Spin und Chill
Überblick
Quelle: Michael G. Benton und Kerry M. Dooley, Department of Chemical Engineering, Louisiana Landesuniversität, Baton Rouge, LA
Der Spin und Chill nutzt die Grundlagen der Wärmeübertragung und Flüssigkeitsströmung Getränke 38 f in nur 2 Minuten zu entspannen. Man bräuchte einen Kühlschrank ca. 240 min und eine Kühlbox 40 min, um die gleiche Temperatur zu erreichen. Der Spin und Chill behauptet auch, dass dies erreicht wird, durch "sanft" Spinnen bei 500 u/min, die wenig oder gar keine Schaumbildung schafft.
In diesem Experiment wird die Fähigkeit ein Schiffes zu spinnen, ein alkoholfreies Getränk an Rekordgeschwindigkeiten cool ausgewertet werden. Der Spin und Chill soll die Verwendung von ein Eis Brust zu Gunsten der Getränke zu kühlen, schnell und individuell zu entkräften. Verschiedene Betriebsparameter, wie unterschiedlich die Drehzahl des Gerätes, werden bewertet werden, um ihre Auswirkungen auf die Wärmeübertragung zu bestimmen. Darüber hinaus werden die konzentrierte Parameter Analyse und transient Heat Conduction Analyse zur Wärmeübertragung herangezogen werden.
Grundsätze
Der Spin und Chill transiente Wärmeleitung und konvektive Wärmeübertragung nutzt. Durch Drehen der Dose, warme Flüssigkeit aus der Mitte der Dose bewegt sich nach außen und kommt in Kontakt mit der kalten Oberfläche. Dann wird Energie an die kalte Oberfläche in Form von Wärme aus der warmen Flüssigkeit übertragen. Dies wird fortgesetzt, bis der gesamte Behälter gekühlt wurde. Kältetechnik nutzt einen ähnlichen Prozess1. In der Kältetechnik Kältemittel durchläuft das System, und erfährt einen Rückgang der Druck1. Als Reaktion darauf nimmt die Temperatur des Kältemittels stark nach unten die Temperatur der Raum gekühlt1. Diese Temperaturdifferenz führt zu Hitze bewegt natürlich aus dem wärmeren Raum auf dem Kühler Kältemittel, wo es ist, später ausgegeben, und der Vorgang wiederholt sich1.
Spin und Chill ist analog zur Kühlung eines Batch-Schiffes und etwas analog zur Kühlung einer Flüssigkeit in einem Rohr fließt. Für Flüssigkeit in einem Batch-Behälter mit Rührwerk und in einem Rohr ist die durchschnittliche Fluidgeschwindigkeit bekannt. Theorie und Korrelationen stehen Wärmeübertragungskoeffizienten vorherzusagen (h) Werte. Wärmestrom in den Spin und Chill wird durch Widerstände gesteuert. Wir möchten auf zwei begrenzende Fälle zu konzentrieren.
Die konzentrierte Parameter-Analyse reduziert eine Anlage auf eine Reihe von diskreten "Klumpen", wo die Temperaturdifferenz in jeder Klumpen als vernachlässigbar angesehen wird.

In dieser Gleichung, T ist Temperatur, h ist Wärmeübergangskoeffizient, A ist Bereich, t Laufzeit, ρ ist Dichte Cp ist die Wärmekapazität und V ist Volumen.
Wärmestrom aus dem Wasser in die Dose auf dem Eis beinhaltet einen Innenwiderstand, eine Wand, und eine externe Beständigkeit (Abbildung 1). Für den Fall einer anwendbar muss sowohl das Wasser in die Dose und das Eis gut gemischt werden. Dies vereinfacht den Fall an eine eindimensionale Hitzeproblem Transfer.
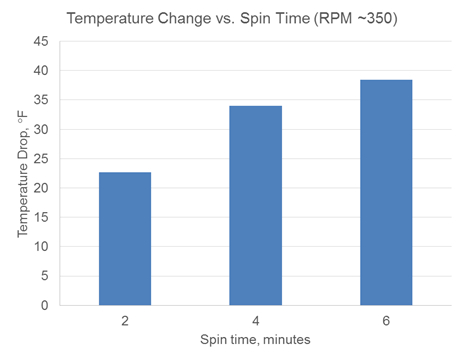
Abbildung 1: Eine schematische Darstellung des Temperaturbedingungen für den Fall einer.
In diesem Fall die Wand ist sehr dünn und der Wand Widerstand vernachlässigt werden kann. Hier ist die Wärmeübertragung überwiegend durch den Innenwiderstand gesteuert. Dies führt zu der konzentrierten Parameter-Analyse, die Bestimmung des Innenwiderstands ermöglicht.
Die Biot-Zahl ist ein Index des Verhältnisses der Hitze Übergangswiderstände innerhalb und außerhalb einer Membran,
BI = Lh/k
wo Bi ist das Biot-Zahl, L ist die charakteristische Länge (Volumen dividiert durch Fläche) ist der Wärmeübergangskoeffizient h und k ist die Wärmeleitfähigkeit. Diese Nummer wird verwendet, um Wärme Übergangswiderstände zwischen verschiedenen Körpern zu vergleichen.
Fall zwei nutzt eine eindimensionale transiente Wärmeleitung Analyse.

Wo τ Zeitkonstante, α ist die thermische Diffusivität, t ist Zeit und R0 ist der anfängliche Radius. Diese Formel wird verwendet, um thermische Diffusivität zu finden, die der Wärmeleitfähigkeit, k, geteilt durch die Dichte ρ und Wärmekapazität, Cpbesteht.

Wenn das Wasser eine echte "Festkörper", Wasser Massentemperatur werden nicht gleichmäßige Temperatur und Wärmestrom aus dem Wasser wird durch Wärmeleitung gesteuert werden. Mit der Zeit wird die Temperatur an der Mittellinie der Dose (Abbildung 2) entwickeln. Wärmestrom aus dem Wasser zu Eis beinhaltet Wärmeleitung durch die "Solid" und einen Innenwiderstand.
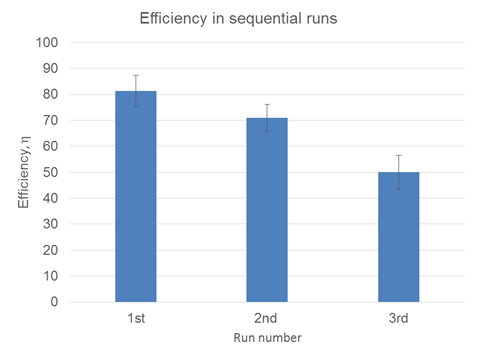
Abbildung 2: Eine schematische Darstellung des Temperaturbedingungen für Fall 2.
Wenn Sie eine Eis Brust zu verwenden, die Flüssigkeit in der Dose ist nicht als "solide" auch ohne sich zu vermischen, und natürlicher Konvektion aufgrund der Temperaturgradienten eingerichtet werden. Die Kerntemperatur Linie lässt sich den scheinbaren Innenwiderstand bestimmen durch die Annahme eines langen Zylinders mit Wärmeleitung in radialer Richtung.
Verfahren
(1) die Prüfung der Spin und Chill
- Die Aluminium-Cola-Dose mit Raumtemperaturwasser füllen und dann die Temperatur aufzeichnen.
- Messen Sie das Gesamtgewicht des Eises mit der Balance, genug verwendet wird, um den Spin und Chill umgeben.
- Siegel der Aluminium-Soda können Deckel mit Kunststoff Abdichtung und fügen Sie die Assembly in den drehen und Chill.
- Aktivieren Sie die Spin und kalt stellen. Es sollte laufen ca. 2 min bei ~ 500 u/min.
- Entfernen Sie die Aluminium-Cola-Dose aus dem Spin und Chill und entfernen Sie die Kunststoff-Deckel verschließen. Aufzeichnen kann die Endtemperatur des Wassers innerhalb der Aluminium-Soda.
- Notieren Sie die Menge des Eises, das geschmolzen, um Wasser mit einem Messzylinder oder ein Gleichgewicht.
(2) konzentrierte Parameter Modell
- Führen Sie ausgehend von der Dose eine Raumtemperatur, ~ 4 Einzelfahrten gedacht mit dem Spin und Chill (~ 4). Es sollte laufen für ~ 2 min bei ~ 500 u/min.
- Notieren Sie die Endtemperatur des Wassers innerhalb der kann nach jedem Lauf.
- Führen Sie dann die Spin und Chill nacheinander drei Zeiten, beginnend mit einer warmen Dose. Führen Sie eine angemessene Anzahl von Wiederholungen für die sequenzielle Spin und Chill- Experiment. Es sollte laufen für ~ 2 min bei ~ 500 u/min.
- Erfassen Sie die Menge an Eis geschmolzen und Endtemperatur nach jedem Lauf. Seien Sie vorsichtig, wenn Sie die Dose zu öffnen - es kann oder kann nicht schäumen.
- Dann wiederholen Sie und variieren Sie die Betriebsdrehzahl der Spin und Chill. Beginnen Sie mit der Dose bei Raumtemperatur und durchführen Sie 2 min läuft bei u/min reichen von wenigen bis zu 500 u/min.
(3) vorübergehende Leitung Modell
- Durchführen Sie die gleichen Experimente wie oben beschrieben. Laden Sie den Spin und chill mit Eis und einem soliden Aluminium-Zylinder (mit einem kleinen Loch in der Mittellinie für Temperaturmessungen gebohrt).
- Alle paar Minuten messen und Aufzeichnen der Temperatur in der Mitte der Dose und die Aluminium-Zylinder - achten Sie darauf, rühren oder stören kann Inhalt.
Ergebnisse
Das konzentrierte Parameter-Modell dient zur Bestimmung der Wärmeübergangskoeffizient h, für die verschiedenen experimentellen Bedingungen. Die beobachteten Effizienz ist keine einschränkende Fall oder Hitze Transfermechanismus abhängig. Um die Effizienz zu berechnen, ermitteln wir zuerst die Energie ins Eis und aus dem Wasser. Wenn das System adiabatischen (100 % Wirkungsgrad), QWasser + QEis = 0. Die Effizienz wird durch die Aufteilung der Absolute Wert der Wärmeenergie des Wassers (QWasser) durch die Wärmeenergie des Eises (QEis) bestimmt (Tabelle 1). Für die sequentielle läuft der Wirkungsgrad η, sinkt von 78 % auf 71 % und dann auf 50 %, wenn die Temperatur nähert sich 32 F (Tabelle 2). Die Effizienz nimmt η mit sequentiellen läuft. Und zwar deshalb, weil die Effizienz der Wärmeübertragung reduziert wird, wenn Temperaturen nahe beieinander sind. Die Flüssigkeit im Inneren der Dose nähert sich die Temperatur des Eises außerhalb, wodurch Effizienz. Die Biot-Zahl befanden sich rund 10 für die einzelnen Läufe werden. Diese nicht den erwarteten Wert von 0,1 deutlich überschreiten. Die viel größere Wert zeigt größere thermischen Widerstand außerhalb der Dose als im Inneren. Die Biot-Zahl ist genauer als die externen Widerstand, Wärmestrom, dividiert durch den Innenwiderstand angegeben. Hier sind größere Zahlen für h und k Indikator für weniger Widerstand oder "größer" Wärmestrom. Eine sehr große k entstünde eine gleichmäßige Temperatur in diesem "k" Phase. Drehen die Dose scheint ein gepflegten Schiffes zu erstellen. Die konzentrierte Parameter-Analyse ist perfekt.
| Test # | lbs Wasser | Anfängliche Temperatur (°F) | Endgültige Temp (°F) | Δ T (°F) | Eis Δm (lbs.) | Q-Eis | Q-Wasser | Η | h (Btu/hr-ft2-F) |
h (W/m2- C) |
| 1 | 0.783 | 77 | 53.42 | 23.58 | 0.172 | 24.768 | 18.463 | 74.54 | 70.545 | 400.574 |
| 2 | 0.783 | 84.74 | 60.08 | 24.66 | 0,17 | 24,48 | 19.309 | 78.88 | 59.899 | 340.126 |
| 3 | 0.783 | 86 | 59.72 | 26.28 | 0,175 | 25.2 | 20.577 | 81.66 | 63.369 | 359.829 |
| 4 | 0.783 | 83.12 | 55,4 | 27,72 | 0.195 | 28.08. | 21.705 | 77.30 | 74.261 | 421.674 |
| 6 | 0.783 | 81.86 | 52.34 | 29,52 | 0.212 | 30.528 | 23.114 | 75.71 | 85.207 | 483.832 |
| 7 | 0.783 | 83,66 | 58.28 | 25,38 | 0.171 | 24.624 | 19.873 | 80,70 | 64.229 | 364.710 |
| 8 | 0.783 | 79,16 | 50.72 | 28.44 | 0.203 | 29.232 | 22.269 | 76.18 | 87.804 | 498.576 |
| 9 | 0.783 | 81.68 | 56,3 | 25,38 | 0.181 | 26.064 | 19.873 | 76,25 | 67.959 | 385.890 |
| 10 | 0.783 | 81.86 | 56.66 | 25.2 | 0.173 | 24.912 | 19.732 | 79.21 | 66.905 | 379.906 |
| AVG. | 0.783 | 82.12 | 55,88 | 26,24 | 0.18 | 26.43 | 20,55 | 77.73 | 70.454 | 400.057 |
Tabelle 1: Single-Run Solltemperatur ändern von 82 F bis 56 F.
| Test # | lbs Wasser | Anfängliche Temperatur (°F) | Endgültige Temp (°F) | Δ T (°F) | Eis Δm (lbs.) | Q-Eis | Q-Wasser | h | h (Btu/hr-ft2-F) |
h (W/m2- C) |
| 1a | 0.783 | 80.78 | 53,6 | 27.18 | 0,176 | 25.344 | 21.282 | 83.97 | 77.414 | 439.582 |
| 1 b | 0.783 | 53,6 | 41,9 | 11.7 | 0.095 | 13,68 | 9.161 | 67,10 | 74.335 | 422.095 |
| 1c | 0.783 | 41,9 | 38,3 | 3.6 | 0,038 | 5.472 | 2.819 | 51,77 | 43.223 | 245.430 |
| 2a | 0.783 | 74.48 | 55.76 | 18,72 | 0.137 | 19.728 | 14.658 | 74,30 | 55.216 | 313.530 |
| 2 b | 0.783 | 55.76 | 43.34 | 12,42 | 0,088 | 12.672 | 9.725 | 76.90 | 70.477 | 400.188 |
| 2c | 0.783 | 43.34 | 37,04 | 6.3 | 0,062 | 8.928 | 4.933 | 55.53 | 77.548 | 440.340 |
| 3a | 0.783 | 71.42 | 49.28 | 22.14 | 0.141 | 20.304 | 17.336 | 85.38 | 78.374 | 445.030 |
| 3 b | 0.783 | 49.28 | 39.56 | 9,72 | 0.077 | 11.088 | 7.611 | 68.78 | 78.767 | 447.264 |
| 3c | 0.783 | 39.56 | 35.96 | 3.6 | 0.046 | 6.624 | 2.819 | 42,77 | 61.836 | 351.122 |
Tabelle 2: Daten aus drei sequenziellen läuft mit geringen Temperaturschwankungen.
Eine erste Berechnung der Temperatur des Zentrums mit den vorgeschlagenen Parametern schlägt eine unmögliche Verletzung des zweiten Hauptsatzes der Thermodynamik. Das Problem ist jedoch, dass diese Gleichung eine kurzfristig Lösung, nur Lösungen über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht zur Verfügung stellt. Zusätzliche Parameter müssen hinzugefügt werden, um kürzere Zeiträume zu befriedigen.



Betrachten Sie Hitze Übergangswiderstände im Wasser und Aluminium, h, und reine Wärmeleitung, k. Wenn die Wärmeleitung pur - wie in einem Festkörper - auftritt ist, sollte die beobachteten h Werte für beide Systeme gleich sein. Für das Wassersystem auftreten einige natürlicher Konvektion, daher die h -Werte nicht für den beiden Systemen gleich sein sollen.
Wenn die Drehzahl variiert, wurde es festgestellt, dass die durchschnittliche Temperatur der Flüssigkeit im Inneren der Dose umgekehrt proportional zur Drehzahl. Höhere Drehzahlen führte zu flüssigen Temperaturen senken näher an die ideale Temperatur, während eine geringere Drehzahl zu höheren Durchschnittstemperaturen führte. Höhere Drehzahlen reduziert die Temperatur der Flüssigkeit mehr erfolgreich als niedrigere Drehzahlen.
Ein ähnliches Verhältnis fand zwischen Laufzeit und Temperatur bei konstanter Drehzahl. Wenn die Dose für einen reduzierten Betrag der Zeit gedreht wurde, war die durchschnittliche Temperatur wärmer als wenn die Dose für den vollen Betrag der Zeit gesponnen wurde. Die Beziehung erwies sich, dass eine Erhöhung der Laufzeit zu einer erhöhten Veränderung Temperatur und eine insgesamt kühlere Temperatur im Durchschnitt führt.
Anwendung und Zusammenfassung
Dieses Experiment dient zur Beurteilung der Fähigkeit eines drehenden Schiffs ein alkoholfreies Getränk an Rekordgeschwindigkeiten, den Spin und Schüttelfrostabkühlen lassen. Runde eins untersucht die Spin und Chill mit einem konzentrierten Parameter-Modell. Runde zwei untersucht die Spin und Chill mit dem vorübergehenden Hitze Wärmeleitung Modell in langen Zylinder. Runde drei vergleicht unsere Spin und Chill Versuchsergebnisse mit Ergebnissen und Korrelationen gefunden in einem anderen Forschung Experiment. Theorie und Korrelationen stehen h Werte Vorhersagen. Wärmestrom in den Spin und Chill wird durch Widerstände gesteuert werden.
Die Effizienz Tropfen gefunden in sequentiellen Läufen wurde erwartet. Die Biot-Zahl erwiesen sich rund 10 für alle Läufe in der ersten Runde. Diese überschreiten stark den erwarteten Wert von 0,1. Die gesammelten Daten Anrufe in Frage die Fähigkeit der Spin und Chill am warmen Dose Cola, 38F in 2 Minuten abkühlen lassen. Mit drei sequenziellen verwendet und einen Zeitraum von ca. 6 Minuten, kann jedoch die Spin und Chill das Erfrischungsgetränk auf die gewünschte Temperatur 38F kühlen. Während der ersten Forderungen für ungültig erklärt wurden, bietet das Konzept einer erweiterten Kühlungsmethode mit mehr Tests in Zukunft effizienter gestaltet werden könnte.
Das konzentrierte Parameter-Modell wurde in den unterschiedlichsten Bereichen angewandt. Durch Verwendung einer konzentrierten Parameter-Analyse können forensischen Labors Tod eines menschlichen Körpers2bestimmen. Forensische Wissenschaftler behandeln den Körper als eine konzentrierte System2. Die bisherige Forschung wurde beim Abkühlen, wenn man Faktoren wie Körper Größe und Form2durchgeführt. Differentialgleichungen sind dann mit diesen bekannten kühlenden Faktoren verwendet, um relative Zeit des Todes2festzustellen.
Eine weitere Verwendung des Modells konzentrierte Parameter ist in der Weiterentwicklung der HLK (Heizung, Lüftung und Klimaanlage) Systeme3. Hitze-Lastverteilung kann rechnerisch mit einem konzentrierten Parameter-Modell zur Maximierung der Energie-Effizienz-3vorhergesagt werden. Diese Modelle machen Fluidtransport, Energietransport, Thermodynamik und psychrometrischen3. Durch den Einbau von HLK-Anlagen zu einem konzentrierten Modell, können Ingenieure ihre Effizienz zu maximieren, Reduzierung von Kosten und Energieverbrauch, während die Wirksamkeit der Climate Control System3.
Transient Heat Conduction Modellierung ist in einer Vielzahl von technischen Bereichen, einschließlich der Materialbearbeitung, Kraftwerk, engineering und Kühlung wichtig. Wärmetauscher sind eine häufige Anwendung von transienten Wärmeleitung4. Diese Geräte nehmen Energie aus einem heißen Bach und es verwenden, um ein kühler4erhitzen. Shell und Rohr sind die häufigste Art der Wärmetauscher4. Sie sind normalerweise lange Zylinder, ähnlich wie das Modell für dieses Experiment, aber viel größer im Umfang4. Mehrere Röhren in einem größeren Zylinder Schale enthalten eine fließende Flüssigkeit, während eine Separate, wie man durch die Schale4fließt. Flow kann in der gleichen oder unterschiedlichen Richtungen sein. Wärme fließt von den heißesten Stream auf der kälteren eine4. Diese Tools können verwendet werden, in vielen Branchen, wie z. B. Herstellung von Chemikalien und Erdölverarbeitung, wo sie auf Wärme oder kühle Chemikalien oder Öl4eingesetzt werden können.
pringen zu...
Videos aus dieser Sammlung:

Now Playing
Spin und Chill
Chemical Engineering
7.4K Ansichten

Prüfung der Wärmeübertragungseffizienz eines Rippenrohrwärmetauschers
Chemical Engineering
18.0K Ansichten

Ein Tablett mit Trockner, leitfähige und konvektive Wärmeübertragung zu untersuchen
Chemical Engineering
44.0K Ansichten

Viskosität von Propylenglykol-Lösungen
Chemical Engineering
33.2K Ansichten

Porosimetrie eines Aluminiumsilikatpulvers
Chemical Engineering
9.7K Ansichten

Demonstration des Potenzgesetzmodells durch Extrusion
Chemical Engineering
10.3K Ansichten

Gas-Absorber
Chemical Engineering
36.9K Ansichten

Dampf-Flüssigkeits-Gleichgewicht
Chemical Engineering
89.6K Ansichten

Der Einfluss des Rückflussverhältnisses auf die Effizienz der Tray-Destillation
Chemical Engineering
77.9K Ansichten

Effizienz der Flüssig-Flüssig-Extraktion
Chemical Engineering
48.6K Ansichten

Flüssigphasenreaktor: Inversion von Saccharose
Chemical Engineering
9.7K Ansichten

Kristallisation von Salicylsäure durch chemische Modifikation
Chemical Engineering
24.3K Ansichten

Einphasen- und Zweiphasenströmung in einem Festbettreaktor
Chemical Engineering
19.0K Ansichten

Kinetik der Additionspolymerisation zu Polydimethylsiloxan
Chemical Engineering
16.4K Ansichten

Katalytischer Reaktor: Hydrierung von Ethylen
Chemical Engineering
30.5K Ansichten
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten