Method Article
一个鼠标,两种文化:隔离和成人神经的培养干细胞从单个小鼠的两个神经源性区
Erratum Notice
摘要
在这里,我们描述的同时产生神经前体细胞培养的一个详细的协议,因为无论是贴壁单层或神经球,从脑室下区和个体成年小鼠海马齿状回。
摘要
神经球法和贴壁单层培养系统是有价值的工具,以确定潜在的成体神经干细胞的体外 (细胞增殖或分化)。这些测定法可用于比较的细胞从遗传上不同或差分处理的动物中分离的前体电位,以确定外源因素对神经前体细胞的增殖和分化的影响,并产生可被检测过的连续传代的神经前体细胞系。神经球法是传统上用于事后识别干细胞,主要是由于缺乏明确的标记,使他们能够从主组织中分离出来,并具有使前体细胞数的快速估计脑组织中的主要优点来源于动物个体。贴壁单层培养物,与此相反,没有传统上用来比较个别动物之间的扩散,因为每一种文化一般是由动物的5-8之间的联合组织发起的。然而,它们具有不同于神经球,它们由前体细胞的一个主要同质种群的和是在单细胞以下的分化过程有用的主要优势。在这里,我们描述,详细地说,神经球培养物的产生,并在第一次,从个别动物贴壁培养物。这具有多方面的重要意义,包括在这两个脑室下区(SVZ)和处理过的或遗传上不同小鼠品系的齿状回(DG)增殖和/或分化潜能的配对分析,以及一个显著减少动物的使用。
引言
神经球试验1,2和贴壁单层培养3,4,在90年代初发达国家,仍留在体外神经干细胞检测的金标准。在这些测定中,主要的组织是微从特定脑区域解剖,解离成单细胞悬浮液,并在有丝分裂原表皮生长因子(EGF)和成纤维细胞生长的存在下培养因子-2(FGF2),以形成任一自由浮动的集群(神经球)或贴壁单层。这两个系统有一些优点和缺点,并小心,应考虑到的是一个或另一个系统被选择之前必须解决的问题。
神经球允许一个简单的读出的前体细胞数和电位差。此外,神经球也从它们的正常的外部环境中取出时,研究细胞的内在规范的有用工具。 Extrin原文线索可以通过简单地增加所关心的生长培养基中的因子和量化所产生的神经球的数目和大小来研究。神经球的主要缺点然而,就是它们形成自己的特殊的,与细胞的神经球(特别大的神经球)比那些表面5上更加分化的中心。神经球含有干细胞,致力于祖细胞,并且分化的细胞及神经球内的细胞 - 细胞相互作用抵消干细胞的维持的混合。这就是为什么神经球只包含少数真正的干细胞6-8中。
单层贴壁培养也提供了良好的体外系统在体内增殖模型。贴壁培养,其中的细胞保持更加孤立且均匀,能消除神经球的异质性。在这些生长条件下的前体细胞增殖RAPIDLY和几乎所有的细胞分裂和表达特征的神经前体标志物巢蛋白,Sox2和BLBP。对单层培养系统相比,神经球试验中的主要缺点是单个前体衍生的克隆都无法被监控和量化。
大多数协议的这两种类型的培养物的一个缺点一直是使用相对大量的动物的必要性,因为隔离策略的产率往往是很差。在同一时间,它已经很清楚,成年神经有助于大脑9的个性化,导致需要进行个性化的体外模型为好。本报告中所述的这些需求能够得到满足的“一鼠一文化”的协议。
下面的视觉协议描述的同时产生的动物个体都SVZ和DG无论是作为粘附米的神经前体文化onolayers或神经球。从动物个体培养物的产生是当需要单独处理的动物或各种单个转基因或野生型小鼠之间进行比较时特别有用。这个协议包括用于从成年小鼠的SVZ和DG区的同时显微切割的详细说明,其解离成单细胞悬液, 在体外培养的任何贴壁单层培养物或神经球和multipotentiality和长期潜力的分析,两个基数一个真正的骨干细胞的特性。
研究方案
1。基本设置和培养基的制备
- 之前在开始实验至少两天,准备聚-D-赖氨酸(PDL)/层粘连蛋白涂层板为单层贴壁培养。为了准备井/瓶补充足够的PDL(10毫克/毫升的DH 2 O)涂在表面,孵育过夜在室温下。从培养皿中取出溶液并用dH 2 O洗涤培养皿3次风干。添加层粘连蛋白(5毫克/毫升冷的DMEM:F12),并在37℃过夜。移除层粘连蛋白和可以立即使用平板或与层粘连蛋白在-20℃下储存直到需要。
- 通过旋转玻璃巴斯德吸管在火焰直到边缘变得圆润准备火抛光的吸管与“中等”和“小”孔。高压灭菌消毒。
- 在夹层的一天,通过混合神经基础培养基有2%B27,1 GlutaMAX的,2毫克/毫升肝素,准备培养基适量50单位/ ml青霉素/链霉素,20毫微克/毫升的纯化的小鼠受体同类表皮生长因子(EGF),和20纳克/毫升的重组牛成纤维细胞生长因子(FGF-2)。温热的培养基中,以37℃的水浴中。
- 对于SVZ解离,准备0.05%胰蛋白酶-EDTA和0.125毫克/毫升的胰蛋白酶抑制剂含有0.01毫克/毫升DNA酶I。平衡这些解决方案,以37°C。
- 设置一个解剖显微镜和准备需要取出大脑(剪刀和小刮刀)和SVZ和DG解剖(手术刀,附着于1ml注射器,27号针头,1×#7镊子,1×#四十五分之五的工具镊子)通过浸泡在70%乙醇中。
2。成年小鼠大脑和SVZ / DG Microdissections收获
- 根据相应的机构准则麻醉单身成人(8周龄)小鼠。进行颈椎脱位。
- 喷雾头,用70%乙醇消毒的区域,并减少毛发的量,一个dheres到剪刀和脑。使用锋利的剪刀斩首动物在脑干的基础。
- 握住头颅骨的基础上,通过放置一个小剪刀一个刀片到每只眼睛腔和切割切冠两嗅球的头骨。接下来,在颅底两个侧切口,其次是纵切口,通过沿矢状缝颅骨注意 :确保剪刀的角度尽可能浅,以免损坏底层的大脑。
- 通过剥离回来的剪刀或者刀片或一对弯钳的颅骨暴露大脑。从头骨用小铲放冷PBS释放大脑。
- 大脑冲洗用PBS以去除血液和皮毛。
- 传送到大脑的PBS含10厘米的塑料培养皿
- 将含有大脑培养皿在解剖显微镜低倍下和定位伯莱Ñ在其腹面。用细弯钳取出嗅球同时保持大脑中的位置由小脑。
- 旋转到大脑背侧和视交叉的水平,通过大脑用手术刀做冠状切口
- 要microdissect的SVZ(更详细的说明,请参见AZARI 等 10),将大脑延髓部分,以使冠状切开表面朝上,并在显微镜聚焦到一个更高的放大倍率。取出并用细弯钳丢弃隔。
- 通过立即放置的一对细弯钳在马上的胼胝体和其他大约1mm下侧脑室外侧拐角的一个叶片的尖端进入组织解剖SVZ(薄层组织周围的脑室)相邻的心室。按下向下朝向盘的基部并朝向ventr的腹侧方面的钳子ICLE删除一个小三角片组织。将解剖SVZ成冰培养皿。
- 要microdissect危险品(更详细的说明,请参见萩原等人 11),将大脑的尾部分在培养皿中,用手术刀沿纵向裂缝切割。
- 在解剖镜下,取出用血管钳在小脑和间脑。
- 重新聚焦显微镜,让周围的DG边界现在是可见的。要删除齿状回,插入一个27号针头和幻灯片沿DG和阿蒙的角之间的边界的一角。用细镊子,释放DG从周围的组织。
3。 SVZ组织解离
- 用手术刀刀片约1分钟剁碎的组织,直到没有大块依然存在。
- 转移的组织糜至15ml试管用1ml预热的0.05%胰蛋白酶-EDTA,并在孵育7分钟水浴设定为37℃。
- 以终止酶促反应,加入1毫升含有DNA酶I胰蛋白酶抑制剂和轻弹管混合内容物。
- 通过离心分离沉淀的悬浮液在300×g离心5分钟,弃上清
- 重悬沉淀于1毫升生长培养基,并通过使用P1000的吸管小心轻轻吹打向上和向下约7至10倍分解:在研制过程中,能够增加细胞死亡,并会在随后的细胞生长产生负面影响。
- 加生长培养基中至5毫升的总体积,并通过细胞悬浮液通过40 mm筛以除去碎片和未解离的组织团块。
- 离心机在300×g离心5分钟,弃去上清,重悬所得的粒料在200毫升生长培养基中。
4。 DG组织解离
- 用手术刀刀片约1分钟剁碎的组织,直到没有大块的保持和转移进入预热PDD的酶混合物(木瓜蛋白酶2.5单位/毫升,分散酶1 U / ml时,DNA酶I 250单位/毫升)。孵育20分钟,在37℃,颠倒试管,每3-5分钟混合。
- 分离机械使用中等口径的组织,火抛光,巴斯德吸管吹打向上和向下轻轻的10倍。
- 孵育另外的10分钟,在37℃,颠倒试管,每3-5分钟混合。
- 进一步分离机械使用小口径的组织,火抛光的巴斯德吸管吹打向上和向下轻轻的10倍。
- 离心机在130×g离心5分钟。
- 去除上清,重悬沉淀在1ml缓冲液(1×HBSS,30mM的葡萄糖,2毫摩尔HEPES(pH 7.4)中,26毫米碳酸氢钠3)。补至10ml用缓冲溶液。
- 离心机在130×g离心5分钟。
- 去除上清,重悬沉淀在5毫升20%的Percoll的。 (要准备90%的Percoll,加4.5毫升100%的Percoll〜0.5毫升10X PBS再进一步稀释这20%通过添加1.1毫升90%的Percoll到3.9毫升的1X PBS)中。
- 离心450×g离心15分钟。
- 去除上清,重悬沉淀在10毫升缓冲液。
- 离心机在130×g离心5分钟。
- 重悬沉淀在200μl生长培养基。
5。的单层贴壁培养一代
- 铠解离SVZ或DG组织成一个单一的PDL /层粘连蛋白的96孔板中包被的孔,并在37℃,5%CO 2。
- 约24小时后镀,一旦细胞已经附着在涂层表面,更换生长培养基中,以进一步除去过量的碎片。
- 以后每3-4天,用新鲜培养基以补充生长因子的生长培养基的交换一半。
- 重复,直到细胞达到约80%汇合,并准备传代注 :电镀和第一通道之间的时间可长达2-3周。
- 当培养物达到大约80%汇合时从井中取出介质和洗涤用PBS。
注意:不要使细胞达到90%汇合,因为这可能会导致细胞的分离和神经球的形成,此外,细胞死亡水平的提高。 - 加入50 mL的Accutase和孵化在37℃2-3分钟(检查是否细胞是圆形的和分离的)。
- 除去细胞到15ml管,洗井一次,用PBS和传送到同一管中。
- 稀释细胞至5ml,用PBS离心300×g离心5分钟。
- 对于第一通道,稀释细胞至1ml和板成PDL /层粘连蛋白24孔板中包被的孔。
- 对于后续的段落,重悬细胞于200毫升生长培养基和计数使用血球。板上,在1×10 4个细胞/ cm 2在适当大小的包衣井或烧瓶。 我>
7。的单层贴壁培养分化
- 区分贴壁单层培养物,板增殖细胞到PDL /层粘连蛋白包被的盖玻片以1×10 4个细胞/含有20纳克/毫升EGF和10毫微克/毫升的bFGF厘米2在生长培养基中的密度。
- 当细胞达到约80%汇合(通常为2天),用含5毫微克/毫升的bFGF和0纳克/毫升EGF的培养基更换生长培养基。
- 以下在5毫微克/毫升的bFGF 2天,用生长培养基代替培养基中不存在两个分裂素的另外3天注 :在此期间会发生显著量的细胞死亡。
- 共5天之后,洗分化的细胞,用PBS以除去任何死细胞,然后用4%多聚甲醛(PFA)20分钟,在室温下固定。
- 用PBS再次洗涤以除去任何的PFA和存储盖玻片在井于1ml的PBS在4℃下
- 从一个动物稀解离SVZ或DG组织在20ml培养基中,并用10ml的移液管multidoser板200毫升/井穿过一个96孔板中。
- 在37℃,5%CO 2的6-7天的SVZ来源的神经球和10-12天的DG-衍生的神经球。
注:生长为比上述建议的孵育时间较长,将导致过度生长,并导致细胞死亡的神经球,和/或自发附着和分化的中心。 - 计数,并使用安装在一个直立的光显微镜的目镜刻度测量神经球的直径
9。传代神经球
当主神经球已经算及它们的大小记录它们可以扩大在几个段落与任何一个单一的神经球或散装的文化开始。
- 散文化的扩张神经球
- 到通道结合神经球作为批量培养,除去含有从板的神经球的介质,转移到15毫升管中,离心分离机,在300×g离心5分钟。
- 弃去上清,重悬的神经球在1ml预热的0.05%胰蛋白酶-EDTA,并在室温下孵育3分钟。
- 添加含有DNA酶I胰蛋白酶抑制剂等体积拌匀。
- 离心5分钟,在300×g离心,去除上清,加入1 ml生长培养基。
- 磨碎上下约10倍与P1000的吸管分离的神经球。
- 除去将10ml细胞悬浮液,并用台盼蓝等体积混合并使用血细胞计数器进行活细胞计数。
- 重新植入的细胞以1×10 4个细胞/ cm 2在适当大小的细胞培养物以及或烧瓶中的密度。
- 在37°C用5%的CO 2,直到次级神经球的形式。
- 单个神经球扩张
- 到通道个别神经球选择包含单个神经球孔并小心地从每个孔中,而不会干扰神经球取出并丢弃大约160微升生长培养基。
- 加入100 ml的0.05%胰蛋白酶-EDTA至各孔,以进行传代,并在室温下孵育3分钟。
- 加入100μl胰蛋白酶抑制剂含有DNA酶I,停止反应。
- 磨碎约10倍上下P200的移液器掰开的神经球。
- 传输200毫升含有解离的神经球含有1.5毫升生长培养基的24孔平板的新井。在37℃,5%CO2,直到二次神经球的形式。
注:确定长期的潜力,真正的神经S中的大是大非的属性之一TEM小室,神经球应该传代,至少5-10通道。另见有关业绩的12-14部分有争议的解释文献。
10。培养神经球分化
小学或神经球传代可以区别来确定multipotentiality。
- 从他们的培养板或烧瓶中悬浮的神经球取出并将它们转移到10厘米的塑料培养皿中。
- 根据解剖显微镜从使用P20移液管的介质除去约15-20神经球并转移到一个24孔板中含有的培养基不含生长因子和PDL /层粘连蛋白包被的盖玻片。
- 分化为大约7天后,在37℃,5%的CO 2。
- 洗分化的神经球用PBS以除去任何死细胞,然后用4%PFA中20分钟,在室温下固定。
- 用PBS洗一遍对r任何的eMove PFA和盖玻片店水井1毫升的PBS在4℃
11。神经球和贴壁培养的免疫染色
注 :为了与O4抗体染色省略的Triton从阻塞和染色步骤,记得使用适当的IgM第二抗体。
- 孵育含在封闭液(10%正常驴血清的PBS中含有0.2%的Triton X-100)在室温下60分钟的分化的神经球或贴壁单层培养的盖玻片。
- 孵育在含有伯BIII-微管蛋白,Map2a + B,胶质纤维酸性蛋白(GFAP)或O4抗体60分钟于室温新鲜阻断溶液。
- 用PBS洗3次。
- 孵育在含有适当的荧光标记的二抗和4,6 - 二脒基-2 - 苯基新鲜阻断溶液(DAPI; 1:5,000)处理30分钟,在室温下在黑暗中。
- 洗3次,用PBS。
- 用荧光封固剂和空气干燥在黑暗中过夜安装到盖玻片显微镜载玻片
- 查看和图像使用荧光显微镜。
结果
虽然成年小鼠大脑两个两个神经源性区包含神经前体细胞,这些细胞可以表现相当不同的方式在体外培养时。从两个区域产生的贴壁单层培养出现形态上没有区别( 图1A),然而,SVZ来源的贴壁培养物增殖快,需要进行传代,平均早于从DG衍生1-2天。作为神经球的SVZ来源的前体细胞的增殖也更快,形成较大的神经球( 图1B)比DG-衍生的前体细胞( 图1C)。虽然SVZ来源的神经球是在培养6-7天一般计算,DG-衍生的神经球被后10-12天,通常量化。此外,一个更大的数字神经前体细胞驻留在SVZ相比,DG,就证明了近10倍的数字神经球,可属的特德从本地区(SVZ:1,173±74.9与DG:145.3±26.4,P = <0.0001,每组n = 10只动物; 图2A)。
研究表明,在SVZ和DG中的前体细胞,以不同的刺激做出反应。被前体细胞在DG特定类型的空间学习和刺激如环境富集和体力活动启动,而SVZ前体细胞是由嗅觉学习和嗅觉富集激活。与此相一致,我们(TLW)的一个先前表明,DG包含了潜在的干细胞和祖细胞,它可以通过神经兴奋15-18被激活的人口。与此相反,我们发现,SVZ前体细胞反应相当不同,以这种刺激,并在神经球数目减少响应于去极化的KCl 17的水平。在这里,我们已经重复了这个实验,电镀一半来自IND的SVZ和DG产生的分离细胞在去极化的KCl水平和控制水平氯化钾另一半ividual动物。我们证明,如前面,虽然对DG前体细胞被去极化(101.2±17.4对184.8±12.5,p值= 0.005,每组 5只动物)被激活,SVZ来源的细胞的增殖实际上显著下降( 368.0±62.9比266.6±41.6,P = 0.02,每组 5只动物; 图2B)。
为了确认长期潜力,一个真正的干细胞,单神经球或单层贴壁培养的主要特征之一必须是能够扩展的扩展,即在至少10代。在每个通道中,单细胞悬浮液的制备如下,细胞的数目进行计数,并折叠扩展计算。理论上的细胞总数,然后通过该通道由从先前通道的理论总期间乘以倍扩展计算。这是DISP奠定作为线图与通道数作图的理论总细胞数目的log10的(参见例如图3)。以确认multipotentiality,无论单层培养和神经球可通过有丝分裂原撤出来区分并显示给产生两个神经元和神经胶质细胞( 图4)。
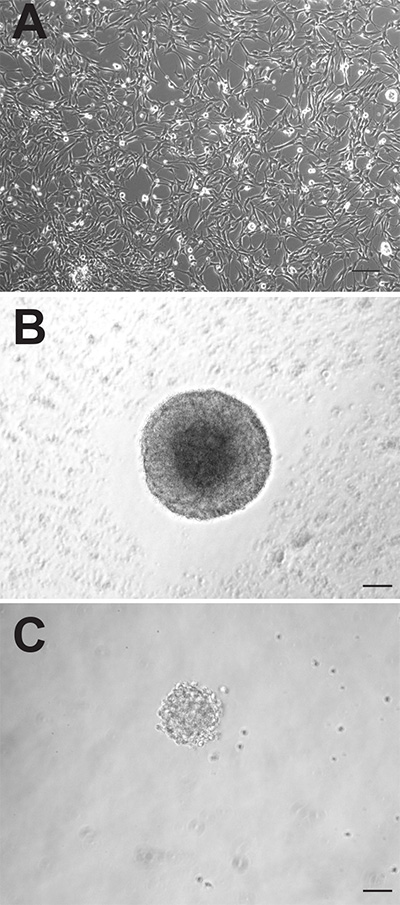
图1成年小鼠前体细胞可以培养为单层贴壁培养(A)或神经球(B:SVZ,C:DG)。比例尺为50mm 点击这里查看大图。
load/51225/51225fig2highres.jpg“SRC =”/ files/ftp_upload/51225/51225fig2.jpg“/>
图2。值得注意从SVZ产生更多的神经球相比,单小 鼠的DG(A)。的SVZ和DG细胞前体细胞的反应不同,以在体外去极化(B)。

图3为了证实长时程增强,神经球被扩展为超过10次传代。

图4。神经球可以分化成BIII-徒步鞋LIN +神经元(A:红色),GFAP +星形胶质细胞(答:绿色),O4 +少突胶质细胞(B:红色)和Map2ab +神经元(C:红色)。 点击这里查看大图。
讨论
本文提出了神经前体的文化,无论是作为单层贴壁和神经球,从成年小鼠大脑的两个主要神经区的启动一个详细的协议。有一些必须在尝试要么这些在体外培养系统中时,必须牢记的重要的点。首先,分离方法的选择是非常重要的,是组织依赖。在我们手中,0.05%胰蛋白酶-EDTA是非常有效的SVZ组织的离解,结果在许多神经球的更高利用木瓜蛋白酶为基础的分解方法时比。对于危险品组织的分解然而,我们强烈建议木瓜蛋白酶为基础的分离方法。当直接比较对DG组织两个分离的方法,我们观察到活细胞的一个显著产量较低,大约使用胰蛋白酶时10倍更少的神经球。在解离这种差异可能是由于在组织构成项目的差两个地区之间的ñ。危险品的紧凑型组织是由大量的神经纤维包围和细胞过程的广泛损害可发生解离过程中。
要注意的第二个重要点是,虽然神经球法可以做出关于存在于给定组织样品中的前体细胞的数目定量陈述有用,有些必须谨慎,但是,在这些绝对数字的解释使用。神经球的融合可以是一个主要的混杂因素。一些研究表明,神经元是高度运动,并且可以熔化,甚至在什么是所谓“克隆”条件7,19。将得到的神经球的频率可以非常依赖于因素,包括培养基成分,解剖过程和离解过程。即使是经验丰富的处理从假定相同的样品产生的神经球的数量有些变化是明显的( 见图1A。)更多有用的,是两个给定的样本( 即控制与处理或野生型与基因敲除)处理由同一个人在同一个实验,而不是总的定量语句之间的前体频率的直接比较前体细胞数。
当决定哪两个培养方法是最适合于特定的实验是要注意,这两种培养系统中产生的细胞类型的均匀性差是重要的。相比,增殖贴壁细胞培养物,其显示出相当均匀的前体细胞池(〜98%的细胞是Sox2的+)20,神经球更异构和包含,以及增殖前体细胞,分化的神经元,星形胶质细胞和21,22。这是很重要的神经球是不是为通道之间的长时间,作为更大的培养的神经球变得越有可能是找到在其核心分化的细胞类型。
传统上,我们开始从5-8之间的小鼠DG组织单层贴壁神经前体文化。因此,尝试建立从一个单一的鼠标的DG或SVZ的单层贴壁培养时,悉心照顾需要组织解离过程中应采取以避免在组织研制过程中过量引起的细胞死亡,或采取延长解剖和最终培养步骤之间的时间段。这个协议描述,对于第一次,从个别动物两者的SVZ和DG贴壁单层培养物的前体的生成。有许多情况需要在一个单一的动物基础制成的前体的增殖和分化的比较时。这些措施包括,以直接比较DG和使用统计数据配对动物个体的SVZ和配对的个体行为或生理数据9文化数据的能力。单个动物的文化也人低遗传关联研究利用难得的转基因动物,其中年龄匹配的每个文化5-8捐助池是不可能的,以及独特的动物( 如 F2杂交或出繁殖的动物)的。
披露声明
作者什么都没有透露。
致谢
特力屋是由居里夫人国际来电奖学金支持。这项工作也从基本的制度资金拨付,Bundesministerium毛皮教化和Forschung(BMBF)资助,部分与支持优先研究发展计划(SFB)655到GK。作者要感谢安妮Karasinsky的保养和维护在这项研究中使用的所有动物和奥黛特雷特,苏珊Ruhwald,范妮博梅和理查德·韦策尔的细胞培养和显微镜的帮助。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Poly-D-lysine | Sigma | P7280-5MG | |
| Laminin | Roche | 11243217001 | |
| Glass Pastuer pipettes | Volac | BS5732 | |
| DMEM:F12 (1:1) 1x | Life Technologies | 21331-020 | |
| Neural Basal Medium (1x) | Life Technologies | 21103-049 | |
| B27 supplements (50x) | Life Technologies | 17504-044 | |
| GlutaMAX | Life Technologies | 35050-038 | |
| Heparin | Sigma | H3393 | |
| Penacillin/Streptomycin | Life Technologies | 15140-122 | |
| EGF | PeproTech | AF-100-15 | |
| bFGF | PeproTech | 100-18B | |
| 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA | Life Technologies | 25300-054 | |
| Trypsin inhibitor | Sigma | T6522 | |
| DNaseI | Roche | 10104159001 | |
| Accutase | PAA | L11-007 | |
| Papain | Worthington | LS003120 | |
| Dispase | Life Technologies | 17105-041 | |
| Percoll | GE Healthcare | 17-0891-02 | |
| HBSS (with Calcium and Magnesium) | Life Technologies | 14025-050 | |
| Glucose | Roth | X997.2 | |
| HEPES | Sigma | H3375-500G | |
| NaHCO3 | Merck | K39347429847 | |
| 1 ml Syringes | Braun | 2016-10 | |
| 27 G Needles | Braun | 4657705 | |
| Scalpels (#22 disposable) | Braun | BA222 | |
| Dumont #7 forceps | FST | 11271-30 | |
| Dumont 5/45 forceps | FST | 11251-35 | |
| Scissors | FST | 14060-10 | |
| Iris spatula | FST | 10093-13 | |
| 70% Ethanol | |||
| PBS | Life Technologies | 14040-091 | |
| flasks/well plates | TPP | 92696 | |
| PFA (4%) | Sigma | P6148 | |
| Hemocytometer | Marienfeld | 650010 | |
| Trypan blue (0.4%) | Sigma | T8154 | |
| NDS | Millipore | 530 | |
| TritonX-100 | Sigma | T9284 | |
| Mouse monoclonal bIII-tubulin antibody | Promega | G712A | |
| Rabbit polyclonal glial fibrillary acidic protein antibody | Dako | 20334 | |
| O4 | R&D Systems | MAB1326 | |
| Map2a+b | Sigma | M1406 | |
| Donkey anti-mouse Cy3 antibody | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 715-505-151 | |
| Donkey anti-rabbit Alexa488 | Dianova | 711-545-152 | |
| 4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) | Invitrogen | 861405 | |
| Aqua Polymount | Polysciences Inc | 18606 | |
| 10 ml Combi tips | Eppendorf | 30089677 | |
| Plastic 10 ml and 25 ml serological pipettes | Corning | 4488/4489 | |
| EQUIPMENT | |||
| Pipetboy | Integra Biosciences | 521942 | |
| Multidoser pipette | Eppendorf | ||
| 37 °C waterbath | |||
| Dissecting microscope | |||
| 37 °C:5% CO2 incubator | |||
| Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5810R |
参考文献
- Reynolds, B. A., Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 255, 1707-1710 (1992).
- Reynolds, B. A., Weiss, S. Clonal and population analyses demonstrate that an EGF-responsive mammalian embryonic CNS precursor is a stem cell. Dev. Biol. 175, 1-13 (1996).
- Palmer, T. D., Ray, J., Gage, F. H. FGF-2-responsive neuronal progenitors reside in proliferative and quiescent regions of the adult rodent brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 6, 474-486 (1995).
- Ray, J., Raymon, H. K., Gage, F. H. Generation and culturing of precursor cells and neuroblasts from embryonic and adult central nervous system. Methods Enzymol. 254, 20-37 (1995).
- Bez, A., et al. Neurosphere and neurosphere-forming cells: morphological and ultrastructural characterization. Brain Res. 993, 18-29 (2003).
- Babu, H., Cheung, G., Kettenmann, H., Palmer, T. D., Kempermann, G. Enriched monolayer precursor cell cultures from micro-dissected adult mouse dentate gyrus yield functional granule cell-like neurons. PLoS One. 2, (2007).
- Jessberger, S., Clemenson, G. D., Gage, F. H. Spontaneous fusion and nonclonal growth of adult neural stem cells. Stem Cells. 25, 871-874 (2007).
- Reynolds, B. A., Tetzlaff, W., Weiss, S. A multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell produces neurons and astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 12, 4565-4574 (1992).
- Freund, J., et al. Emergence of individuality in genetically identical mice. Science. 340, 756-759 (2013).
- Azari, H., Rahman, M., Sharififar, S., Reynolds, B. A. Isolation and expansion of the adult mouse neural stem cells using the neurosphere assay. J. Vis. Exp. , (2010).
- Hagihara, H., Toyama, K., Yamasaki, N., Miyakawa, T. Dissection of hippocampal dentate gyrus from adult mouse. J. Vis. Exp. , (2009).
- Jensen, J. B., Parmar, M. Strengths and limitations of the neurosphere culture system. Mol. Neurobiol. 34, 153-161 (2006).
- Pastrana, E., Silva-Vargas, V., Doetsch, F. Eyes wide open: a critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell. Stem Cell. 8, 486-498 (2011).
- Reynolds, B. A., Rietze, R. L. Neural stem cells and neurospheres- re-evaluating the relationship. Nat. Methods. 2, 333-336 (2005).
- Walker, T. L., Turnbull, G. W., Mackay, E. W., Hannan, A. J., Bartlett, P. F. The latent stem cell population is retained in the hippocampus of transgenic Huntington's disease mice but not wild-type mice. PLoS One. 6, (2011).
- Walker, T. L., et al. Prolactin stimulates precursor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus. PLoS One. 7, (2012).
- Walker, T. L., et al. Latent stem and progenitor cells in the hippocampus are activated by neural excitation. J. Neurosci. 28, 5240-5247 (2008).
- Walker, T. L., et al. Prominin-1 allows prospective isolation of neural stem cells from the adult murine hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 33, (2013).
- Singec, I., et al. Defining the actual sensitivity and specificity of the neurosphere assay in stem cell biology. Nat. Methods. 3, 801-806 (2006).
- Babu, H., et al. A protocol for isolation and enriched monolayer cultivation of neural precursor cells from mouse dentate gyrus. Front. Neurosci. 5, 89 (2011).
- Parmar, M., Sjoberg, A., Bjorklund, A., Kokaia, Z. Phenotypic and molecular identity of cells in the adult subventricular zone in vivo and after expansion in vitro. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 24, 741-752 (2003).
- Suslov, O. N., Kukekov, V. G., Ignatova, T. N., Steindler, D. A. Neural stem cell heterogeneity demonstrated by molecular phenotyping of clonal neurospheres. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 14506-14511 (2002).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: One Mouse, Two Cultures: Isolation and Culture of Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Two Neurogenic Zones of Individual Mice
Posted by JoVE Editors on 11/26/2014. Citeable Link.
A correction was made to One Mouse, Two Cultures: Isolation and Culture of Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Two Neurogenic Zones of Individual Mice. Many micro symbols were changed into milli symbols by accident: In the Protocols, sections 1.1, 1.3, 3.6, 3.7, 6.2, 6.6, 8.1, 9.1.6, 9.2.2, and 9.2.5 need to be fixed, as does Figure 1 description in the Results section.
Protocol section 1.1 was changed from:
At least two days prior to commencing the experiment, prepare Poly-D-lysine (PDL)/Laminin coated plates for adherent monolayer cultures. To prepare wells/flasks add enough PDL (10 mg/ml in dH2O) to coat the surface and incubate overnight at room temperature. Remove the solution from the dish and wash the dish three times with dH2O. Allow to air dry. Add Laminin (5 mg/ml in cold DMEM:F12) and incubate at 37 °C overnight. Remove the Laminin and either use the plates immediately or store with the Laminin at -20 °C until required.
to:
At least two days prior to commencing the experiment, prepare Poly-D-lysine (PDL)/Laminin coated plates for adherent monolayer cultures. To prepare wells/flasks add enough PDL (10 µg/ml in dH2O) to coat the surface and incubate overnight at room temperature. Remove the solution from the dish and wash the dish three times with dH2O. Allow to air dry. Add Laminin (5 µg/ml in cold DMEM:F12) and incubate at 37 °C overnight. Remove the Laminin and either use the plates immediately or store with the Laminin at -20 °C until required.
Protocol section 1.3 was changed from:
On the day of dissection, prepare the appropriate amount of culture medium by mixing Neural Basal Medium with 2% B27, 1x GlutaMAX, 2 µg/ml heparin, 50 units/ml Penicillin/Streptomycin, 20 ng/ml purified mouse receptor-grade epidermal growth factor (EGF), and 20 ng/ml recombinant bovine fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Warm the culture medium to 37 °C in a water bath.
to:
On the day of dissection, prepare the appropriate amount of culture medium by mixing Neural Basal Medium with 2% B27, 1x GlutaMAX, 2 mg/ml heparin, 50 units/ml Penicillin/Streptomycin, 20 ng/ml purified mouse receptor-grade epidermal growth factor (EGF), and 20 ng/ml recombinant bovine fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2). Warm the culture medium to 37 °C in a water bath.
Protocol section 3.6 was changed from:
Add growth medium to a total volume of 5 ml and pass the cell suspension through a 40 mm sieve to remove debris and undissociated tissue clumps.
to:
Add growth medium to a total volume of 5 ml and pass the cell suspension through a 40 µm sieve to remove debris and undissociated tissue clumps.
Protocol section 3.7 was changed from:
Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min, discard the supernatant and resuspend the resulting pellet in 200 ml growth medium.
to:
Centrifuge at 300 x g for 5 min, discard the supernatant and resuspend the resulting pellet in 200 µl growth medium.
Protocol section 6.2 was changed from:
Add 50 ml Accutase and incubate at 37 °C for 2-3 min (checking to see if the cells are rounded and detached).
to:
Add 50 µl Accutase and incubate at 37 °C for 2-3 min (checking to see if the cells are rounded and detached).
Protocol section 6.6 was changed from:
For subsequent passages, resuspend cells in 200 ml growth medium and count using a hemocytometer. Plate at 1 x 104 cells/cm2 in the appropriate sized coated well or flask.
to:
For subsequent passages, resuspend cells in 200 µl growth medium and count using a hemocytometer. Plate at 1 x 104 cells/cm2 in the appropriate sized coated well or flask.
Protocol section 8.1 was changed from:
Dilute the dissociated SVZ or DG tissue from one animal in 20 ml of culture medium and plate 200 ml/well across a 96-well plate using a 10 ml multidoser pipette.
to:
Dilute the dissociated SVZ or DG tissue from one animal in 20 ml of culture medium and plate 200 µl/well across a 96-well plate using a 10 ml multidoser pipette.
Protocol section 9.1.6 was changed from:
Remove 10 ml of the cell suspension and mix with an equal volume of trypan blue and perform a live cell count using a hemocytometer.
to:
Remove 10 µl of the cell suspension and mix with an equal volume of trypan blue and perform a live cell count using a hemocytometer.
Protocol section 9.2.2 was changed from:
Add 100 ml of 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA to each well to be passaged and incubate at room temperature for 3 min.
to:
Add 100 µl of 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA to each well to be passaged and incubate at room temperature for 3 min.
Protocol section 9.2.5 was changed from:
Transfer the 200 ml containing the dissociated neurosphere to a new well of a 24-well plate containing 1.5 ml of growth medium. Incubate at 37 °C with 5% CO2 until secondary neurospheres form.
to:
Transfer the 200 µl containing the dissociated neurosphere to a new well of a 24-well plate containing 1.5 ml of growth medium. Incubate at 37 °C with 5% CO2 until secondary neurospheres form.
Figure 1 description was updated from:
Figure 1. Adult mouse precursor cells can be cultured as adherent monolayer cultures (A) or as neurospheres (B: SVZ, C: DG). Scale bar is 50 mm.
to:
Figure 1. Adult mouse precursor cells can be cultured as adherent monolayer cultures (A) or as neurospheres (B: SVZ, C: DG). Scale bar is 50 µm.
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。