The Factorial Experiment
Overview
Source: Laboratories of Gary Lewandowski, Dave Strohmetz, and Natalie Ciarocco—Monmouth University
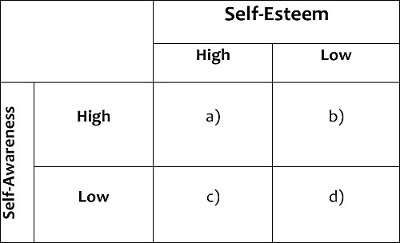
A factorial design is a common type of experiment where there are two or more independent variables. This video demonstrates a 2 x 2 factorial design used to explore how self-awareness and self-esteem may influence the ability to decipher nonverbal signals. This video leads students through the basics of a factorial design including, the nature of a factorial design and what distinguishes it from other designs, the benefits of factorial design, the importance and nature of interactions, main effect and interaction hypotheses, and how to conduct a factorial experiment.
Procedure
1. Introduction of topic/research question
- Research question: Human behavior is complex, such that a person’s thoughts and behaviors are the results of several causes or factors. For example, if you wanted to know why some people are better at reading another person’s facial expressions, there are many factors that can influence that ability.
- Justifying a factorial design: Rather than test potential explanations one at a time, you can use a factorial design, which is unique because it al
Results
After collecting data from 136 people, a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to test the two main effects and interactions. As shown in Figure 1, contrary to the hypothesized pattern, when participants had high self-awareness, they were more accurate when they had low self-esteem; however, when they had low self-awareness, they were more accurate when they had high self-esteem.
Beyond their influence on deciphering the meaning in a person’s eyes, gre
Application and Summary
A factorial design is commonly used in psychology experiments. This design is beneficial for a variety of topics, ranging from pharmacological influences on fear responses to the interactions of varying levels of stress and types of exercise.
Skip to...
Videos from this collection:

Now Playing
The Factorial Experiment
Experimental Psychology
73.3K Views

From Theory to Design: The Role of Creativity in Designing Experiments
Experimental Psychology
18.7K Views

Ethics in Psychology Research
Experimental Psychology
29.3K Views

Realism in Experimentation
Experimental Psychology
8.3K Views

Perspectives on Experimental Psychology
Experimental Psychology
5.7K Views

Pilot Testing
Experimental Psychology
10.3K Views

Observational Research
Experimental Psychology
13.2K Views

The Simple Experiment: Two-group Design
Experimental Psychology
74.6K Views

The Multi-group Experiment
Experimental Psychology
22.9K Views

Within-subjects Repeated-measures Design
Experimental Psychology
23.1K Views

Self-report vs. Behavioral Measures of Recycling
Experimental Psychology
11.8K Views

Reliability in Psychology Experiments
Experimental Psychology
8.6K Views

Placebos in Research
Experimental Psychology
11.6K Views

Manipulating an Independent Variable through Embodiment
Experimental Psychology
8.5K Views

Experimentation using a Confederate
Experimental Psychology
17.8K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved