the fetal heart using radial undersampling and compressed sensing. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 19 (1), 29(2017).
- van Amerom, J. F. P., et al. Fetal cardiac cine imaging using highly accelerated dynamic MRI with retrospective motion correction and outlier rejection. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 79 (1), 327-338 (2018).
- Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J. M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 58 (6), 1182-1195 (2007).
- Edwards, D. D., Edwards, J. S. Fetal movement: development and time course. Science. 169 (3940), New York, N.Y. 95-97 (1970).
- Malamateniou, C., et al. Motion-Compensation Techniques in Neonatal and Fetal MR Imaging. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 34 (6), 1124-1136 (2013).
- Rutherford, M., et al. MR imaging methods for assessing fetal brain development. Developmental Neurobiology. 68 (6), 700-711 (2008).
- Haris, K., et al. Self-gated fetal cardiac MRI with tiny golden angle iGRASP: A feasibility study: Self-Gated Fetal Cardiac MRI with iGRASP. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 46 (1), 207-217 (2017).
- Glenn, O. A. MR imaging of the fetal brain. Pediatric Radiology. 40 (1), 68-81 (2010).
- Rodríguez-Soto, A. E., et al. MRI Quantification of Human Fetal O2 Delivery Rate in the Second and Third Trimesters of Pregnancy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 80 (3), 1148-1157 (2018).
- Sameni, R., Clifford, G. D. A Review of Fetal ECG Signal Processing; Issues and Promising Directions. The Open Pacing, Electrophysiology & Therapy Journal. 3, 4-20 (2010).
- Millis, R. Advances in Electrocardiograms: Methods and Analysis. BoD - Books on Demand. , (2012).
- Jansz, M. S., et al. Metric optimized gating for fetal cardiac MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 64 (5), 1304-1314 (2010).
- Yamamura, J., et al. Cardiac MRI of the fetal heart using a novel triggering method: initial results in an animal model. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: JMRI. 35 (5), 1071-1076 (2012).
- Larson, A. C., et al. Self-gated cardiac cine MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 51 (1), 93-102 (2004).
- Knoll, F., Schwarzl, A., Diwoky, C., Sodickson, D. K. gpuNUFFT-An open source GPU library for 3D regridding with direct Matlab interface. Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Meeting of ISMRM. , (2014).
- Klein, S., Staring, M., Murphy, K., Viergever, M. A., Pluim, J. P. W. elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 29 (1), 196-205 (2010).
- Walker, P. G., et al. Semiautomated method for noise reduction and background phase error correction in MR phase velocity data. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. 3 (3), 521-530 (1993).
- Heiberg, E., et al. Design and validation of Segment - freely available software for cardiovascular image analysis. BMC Medical Imaging. 10 (1), 1(2010).
- Inder, T. E., Volpe, J. J. Chapter 17 - Intrauterine, Intrapartum Assessments in the Term Infant. Volpe's Neurology of the Newborn (Sixth Edition). , 458-483 (2018).
- Pelc, N. J., Herfkens, R. J., Shimakawa, A., Enzmann, D. R. Phase contrast cine magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance Quarterly. 7 (4), 229-254 (1991).
- Steeden, J. A., Atkinson, D., Hansen, M. S., Taylor, A. M., Muthurangu, V. Rapid flow assessment of congenital heart disease with high-spatiotemporal-resolution gated spiral phase-contrast MR imaging. Radiology. 260 (1), 79-87 (2011).
- Kowalik, G. T., Knight, D., Steeden, J. A., Muthurangu, V. Perturbed spiral real-time phase-contrast MR with compressive sensing reconstruction for assessment of flow in children. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 83 (6), 2077-2091 (2020).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved