Aseptic Technique in Environmental Science
Overview
Source: Laboratories of Dr. Ian Pepper and Dr. Charles Gerba - The University of Arizona
Demonstrating Author: Luisa Ikner
Aseptic technique is a fundamental skill widely practiced in the field of environmental microbiology that requires a balance of mindfulness and practice in the laboratory. Proper use of this technique reduces the likelihood of bacterial or fungal contamination of reagents, culture media, and environmental samples. Aseptic technique is also vital to ensure data integrity and maintain the purity of culture libraries that may be comprised of very rare and difficult to culture isolates. Sources of contamination in the laboratory environment include airborne microorganisms (including those adhering to dust and lint particles), microbes present on the laboratory bench workspace or on unsterilized glassware or equipment, and microbes transferred from the body and hair of the researcher. The use of aseptic technique is also a safety measure that lowers the potential for the transmission of microorganisms to researchers, which is particularly important when working with pathogens.
Procedure
1. Preparation for Aseptic Work
- Obtain and apply the following PPE items: lab coat, latex or nitrile gloves (free from tears or holes), and safety goggles (Figure 1). For safety in the event of using an open flame, tie back long hair.

Figure 1: PPE: A lab coat, latex gloves, and safety goggles. - A second important aspect of aseptic technique is the proper sterilization and storage of med
Results
The outcome of the procedure demonstrates proper aseptic technique and poor aseptic technique. Figure 7 illustrates the contamination that can arise from poor aseptic technique when pouring agarose plates (top plate: sterile medium; bottom plates: contaminated media).
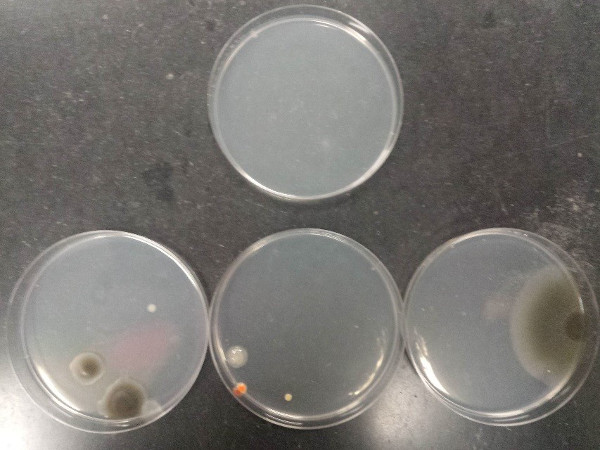
Figure 7: Contamination that can arise from poor aseptic technique when pouring agarose plate
Application and Summary
Other than using Bunsen burners, aseptic working environments can also be maintained in specialized workstations known as laminar flow hoods, which use directed airflow and filters to maintain sterility.
Proper use of aseptic technique is vital for environmental microbiologists when sampling in the field and in the laboratory when working with media, reagents, and cultured isolates. Poor aseptic technique in the field can result in the transfer of microorganisms from the technician to cr
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
Aseptic Technique in Environmental Science
Environmental Microbiology
126.4K Views

Determination of Moisture Content in Soil
Environmental Microbiology
359.2K Views

Gram Staining of Bacteria from Environmental Sources
Environmental Microbiology
100.2K Views

Visualizing Soil Microorganisms via the Contact Slide Assay and Microscopy
Environmental Microbiology
42.2K Views

Filamentous Fungi
Environmental Microbiology
57.3K Views

Community DNA Extraction from Bacterial Colonies
Environmental Microbiology
28.8K Views

Detecting Environmental Microorganisms with the Polymerase Chain Reaction and Gel Electrophoresis
Environmental Microbiology
44.5K Views

RNA Analysis of Environmental Samples Using RT-PCR
Environmental Microbiology
40.4K Views

Quantifying Environmental Microorganisms and Viruses Using qPCR
Environmental Microbiology
47.8K Views

Water Quality Analysis via Indicator Organisms
Environmental Microbiology
29.5K Views

Isolation of Fecal Bacteria from Water Samples by Filtration
Environmental Microbiology
39.3K Views

Detection of Bacteriophages in Environmental Samples
Environmental Microbiology
40.7K Views

Culturing and Enumerating Bacteria from Soil Samples
Environmental Microbiology
184.2K Views

Bacterial Growth Curve Analysis and its Environmental Applications
Environmental Microbiology
295.9K Views

Algae Enumeration via Culturable Methodology
Environmental Microbiology
13.8K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved




