需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
恢复成年斑马鱼的心脏的高通量应用
摘要
Use of zebrafish for cardiovascular research is expanding towards research on adult hearts. For these applications, quick and simple isolation of cardiac tissues is key to avoid post-mortem changes and to obtain an adequate number of samples. Here, we describe a fast and reproducible method for dissecting adult zebrafish hearts.
摘要
用于研究发育,再生,和疾病正在扩大向着使用成年心脏细胞解离和RNA,DNA和蛋白质的纯化使用斑马鱼模型系统。所有这些应用都需要显著数字斑马鱼的心的迅速恢复,以避免基因调控,代谢和死亡后开始发生转变。也需要研究心脏结构,适用于各种突变体和研究心脏再生的成年斑马鱼的心。然而,传统的斑马鱼心脏解剖是缓慢而艰难的,需要专门的工具,使得成年斑马鱼心中大规模清扫乏味。传统的方法也怀有解剖过程中损坏心脏的风险。在这里,我们描述的方法对成年斑马鱼解剖心中是快速,可重复,并保留心脏结构。此外,这种方法不需要专门的工具,是无痛的斑马鱼,可以在新鲜的或固定的标本进行的,并且可以对斑马鱼年仅一个月大进行。所描述的方法扩展了使用成年斑马鱼的心血管研究。
引言
Zebrafish are an excellent model for studying heart development and human disease1,2. Specific advantages include the translucent nature of zebrafish embryos, the availability of many genetic mutants and transgenic reporter lines, and the availability of genome editing technologies. In addition to their advantages for studying early heart development, zebrafish are an ideal system for studying vertebrate heart regeneration3.
More recently, adult zebrafish are playing an important part in bioinformatics approaches to studying cardiovascular development and disease, due to their relatively large clutch size and relatively quick and inexpensive breeding compared to other vertebrate models. Promising techniques include ribosome profiling, RNA-Seq, and cell dissociation and FACS sorting4-7. However, for these techniques the quality of the data can depend on obtaining a large number of samples in a rapid, efficient, and reproducible manner, before gene regulatory, metabolic, transcriptional, and other changes occur.
Dissection of adult zebrafish organs has been described in the past8,9. However, previous approaches to dissection of the heart were slow, ran the risk of damaging the heart during dissection, required special tools, and/or required fixation of the zebrafish prior to dissection; for these reasons, past approaches to zebrafish adult heart dissection were not optimized for high-throughput applications and/or applications requiring fresh tissue.
Here, we describe a method for adult zebrafish heart dissection that is simple, fast, efficient, and reproducible, while preserving cardiac morphology. This method does not include cutting into the pericardial space and therefore does not risk damaging the heart during dissection. Instead, this method relies on anatomical landmarks of the zebrafish, and therefore, it is highly reproducible. This dissection method is also versatile in that it can be used on fresh or fixed fish, and on zebrafish as young as one month old. Finally, this method results in minimal suffering to the zebrafish because after anesthesia and/or rapid cooling, the fish is additionally decapitated and pithed in the course of the dissection procedure.
研究方案
注:请始终确保IACUC或伦理委员会的批准到位开始使用斑马鱼的任何实验过程之前。
1.准备试剂和设置
- 准备了以下解决方案。找到食谱所有这些解决方案在标准的斑马鱼手册10。
- 500毫升蛋水
- 200毫升0.03%三卡因在水蛋
- 百毫升1X磷酸盐缓冲盐水的(PBS)中
- RBC裂解液(可选)
- 选择的(固定剂,Trizol试剂,PBS 等 ),在冰上1.5 ml离心管目标缓冲区
注意:固色剂和Trizol法是有毒的,如果他们接触到皮肤接触。处理这些物质时戴上手套。
- 准备剥离的设置:
- 定位鹅颈光源在解剖显微镜。放置在解剖显微镜阶段9厘米培养皿的盖子,并倒入一薄层的1×PBS的成它(盖被使用,因为盘本身过深为易于解剖)。
- 放置在培养皿本身(而不是盖)附近的解剖范围的台面和倒在它大约15毫升1X PBS的。使用此解剖后洗的心脏。另外,使用红细胞裂解液。
- 地方刀片,两对镊子,microscissors(可选),以及显微镜旁移液管。获得的冰的容器,如果安乐死通过快速冷却被选择。
- 倾200毫升0.03%三卡因的蛋水到250ml玻璃烧杯中,如果安乐死由三卡因被选择。准备一个小袋子生物危害处置斑马鱼的尸体。
2.准备斑马鱼
- 固定鱼,带来固定鱼,用PBS漂洗,在显微镜的设置。
- 安乐死迅速冷却用冰> 10分钟,整个成年斑马鱼。
- 使用镊子,使皮肤中的一个洞在腹膜(远离心脏),以帮助固定液的渗透,然后把它们放在4%多聚甲醛固定缓冲10 2小时在室温或O / N在4℃。
- 另外,对于鲜鱼,地方鱼被安乐死在小保持槽和带至显微镜设置。取决于个人设施的鱼协议和下游用途的解剖鱼心,用三卡因麻醉鱼或断头之前通过快速冷却安乐死。
- 用冰,拿起一条鱼的渔网,地点在冰水中待鱼停止移动,约5分钟。
- 可替代地,使用三卡因,拿起在溶液的烧杯1鱼用鱼网和地点直到鳃的动作停止。
- 赶快拿起安乐死的鱼其尾鳍,并将其放在其在培养皿盖被充满1X PBS的一面。使用镊子解除胸鳍用一只手,而使用razoř刀片用另一只手斩首鱼,只是后侧的胸鳍( 图1A)的附接。无论是看通过显微镜或干脆直接在显微镜舞台上可视化鱼执行此步骤。
注意:新鲜的鱼安乐死仍然将斩首后出血。
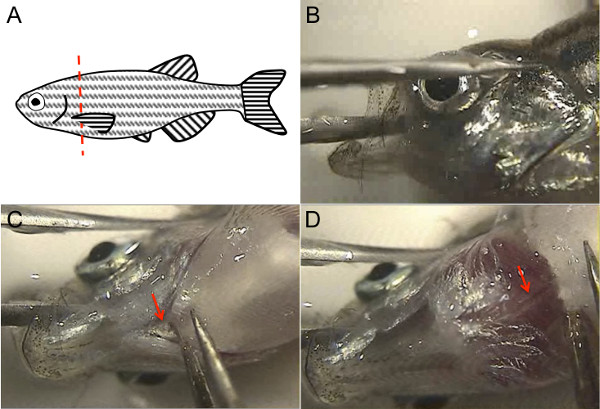
图1.斑马鱼成人心脏解剖利用斑马鱼解剖标志。 (一)要杀头鱼,解除胸鳍有镊子,用锋利的干净的刀片沿着红色虚线所示。(B)以稳定的鱼头,把镊子的一个叉在鱼嘴里一边其他齿在于整个眼睛,然后打开鱼嘴使腹面是和镊子的两个齿是稳定对培养皿底部。(C)使用免费FORCEPS切割厣(箭头)。(D)提升本的附件,背主动脉是白色结构,粉红色的条纹表示管腔血(箭头)可见。 请点击此处查看该图的放大版本。
3.解剖心
- 可视化在显微镜下鱼头。与一个钳,稳鱼嘴通过将钳子之一齿在鱼口,通过大脑,而另一叉是头部外,整个眼睛( 图1B)。确保钳子的两个尖齿是稳定对抗培养皿的底部。抱着鱼头这样一来,其腹面应朝上。
- 用另一只手,使用第2钳子切断厣腹侧附着到主体(箭头, 图1C)。用钳子轻轻抬起这一点,对Dorsal主动脉下方会出现一个白色的结构,血红色的条纹在主动脉管腔(箭头, 图1D)。切背主动脉与镊子捏住主动脉和向上拉;可替代地,可使用microscissors削减背主动脉。
- 现在,使用第2钳子从其基部把握胸鳍,包括主体软骨在翅片的基部,并解除这种关闭。重复与其他胸鳍。偶尔,心脏出来的胸鳍,所以研究这些作品,以确保心脏没有连接丢弃它们。
注意:在这一点,心脏应该是可见的,仍然完好无损并连接到其余鱼嘴(虽然偶尔它与胸鳍脱落)。的心脏可以通过它的形状,它的粉红色,而其正被着色的心包包围被识别。因为鱼的安乐死是快速执行,新鲜的鱼安乐死心中仍有可能击败SLOWLY。 - 放开鱼头与第一钳,使双手握住钳都是免费的。同时使用镊子挑逗的心脏远离心包。由背主动脉的剩余把握的心脏,而剩下的心包被拉走。
注意:无论是固定的还是新鲜的,心脏是强大的,以温和的拉动,而周围的结缔组织更加易碎。因此,任何周围的心包组织可走解剖与心脏保持完整。 - 丢弃剩下的鱼胴体在生物危害袋中。
4.准备心下游应用
- 使用镊子,由背主动脉/浙动脉边缘把握的心脏,并将心脏在1X PBS的新鲜菜。另外,用移液管。将心脏来回在PBS约10倍,以洗去尽可能多的血越好。
- 对于应用,其中以除去所有possib是很重要勒血细胞,洗涤,并在9厘米培养皿用15ml的RBC裂解缓冲液代替PBS中,使用相同的背面的往复运动。如果保留了心脏的结构是不适合下游应用的重要( 例如,使得RNA),可以使用钳子或microscissors打开心脏腔和促进漂洗程的血细胞。
- 对于应用程序中单独心脏室所需,使用产钳或microscissors从对方解剖延髓动脉,心房,心室和分开。
- 心脏,或单独室,传输到目标缓冲区冰上。
注:常见的目的地包括缓冲区细胞分离,4%多聚甲醛,或Trizol法。
结果
使用这种方法,一个成年人斑马鱼心脏可以解剖在不到1分钟,相比于在5分钟内用传统方法8。心中使用这种方法解剖是可靠完整( 图2A),而传统的方法需要8盲目削减入心包,因此通常导致心房或延髓动脉( 图2B)的损坏或丢失。心切开保持它们的结构完整性,并适合用于组织学( 图2C),电子显微镜( 图2D),以及用于应用的...
讨论
而对于解剖成年斑马鱼心脏的方法已被描述的,这些方法是耗时的,而且经常造成夹层期间对心脏的损伤。执行实验中,可能需要大量的成人心,和/或当避免心脏组织的降解是用于下游应用重要,用传统的剥离工艺所需要的时间是令人望而却步。同样,重复获得完好的,完整的心是心脏结构的研究及免疫组化和显微镜方法很重要。我们发现,即使在初学者的手中,心切开的100%回收得到结构完整...
披露声明
The authors have no disclosures.
致谢
The authors would like to thank Dr. Shaun Coughlin for hosting the filming of this procedure in his laboratory, and for general support. R.A. was supported by the NIH (F32HL110489) and the Sarnoff Cardiovascular Research Foundation. S.R. was supported by a Research Fellowship of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and the American Heart Association (AHA). D.Y.R.S was supported by the NIH (RO1HL54737), the Packard Foundation, and the Max Planck Society.
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Small tank for transporting fish | Aquaneering | ZHCT100 | |
| Fish net | Petsmart | 36-16731 | |
| 250 ml glass beaker | Kimble | 14005-250 | |
| 9 cm polystyrene Petri dish | Nunc | 172958 | |
| Razor blade | Personna American Safety Razor Company | 94-120-71 | |
| 2 Dumont #5SF forceps | Fine Science Tools | 11252-00 | |
| Dissecting microscope | Olympus | SZX16 | |
| Tricaine | Sigma | A-5040 | |
| Plastic transfer pipette | Thermo Scientific | 202-20S | |
| Gooseneck light source | Dolan-Jenner Industries, Inc | Fiber-Lite 180 Illuminator, 181 Dual Gooseneck System | |
| Fluorescent light source | Lumen Dynamics | X-Cite 120Q | optional |
| Micro-scissors | Biomedical Research Instruments, Inc | 11-1000 | optional |
| RBC lysis buffer | eBioscience | 00-4333-57 | optional |
参考文献
- Arnaout, R., et al. Zebrafish model for human long QT syndrome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (27), 11316-11321 (2007).
- Chi, N. C., et al. Genetic and physiologic dissection of the vertebrate cardiac conduction system. PLoS Biology. 6 (5), 109 (2008).
- Poss, K. D. Getting to the heart of regeneration in zebrafish. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 18 (1), 36-45 (2007).
- Fang, Y., et al. Translational profiling of cardiomyocytes identifies an early Jak1/Stat3 injury response required for zebrafish heart regeneration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (33), 13416-13421 (2013).
- Manoli, M., Driever, W. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of fluorescently tagged cells from zebrafish larvae for RNA isolation. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2012 (8), (2012).
- Cannon, J. E., et al. Global analysis of the haematopoietic and endothelial transcriptome during zebrafish development. Mechanisms of Development. 130 (2-3), 122-131 (2013).
- Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nature Reviews Genetics. 10 (1), 57-63 (2009).
- Gupta, T., Mullins, M. C. Dissection of organs from the adult zebrafish. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 37, (2010).
- Singleman, C., Holtzman, N. G. Heart dissection in larval, juvenile and adult zebrafish, Danio rerio. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 55, (2011).
- Westerfield, M. . The zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio. , (1993).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。