A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Static Strength Training Method for Type 2 Diabetic Mice
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol provides a simple method of making static training equipment for mice. The device maintains the muscle isometric contraction of the limbs of mice so as to verify the intervention effect of traditional exercise on type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and provides new exercise therapy for the clinical treatment of T2DM.
Abstract
The treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major difficulty in improving patient health. Exercise is one of the main interventions for T2DM. Static strength training is one of the key forms of traditional sports in China. Research shows that static strength training is an effective clinical method for T2DM intervention, but there is no experimental device suitable for static training in mice. One of the difficulties in moving from clinical to basic research is to design appropriate experimental devices. In order to further study the mechanism of static training intervention in T2DM, a simple method for making a static training device for mice is introduced in this paper. This device has the advantages of simple operation, cheap material, and high feasibility. Previous studies conducted under this protocol have shown that static training can effectively reduce blood glucose levels and improve the mitochondrial function of skeletal muscle cells in T2DM mice. The purpose of introducing this device is to promote research on the mechanism of traditional exercise in the intervention of T2DM and to lay a foundation for the quantitative intervention of exercise.
Introduction
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic disease characterized by insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction that is a significant threat to global health1. Exercise is a crucial intervention in the management of type 2 diabetes. Numerous studies have shown that traditional Chinese exercise methods, such as Tai Chi and Ba Duan Jin, significantly improve blood glucose levels and quality of life for individuals with T2DM2,3,4,5. To execute these movements, the trainer must maintain a stable body and joint position for a period of time. The static position is sustained by performing static muscle contractions, which is commonly referred to as static strength6.
However, the mechanism of static strength training intervention in T2DM has not been clarified. To answer this question, animal experiments are essential. During isometric exercises, muscles are activated, maintain a constant length, and safely achieve maximum tension7. In experiments with static strength training, the test animal is required to perform isometric muscle contractions and to maintain this state of muscular contraction. How to implement static strength training on mice, rats, and other laboratory animals has become a big problem in research. First, animals struggle to obey commands and contract their muscles as required. Secondly, it is difficult for the animal to maintain a stable position under resistance, and the purpose of isometric muscle contraction cannot be achieved. While letting animals train as required, it is important to address concerns related to animal welfare, such as relieving stress and anxiety, minimizing pain, and improving overall conditions. This protocol pertains to a static training model for rats8,9, and here we introduce a simple device for static training of mice. When the hind legs of mice are lifted, their abdominal muscles contract due to the righting reflex, the forepaws grasp the cross-bar in front, and then the front and back limbs contract against gravity. The mice cannot move after grasping the short bar, resulting in their muscles being in a state of isometric contraction.
Protocol
All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (permission no. 202209A033). Healthy male C57BL/6J mice with SPF grade, 8 weeks of age, and body weight of 20 ± 4 g were selected. The mice were housed in a 12 h light/dark cycle at a temperature of 20-22 °C, and a relative humidity of 45%-50% was maintained. The animals eat and drink freely.
1. Establishment of a mouse model of T2DM
- Feed the mice for 1 week on a regular diet first and let the mice adapt to the new environment of the animal center. After 1 week, provide a high-fat diet (diet composition: 20.0% lard, 10.0% sucrose, 2.5% cholesterol, 1.0% cholate, 66.5% conventional diet) for a period of 4 weeks.
- From the 1st day of the 5th week, intraperitoneally inject mice with streptozotocin solution at a dose of 35 mg/kg each day for 3 consecutive days. Prepare 1 mL of the streptozotocin solution with 10 mg of streptozotocin powder, with 0.1 M/L sodium citrate buffer as the solvent.
NOTE: The injection should be completed within 30 min after the solution is prepared, and the solution should be kept away from light during use. - Randomly test blood glucose on day 5 and day 7 after the first injection of streptozotocin solution was administered. Animals with two random blood sugar levels higher than 16.7 mM/L are considered successful T2DM models.
- Begin training intervention on day 8 after the first injection of streptozotocin solution.
2. Grouping and treatment in mice
- Divide the T2DM mice into a model group, training group, and metformin group using the random number table method, with 6 mice in each group.
- Perform no intervention for the model group.
- Grind metformin tablets into powder and dissolve in pure water. Give metformin to the metformin group by gavage at a dose of 200 mg/kg, once per day, for 3 weeks.
- Let the training group do 30 min of static strength training, once a day, 5 days a week, for 3 weeks. Training is held every Monday to Friday afternoon.
- Randomly assign 6 non-T2DM mice as control group. These mice do not undergo modeling and intervention.
3. Manufacturing the static strength training device
- Prepare a 5 mm thick transparent acrylic board with dimensions of 20 cm x 20 cm. Use a transparent board in order to observe the mice training.
- Get wooden sticks with a diameter of 3 mm and a roll of tape with a width of 1 cm. Use a paper cutter to cut two 4 cm long sticks and four 1 cm long sticks.
- Attach two sticks, each with a length of 1 cm, to the ends of a stick with a length of 4 cm using tape (Figure 1A). The short sticks should be fixed on the same side as the long stick.
- Place the transparent board on a flat surface and attach two sets of 1 cm short sticks to the plate using a hot glue gun. Ensure the 4 cm wooden sticks do not come into contact with the board. Allow a 2 cm gap between the long stick and the board to hold the mice in place (Figure 1B). Let the two long sticks be aligned and parallel, with a distance of 6 cm between them (Figure 1C).
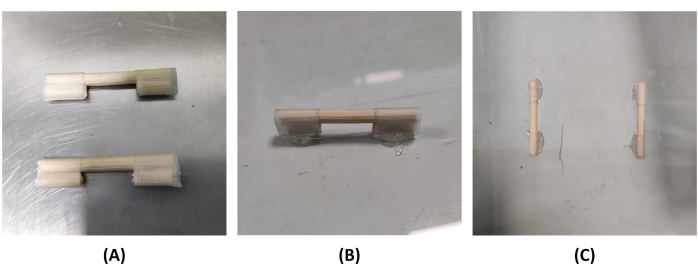
Figure 1: Assemble and secure the sticks to the transparent board. (A) Tape the 1 cm stick to both ends of the 4 cm stick. (B) Use hot melt adhesive to connect the 1 cm long stick and transparent board, and the gap length is 2 cm. (C) Two 4 cm sticks spaced 6 cm apart. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Static strength training in mice
- Cut two pieces of woolen yarn 15 cm long. Use a slipknot to tie a piece of woolen yarn on each of the mouse's upper ankle (Figure 2A).
NOTE: Elastic rope cannot fix the posture of mice, and hemp rope will wear the ankles of mice, so inelastic but soft woolen yarn is chosen here. - Place the board horizontally on the table with sticks up. Press the mouse carefully between two long sticks, positioning its head and tail to align with the gaps below the sticks.
- Pass the yarn through the gap at the end of the tail. Then, adjust the yarn until the ankles of the mouse fit snugly against the edge of the stick.
- Secure the woolen yarn with tape (Figure 2B). The end of the woolen yarn should be secured otherwise, the mouse will climb the fallen wool. Pull the wool as tight as possible or the mouse will easily break free.
- Invert the transparent board. Get 2 boxes of the same height (15-20 cm tall) on either end of the transparent board. Place the board horizontally at a certain height. The box is located at either end of the mouse's head and tail. If it is too high, the experimenter will not be able to handle it easily; if it is too low, the mouse may touch the tabletop.
- Once the board is overturned, the mouse hangs upside down. Due to the righting reflex, mice curl their abdomen and extend their forelimbs to grasp their hindlimbs or sticks. At this stage, position a 20 cm stick in front of the mouse and carefully guide it to grasp the stick with its forelimbs. Repeat the process until the mouse becomes proficient at grasping the mobile stick.
- Use the stick to move the forelimb of the mouse to another 4 cm stick on the transparent board. Constantly adjust the angle of the stick to enable the mice to actively grasp the stationary 4 cm stick on the board (Figure 2C).
- Repeat the previous step as the mouse releases the front paw until the mouse is exhausted. After 30 minutes, most of the rats were unable to lift their upper body and grasp the stick with their forelimbs.
NOTE: Before implementing the intervention, a week of habituation training on mice is necessary. The initial training duration is 10 minutes per day, which should then be increased by 5 minutes each day until reaching a total of 30 minutes per day. - After 30 min of training, immediately release the mouse and untangle the wool to prevent red and swollen feet caused by prolonged binding.
- If skin lesions appear on the ankle of the mice after training, stop training the mice and seek veterinary professional care until the ankle is healthy.
- Some mice may occasionally manage to free themselves through intense struggle during training. The mice struggle when their hind legs were not firmly fixed. To avoid injury due to struggle, observe the mice throughout the training. When it is found that the hind limbs are not firmly fixed or the mice begin to struggle, loosen the mice and re-fix.
NOTE: Previous experiments have shown that hanging mice upside down for 30 min a day, 5 days a week, does not cause ankle wear, provided they are freed in due time10. Mice can learn and get used to the training in 1-3 sessions.

Figure 2: Fixation method in mouse. (A) Tie the top of the ankle with a slipknot. (B) The end of the rope is passed through the gap and pulled tight, then secured with tape. (C) Static strength training in mice. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Results
Following the above protocol, the hind limbs of the mouse are fixed, and the forelimbs autonomously grasp the front bar. The narrow range of motion keeps the mouse in a relatively fixed position. The muscles of mice can be confirmed to contract by touching the muscles of their abdomen and legs. This is consistent with the need for the state of isometric muscle contraction in static strength training. Training mice according to the protocol, with the increase in training times, will help the mice adapt to the training whi...
Discussion
Static strength training can reduce fat accumulation, aid weight loss, and increase metabolism8. In addition, it enhances the expression of PGC-1α and mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle cells, leading to improved glucose metabolism in mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a consequent reduction in blood glucose levels11. To confirm the impact and mechanism of static training on T2DM, appropriate devices need to be developed for performing static training on e...
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the second batch of special scientific research projects of the National Clinical Research Base of Traditional Chinese Medicine (JDZX2015127, based on Anhui Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Acrylic boards | Transparent acrylic boards with 5mm thickness. The size should be larger than 20cm×20cm | ||
| Boxes | Two boxes of the same height (15~20cm) | ||
| ELISA KIT | H203-1-2 | Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute | |
| Hot melt glue gun | Avoid touching the gun head to cause burns | ||
| Knives | No special requirement | ||
| Metformin tablets | 1396309 | Sigma | |
| scissors | No special requirement | ||
| Sticks | Several wooden sticks with a diameter of 3mm | ||
| Streptozotocin | S0130 | Sigma | |
| Tape | No special requirement | ||
| Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) | HT7700 | HITACHI |
References
- Zheng, Y., Ley, S. H., Hu, F. B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrino. 14 (2), 88-98 (2018).
- Li, X., et al. Effects of fitness qigong and tai chi on middle-aged and elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Public Lib Sci. 15 (12), e0243989 (2020).
- Qin, J., et al. Effect of tai chi on quality of life, body mass index, and waist-hip ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrino. 11, 543627 (2020).
- Yang, H., Wu, X., Wang, M. Effect of conventional medical treatment plus Qigong exercise on type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese patients: A Meta-analysis. J Trad Chinese Med. 38 (2), 167-174 (2018).
- Yu, X., Chau, J. P. C., Huo, L. The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine-based lifestyle interventions on biomedical, psychosocial, and behavioral outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 80, 165-180 (2018).
- Ağgön, E., et al. Effect of dynamic and static strength training on hormonal activity in elite boxers. Baltic J Health Phys Activity. 12 (3), 1-10 (2020).
- Merico, A., et al. Effects of combined endurance and resistance training in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A pilot, randomized, controlled study. Eur J Translat Myo. 28 (1), 7278 (2018).
- Liu, Y., et al. Eight weeks of high-intensity interval static strength training improves skeletal muscle atrophy and motor function in aged rats via the PGC-1α/FNDC5/UCP1 pathway. Clin Interven Aging. 16, 811-821 (2021).
- Jun, X., et al. Animal model for static massage training. Massage Guid. (02), 5-6 (2000).
- Wei, J., et al. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes. Chinese J Tiss Eng Res. 28 (08), 1271-1276 (2024).
- Zhenrui, L., Fang, L., Wu, W., Huang, J. The effect of static training on upper limb motor ability in aged rats was studied based on PGC-1α signal pathway RNA interference. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research. 30 (01), 247-249 (2019).
- Lee, S. H., Park, S. Y., Choi, C. S. Insulin resistance: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Diab Metab J. 46 (1), 15-37 (2022).
- Campos, J. C., et al. Exercise preserves physical fitness during aging through AMPK and mitochondrial dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 120 (2), e2204750120 (2023).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved