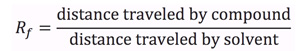Performing 1D Thin Layer Chromatography
Visión general
Source: Laboratory of Dr. Yuri Bolshan — University of Ontario Institute of Technology
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a chromatographic method used to separate mixtures of non-volatile compounds. A TLC plate consists of a thin layer of adsorbent material (the stationary phase) fixed to an appropriate solid support such as plastic, aluminum, or glass1. The sample(s) and reference compound(s) are dissolved in an appropriate solvent and applied near the bottom edge of the TLC plate in small spots. The TLC plate is developed by immersing the bottom edge in the developing solvent consisting of an appropriate mobile phase. Capillary action allows the mobile phase to move up the adsorbent layer. As the solvent moves up the TLC plate, it carries with it the components of each spot and separates them based on their physical interactions with the mobile and stationary phases.
Procedimiento
1. TLC Plates
- Common adsorbents for TLC are silica gel, alumina, and cellulose. TLC plates are commercially available with a variety of properties. Choose a TLC plate and cut it down to an appropriate size (approximately 5 cm x 5 cm is sufficient for most applications). For glass-backed TLC plates, score the glass using a ruler and a glass cutter, then carefully break along the line.
2. Spotting
- Dissolve the sample in a suitable solvent to make an approximately 1
Resultados
An example of a typical TLC plate is shown in Figure 1. An unknown compound 'A' may be compared to known standards 'B' through 'E'. Determination of the Rf value for each component is achieved by spotting of each respective compound, developing the TLC plate, and visualization. The Rf of unknown compound 'A' is calculated by measuring the spot height (y) and dividing by the solvent height (z). Comparing this
Aplicación y resumen
TLC has a number of practical applications in the laboratory. TLC may be used to identify unknown compounds and unknown components of mixtures via comparison with standards. TLC is commonly used to monitor the course of a chemical reaction, and to assess the purity of the product through the comparison of relative amounts of reactants, products, and by-products on successive chromatograms over time. TLC can also be used to determine if a substance purified by other methods (such as recrystallization or distillation) stil
Referencias
- Lehman, J. W. The student's lab companion: laboratory techniques for organic chemistry: standard scale and microscale. Pearson College Div, (2008).
- Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M., Kriz, G. S., & Engel, R. G. Microscale and Macroscale Techniques. Thomson Wadsworth, (2006).
- Pannkuk, E. L., Risch, T. S., Savary, B. J. Profiling the Triacylglyceride Contents in Bat Integumentary Lipids by Preparative Thin Layer Chromatography and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. J. Vis. Exp. (79), e50757, (2013).
- Kagan, I. A., Flythe, M. D. Thin-layer Chromatographic (TLC) Separations and Bioassays of Plant Extracts to Identify Antimicrobial Compounds. J. Vis. Exp. (85), e51411, (2014).
Tags
Saltar a...
Vídeos de esta colección:

Now Playing
Performing 1D Thin Layer Chromatography
Organic Chemistry
289.8K Vistas

Introducción a la catálisis
Organic Chemistry
34.5K Vistas

Montaje de un sistema de reflujo para reacciones químicas calientes
Organic Chemistry
167.5K Vistas

Realizar reacciones por debajo de la temperatura ambiente
Organic Chemistry
70.7K Vistas

Líneas de Schlenk para transferencia de disolventes
Organic Chemistry
41.6K Vistas

Desgasificación de líquidos con ciclos de congelación-bomba-descongelación
Organic Chemistry
56.1K Vistas

Preparación de equipos y reactivos anhidros
Organic Chemistry
79.4K Vistas

Purificación de compuestos por recristalización
Organic Chemistry
708.7K Vistas

Separación de mezclas por precipitación
Organic Chemistry
157.8K Vistas

Extracción sólido-líquida
Organic Chemistry
237.8K Vistas

Evaporación rotatoria para eliminar solventes
Organic Chemistry
212.9K Vistas

Destilación fraccionada
Organic Chemistry
334.5K Vistas

Crecimiento de cristales para el análisis de difracción de rayos x
Organic Chemistry
32.4K Vistas

Cromatografía en columna
Organic Chemistry
360.2K Vistas

Espectroscopia de resonancia magnética nuclear (RMN)
Organic Chemistry
247.9K Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados