需要订阅 JoVE 才能查看此. 登录或开始免费试用。
Method Article
眼柄消融术可增加泥蟹卵巢成熟
Erratum Notice
摘要
对麻醉的雌蟹进行了两种眼柄消融方案(即烧灼和 手术方法)。泥蟹的眼柄消融加速了卵巢的成熟,而不会降低存活率。
摘要
泥蟹(Scylla spp.)是具有重要商业价值的甲壳类动物,遍布印度-西太平洋地区。在养殖过程中,诱导卵巢成熟对于满足消费者对成熟泥蟹的需求和加速种子生产非常重要。眼柄消融术是促进泥蟹卵巢成熟的有效工具。然而,泥蟹的眼柄消融没有标准方案。在这项研究中,描述了两种眼柄消融技术:烧灼(使用热金属消融麻醉蟹的眼柄)和手术(使用手术剪刀去除眼柄)。在眼柄消融术之前,性成熟的雌性(CW > 86 mm)使用装有海水的冰袋(-20°C)麻醉。当水温达到4°C时,将冰袋从水中取出。流海水(环境温度:28°C)用于眼柄消融后立即从麻醉中恢复。在眼柄消融过程中或之后没有发生死亡。这里介绍的眼柄消融方案加速了泥蟹的卵巢成熟。
引言
属于Scylla属的所有四种泥蟹物种都是水产养殖中具有重要商业价值的甲壳类物种1,2。甲壳类动物(包括泥蟹)的生长及其从早熟(亚成体或青春期)阶段到性成熟(成年)阶段的转变是通过蜕皮过程发生的,该过程涉及较老和较小的外骨骼的周期性脱落。甲壳宽度 (CW)、螯部和腹部瓣形态被广泛用于确定镰刀属的性成熟度。3,4,5.蜕皮过程受各种激素的作用调节,需要大量的能量6。除了正常的蜕皮过程外,肢体的丧失,无论是自愿的还是由外部因素引起的,都会加速螃蟹的蜕皮,而不会影响它们的存活率7,8,9。因此,肢体自体切开术常用于软壳泥蟹养殖业的蜕皮诱导7,9。
单侧或双侧眼柄消融术在淡水虾和海虾中最为流行,用于性腺成熟和苗种生产10,11,12,13。甲壳类动物中常见的眼柄消融技术包括:(i)使用绳子14,15在眼柄底部结扎;(ii)使用热镊子或电灼装置烧灼眼柄16;(iii) 去除或直接捏住眼柄以留下开放性伤口12;(iv)用剃刀切开眼睛的远端部分后,通过切口去除眼柄内容物17.眼柄X器官是甲壳类动物中重要的内分泌器官,因为它们调节甲壳类动物的高血糖激素(CHH),蜕皮抑制激素(MIH)和玻璃体生成抑制激素(VIH)6,18,19,20,21,22。眼柄X器官(或窦腺复合物)合成并释放性腺抑制激素(GIH),也称为玻璃体生成抑制激素(VIH),属于神经肽激素家族6。单侧或双侧眼柄消融术可减少GIH合成,导致刺激激素(即促性腺激素,GSH)占主导地位,并加速甲壳类动物卵巢成熟过程23,24,25,26。没有眼柄消融后GIH的影响,雌性甲壳类动物将精力用于卵巢发育27。已经发现,单侧眼柄消融足以诱导甲壳类动物卵巢成熟11,虾和蟹的消融眼柄在几次蜕皮后可以再生28。Scylla spp.记录了四个卵巢发育阶段:i)未成熟(阶段-1),ii)早熟(阶段-2),iii)早熟(阶段-3)和iv)完全成熟(阶段-4)29,30。未成熟的卵巢阶段见于未成熟的女性。在青春期蜕皮和交配后,未成熟的卵巢开始发育并最终成熟(第 4 阶段),然后产卵31。
眼柄消融方案对于泥蟹亲鱼的发育和苗种生产至关重要。在全球食品市场中,具有完全成熟卵巢(第4阶段)的成熟泥蟹而不是肌肉含量较高的螃蟹受到消费者的青睐,因此具有更高的商业价值,甚至高于大型雄性。泥蟹的眼柄消融没有完整的方案。这项工作中的眼柄消融方案通过使用完全麻醉的螃蟹来最大限度地减少压力,并最大限度地减少螃蟹咬伤对人员的身体伤害。该协议简单且具有成本效益。在这里,我们提出了一种可以诱导性腺成熟的 Scylla spp .眼柄消融方案。测试了两种眼柄消融技术(烧灼和手术),并根据雌性泥蟹的性腺发育速度比较了它们的效率。
研究方案
该协议遵循马来西亚实验动物科学协会概述的马来西亚科学用途护理和使用动物行为守则。实验样品的牺牲是根据美国国立卫生研究院实验动物护理和使用指南(NIH出版物第8023号,1978年修订)进行的。性早熟雌性泥蟹(橙泥蟹 S. olivacea)是从马来西亚Setiu湿地的当地市场(5°66′62′′N,102°72′33′′E)收集的。根据形态特征鉴定泥蟹种类1.
1. 样本采集和消毒
- 收集健康,活跃和早熟的雌性泥蟹(图1)。
注意:早熟雌蟹具有三角形和浅色腹部瓣,CW范围为80-85毫米。 - 用氯化自来水(淡水)清洗螃蟹,以去除碎屑和嗜渗透寄生虫。
- 将螃蟹浸泡在150 ppm甲醛和20 ppt盐度中30分钟。
- 在甲醛处理过程中,用空气石保持连续温和的曝气。曝气源可以来自中央曝气管线或水族箱曝气泵。
- 用流动的海水清洗螃蟹,去除残留的甲醛。
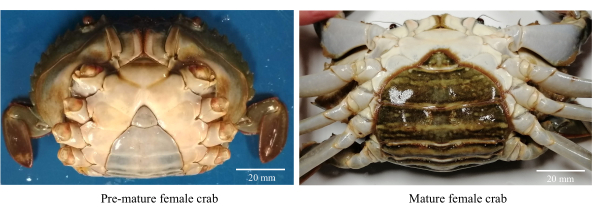
图1:用于识别性成熟阶段的雌性泥蟹的腹部形态。 请点击此处查看此图的大图。
2. 适应环境
- 将每个消毒的女性转移到单独的 32 L 圆形水箱中。
- 以20 ppt盐度饲养雌鱼3天,每天继续喂食两次(早上09:00和晚上20:00),切碎的海鱼约占螃蟹体重的4%-5%。
- 在早晨喂食前通过虹吸去除多余的和未食用的饲料。
- 每天交换10%的螃蟹养殖海水(20 ppt)。
3.诱导蜕皮促进性成熟
- 用消毒剪刀剪掉除游泳腿以外的所有腿。
- 用勺网捕捉螃蟹,并小心握住螃蟹。先剪两个螯部,然后用剪刀在第二个关节处剪下行走腿。螃蟹会自动切割损坏的附属物。肢体自体切开术不需要麻醉。
- 肢体自体切断后立即用淡水清洗螃蟹。
- 将肢体自动切开的螃蟹单独转移到穿孔塑料篮(28 厘米长 x 22 厘米宽 x 7 厘米高)中,并将它们放入玻璃纤维罐(305 厘米长 x 120 厘米宽 x 60 厘米高)。
注意:两个篮子可以绑在一起。顶部篮子用作盖子,使螃蟹无法从篮子中逃脱。 - 使用盐度为20 ppt、水深至少为10厘米的循环水产养殖系统(RAS),以确保整个塑料篮被淹没。
- 继续每天两次用切碎的海鱼喂养肢体自动切开的雌蟹,体重为螃蟹体重的5%-7%。
- 饲养螃蟹,直到通过蜕皮(35天)进行性成熟。
注意:对于商业卵巢成熟和野生成熟雌性泥蟹的种子生产,可以跳过诱导蜕皮。从野外收获的成熟雌性必须适应环境,并直接接受冷休克麻醉和随后的眼柄消融。
4. 麻醉
- 选择性成熟的女性,腹瓣呈深色椭圆形,CW >86 mm(图1)。
- 用勺网捕捉螃蟹,并将它们单独保存在小水族箱中进行麻醉。
- 适应期5分钟后,向每个水族箱中加入2-苯氧乙醇(2-PE),并允许15分钟的麻醉治疗。
- 确保螃蟹因缺乏自发运动而完全麻醉。
5. 眼柄消融术
- 烧灼技术
- 在桌子顶部和开放区域执行所有程序。
- 取一根带有木制或塑料手柄的平头镍钢金属棒(例如螺丝刀),并用湿棉毛巾盖住手柄。
- 在高压灭菌器中对两个不锈钢手术钳进行消毒。
- 在喷雾瓶中准备70%乙醇,使其远离任何与火灾相关的来源,例如喷灯和红色热螺丝刀。准备好薄纸。
注意:乙醇是高度易燃的。与火源保持安全距离。 - 将喷灯牢固地连接到气瓶(丁烷)。
注意:按照喷灯和气瓶上的说明进行操作。确保在与气瓶连接时关闭喷灯。阅读并遵守气瓶上提到的所有消防安全预防措施。 - 戴上厚棉手套,以免被热物伤害。
- 将金属棒的尖端置于喷灯的火焰下,直到金属棒呈鲜红色。
- 用湿棉巾盖住麻醉的螃蟹。
注意:盖住螃蟹的触角,以免造成不必要的损坏。 - 用消毒的镊子握住螃蟹的一只眼睛。
注意:在高压灭菌器中对镊子进行消毒以供首次使用,并使用70%乙醇消毒,以便随后用于其他螃蟹。 - 将炽热的金属扁尖放在蟹眼上,轻轻按压约10-15秒,直到眼柄变成橙色或红橙色。执行此步骤时要小心,以免损坏相邻结构。
注意:按照烧灼方法执行眼柄消融术需要两个人:一个握住螃蟹,另一个人执行消融程序。 - 用70%乙醇喷雾消毒镊子,以确保螃蟹之间没有交叉污染。
注意:仅在眼柄消融程序后至少等待5分钟执行此步骤,以确保在使用70%乙醇消毒之前将镊子冷却,以防止潜在的火灾危险。 - 对所有螃蟹进行眼柄消融后,将热镍钢金属棒(螺丝刀)浸入自来水中。
- 重复使用前对毛巾进行消毒。可以使用多条毛巾以节省时间。
注意:用自来水清洗毛巾,然后将其浸入30 ppm氯化水中5分钟。然后,再次用自来水清洗毛巾,并将其浸入1 g / L硫磺酸钠溶液中。 - 关闭喷灯后,将喷灯放在安全的地方,等到它恢复到环境温度(约30分钟)后再断开连接。
- 手术技术
- 在通风良好的地方执行该程序。
- 在高压灭菌器中对两把手术剪刀和镊子进行消毒。
- 将 50 mL 70% 乙醇倒入 100 mL 玻璃烧杯中。
- 戴厚棉手套。
- 握住麻醉的螃蟹,用湿棉巾盖住。
- 用消毒的镊子握住螃蟹的一只眼睛。
- 用消毒的手术剪刀迅速切断眼柄。
注意:螃蟹受伤部位的血淋巴可能会丢失。 - 每次使用后将剪刀和镊子浸入70%乙醇中,并在重复使用前使用薄纸将其擦干。
6. 麻醉后护理
- 准备20 ppt过滤海水,并保存在具有连续曝气的头顶水箱中。
- 将柔性管道与高架水箱连接,以实现重力水流。
- 眼柄消融后,立即将螃蟹放入篮子中,并将螃蟹置于来自头顶水箱的流动海水(环境水温:28°C)中。
- 保持海水流动,并监测螃蟹,直到它可以自发移动,这表明从麻醉中恢复。
注意:海水可以在地下水箱中制备,潜水水泵可用于水流。 - 将螃蟹单独保存在20 ppt海水中,并在水族箱中曝气30分钟,以便进一步观察。
注意:回收的螃蟹将在随后的亲鱼养殖过程中单独养殖。
7.卵巢成熟的观察
- 亲鱼养殖
- 将成熟的螃蟹转移到单独的32升圆形水箱中。
- 继续每天两次(早上09:00上午和晚上20:00下午)用切碎的海鱼(在-20°C冷冻)喂食,并在早晨喂食前去除未食用的饲料。
- 以20 ppt盐度单独饲养亲鱼30天。
- 清除粪便,每天交换10%的海水(20 ppt)。
- 解剖
- 用 70% 乙醇清洁解剖托盘、剪刀和镊子。
- 用2-PE浸没麻醉方法单独麻醉女性。
- 随机选择未经过眼柄消融术的新成熟雌性(早熟雌性蜕皮后)以确认其性腺阶段。
- 单独牺牲所有眼柄消融的实验雌性,并确定性腺成熟阶段。使用锋利的无菌锥子破坏螃蟹的胸神经节。首先去除顶部甲壳,然后去除肝胰腺,使卵巢可见。观察卵巢颜色,并确定卵巢成熟阶段(图2)。
- 卵巢成熟阶段识别
- 用肉眼或在体视显微镜下观察卵巢颜色。
- 根据着色30识别卵巢成熟阶段:未成熟(阶段-1)呈现半透明或乳白色;早熟(第2阶段)呈淡黄色至浅黄色;(iii)预成熟(第3阶段)呈黄色至浅橙色;(iv)完全成熟(第4阶段)呈现深橙色至红色。
结果
性腺成熟
在进行眼柄消融术之前,在100%的解剖女性(n = 6)中发现了乳白色的卵巢组织(未成熟的卵巢,1期)(图2)。与未进行眼柄消融的雌蟹相比,眼柄消融的雌蟹(n = 63;烧灼技术为31只雌蟹,手术技术为32只雌蟹)的性腺成熟率高于未进行眼柄消融的雌蟹(n = 31)(图3)。在眼柄消融的雌蟹中发现的早熟卵巢百分比最高(第3阶段?...
讨论
该方案是为泥蟹 Scylla spp .的眼柄消融而开发的,可以作为诱导性腺成熟的有效方法。该方案可以很容易地复制用于泥蟹的商业卵巢成熟,并且可以实施以减少泥蟹种子生产中的潜伏期(从一个产卵到另一个产卵的时间)。
甲壳类动物(即淡水虾、海虾)的眼柄消融通常是为了诱导性腺成熟和反季节产卵11,12,
披露声明
作者均无任何利益冲突。
致谢
这项研究得到了马来西亚教育部的支持,在马来西亚高等院校卓越中心(HICoE)计划下,获得了马来西亚登嘉楼大学热带水产养殖和渔业研究所的认可(Vot No. 63933和Vot No. 56048)。我们感谢马来西亚登嘉楼大学和Sayap Jaya私人有限公司通过私人伙伴关系研究基金(Vot.No. 55377) 提供 的支持。马来西亚理科大学到Khor Waiho和Hanafiah Fazhan的兼职学术研究员职位也得到了认可。
材料
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Aeration tube | Ming Yu Three | N/A | aquarium and pet shop |
| Airstone | Ming Yu Three | N/A | aquarium and pet shop |
| Autoclave machine | HIRAYAMA MANUFACTURING CORPORATION | N/A | MADE IN JAPAN |
| Bleaching powder (Hi-Chlon 70%) | Nippon Soda Co.Ltd,Japan | N/A | N/A |
| Blow torch | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Circular tank (32L) | BEST PLASTIC INDUSTRY SDN. BHD. | N/A | N/A |
| Cotton hand gloves (thick) | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Cotton towel | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Digital thermometer | Hanna Instrument | HI9814 | Hanna Instruments GroLine Hydroponics Waterproof pH / EC / TDS / Temp. Portable Meter HI9814 |
| Digital Vernier Caliper | INSIZE Co., Ltd. | N/A | |
| Dissecting tray | Hatcheri AKUATROP | N/A | Research Center of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu |
| Dropper bottle/Plastic Pipettes Dropper | Shopee Malaysia | N/A | N/A |
| Ethanol 70% | Thermo Scientific Chemicals | 033361.M1 | Diluted to 70% using double distilled water |
| Fiberglass tank (1 ton) | Hatcheri AKUATROP | N/A | Research Center of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu |
| Fine sand | N/A | N/A | collected from Sea beach of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu |
| First Aid Kits | Watsons Malaysia | N/A | N/A |
| Flat head nickel steel metal rod (Screw driver) | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Formaldehyde | Thermo Scientific Chemicals | 119690010 | |
| Gas cylinder (butane gas) for blow torch | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Gas lighter gun (long head) | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Glass beaker (100 mL)) | Corning Life Sciences | 1000-100 | |
| Ice bag | Watsons Malaysia | N/A | N/A |
| Perforated plastic baskets | Eco-Shop Marketing Sdn. Bhd. | N/A | N/A |
| PVC pipe 15mm | Bina Plastic Industries Sdn Bhd (HQ) | N/A | N/A |
| Refractometer | ATAGO CO.,LTD. | ||
| Refrigerator | Sharp Corporation Japan | N/A | Chest Freezer SHARP 110L - SJC 118 |
| Scoop net | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | |
| Seawater | Hatcheri AKUATROP | N/A | Research Center of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu |
| Siphoning pipe | MR D.I.Y. Group Berhad | N/A | N/A |
| Spray bottle | Mr. DIY Sdn Bhd | N/A | N/A |
| Stainless surgical forceps | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Stainless surgical scissors | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Submersible water pump | AS | N/A | model: Astro 4000 |
| Tincture of iodine solution (Povidone Iodine) | Farmasi Fajr Sdn Bhd | N/A | N/A |
| Tissue paper | N/A | N/A | |
| Transparent plastic aquarium | Ming Yu Three | N/A | aquarium and pet shop |
| Waterproof table | Hatcheri AKUATROP | N/A | Research Center of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu |
参考文献
- Keenan, C. P., Davie, P. J. F., Mann, D. L. A revision of the genus Scylla de Haan, 1833 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunidae). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 46 (1), 217-245 (1998).
- Fazhan, H., et al. Morphological descriptions and morphometric discriminant function analysis reveal an additional four groups of Scylla spp. PeerJ. 8, e8066 (2020).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Hilmi, M. G., Azmie, G., Zakaria, M. Z. Species diversity, carapace width-body weight relationship, size distribution and sex ratio of mud crab, genus Scylla from Setiu Wetlands of Terengganu coastal waters Malaysia. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 97-109 (2010).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Mohd Faizal, W. W. Y., Azmie, G., Abol-Munafi, A. B. Size of maturity of mud crab Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) from mangrove areas of Terengganu coastal waters. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 134-147 (2010).
- Waiho, K., et al. On types of sexual maturity in brachyurans, with special reference to size at the onset of sexual maturity. Journal of Shellfish Research. 36 (3), 807-839 (2017).
- Mykles, D. L., Chang, E. S. Hormonal control of the crustacean molting gland: Insights from transcriptomics and proteomics. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 294, 113493 (2020).
- Fujaya, Y., et al. Is limb autotomy really efficient compared to traditional rearing in soft-shell crab (Scylla olivacea) production. Aquaculture Reports. 18, 100432 (2020).
- Waiho, K., et al. Moult induction methods in soft-shell crab production. Aquaculture Research. 52 (9), 4026-4042 (2021).
- Rahman, M. R., et al. Evaluation of limb autotomy as a promising strategy to improve production performances of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) in the soft-shell farming system. Aquaculture Research. 51 (6), 2555-2572 (2020).
- Okumura, T., et al. Expression of vitellogenin and cortical rod proteins during induced ovarian development by eyestalk ablation in the kuruma prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 143 (2), 246-253 (2006).
- Pervaiz, P. A., Jhon, S. M., Sikdar-bar, M. Studies on the effect of unilateral eyestalk ablation in maturation of gonads of a freshwater prawn Macrobrachium dayanum. World Journal of Zoology. 6 (2), 159-163 (2011).
- Primavera, J. H. Induced maturation and spawning in five-month-old Penaeus monodon Fabricius by eyestalk ablation. Aquaculture. 13 (4), 355-359 (1978).
- Shyne Anand, P. S., et al. Reproductive performance of wild brooders of Indian white shrimp, Penaeus indicus: Potential and challenges for selective breeding program. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 65 (2019).
- Diarte-Plata, G., et al. Eyestalk ablation procedures to minimize pain in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 140 (3-4), 172-178 (2012).
- Vargas-Téllez, I., et al. Impact of unilateral eyestalk ablation on Callinectes arcuatus (Ordway, 1863) under laboratory conditions: Behavioral evaluation. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research. 49 (4), 576-594 (2021).
- Chu, K. H., Chow, W. K. Effects of unilateral versus bilateral eyestalk ablation on molting and growth of the shrimp, Penaeus chinensis Osbeck, 1765) (Decapoda, Penaeidea). Crustaceana. 62 (3), 225-233 (1992).
- Taylor, J. Minimizing the effects of stress during eyestalk ablation of Litopenaeus vannamei females with topical anesthetic and a coagulating agent. Aquaculture. 233 (1-4), 173-179 (2004).
- Wang, M., Ye, H., Miao, L., Li, X. Role of short neuropeptide F in regulating eyestalk neuroendocrine systems in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 560, 738493 (2022).
- Nagaraju, G. P. C. Reproductive regulators in decapod crustaceans: an overview. Journal of Experimental Biology. 214 (1), 3-16 (2011).
- Kornthong, N., et al. Characterization of red pigment concentrating hormone (RPCH) in the female mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and the effect of 5-HT on its expression. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 185, 28-36 (2013).
- Kornthong, N., et al. Molecular characterization of a vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone (VIH) in the mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and temporal changes in abundances of VIH mRNA transcripts during ovarian maturation and following neurotransmitter administration. Animal Reproduction Science. 208, 106122 (2019).
- Liu, C., et al. VIH from the mud crab is specifically expressed in the eyestalk and potentially regulated by transactivator of Sox9/Oct4/Oct1. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 255, 1-11 (2018).
- Chen, H. -. Y., Kang, B. J., Sultana, Z., Wilder, M. N. Variation of protein kinase C-α expression in eyestalk removal-activated ovaries in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 237 (300), 110552 (2019).
- Rotllant, G., Nguyen, T. V., Aizen, J., Suwansa-ard, S., Ventura, T. Toward the identification of female gonad-stimulating factors in crustaceans. Hydrobiologia. 825 (1), 91-119 (2018).
- Supriya, N. T., Sudha, K., Krishnakumar, V., Anilkumar, G. Molt and reproduction enhancement together with hemolymph ecdysteroid elevation under eyestalk ablation in the female fiddler crab, Uca triangularis (Brachyura: Decapoda). Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology. 35 (3), 645-657 (2017).
- Wilder, M. N. Advances in the science of crustacean reproductive physiology and potential applications to new seed production technology. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 6-10 (2019).
- Arcos, G. F., Ibarra, A. M., Vazquez-Boucard, C., Palacios, E., Racotta, I. S. Haemolymph metabolic variables in relation to eyestalk ablation and gonad development of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Boone. Aquaculture Research. 34 (9), 749-755 (2003).
- Desai, U. M., Achuthankutty, C. T. Complete regeneration of ablated eyestalk in penaeid prawn, Penaeus monodon. Current Science. 79 (11), 1602-1603 (2000).
- Wu, Q., et al. Growth performance and biochemical composition dynamics of ovary, hepatopancreas and muscle tissues at different ovarian maturation stages of female mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 515, 734560 (2020).
- Ghazali, A., Azra, M. N., Noordin, N. M., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian morphological development and fatty acids profile of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) fed with various diets. Aquaculture. 468 (Part 1), 45-52 (2017).
- Farhadi, A., et al. The regulatory mechanism of sexual development in decapod crustaceans. Frontiers in Marine Science. 8, (2021).
- Sukardi, P., Prayogo, N. A., Harisam, T., Sudaryono, A. Effect of eyestalk-ablation and differences salinity in rearing pond on molting speed of Scylla serrata. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2094, 020029 (2019).
- Stella, V. S., López Greco, L. S., Rodríguez, E. M. Effects of eyestalk ablation at different times of the year on molting and reproduction of the estuarine grapsid crab Chasmagnathus granulata (Decapoda, Brachyura). Journal of Crustacean Biology. 20 (2), 239-244 (2000).
- Jang, I. K., et al. The effects of manipulating water temperature, photoperiod, and eyestalk ablation on gonad maturation of the swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus. Crustaceana. 83 (2), 129-141 (2010).
- Millamena, O. M., Quinitio, E. The effects of diets on reproductive performance of eyestalk ablated and intact mud crab Scylla serrata. Aquaculture. 181 (1-2), 81-90 (2000).
- Zeng, C. Induced out-of-season spawning of the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain (Estampador) and effects of temperature on embryo development. Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1478-1485 (2007).
- Rana, S. Eye stalk ablation of freshwater crab, Barytelphusa lugubris: An alternative approach of hormonal induced breeding. International Journal of Pure and Applied Zoology. 6 (3), 30-34 (2018).
- Yi, S. -. K., Lee, S. -. G., Lee, J. -. M. Preliminary study of seed production of the Micronesian mud crab Scylla serrata (Crustacea: Portunidae) in Korea. Ocean and Polar Research. 31 (3), 257-264 (2009).
- Azra, M. N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of broodstock improvement to brachyuran crab: Reproductive performance. International Journal of Aquaculture. 5 (38), 1-10 (2016).
- Archibald, K. E., Scott, G. N., Bailey, K. M., Harms, C. A. 2-phenoxyethanol (2-PE) and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) immersion anesthesia of American horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus). Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. 50 (1), 96-106 (2019).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of steroid hormones 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone on ovary external morphology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea. Asian Journal of Cell Biology. 9 (1), 23-28 (2013).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of vertebrate steroid hormones on the ovarian maturation stages of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796). Aquaculture. 451, 78-86 (2016).
- Ghazali, A., Mat Noordin, N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian maturation stages of wild and captive mud crab, Scylla olivacea fed with two diets. Sains Malaysiana. 46 (12), 2273-2280 (2017).
- Aaqillah-Amr, M. A., Hidir, A., Noordiyana, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Morphological, biochemical and histological analysis of mud crab ovary and hepatopancreas at different stages of development. Animal Reproduction Science. 195, 274-283 (2018).
- Amin-Safwan, A., Muhd-Farouk, H., Mardhiyyah, M. P., Nadirah, M., Ikhwanuddin, M. Does water salinity affect the level of 17β-estradiol and ovarian physiology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) in captivity. Journal of King Saud University - Science. 31 (4), 827-835 (2019).
- Wu, X., et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of phospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductive performance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock. Aquaculture. 273 (4), 602-613 (2007).
- Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of maturation diets for mud crab genus Scylla broodstock: Present research, problems and future perspective. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 23 (2), 257-267 (2016).
- Maschio Rodrigues, M., López Greco, L. S., de Almeida, L. C. F., Bertini, G. Reproductive performance of Macrobrachium acanthurus (Crustacea, Palaemonidae) females subjected to unilateral eyestalk ablation. Acta Zoologica. 103 (3), 326-334 (2022).
- Zhang, C., et al. Changes in bud morphology, growth-related genes and nutritional status during cheliped regeneration in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. PLoS One. 13 (12), e0209617 (2018).
- Zhang, C., et al. Hemolymph transcriptome analysis of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with intact, left cheliped autotomy and bilateral eyestalk ablation. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 81, 266-275 (2018).
- Diarte-Plata, G., Sainz-Hernandez, J. C., Aguiñaga-Cruz, J. A., Fierro-Coronado, J. A., Polanco-Torres, A., Puente-Palazuelos, C. Eyestalk ablation procedures to minimize pain in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 130 (3-4), 172-178 (2012).
- Mirera, D. O., Moksnes, P. O. Comparative performance of wild juvenile mud crab (Scylla serrata) in different culture systems in East Africa: Effect of shelter, crab size and stocking density. Aquaculture International. 23 (1), 155-173 (2015).
- Ut, V. N., Le Vay, L., Nghia, T. T., Hong Hanh, T. T. Development of nursery cultures for the mud crab Scylla paramamosain (Estampador). Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1563-1568 (2007).
- Fazhan, H., et al. Limb loss and feeding ability in the juvenile mud crab Scylla olivacea: Implications of limb autotomy for aquaculture practice. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 247, 105553 (2022).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs
Posted by JoVE Editors on 5/26/2023. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Eyestalk Ablation to Increase Ovarian Maturation in Mud Crabs. The Introduction, Protocol, Discussion and References were updated.
The forth sentence in the third paragraph of the Introduction has been updated from:
The eyestalk ablation protocol in this work minimizes stress by using fully sedated crabs and minimizes physical injury to personnel from crab bites.
to:
The eyestalk ablation protocol in this work minimizes stress by using fully anesthetized crabs and minimizes physical injury to personnel from crab bites.
The start of the Protocol has been updated from:
This protocol follows the Malaysian Code of Practice for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes outlined by the Laboratory Animal Science Association of Malaysia. The sacrifice of the experimental samples was done according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978). Sexually pre-mature female mud crabs (orange mud crab S. olivacea) were collected from the local market (5°66′62′′N, 102°72′33′′E) at the Setiu Wetlands in Malaysia. The mud crab species was identified based on morphological characteristics1.
to:
This protocol follows the Malaysian Code of Practice for the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes outlined by the Laboratory Animal Science Association of Malaysia and was approved by the Universiti Malaysia Terengganu's Research Ethics Committee (Animal ethics approval number: UMT/JKEPHMK/2023/96). The sacrifice of the experimental samples was done according to the AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition. Sexually pre-mature female mud crabs (orange mud crab Scylla olivacea) were collected from the local market (5°66′62′′N, 102°72′33′′E) at the Setiu Wetlands in Malaysia. The mud crab species was identified based on morphological characteristics1.
Section 4 of the Protocol has been updated from:
4. Cold-shock anesthesia
- Select sexually mature females with a dark-colored oval-shaped abdominal flap with a CW >86 mm (Figure 1).
- Catch the crabs with a scoop net, and keep them individually in small aquariums for cold shock anesthesia.
- Prepare 2 L of 4 °C to 1 °C seawater (20 ppt) in a transparent plastic aquarium. Maintain the temperature using (−20 °C) ice bags for cold shock anesthesia.
NOTE: Check the temperature with a digital thermometer. - Immerse the crab in the 4 °C seawater until sedated (about 3−5 min).
- Ensure the crabs are fully anesthetized by the lack of spontaneous movement. The legs and chelipeds joints will still show minor movements when touched with forceps.
to:
4. Anesthesia
- Select sexually mature females with a dark-colored oval-shaped abdominal flap with a CW >86 mm (Figure 1).
- Catch the crabs with a scoop net, and keep them individually in small aquariums for anesthesia.
- After 5 min of acclimatization period, add 2-phenoxyethanol (2-PE) at 2 mL/L into each aquarium and allow 15 min of anesthesia treatment.
- Ensure the crabs are fully anesthetized by the lack of spontaneous movement.
Section 5 of the Protocol has been updated from:
5. Eyestalk ablation
- Cauterization technique
- Perform all procedures on top of a table and in an open area.
- Take a flat head nickel-steel metal rod (e.g., a screwdriver) with a wooden or plastic handle, and cover the handle with a wet cotton towel.
- Sterilize two stainless surgical forceps in an autoclave.
- Prepare 70% ethanol in a spray bottle. Have tissue paper ready for use.
NOTE: Ethanol is highly flammable. Maintain a safe distance from fire sources. - Connect a blowtorch to a gas cylinder (butane) securely.
CAUTION: Follow the instructions on the blowtorch and gas cylinder. Make sure that the blowtorch is switched off when connecting with the gas cylinder. Read and follow all the fire safety precautions mentioned on the gas cylinder. - Wear thick cotton gloves to avoid injury from hot objects.
- Subject the tip of the metal rod to the fire of the blowtorch until the metal rod is bright red.
- Cover the anesthetized (sedated) crab with a wet cotton towel.
NOTE: Cover all the tentacles of the crab to avoid unnecessary damage. - Hold one eye of the crab with sterilized forceps.
NOTE: Sterilize the forceps in an autoclave for first-time use, and disinfect using 70% ethanol for subsequent use on other crabs. - Hold the red-hot metal flat tip onto the eye of the crab and press slightly for about 10−15 s until the eyestalk turns an orange or reddish-orange color.
NOTE: Two people are needed to execute eyestalk ablation following the cauterization method: one to hold the crab and another to perform the ablation procedure. - Disinfect the forceps with 70% ethanol spray to ensure no cross-contamination between crabs.
- After performing the eyestalk ablation on all crabs, dip the hot nickel steel metal rod (screwdriver) into tap water.
- Disinfect the towel before reuse. Multiple towels can be used to save time.
NOTE: Wash the towel with tap water, and dip it into 30 ppm chlorinated water for 5 min. Then, wash the towel with tap water again, and dip it in a 1 g/L sodium thiosulphate solution. - Keep the blowtorch in a safe place after turning it off, and wait until it returns to environmental temperature (about 30 min) before disconnecting.
- Surgery technique
- Perform the procedure in a well-ventilated area.
- Sterilize two surgical scissors and forceps in an autoclave.
- Pour 50 mL of 70% ethanol into a 100 mL glass beaker.
- Prepare the tincture of iodine solution in a dropper bottle.
NOTE: Tincture of iodine (iodine tincture or weak iodine solution) is made up of 2%-7% elemental iodine and potassium iodide, or sodium iodide, dissolved in ethanol and water. - Wear thick cotton gloves.
- Hold the sedated crab, and cover it with a wet cotton towel.
- Hold one eye of the crab with sterilized forceps.
- Swiftly cut off the eyestalk using sterilized surgical scissors.
NOTE: Hemolymph may be lost from the wounded part of the crab. - Dip the scissors and forceps in 70% ethanol after every use, and dry them using tissue paper before reuse.
- Apply two to three drops of iodine tincture to the wounded part of the eyestalk immediately after cutting it off.
NOTE: Tincture of iodine is used for healing and to prevent infection.
to:
5. Eyestalk ablation
- Cauterization technique
- Perform all procedures on top of a table and in an open area.
- Take a flat head nickel-steel metal rod (e.g., a screwdriver) with a wooden or plastic handle, and cover the handle with a wet cotton towel.
- Sterilize two stainless surgical forceps in an autoclave.
- Prepare 70% ethanol in a spray bottle and keep it away from any fire-related sources, such as blow torch and red hot screwdriver. Have tissue paper ready for use.
NOTE: Ethanol is highly flammable. Maintain a safe distance from fire sources. - Connect a blowtorch to a gas cylinder (butane) securely.
CAUTION: Follow the instructions on the blowtorch and gas cylinder. Make sure that the blowtorch is switched off when connecting with the gas cylinder. Read and follow all the fire safety precautions mentioned on the gas cylinder. - Wear thick cotton gloves to avoid injury from hot objects.
- Subject the tip of the metal rod to the fire of the blowtorch until the metal rod is bright red.
- Cover the anesthetized crab with a wet cotton towel.
NOTE: Cover the antennae of the crab to avoid unnecessary damage. - Hold one eye of the crab with sterilized forceps.
NOTE: Sterilize the forceps in an autoclave for first-time use, and disinfect using 70% ethanol for subsequent use on other crabs. - Hold the red-hot metal flat tip onto the eye of the crab and press slightly for about 10−15 s until the eyestalk turns an orange or reddish-orange color. Be careful when conducting this step to avoid damage to adjacent structures.
NOTE: Two people are needed to execute eyestalk ablation following the cauterization method: one to hold the crab and another to perform the ablation procedure. - Disinfect the forceps with 70% ethanol spray to ensure no cross-contamination between crabs.
NOTE: Only perform this step at least waiting for 5 min after the eyestalk ablation procedure to ensure the forceps are cooled down before disinfection using 70% ethanol to prevent potential fire hazards. - After performing the eyestalk ablation on all crabs, dip the hot nickel steel metal rod (screwdriver) into tap water.
- Disinfect the towel before reuse. Multiple towels can be used to save time.
NOTE: Wash the towel with tap water, and dip it into 30 ppm chlorinated water for 5 min. Then, wash the towel with tap water again, and dip it in a 1 g/L sodium thiosulphate solution. - Keep the blowtorch in a safe place after turning it off, and wait until it returns to environmental temperature (about 30 min) before disconnecting.
- Surgery technique
- Perform the procedure in a well-ventilated area.
- Sterilize two surgical scissors and forceps in an autoclave.
- Pour 50 mL of 70% ethanol into a 100 mL glass beaker.
- Wear thick cotton gloves.
- Hold the anesthetized crab, and cover it with a wet cotton towel.
- Hold one eye of the crab with sterilized forceps.
- Swiftly cut off the eyestalk using sterilized surgical scissors.
NOTE: Hemolymph may be lost from the wounded part of the crab. - Dip the scissors and forceps in 70% ethanol after every use, and dry them using tissue paper before reuse.
Step 7.2.2 of the Protocol has been updated from:
Sedate the females individually with the cold shock anesthesia method.
to:
Anesthetize the females individually with the 2-PE immersion anesthesia method.
The Discussion has been updated from:
This protocol was developed for the eyestalk ablation of the mud crab, Scylla spp., and can be applied as an efficient method to induce gonad maturation. This protocol can be easily replicated for the commercial ovary maturation of mud crabs and can be implemented to reduce the latent period (time from one spawning to another) in mud crab seed production.
The eyestalk ablation of crustaceans (i.e., freshwater prawn, marine shrimp) is typically done to induce gonad maturation and out-of-season spawning11,12,13. Eyestalk ablation in brachyuran crabs has also been done to study molting25,32,33, hormonal regulation18, gonad maturation34, and induced breeding and reproductive performance35,36,37,38,39. Unilateral or bilateral eyestalk ablation influences the physiology of the crustacean. Eyestalk ablation following the protocol stated in this study also influences the ovarian maturation rate of mud crabs. In the control treatment (without eyestalk ablation), 43.33% ± 5.77% of female crabs had an immature ovary (stage-1). However, in the same rearing period (30 days), eyestalk-ablated female crabs had pre-maturing ovaries (stage-3; 56.67% ± 11.55% and 53.33% ± 15.28% with the cauterization and surgery techniques, respectively), which shows that eyestalk ablation can increase the gonad maturation of mud crabs. Previous studies have also reported that the ovarian development of intact crabs (without eyestalk ablation) is slower than that of eyestalk-ablated crabs25,31. Due to the slower gonadal development in intact crustaceans, eyestalk ablation is widely done in commercial prawn and shrimp hatcheries. In this protocol, the eyestalk-ablated female crabs achieved higher percentages of ovarian maturation compared to the female crabs without the eyestalk ablation treatment (Figure 3).
The gonad maturation of the mud crab is regulated by hormones21,40,41. The eyestalk contains important endocrine glands (i.e., the X-organ-sinus gland complex) that play vital roles in the gonadal maturation process of mud crabs18,21. Unilateral eyestalk ablation, either by cauterization or surgery, damages one of the major endocrine glands that is involved in the synthesis and release of inhibiting hormones (e.g., VIH), thereby resulting in a higher level of gonad-stimulating hormones (i.e., VSH).
The ovarian maturation stages of Scylla spp. can be differentiated by observing the ovarian tissue coloration with the naked eye29,30,42. Translucent or creamy white ovarian tissues are indications of immature ovaries29,30,42,43. In this study, immature ovaries (stage-1) were still found in the group of female crabs without eyestalk ablation due to the slower ovarian maturation process. However, the crabs in the eyestalk-ablated groups (both by the cauterization and surgery techniques) mostly showed pre-maturing ovaries (stage-3), with some individuals exhibiting fully matured ovaries (stage-4). Therefore, the protocol of eyestalk ablation described here can be used to increase ovarian maturation in female mud crabs. This protocol can also be applied directly to wild-collected mature female mud crabs to hasten their seed production. To evaluate the effectiveness of cauterization and surgery methods on mud crab gonad maturation and to ensure the accurate estimation of molting duration, sexually pre-mature crabs were used. After the (induced) molting of sexually pre-mature female crabs, we noticed that their ovaries were still in the immature or early developing stages29,44. After 30 days of rearing the newly mature female crabs (either eyestalk-ablated or without eyestalk ablation), the ovarian development stages (stage-1 to stage-4) were determined by the color of the ovarian tissues. This protocol encourages the use of the cauterization technique to perform eyestalk ablation in mud crabs to avoid any hemolymph loss and prevent infection at the ablated sites. Cauterization immediately seals the wound, whereas the surgery technique requires an additional step of disinfection using iodine. For commercial purposes, larger mature crabs, preferably at a later stage of ovarian maturation, should be selected for eyestalk ablation to shorten the time to reach the fully matured ovary stage for subsequent commerce or brood stock culture. In addition to eyestalk ablation, individual rearing with sand substrate and sufficient feeding, preferably with live feed, can increase the gonad maturation rate of mud crabs in captivity30,35,45,46.
Crustacean blood is called hemolymph and can be lost during eyestalk ablation. An excessive loss of hemolymph may lead to the death of eyestalk-ablated crabs, especially when performing surgery to remove the eyestalk. The hemolymph can coagulate in the wounded part to prevent loss. The application of a tincture of iodine can prevent infection of the wounded part. However, in comparison to the surgery technique, the cauterization technique seals the wounded part immediately, thereby preventing the loss of hemolymph and possible infection.
Mud crab mortality after unilateral eyestalk ablation with either cauterization or surgery was not found within the first 7 days. Thus, eyestalk ablation can be done with a higher survival rate. Unilateral eyestalk ablation does not hamper the survival rate of the crab33.
Stress during crab handling and eyestalk ablation may contribute to crab mortality. Proper anesthesia is needed to minimize handling stress during eyestalk ablation. In crustacean eyestalk ablation, chemical anesthetics (i.e., xylocaine, lidocaine) are used at the base of the eyestalk before eyestalk ablation14,15,17,47. However, due to the aggressive nature and large size of mud crabs, the use of anesthesia only at the base of the eyestalk is not sufficient and might result in additional stress to the animals during the injection. On the other hand, anesthesia by subjecting them to a lower water temperature is more economical and safer. The use of cold water for anesthesia in mud crabs is common and has been used in other studies due to its efficiency, simplicity, and minimal impact on recovery and survival37,48,49.
Although eyestalk ablation using both cauterization and surgery methods has a minimal effect on crab survival and enhances ovarian maturation, performing eyestalk ablation requires professional mastery of the techniques. The timing between the steps is critical as any delay between protocols adds additional stress for the crabs. Unlike the surgery technique, the cauterization technique is dangerous because it involves the use of flammable equipment (i.e., a blow torch and butane gas). Thus, extra caution is needed when performing the cauterization technique.
Crabs are cannibalistic in nature, and they are known to prey on others that have just completed their molt and are still in their soft-shell conditions7,50,51. Thus, rearing the crabs individually can avoid unnecessary mortality due to cannibalism. The use of individual rearing in mud crab culture is commonly practiced, both in high-density culture and pond culture, for fattening and soft-shell crab farming purposes8,52. This protocol also utilized individual rearing and maintenance. During the transportation of the crabs for rearing or commerce, the crab chelipeds are tied up securely (or even autotomized) to prevent fighting, unnecessary injury, and limb loss34.
The described protocol for eyestalk ablation should be performed with multiple persons. After completing the eyestalk ablation, non-disposable equipment (e.g., the aquarium, tray, towel, etc.) should be disinfected with 30 ppm chlorine. The crabs must be monitored at least twice per day. Any dead crabs, uneaten feed, ablated limbs, or molted crab shells should be swiftly disposed of (i.e., buried in soil with bleaching powder) to prevent any potential for disease spread.
to:
This protocol was developed for the eyestalk ablation of the mud crab, Scylla spp., and can be applied as an efficient method to induce gonad maturation. This protocol can be easily replicated for the commercial ovary maturation of mud crabs and can be implemented to reduce the latent period (time from one spawning to another) in mud crab seed production.
The eyestalk ablation of crustaceans (i.e., freshwater prawn, marine shrimp) is typically done to induce gonad maturation and out-of-season spawning11,12,13. Eyestalk ablation in brachyuran crabs has also been done to study molting25,32,33, hormonal regulation18, gonad maturation34, and induced breeding and reproductive performance35,36,37,38,39. Anesthesia via immersion in 2-phenoxyethanol was used as it is comparable to the use of tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) in arthopods but cheaper and does not require the use of additional buffer40. Unilateral or bilateral eyestalk ablation influences the physiology of the crustacean. Eyestalk ablation following the protocol stated in this study also influences the ovarian maturation rate of mud crabs. In the control treatment (without eyestalk ablation), 43.33% ± 5.77% of female crabs had an immature ovary (stage-1). However, in the same rearing period (30 days), eyestalk-ablated female crabs had pre-maturing ovaries (stage-3; 56.67% ± 11.55% and 53.33% ± 15.28% with the cauterization and surgery techniques, respectively), which shows that eyestalk ablation can increase the gonad maturation of mud crabs. Previous studies have also reported that the ovarian development of intact crabs (without eyestalk ablation) is slower than that of eyestalk-ablated crabs25,31. Due to the slower gonadal development in intact crustaceans, eyestalk ablation is widely done in commercial prawn and shrimp hatcheries. In this protocol, the eyestalk-ablated female crabs achieved higher percentages of ovarian maturation compared to the female crabs without the eyestalk ablation treatment (Figure 3).
The gonad maturation of the mud crab is regulated by hormones21,41,42. The eyestalk contains important endocrine glands (i.e., the X-organ-sinus gland complex) that play vital roles in the gonadal maturation process of mud crabs18,21. Unilateral eyestalk ablation, either by cauterization or surgery, damages one of the major endocrine glands that is involved in the synthesis and release of inhibiting hormones (e.g., VIH), thereby resulting in a higher level of gonad-stimulating hormones (i.e., VSH).
The ovarian maturation stages of Scylla spp. can be differentiated by observing the ovarian tissue coloration with the naked eye29,30,43. Translucent or creamy white ovarian tissues are indications of immature ovaries29,30,43,44. In this study, immature ovaries (stage-1) were still found in the group of female crabs without eyestalk ablation due to the slower ovarian maturation process. However, the crabs in the eyestalk-ablated groups (both by the cauterization and surgery techniques) mostly showed pre-maturing ovaries (stage-3), with some individuals exhibiting fully matured ovaries (stage-4). Therefore, the protocol of eyestalk ablation described here can be used to increase ovarian maturation in female mud crabs. This protocol can also be applied directly to wild-collected mature female mud crabs to hasten their seed production. To evaluate the effectiveness of cauterization and surgery methods on mud crab gonad maturation and to ensure the accurate estimation of molting duration, sexually pre-mature crabs were used. After the (induced) molting of sexually pre-mature female crabs, we noticed that their ovaries were still in the immature or early developing stages29,45. After 30 days of rearing the newly mature female crabs (either eyestalk-ablated or without eyestalk ablation), the ovarian development stages (stage-1 to stage-4) were determined by the color of the ovarian tissues. This protocol encourages the use of the cauterization technique to perform eyestalk ablation in mud crabs to avoid any hemolymph loss and prevent infection at the ablated sites. Cauterization immediately seals the wound, whereas the surgery technique takes time for the wound to heal and this would allow for chance of infection. For commercial purposes, larger mature crabs, preferably at a later stage of ovarian maturation, should be selected for eyestalk ablation to shorten the time to reach the fully matured ovary stage for subsequent commerce or brood stock culture. In addition to eyestalk ablation, individual rearing with sand substrate and sufficient feeding, preferably with live feed, can increase the gonad maturation rate of mud crabs in captivity30,35,46,47.
Crustacean blood is called hemolymph and can be lost during eyestalk ablation. An excessive loss of hemolymph may lead to the death of eyestalk-ablated crabs, especially when performing surgery to remove the eyestalk. The hemolymph can coagulate in the wounded part to prevent loss. However, in comparison to the surgery technique, the cauterization technique seals the wounded part immediately, thereby preventing the loss of hemolymph and possible infection.
Mud crab mortality after unilateral eyestalk ablation with either cauterization or surgery was not found within the first 7 days. Thus, eyestalk ablation can be done with a higher survival rate. Unilateral eyestalk ablation does not hamper the survival rate of the crab33.
Stress during crab handling and eyestalk ablation may contribute to crab mortality. Proper anesthesia is needed to minimize handling stress during eyestalk ablation. In crustacean eyestalk ablation, chemical anesthetics (i.e., xylocaine, lidocaine) are used at the base of the eyestalk before eyestalk ablation14,15,17,48. However, due to the aggressive nature and large size of mud crabs, the use of anesthesia only at the base of the eyestalk is not sufficient and might result in additional stress to the animals during the injection. On the other hand, anesthesia by subjecting them to a lower water temperature is more economical and safer. The use of cold water for anesthesia in mud crabs is common and has been used in other studies due to its efficiency, simplicity, and minimal impact on recovery and survival37,49,50. In addition, future research on pain assessment following eyestalk ablation on mud crabs is recommended to highlight the change in behaviours associated with pain and stress, as evident in freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum51.
Although eyestalk ablation using both cauterization and surgery methods has a minimal effect on crab survival and enhances ovarian maturation, performing eyestalk ablation requires professional mastery of the techniques. The timing between the steps is critical as any delay between protocols adds additional stress for the crabs. Unlike the surgery technique, the cauterization technique is dangerous because it involves the use of flammable equipment (i.e., a blow torch and butane gas). Thus, extra caution is needed when performing the cauterization technique.
Crabs are cannibalistic in nature, and they are known to prey on others that have just completed their molt and are still in their soft-shell conditions7,52,53. Thus, rearing the crabs individually can avoid unnecessary mortality due to cannibalism. The use of individual rearing in mud crab culture is commonly practiced, both in high-density culture and pond culture, for fattening and soft-shell crab farming purposes8,53. This protocol also utilized individual rearing and maintenance. During the transportation of the crabs for rearing or commerce, the crab chelipeds are tied up securely (or even autotomized) to prevent fighting, unnecessary injury, and limb loss34.
The described protocol for eyestalk ablation should be performed with multiple persons. After completing the eyestalk ablation, non-disposable equipment (e.g., the aquarium, tray, towel, etc.) should be disinfected with 30 ppm chlorine. The crabs must be monitored at least twice per day. Any dead crabs, uneaten feed, ablated limbs, or molted crab shells should be swiftly disposed of (i.e., buried in soil with bleaching powder) to prevent any potential for disease spread.
The References have been updated from:
- Keenan, C. P., Davie, P. J. F., Mann, D. L. A revision of the genus Scylla de Haan, 1833 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunidae). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 46 (1), 217-245 (1998).
- Fazhan, H. et al. Morphological descriptions and morphometric discriminant function analysis reveal an additional four groups of Scylla spp. PeerJ. 8, e8066 (2020).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Hilmi, M. G., Azmie, G., Zakaria, M. Z. Species diversity, carapace width-body weight relationship, size distribution and sex ratio of mud crab, genus Scylla from Setiu Wetlands of Terengganu coastal waters, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 97-109 (2010).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Mohd Faizal, W. W. Y., Azmie, G., Abol-Munafi, A. B. Size of maturity of mud crab Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) from mangrove areas of Terengganu coastal waters. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 134-147 (2010).
- Waiho, K. et al. On types of sexual maturity in brachyurans, with special reference to size at the onset of sexual maturity. Journal of Shellfish Research. 36 (3), 807-839 (2017).
- Mykles, D. L., Chang, E. S. Hormonal control of the crustacean molting gland: Insights from transcriptomics and proteomics. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 294, 113493 (2020).
- Fujaya, Y. et al. Is limb autotomy really efficient compared to traditional rearing in soft-shell crab (Scylla olivacea) production? Aquaculture Reports. 18, 100432 (2020).
- Waiho, K. et al. Moult induction methods in soft-shell crab production. Aquaculture Research. 52 (9), 4026-4042 (2021).
- Rahman, M. R. et al. Evaluation of limb autotomy as a promising strategy to improve production performances of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) in the soft-shell farming system. Aquaculture Research. 51 (6), 2555-2572 (2020).
- Okumura, T. et al. Expression of vitellogenin and cortical rod proteins during induced ovarian development by eyestalk ablation in the kuruma prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 143 (2), 246-253 (2006).
- Pervaiz, P. A., Jhon, S. M., Sikdar-bar, M. Studies on the effect of unilateral eyestalk ablation in maturation of gonads of a freshwater prawn Macrobrachium dayanum. World Journal of Zoology. 6 (2), 159-163 (2011).
- Primavera, J. H. Induced maturation and spawning in five-month-old Penaeus monodon Fabricius by eyestalk ablation. Aquaculture. 13 (4), 355-359 (1978).
- Shyne Anand, P. S. et al. Reproductive performance of wild brooders of Indian white shrimp, Penaeus indicus: Potential and challenges for selective breeding program. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 65 (2019).
- Diarte-Plata, G. et al. Eyestalk ablation procedures to minimize pain in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 140 (3-4), 172-178 (2012).
- Vargas-Téllez, I. et al. Impact of unilateral eyestalk ablation on Callinectes arcuatus (Ordway, 1863) under laboratory conditions: Behavioral evaluation. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research. 49 (4), 576-594 (2021).
- Chu, K. H., Chow, W. K. Effects of unilateral versus bilateral eyestalk ablation on molting and growth of the shrimp, Penaeus chinensis (Osbeck, 1765) (Decapoda, Penaeidea). Crustaceana. 62 (3), 225-233 (1992).
- Taylor, J. Minimizing the effects of stress during eyestalk ablation of Litopenaeus vannamei females with topical anesthetic and a coagulating agent. Aquaculture. 233 (1-4), 173-179 (2004).
- Wang, M., Ye, H., Miao, L., Li, X. Role of short neuropeptide F in regulating eyestalk neuroendocrine systems in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 560, 738493 (2022).
- Nagaraju, G. P. C. Reproductive regulators in decapod crustaceans: an overview. Journal of Experimental Biology. 214 (1), 3-16 (2011).
- Kornthong, N. et al. Characterization of red pigment concentrating hormone (RPCH) in the female mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and the effect of 5-HT on its expression. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 185, 28-36 (2013).
- Kornthong, N. et al. Molecular characterization of a vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone (VIH) in the mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and temporal changes in abundances of VIH mRNA transcripts during ovarian maturation and following neurotransmitter administration. Animal Reproduction Science. 208, 106122 (2019).
- Liu, C. et al. VIH from the mud crab is specifically expressed in the eyestalk and potentially regulated by transactivator of Sox9/Oct4/Oct1. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 255, 1-11 (2018).
- Chen, H.-Y., Kang, B. J., Sultana, Z., Wilder, M. N. Variation of protein kinase C-α expression in eyestalk removal-activated ovaries in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 237 (300), 110552 (2019).
- Rotllant, G., Nguyen, T. V., Aizen, J., Suwansa-ard, S., Ventura, T. Toward the identification of female gonad-stimulating factors in crustaceans. Hydrobiologia. 825 (1), 91-119 (2018).
- Supriya, N. T., Sudha, K., Krishnakumar, V., Anilkumar, G. Molt and reproduction enhancement together with hemolymph ecdysteroid elevation under eyestalk ablation in the female fiddler crab, Uca triangularis (Brachyura: Decapoda). Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology. 35 (3), 645-657 (2017).
- Wilder, M. N. Advances in the science of crustacean reproductive physiology and potential applications to new seed production technology. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 6-10 (2019).
- Arcos, G. F., Ibarra, A. M., Vazquez-Boucard, C., Palacios, E., Racotta, I. S. Haemolymph metabolic variables in relation to eyestalk ablation and gonad development of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Boone. Aquaculture Research. 34 (9), 749-755 (2003).
- Desai, U. M., Achuthankutty, C. T. Complete regeneration of ablated eyestalk in penaeid prawn, Penaeus monodon. Current Science. 79 (11), 1602-1603 (2000).
- Wu, Q. et al. Growth performance and biochemical composition dynamics of ovary, hepatopancreas and muscle tissues at different ovarian maturation stages of female mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 515, 734560 (2020).
- Ghazali, A., Azra, M. N., Noordin, N. M., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian morphological development and fatty acids profile of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) fed with various diets. Aquaculture. 468 (Part 1), 45-52 (2017).
- Farhadi, A. et al. The regulatory mechanism of sexual development in decapod crustaceans. Frontiers in Marine Science. 8 (2021).
- Sukardi, P., Prayogo, N. A., Harisam, T., Sudaryono, A. Effect of eyestalk-ablation and differences salinity in rearing pond on molting speed of Scylla serrata. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2094, 020029 (2019).
- Stella, V. S., López Greco, L. S., Rodríguez, E. M. Effects of eyestalk ablation at different times of the year on molting and reproduction of the estuarine grapsid crab Chasmagnathus granulata (Decapoda, Brachyura). Journal of Crustacean Biology. 20 (2), 239-244 (2000).
- Jang, I. K. et al. The effects of manipulating water temperature, photoperiod, and eyestalk ablation on gonad maturation of the swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus.Crustaceana. 83 (2), 129-141 (2010).
- Millamena, O. M., Quinitio, E. The effects of diets on reproductive performance of eyestalk ablated and intact mud crab Scylla serrata. Aquaculture. 181 (1-2), 81-90 (2000).
- Zeng, C. Induced out-of-season spawning of the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain (Estampador) and effects of temperature on embryo development. Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1478-1485 (2007).
- Rana, S. Eye stalk ablation of freshwater crab, Barytelphusa lugubris: An alternative approach of hormonal induced breeding. International Journal of Pure and Applied Zoology. 6 (3), 30-34 (2018).
- Yi, S.-K., Lee, S.-G., Lee, J.-M. Preliminary study of seed production of the Micronesian mud crab Scylla serrata (Crustacea: Portunidae) in Korea. Ocean and Polar Research. 31 (3), 257-264 (2009).
- Azra, M. N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of broodstock improvement to brachyuran crab: Reproductive performance. International Journal of Aquaculture. 5 (38), 1-10 (2016).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of steroid hormones 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone on ovary external morphology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea. Asian Journal of Cell Biology. 9 (1), 23-28 (2013).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of vertebrate steroid hormones on the ovarian maturation stages of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796). Aquaculture. 451, 78-86 (2016).
- Ghazali, A., Mat Noordin, N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian maturation stages of wild and captive mud crab, Scylla olivacea fed with two diets. Sains Malaysiana. 46 (12), 2273-2280 (2017).
- Aaqillah-Amr, M. A., Hidir, A., Noordiyana, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Morphological, biochemical and histological analysis of mud crab ovary and hepatopancreas at different stages of development. Animal Reproduction Science. 195, 274-283 (2018).
- Amin-Safwan, A., Muhd-Farouk, H., Mardhiyyah, M. P., Nadirah, M., Ikhwanuddin, M. Does water salinity affect the level of 17β-estradiol and ovarian physiology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) in captivity? Journal of King Saud University - Science. 31 (4), 827-835 (2019).
- Wu, X. et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of phospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductive performance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock. Aquaculture. 273 (4), 602-613 (2007).
- Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of maturation diets for mud crab genus Scylla broodstock: Present research, problems and future perspective. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 23 (2), 257-267 (2016).
- Maschio Rodrigues, M., López Greco, L. S., de Almeida, L. C. F., Bertini, G. Reproductive performance of Macrobrachium acanthurus (Crustacea, Palaemonidae) females subjected to unilateral eyestalk ablation. Acta Zoologica. 103 (3), 326-334 (2022).
- Zhang, C. et al. Changes in bud morphology, growth-related genes and nutritional status during cheliped regeneration in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. PLoS One. 13 (12), e0209617 (2018).
- Zhang, C. et al. Hemolymph transcriptome analysis of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with intact, left cheliped autotomy and bilateral eyestalk ablation. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 81, 266-275 (2018).
- Mirera, D. O., Moksnes, P. O. Comparative performance of wild juvenile mud crab (Scylla serrata) in different culture systems in East Africa: Effect of shelter, crab size and stocking density. Aquaculture International. 23 (1), 155-173 (2015).
- Ut, V. N., Le Vay, L., Nghia, T. T., Hong Hanh, T. T. Development of nursery cultures for the mud crab Scylla paramamosain (Estampador). Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1563-1568 (2007).
- Fazhan, H. et al. Limb loss and feeding ability in the juvenile mud crab Scylla olivacea: Implications of limb autotomy for aquaculture practice. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 247, 105553 (2022).
to:
- Keenan, C. P., Davie, P. J. F., Mann, D. L. A revision of the genus Scylla de Haan, 1833 (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura: Portunidae). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology. 46 (1), 217-245 (1998).
- Fazhan, H. et al. Morphological descriptions and morphometric discriminant function analysis reveal an additional four groups of Scylla spp. PeerJ. 8, e8066 (2020).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Hilmi, M. G., Azmie, G., Zakaria, M. Z. Species diversity, carapace width-body weight relationship, size distribution and sex ratio of mud crab, genus Scylla from Setiu Wetlands of Terengganu coastal waters, Malaysia. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 97-109 (2010).
- Ikhwanuddin, M., Bachok, Z., Mohd Faizal, W. W. Y., Azmie, G., Abol-Munafi, A. B. Size of maturity of mud crab Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) from mangrove areas of Terengganu coastal waters. Journal of Sustainability Science and Management. 5 (2), 134-147 (2010).
- Waiho, K. et al. On types of sexual maturity in brachyurans, with special reference to size at the onset of sexual maturity. Journal of Shellfish Research. 36 (3), 807-839 (2017).
- Mykles, D. L., Chang, E. S. Hormonal control of the crustacean molting gland: Insights from transcriptomics and proteomics. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 294, 113493 (2020).
- Fujaya, Y. et al. Is limb autotomy really efficient compared to traditional rearing in soft-shell crab (Scylla olivacea) production? Aquaculture Reports. 18, 100432 (2020).
- Waiho, K. et al. Moult induction methods in soft-shell crab production. Aquaculture Research. 52 (9), 4026-4042 (2021).
- Rahman, M. R. et al. Evaluation of limb autotomy as a promising strategy to improve production performances of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) in the soft-shell farming system. Aquaculture Research. 51 (6), 2555-2572 (2020).
- Okumura, T. et al. Expression of vitellogenin and cortical rod proteins during induced ovarian development by eyestalk ablation in the kuruma prawn, Marsupenaeus japonicus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 143 (2), 246-253 (2006).
- Pervaiz, P. A., Jhon, S. M., Sikdar-bar, M. Studies on the effect of unilateral eyestalk ablation in maturation of gonads of a freshwater prawn Macrobrachium dayanum. World Journal of Zoology. 6 (2), 159-163 (2011).
- Primavera, J. H. Induced maturation and spawning in five-month-old Penaeus monodon Fabricius by eyestalk ablation. Aquaculture. 13 (4), 355-359 (1978).
- Shyne Anand, P. S. et al. Reproductive performance of wild brooders of Indian white shrimp, Penaeus indicus: Potential and challenges for selective breeding program. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 65 (2019).
- Diarte-Plata, G. et al. Eyestalk ablation procedures to minimize pain in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 140 (3-4), 172-178 (2012).
- Vargas-Téllez, I. et al. Impact of unilateral eyestalk ablation on Callinectes arcuatus (Ordway, 1863) under laboratory conditions: Behavioral evaluation. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research. 49 (4), 576-594 (2021).
- Chu, K. H., Chow, W. K. Effects of unilateral versus bilateral eyestalk ablation on molting and growth of the shrimp, Penaeus chinensis (Osbeck, 1765) (Decapoda, Penaeidea). Crustaceana. 62 (3), 225-233 (1992).
- Taylor, J. Minimizing the effects of stress during eyestalk ablation of Litopenaeus vannamei females with topical anesthetic and a coagulating agent. Aquaculture. 233 (1-4), 173-179 (2004).
- Wang, M., Ye, H., Miao, L., Li, X. Role of short neuropeptide F in regulating eyestalk neuroendocrine systems in the mud crab Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 560, 738493 (2022).
- Nagaraju, G. P. C. Reproductive regulators in decapod crustaceans: an overview. Journal of Experimental Biology. 214 (1), 3-16 (2011).
- Kornthong, N. et al. Characterization of red pigment concentrating hormone (RPCH) in the female mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and the effect of 5-HT on its expression. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 185, 28-36 (2013).
- Kornthong, N. et al. Molecular characterization of a vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone (VIH) in the mud crab (Scylla olivacea) and temporal changes in abundances of VIH mRNA transcripts during ovarian maturation and following neurotransmitter administration. Animal Reproduction Science. 208, 106122 (2019).
- Liu, C. et al. VIH from the mud crab is specifically expressed in the eyestalk and potentially regulated by transactivator of Sox9/Oct4/Oct1. General and Comparative Endocrinology. 255, 1-11 (2018).
- Chen, H.-Y., Kang, B. J., Sultana, Z., Wilder, M. N. Variation of protein kinase C-α expression in eyestalk removal-activated ovaries in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology. 237 (300), 110552 (2019).
- Rotllant, G., Nguyen, T. V., Aizen, J., Suwansa-ard, S., Ventura, T. Toward the identification of female gonad-stimulating factors in crustaceans. Hydrobiologia. 825 (1), 91-119 (2018).
- Supriya, N. T., Sudha, K., Krishnakumar, V., Anilkumar, G. Molt and reproduction enhancement together with hemolymph ecdysteroid elevation under eyestalk ablation in the female fiddler crab, Uca triangularis (Brachyura: Decapoda). Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology. 35 (3), 645-657 (2017).
- Wilder, M. N. Advances in the science of crustacean reproductive physiology and potential applications to new seed production technology. Journal of Coastal Research. 86 (sp1), 6-10 (2019).
- Arcos, G. F., Ibarra, A. M., Vazquez-Boucard, C., Palacios, E., Racotta, I. S. Haemolymph metabolic variables in relation to eyestalk ablation and gonad development of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Boone. Aquaculture Research. 34 (9), 749-755 (2003).
- Desai, U. M., Achuthankutty, C. T. Complete regeneration of ablated eyestalk in penaeid prawn, Penaeus monodon. Current Science. 79 (11), 1602-1603 (2000).
- Wu, Q. et al. Growth performance and biochemical composition dynamics of ovary, hepatopancreas and muscle tissues at different ovarian maturation stages of female mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture. 515, 734560 (2020).
- Ghazali, A., Azra, M. N., Noordin, N. M., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian morphological development and fatty acids profile of mud crab (Scylla olivacea) fed with various diets. Aquaculture. 468 (Part 1), 45-52 (2017).
- Farhadi, A. et al. The regulatory mechanism of sexual development in decapod crustaceans. Frontiers in Marine Science. 8 (2021).
- Sukardi, P., Prayogo, N. A., Harisam, T., Sudaryono, A. Effect of eyestalk-ablation and differences salinity in rearing pond on molting speed of Scylla serrata. AIP Conference Proceedings. 2094, 020029 (2019).
- Stella, V. S., López Greco, L. S., Rodríguez, E. M. Effects of eyestalk ablation at different times of the year on molting and reproduction of the estuarine grapsid crab Chasmagnathus granulata (Decapoda, Brachyura). Journal of Crustacean Biology. 20 (2), 239-244 (2000).
- Jang, I. K. et al. The effects of manipulating water temperature, photoperiod, and eyestalk ablation on gonad maturation of the swimming crab, Portunus trituberculatus.Crustaceana. 83 (2), 129-141 (2010).
- Millamena, O. M., Quinitio, E. The effects of diets on reproductive performance of eyestalk ablated and intact mud crab Scylla serrata. Aquaculture. 181 (1-2), 81-90 (2000).
- Zeng, C. Induced out-of-season spawning of the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain (Estampador) and effects of temperature on embryo development. Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1478-1485 (2007).
- Rana, S. Eye stalk ablation of freshwater crab, Barytelphusa lugubris: An alternative approach of hormonal induced breeding. International Journal of Pure and Applied Zoology. 6 (3), 30-34 (2018).
- Yi, S.-K., Lee, S.-G., Lee, J.-M. Preliminary study of seed production of the Micronesian mud crab Scylla serrata (Crustacea: Portunidae) in Korea. Ocean and Polar Research. 31 (3), 257-264 (2009).
- Azra, M. N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of broodstock improvement to brachyuran crab: Reproductive performance. International Journal of Aquaculture. 5 (38), 1-10 (2016).
- Archibald, K. E., Scott, G. N., Bailey, K. M., Harms, C. A. 2-phenoxyethanol (2-PE) and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS-222) immersion anesthesia of American horseshoe crabs (Limulus polyphemus). Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine. 50 (1), 96-106 (2019).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of steroid hormones 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone on ovary external morphology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea. Asian Journal of Cell Biology. 9 (1), 23-28 (2013).
- Muhd-Farouk, H., Jasmani, S., Ikhwanuddin, M. Effect of vertebrate steroid hormones on the ovarian maturation stages of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796). Aquaculture. 451, 78-86 (2016).
- Ghazali, A., Mat Noordin, N., Abol-Munafi, A. B., Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Ovarian maturation stages of wild and captive mud crab, Scylla olivacea fed with two diets. Sains Malaysiana. 46 (12), 2273-2280 (2017).
- Aaqillah-Amr, M. A., Hidir, A., Noordiyana, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. Morphological, biochemical and histological analysis of mud crab ovary and hepatopancreas at different stages of development. Animal Reproduction Science. 195, 274-283 (2018).
- Amin-Safwan, A., Muhd-Farouk, H., Mardhiyyah, M. P., Nadirah, M., Ikhwanuddin, M. Does water salinity affect the level of 17β-estradiol and ovarian physiology of orange mud crab, Scylla olivacea (Herbst, 1796) in captivity? Journal of King Saud University - Science. 31 (4), 827-835 (2019).
- Wu, X. et al. Effect of dietary supplementation of phospholipids and highly unsaturated fatty acids on reproductive performance and offspring quality of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards), female broodstock. Aquaculture. 273 (4), 602-613 (2007).
- Azra, M. N., Ikhwanuddin, M. A review of maturation diets for mud crab genus Scylla broodstock: Present research, problems and future perspective. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. 23 (2), 257-267 (2016).
- Maschio Rodrigues, M., López Greco, L. S., de Almeida, L. C. F., Bertini, G. Reproductive performance of Macrobrachium acanthurus (Crustacea, Palaemonidae) females subjected to unilateral eyestalk ablation. Acta Zoologica. 103 (3), 326-334 (2022).
- Zhang, C. et al. Changes in bud morphology, growth-related genes and nutritional status during cheliped regeneration in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. PLoS One. 13 (12), e0209617 (2018).
- Zhang, C. et al. Hemolymph transcriptome analysis of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) with intact, left cheliped autotomy and bilateral eyestalk ablation. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 81, 266-275 (2018).
- Diarte-Plata, G., Sainz-Hernandez, J. C., Aguiñaga-Cruz, J. A., Fierro-Coronado, J. A., Polanco-Torres, A., Puente-Palazuelos, C. Eyestalk ablation procedures to minimize pain in the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium americanum. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 140 (3-4), 172-178 (2012).
- Mirera, D. O., Moksnes, P. O. Comparative performance of wild juvenile mud crab (Scylla serrata) in different culture systems in East Africa: Effect of shelter, crab size and stocking density. Aquaculture International. 23 (1), 155-173 (2015).
- Ut, V. N., Le Vay, L., Nghia, T. T., Hong Hanh, T. T. Development of nursery cultures for the mud crab Scylla paramamosain (Estampador). Aquaculture Research. 38 (14), 1563-1568 (2007).
- Fazhan, H. et al. Limb loss and feeding ability in the juvenile mud crab Scylla olivacea: Implications of limb autotomy for aquaculture practice. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 247, 105553 (2022).
转载和许可
请求许可使用此 JoVE 文章的文本或图形
请求许可探索更多文章
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
版权所属 © 2025 MyJoVE 公司版权所有,本公司不涉及任何医疗业务和医疗服务。