A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Sample Preparation and Relative Quantitation using Reductive Methylation of Amines for Peptidomics Studies
In This Article
Summary
This article describes a sample preparation method based on heat-inactivation to preserve endogenous peptides avoiding degradation post-mortem, followed by relative quantitation using isotopic labeling plus LC-MS.
Abstract
Peptidomics can be defined as the qualitative and quantitative analysis of peptides in a biological sample. Its main applications include identifying the peptide biomarkers of disease or environmental stress, identifying neuropeptides, hormones, and bioactive intracellular peptides, discovering antimicrobial and nutraceutical peptides from protein hydrolysates, and can be used in studies to understand the proteolytic processes. The recent advance in sample preparation, separation methods, mass spectrometry techniques, and computational tools related to protein sequencing has contributed to the increase of the identified peptides number and peptidomes characterized. Peptidomic studies frequently analyze peptides that are naturally generated in cells. Here, a sample preparation protocol based on heat-inactivation is described, which eliminates protease activity, and extraction with mild conditions, so there is no peptide bonds cleavage. In addition, the relative quantitation of peptides using stable isotope labeling by reductive methylation of amines is also shown. This labeling method has some advantages as the reagents are commercially available, inexpensive compared to others, chemically stable, and allows the analysis of up to five samples in a single LC-MS run.
Introduction
"Omics" sciences are characterized by the deep analysis of a molecule set, such as DNA, RNA, proteins, peptides, metabolites, etc. These generated large-scale datasets (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, peptidomics, metabolomics, etc.) have revolutionized biology and led to an advanced understanding of biological processes1. The term peptidomics began to be introduced in the early 20th century, and some authors have referred to it as a branch of proteomics2. However, peptidomics has distinct particularities, where the main interest is to investigate the naturally generated peptides content during cellular processes, as well as the characterization of biological activity of these molecules3,4.
Initially, bioactive peptide studies were restricted to the neuropeptides and hormone peptides through Edman degradation and radioimmunoassay. However, these techniques do not allow a global analysis, depending on the isolation of each peptide in high concentrations, time for the generation of antibodies, besides cross-reactivity possibility5.
Peptidomics analysis was only made possible after several advances in Liquid chromatography coupled mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and genome projects that delivered comprehensive data pools for proteomics/peptidomics studies6,7. Moreover, a specific peptide extraction protocol for peptidomes needed to be established because the first studies that analyzed neuropeptides globally in brain samples showed that detection was affected by the massive degradation of proteins, which occur mainly in this tissue after 1 min post-mortem. The presence of these peptide fragments masked the neuropeptide signal and did not represent the peptidome in vivo. This problem was solved mainly with the application of fast heating inactivation of proteases using microwave irradiation, which drastically reduced the presence of these artifact fragments and allowed not only the identification of neuropeptide fragments but revealed the presence of a set of peptides from cytosolic, mitochondrial, and nuclear proteins, different of degradome6,8,9.
These methodological procedures allowed an expansion of the peptidome beyond the well-known neuropeptides, where hundreds of intracellular peptides generated mainly by the action of proteasomes have been identified in yeast10, zebrafish11, rodent tissues12, and human cells13. Dozens of these intracellular peptides have been extensively shown to have both biological and pharmacological activities14,15. Furthermore, these peptides can be used as disease biomarkers and possibly have clinical significance, as demonstrated in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with intracranial saccular aneurysms16.
Currently, in addition to the identification of peptide sequences, it is possible through mass spectrometry to obtain data of absolute and relative quantitation. In the absolute quantitation, the peptide levels in a biological sample are compared to synthetic standards, while in the relative quantitation, the peptide levels are compared among two or more samples17. Relative quantitation can be performed using the following approaches: 1) "label free"18; 2) in vivo metabolic labeling or 3) chemical labeling. The last two are based on the use of stable isotopic forms incorporated into peptides19,20. In label-free analysis, the peptide levels are estimated by considering the signal strength (spectral counts) during the LC-MS18. However, isotopic labeling can obtain more accurate relative levels of peptides.
Many peptidomic studies used trimethylammonium butyrate (TMAB) labeling reagents as chemical labeling, and more recently, Reductive Methylation of Amines (RMA) with deuterated and non-deuterated forms of formaldehyde and sodium cyanoborohydride reagents have been used11,21,22. However, the TMAB labels are not commercially available, and the synthesis process is very laborious. On the other hand, in the RMA, the reagents are commercially available, inexpensive compared to other labels, the procedure is simple to perform, and the labeled peptides are stable23,24.
The use of RMA involves forming a Schiff base by allowing the peptides to react with formaldehyde, followed by a reduction reaction through the cyanoborohydride. This reaction causes dimethylation of free amino groups on N-terminals and lysine side chains and monomethylates N-terminal prolines. How proline residues are often rare on the N-terminal, practically all peptides with free amines on the N-terminus are labeled with two methyl groups23,24,25.
Protocol
The following procedure for peptide extraction and reductive methylation was adapted from previously published procedures24,25,26,27. This protocol followed the guidelines of the National Council for Animal Experimentation Control (CONCEA) and was approved by the Ethics Commission for Animal Use (CEUA) at Bioscience Institute of Sao Paulo State University. The protocol steps are shown in Figure 1.
NOTE: Prepare all aqueous solutions in ultrapure water.
1. Peptide extraction
- Cell culture
- Cultivate SHSY5Y cells in a 15 cm dish at 37 °C under 5% CO2 in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium containing 15% fetal bovine serum and 1% Penicillin-Streptomycin.
- Use 2-3 plates for each sample. Grow the cells to 100% confluence.
- After treatment intended, wash the cells twice with phosphate-buffered saline. Next, add 10 mL of Phosphate-buffered saline, scrape the cells and collect into a 15 mL tube.
- Centrifugate at 800 x g for 5 min and remove the supernatant. Resuspend the pellet in 1 mL of ultra-purified deionized water at 80 °C.
- Transfer the contents of the tube (cellular lysate) to a 2 mL microfuge tube.
- Animal tissues (mainly nervous tissue):
- Anesthetize wild-type male adult Danio rerio (zebrafish) with a lethal dose of MS 222 (100 mg/L) and immediately subject it to 8 s of microwave radiation to inactivate peptidase and protease.
NOTE: A household-type microwave oven can be used. A 900 W microwave was used for 8 to 10 s at full power. The microwave used must be able to raise the brain temperature to > 80 °C within 10 s. Reproducibility in heating between samples would also be benefited by placing the tissue in the same location in the microwave. - After heat-inactivation, collect the whole brain in a 2 mL microfuge tube and freeze at −80 °C until analysis.
- Resuspend the tissue sample in 1 mL of ultra-purified deionized water at 80 °C. Sonicate the tissue with a probe using 30 pulses (4 Hz) of 1 s.
NOTES: For liver and kidney tissues, use a mechanical homogenizer at 10,000-30,000 rpm for 20 s. For muscular tissues, grind the tissue in liquid nitrogen using a porcelain crucible and pestle. The following steps are the same for the cellular lysate or the homogenate tissue.
- Anesthetize wild-type male adult Danio rerio (zebrafish) with a lethal dose of MS 222 (100 mg/L) and immediately subject it to 8 s of microwave radiation to inactivate peptidase and protease.
- Incubate the cellular lysate or homogenate tissue at 80 °C for 20 min. Next, cool it on ice for 10-30 min.
- Add 10 µL of 1 M HCl stock solution for each 1 mL of sample volume to obtain a final concentration of 10 mM. Mix by vortexing for 20 s and further incubate on ice for 15 min.
NOTE: Before acidifying, ensure the sample is completely cooled to avoid breaking the peptide bonds caused by acidification at elevated temperatures. - Centrifuge the cellular lysate or the homogenate tissue at 12,000 x g at 4 °C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant in low binding protein microcentrifuge tubes and store it at -80 °C.
- Clean the ultrafiltration devices (10 kDa cut-off filters) by adding water and centrifuge at 2300 x g for 3 min. Repeat this step two more times.
- Place the supernatant in the pre-washed 10 kDa cut-off filters and centrifuge at 2,300 x g at 4 °C for 50 min in a refridgerated centrifuge. The flow-through represents the peptide extract.
- Desalt the samples on reversed-phase cleanup columns according to the manufacturer's instructions using acetonitrile (ACN) and trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) solutions as described below:
- Equilibrate the column with 1 mL of 100% ACN.
- Wash the column with 1 mL solution of 5% ACN with 0.1% TFA.
- Load the complete volume of the sample in the column.
- Wash the column with 1 mL solution of 5% ACN with 0.1% TFA
- Elute the peptides from the column with a 1.8 mL solution of 100% ACN with 0.15% TFA in protein low binding microcentrifuge tubes.
- Dry the sample completely in a vacuum centrifuge. Set the concentration method for organic solvents and temperature at 30 °C. The concentration time is monitored on display.
- Store the samples at −80°C until the next step.
2. Peptide quantification with fluorescamine
NOTE: The amount of peptide can be estimated using fluorescamine at pH 6.8 as previously described11,28. This method consists of the attachment of a fluorescamine molecule to the primary amines present in the lysine (K) residues and/or the N-terminal of peptides. The reaction is performed at pH 6.8 to guarantee that the fluorescamine reacts only with the amino groups of the peptides and not with free amino acids. The fluorescamine is measured by using a spectrofluorometer at an excitation wavelength of 370 nm and an emission wavelength of 480 nm.
- Prepare different concentrations of the standard peptide (0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5 and 0.7 µg/µL) and store the aliquots at -20 °C.
NOTE: The peptide 5A (LTLRTKL) is suggested since it has a known composition and concentration. - Prepare fluorescamine stock solution (0.3 mg/mL) in acetone. Aliquot quickly in microcentrifuge tubes (1 mL), seal using parafilm, and store at -20 °C in the dark.
- Prepare 0.2 M Phosphate buffer (PB) at pH 6.8.
NOTE: Prepare 0.2 M PB by adding 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 6.8 (26.85 mL of Na2HPO3 1M) and 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 6.8 (23.15 mL of NaH2PO3 1M) to 250 mL of water - Resuspend the peptide samples in 100-200 µL of ultra-purified water.
- Pipette 2.5 µL of the standard peptide concentrations and samples onto the white 96-well plate for fluorescence assays in triplicate. Add 25 µL of 0.2 M Phosphate buffer.
- Add 12.5 µL of fluorescamine with a multichannel pipette. Homogenize gently for 1 min on the orbital rotator shaker.
- Next, add 110 µL of water with a multichannel pipette to stop the reaction.
NOTE: Transfer the fluorescamine stock solution and ultrapure water to two reservoirs to pipette these solutions with a multichannel pipette. - Adjust the following reading parameters on the spectrofluorometer: Read the samples from the top, excitation wavelength at 370 nm, and emission wavelength at 480 nm.
- Read the plate on the spectrofluorometer.
3. Reductive methylation of amines labeling
NOTE: This isotopic labeling method is based on the dimethylation of amine groups with deuterated and non-deuterated forms of formaldehyde and sodium cyanoborohydride reagents. The final product of this reaction adds 28 Da, 30 Da, 32 Da, 34 Da, or 36 Da to the final mass of each peptide at each available labeling site (lysine or N-terminal). This reaction produces an m/z difference in the peptides labeled with different forms observed in the MS spectrum (Table 1).
CAUTION: Proper safety equipment should be used to handle these compounds, and care should be taken to minimize exposure. Procedures with formaldehyde and sodium cyanoborohydride reagents should be performed in a fume hood because they are very toxic (including weighing the sodium cyanoborohydride). During the quenching reaction and acidification, a toxic gas (hydrogen cyanide) may be generated.
- Prepare the following fresh solutions from the stock or reagents on the day of the procedure in ultrapure water:
- Dilute the stock of 37% Formaldehyde (CH2O) to 4%.
- Dilute the stock of 20% Formaldehyde Deuterated (CD2O) to 4%.
- Dilute the stock of 20 % Deuterated C13 Formaldehyde (13CD2O) to 4%.
- Prepare 0.6 M NaBH3CN.
- Prepare 0.6 M NaBD3CN.
- Prepare a solution of 1% Ammonium bicarbonate.
- Prepare a solution 5% Formic acid.
NOTE: Regarding the relative quantitation of peptides, as different experimental schemes can be performed depending on the number of labels used, attention is necessary during the chemical labeling procedure. It is recommended to separate small aliquots of the labels in separate racks with the respective samples to be labeled to reduce the potential for human error in adding the wrong reagent to the sample tubes.
- Prepare each sample containing up to 25 µg of the peptide. Samples must not contain Tris or Ammonium Bicarbonate.
NOTE: The quantities described below are sufficient for each sample in a volume of 100 µL.
Proceed with steps 3.3-3.8 in a fume hood. - Add 1/10th volume of 1 M TEAB to the samples (final concentration of the solution 100 mM of TEAB). Check the pH with a pH indicator paper; it must be between 5-8. Adjust with HCl or NaOH if needed.
- Add 4 µL of non-deuterated, deuterated Formaldehyde or C13 deuterated Formaldehyde according to the established labeling scheme. Mix for 5 s by vortexing.
- Add 4 µL of NaBH3CN (0.6 M) or NaBD3CN (0.6 M) according to the established labeling scheme. Mix for 5 s by vortexing.
- Incubate in a fume hood for 2 h at room temperature, mixing every 30 min.
- Repeat steps 3.4 and 3.5. Incubate the samples in a fume hood overnight at room temperature.
- Add 16 µL of Ammonium bicarbonate (1%) and mix by vortexing. Place the sample on ice, add 8 µL of formic acid (5%), and mix by vortex for 5 s.
- Combine the samples, adjust the pH to 2-4 and desalt the combined samples on reversed-phase cleanup columns as previously described in step 1.8.
- Dry the sample completely in a vacuum centrifuge. Set the concentration method for organic solvents and temperature at 30 °C. The concentration time is monitored on display.
- Store the samples at -20 °C.
4. Liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry
- Perform LC-MS analysis using a nanoHPLC system coupled to a MS instrument compatible with methyl tags.
NOTE: A variety of MS instruments are compatible with RMA labeling.A nanoHPLC system coupled to Orbitrap is typically used to perform LC-MS analysis through a nanoelectrospray ion source. First, the sample is loaded into a precolumn and peptides separated in an analytical column. The elution of peptides is performed using a linear gradient of 5%-45% acetonitrile, in 0.1% formic acid, during 90 min, with a flow of 200 nL/min. The mass spectrometer is set to function in data-dependent mode. Each full scan is acquired at an intensity of 10-30 eV, 2.3 Kv, and then the ten highest peaks are selected for collision-induced dissociation (CID) fragmentation. The injection time is set on the ion trap at 100 ms, and the Fourier Transform (FT)-MS injection is fixed with a resolution of 1000 ms 30,000 at m/z 300-1800. A minimum of 5000 counts and a dynamic exclusion of 70 s is used to perform fragmentation scanning.
5. Relative quantitation of peptides
NOTE: The MS spectra are analyzed in the mass spectrometer software. Peak groups of labeled peptides with different tags are identified in the MS spectra. The relative quantitation is calculated by the intensity of each monoisotopic peak. Each treated group is compared to the respective control group.
- Right double-click on the raw sample file to open the spectrum analysis software. Load the Retention time (RT) and MS spectrum (EM) chromatograms in two tabs, top and bottom, respectively.
- Right-click once sequentially on the Display and Mass options icons in the software toolbar and set the mass precision to four decimals.
- Position the mouse cursor anywhere on the RT tab. Look for the retention time of the corresponding ion to be analyzed and click the right mouse button. The MS spectrum of the selected time will automatically be shown in the EM tab.
- Position the mouse cursor anywhere on the EM tab. Look for the ions to be analyzed.
- Right-click and hold in an adjacent region to the left near these ions. Then, drag the mouse to the right at the desired range to zoom the region of interest.
- Keep the mouse positioned on the EM tab and click on the right or left keyboard arrows to define the range of ions to be analyzed.
- Position the mouse cursor the RT tab again at the beginning of the desired time interval.
- Right-click and drag the mouse until the chosen time value. Leave the button. The accumulated intensity of the ions will automatically be shown on the EM tab.
- Collect the m/z, z, and ion intensity data on a spreadsheet.
NOTE: The monoisotopic mass of each peptide without added methyl groups is calculated from the following formula:
Mass unmodified peptide = (m/z a x z) - (C a x T) - (1.008 x z)
m/za is the observed mass to charge value for the monoisotopic peak for each peptide labeled with different combinations of tags (a =1, 2, 3, 4 or 5, corresponding to the sample number).
z is charge state.
Ca is the monoisotopic mass of a pair of methyl groups:
For a=1, Ca = 28.0313 (the net addition of two CH3 groups to the primary amine)
For a=2, Ca = 30.0439 for two CHD2 groups
For a=3, Ca = 32.0564 for two CD2H groups
For a=4, Ca= 34.0690 for two CD3 groups
For a=5, Ca = 36.0757 for two 13 CD3 groups
T is the number of pairs of methyl groups incorporated into the peptide. This can be calculated from the following formula when five tags are used: T=z*(m/z5 - m/z1)/8. For peptides that contain a single primary amine and therefore are labeled with only two methyl groups present peak overlaps on the MS spectra when adjacent labels are used. The peak intensity of each labeled peptide can be corrected using the equations described by Tashima and Fricker25.
6. Peptide Identification
- To identify peptides, analyze the MS/MS data using a database search engine29,30.
- To calculate the false discovery rate (FDR) using the decoy fusion method, search a decoy database.
NOTE: The search parameters generally used are no enzyme specificity; precursor mass tolerance set 15-50 ppm; fragment ion mass tolerance of 0.5 Da; variable modifications: reactive amines from Lys residues and N-terminus of the peptides isotopic methylated labels (L1 (+28), L2 (+30), L3 (+32), L4 (+34) and L5 (+36)), oxidized methionine (+15.99 Da) and acetylation (+42.01 Da). - Then, sort the peptides by their average of local confidence to select the best spectra to annotate and filter them by FDR ≤5%.
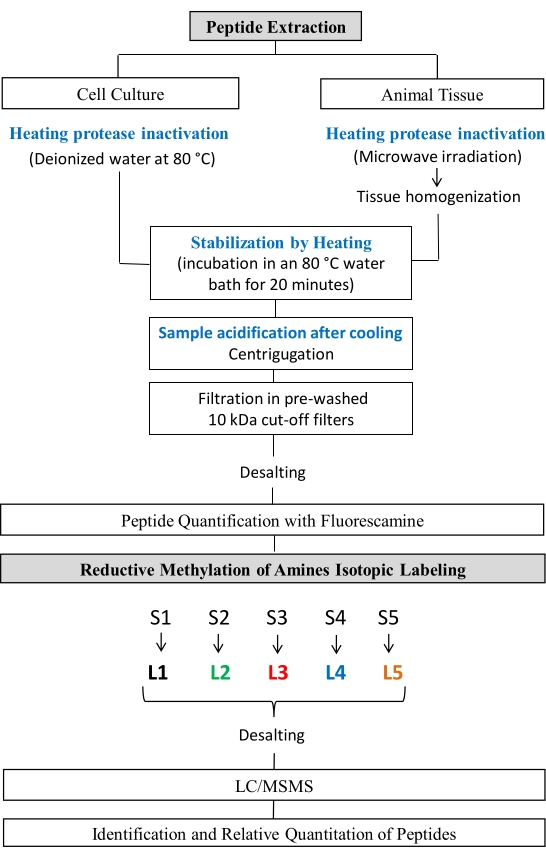
Figure 1: Peptidomic studies workflow. Steps of peptide extraction and Reductive Methylation of amines. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
The results obtained from the runs carried out on the mass spectrometer are stored in raw data files that can be opened in the mass spectrometer software. In the MS spectra, it is possible to observe peak groups representing labeled peptides according to the labeling scheme used, ranging from 2-5 labels. For example, in Figure 2, pairs of peaks detected in a chromatographic time are represented in an experiment where only two isotopic labels were used in two different samples in the same run...
Discussion
In most peptidomics studies, one of the critical steps is, without doubt, the sample preparation that should be carefully performed to avoid the presence of peptide fragments generated by proteases after a few minutes post-mortem. The initial studies on brain extracts prepared from non-microwaved samples showed a large number of protein fragments to be present in the 10-kDa microfiltrates. Different approaches have been described to avoid peptide spectra from protein degradation: focused microwave irradiation animal sacr...
Disclosures
No competing financial interests exist.
Acknowledgements
The development and use of the techniques described here were supported by the Brazilian National Research Council grant 420811/2018-4 (LMC); Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (www.fapesp.br) grants 2019/16023-6 (LMC), 2019/17433-3 (LOF) and 21/01286-1 (MEME). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the article.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 10 kDa cut-off filters | Merck Millipore | UFC801024 | Amicon Ultra-4, PLGC Ultracel-PL Membrane, 10 kDa |
| Acetone | Sigma-Aldrich | 179124 | |
| Acetonitrile | Sigma-Aldrich | 1000291000 | |
| Ammonium bicarbonate | Sigma-Aldrich | 11213 | |
| analytical column (EASY-Column) | EASY-Column | (SC200) | 10 cm, ID75 µm, 3 µm, C18-A2 |
| Ethyl 3-aminobenzoate methanesulfonate | Sigma-Aldrich | E10521 | MS-222 |
| Fluorescamine | Sigma-Aldrich | F9015 | |
| Formaldehyde solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 252549 | |
| Formaldehyde-13C, d2, solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 596388 | |
| Formaldehyde-d2 solution | Sigma-Aldrich | 492620 | |
| Formic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | 33015 | |
| Fume hood | Quimis | Q216 | |
| Hydrochloric acid - HCl | Sigma-Aldrich | 258148 | |
| LoBind-Protein retention tubes | Eppendorf | EP0030108116-100EA | |
| LTQ-Orbitrap Velos | Thermo Fisher Scientific | LTQ Velos | |
| Microwave oven | Panasonic | NN-ST67HSRU | |
| n Easy-nLC II nanoHPLC | Thermo Fisher Scientific | LC140 | |
| PEAKS Studio | Bioinformatics Solutions Inc. | VERSION 8.5 | |
| Phosphate-buffered saline | Invitrogen | 3002 | tablets |
| precolumn (EASY-Column) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | (SC001) | 2 cm, ID100 µm, 5 µm, C18-A1 |
| Refrigerated centrifuge | Hermle | Z326K | for conical tubes |
| Refrigerated centrifuge | Vision | VS15000CFNII | for microtubes |
| Reversed-phase cleanup columns (Oasis HLB 1 cc Cartridge) | Waters | 186000383 | Oasis HLB 1 cc Cartridge |
| Sodium cyanoborodeuteride - NaBD3CN | Sigma-Aldrich | 190020 | |
| Sodium cyanoborohydride - NaBH3CN | Sigma-Aldrich | 156159 | |
| Sodium phosphate dibasic | Sigma-Aldrich | S9763 | NOTE: 0.2 M PB= 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 6.8 (26.85 mL of Na2HPO3 1M) plus 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 6.8 (23.15 mL of NaH2PO3 1M) to 250 ml of water |
| Sodium phosphate monobasic | Sigma-Aldrich | S3139 | |
| Sonicator | Qsonica | Q55-110 | |
| Standard peptide | Proteimax | amino acid sequence: LTLRTKL | |
| Triethylammonium buffer - TEAB 1 M | Sigma-Aldrich | T7408 | |
| Trifluoroacetic acid - TFA | Sigma-Aldrich | T6508 | |
| Ultra purified water | Milli-Q | Direct-Q 3UV | |
| Vacuum centrifuge | GeneVac | MiVac DNA concentrator | |
| Water bath | Cientec | 266 | |
| Xcalibur Software | ThermoFisher Scientific | OPTON-30965 |
References
- Kandpal, R., Saviola, B., Felton, J. The era of 'omics unlimited. Biotechniques. 46 (5), 354-355 (2009).
- Farrokhi, N., Whitelegge, J. P., Brusslan, J. A. Plant peptides and peptidomics. Plant Biotechnology Journal. 6 (2), 105-134 (2008).
- Schulz-Knappe, P., Schrader, M., Zucht, H. D. The peptidomics concept. Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening. 8 (8), 697-704 (2005).
- Dallas, D. C., et al. Current peptidomics: applications, purification, identification, quantification, and functional analysis. Proteomics. 15 (5-6), 1026-1038 (2015).
- Chard, T. An introduction to radioimmunoassay and related techniques (3rd Ed). FEBS Letters. 238 (1), 223 (1988).
- Svensson, M., Sköld, K., Svenningsson, P., Andren, P. E. Peptidomics-based discovery of novel neuropeptides. Journal of Proteome Research. 2 (2), 213-219 (2003).
- Baggerman, G., et al. Peptidomics. Journal of Chromatography B. 803, 3-16 (2004).
- Theodorsson, E., Stenfors, C., Mathe, A. A. Microwave irradiation increases recovery of neuropeptides from brain tissues. Peptides. 11, 1191-1197 (1990).
- Che, F. Y., Lim, J., Pan, H., Biswas, R., Fricker, L. D. Quantitative neuropeptidomics of microwave-irradiated mouse brain and pituitary. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 4, 1391-1405 (2005).
- Dasgupta, S., et al. Analysis of the yeast peptidome and comparison with the human peptidome. PLoS One. 11 (9), 0163312 (2016).
- Teixeira, C. M. M., Correa, C. N., Iwai, L. K., Ferro, E. S., Castro, L. M. Characterization of Intracellular Peptides from Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Brain. Zebrafish. 16 (3), 240-251 (2019).
- Fricker, L. D. Analysis of mouse brain peptides using mass spectrometry-based peptidomics: implications for novel functions ranging from non-classical neuropeptides to microproteins. Molecular BioSystems. 6 (8), 1355-1365 (2010).
- Gelman, J. S., Sironi, J., Castro, L. M., Ferro, E. S., Fricker, L. D. Peptidomic analysis of human cell lines. Journal of Proteome Research. 10 (4), 1583-1592 (2011).
- De Araujo, C. B., et al. Intracellular peptides in cell biology and pharmacology. Biomolecules. 9, 150 (2019).
- Gewehr, M. C. F., Silverio, R., Rosa-Neto, J. C., Lira, F. S., Reckziegel, P., Ferro, E. S. Peptides from natural or rationally designed sources can be used in overweight, obesity, and type 2 diabetes therapies. Molecules. 25 (5), 1093 (2020).
- Sakaya, G. R., et al. Peptidomic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with intracranial saccular aneurysms. Journal of Proteomics. 240 (3), 104188 (2021).
- Fricker, L. Quantitative peptidomics: General considerations. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1719, 121-140 (2018).
- Southey, B. R., et al. Comparing label-free quantitative peptidomics approaches to characterize diurnal variation of peptides in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Analytical Chemistry. 86 (1), 443-452 (2014).
- Chen, X., Wei, S., Ji, Y., Guo, X., Yang, F. Quantitative proteomics using SILAC: Principles, applications, and developments. Proteomics. 15 (18), 3175-3192 (2015).
- Boonen, K., et al. Quantitative peptidomics with isotopic and isobaric tags. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1719, 141-159 (2018).
- Gewehr, M. C. F., et al. The relevance of thimet oligopeptidase in the regulation of energy metabolism and diet-induced obesity. Biomolecules. 10 (2), 321 (2020).
- Fiametti, L. O., Correa, C. N., Castro, L. M. Peptide profile of zebrafish brain in a 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson model. Zebrafish. 18 (1), 55-65 (2021).
- Boersema, P. J., Raijmakers, R., Lemeer, S., Mohammed, S., Heck, A. J. Multiplex peptide stable isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Nature Protocols. 4 (4), 484-494 (2009).
- Dasgupta, S., Castro, L. M., Tashima, A. K., Fricker, L. Quantitative peptidomics using reductive methylation of amines. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1719, 161-174 (2018).
- Tashima, A. K., Fricker, L. D. Quantitative peptidomics with five-plex reductive methylation labels. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 29 (5), 866-878 (2018).
- Che, F. Y., et al. Optimization of neuropeptide extraction from the mouse hypothalamus. Journal of Proteome Research. 6 (12), 4667-4676 (2007).
- Lyons, P. J., Fricker, L. D. Peptidomic approaches to study proteolytic activity. Current Protocols in Protein Science. , 13 (2011).
- Udenfriend, S., et al. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 178 (4063), 871-872 (1972).
- Ma, B., et al. PEAKS: powerful software for peptide de novo sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry. 17 (20), 2337-2342 (2003).
- Zhang, J., et al. PEAKS DB: de novo sequencing assisted database search for sensitive and accurate peptide identification. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 11 (4), 1-8 (2012).
- Sturm, R. M., Dowell, J. A., Li, L. Rat brain neuropeptidomics: tissue collection, protease inhibition, neuropeptide extraction, and mass spectrometric analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 615, 217-226 (2010).
- Fricker, L. D. Limitations of mass spectrometry-based peptidomic approaches. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry. 26 (12), 1981-1991 (2015).
- Ross, , et al. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 3, 1154-1169 (2004).
- Thompson, A., et al. Tandem mass tags: a novel quantification strategy for comparative analysis of complex protein mixtures by MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry. 75, 1895-1904 (2003).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved