Cultures pures et ensemencement des géloses : isolement des colonies bactériennes pures à partir d'un échantillon mixte
Vue d'ensemble
Source: Tilde Andersson1, Rolf Lood1
1 Département des sciences cliniques Lund, Division of Infection Medicine, Biomedical Center, Lund University, 221 00 Lund, Suède
Apparemment impossible à déterminer, la biodiversité microbienne est vraiment stupéfiante avec environ un billion d'espèces coexistantes (1,2). Bien que des climats particulièrement rudes, comme l'environnement acide de l'estomac humain (3) ou les lacs sous-glaciaires de l'Antarctique (4), puissent être dominés par une espèce spécifique, les bactéries se trouvent généralement dans les cultures mixtes. Comme chaque souche peut influencer la croissance d'une autre (5), la capacité de séparer et de cultiver des colonies « pures » (composées uniquement d'un seul type) est devenue essentielle dans les milieux cliniques et académiques. Les cultures pures permettent d'autres examens génétiques (6) et protéomiques (7), l'analyse de la pureté de l'échantillon et, peut-être plus remarquable, l'identification et la caractérisation des agents infectieux à partir d'échantillons cliniques.
Les bactéries ont un large éventail de besoins de croissance et il existe de nombreux types de supports nutritifs conçus pour soutenir à la fois les espèces non exigeantes et exigeantes (8). Les milieuis de croissance peuvent être préparés sous forme liquide (sous forme de bouillon) ou sous forme d'un agent gélifiant typiquement à base d'agar (un agent gélifiant dérivé d'algues rouges). Alors que l'inoculation directe dans le bouillon comporte le risque de générer une population bactérienne génétiquement diversifiée, voire mixte, le placage et le re-streaking crée une culture plus pure où chaque cellule a une composition génétique très similaire. La technique de la plaque de stries est basée sur la dilution progressive d'un échantillon (Figure 1), dans le but de séparer les cellules individuelles les unes des autres. Toute cellule viable (ci-après appelée unité de formation de colonie, CFU) soutenue par les médias et l'environnement désigné peut par la suite trouver une colonie isolée de cellules-filles par fission binaire. En dépit des taux rapides de mutation dans les communautés bactériennes, ce groupe de cellules est généralement considéré comme clonal. La récolte et le re-streaking de cette population assure par conséquent que les travaux ultérieurs ne concernent qu'un seul type bactérien.
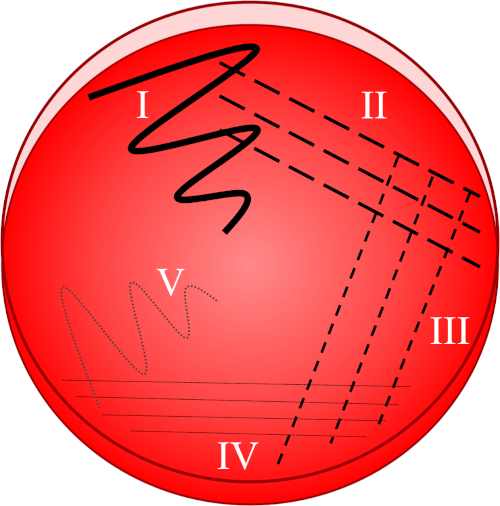
Figure 1 : Une plaque de stries est basée sur la dilution progressive de l'échantillon d'origine. I) L'inoculum est d'abord dispersé à l'aide d'un mouvement en zigzag, créant une zone avec une population bactérienne relativement dense. II-IV) Les stries sont tirées de la zone précédente, à l'aide d'une boucle d'inoculation stérile à chaque fois, jusqu'à ce que le quatrième quadrant soit atteint. V) Un dernier mouvement en zigzag dirigé vers le milieu de la plaque forme une région où l'inoculum a été nettement dilué, permettant aux colonies d'apparaître séparées les unes des autres.
La technique de la plaque de stries peut également être combinée à l'utilisation de supports sélectifs et/ou différentiels. Un milieu sélectif inhibera la croissance de certains organismes(p. ex. par l'ajout d'antibiotiques) tandis qu'un milieu différentiel aidera uniquement à distinguer l'un de l'autre(par exemple par hémolyse sur les plaques d'agar sanguine).
L'utilisation de techniques aseptiques (stériles) sous-tend tous les travaux en microbiologie. Chaque culture bactérienne devrait être considérée comme potentiellement pathogène car il existe un risque de croissance involontaire de souches dangereuses, la formation d'aérosols et la contamination de l'équipement /personnel. Pour minimiser ces risques, tous les aliments pour supports, plastiques, métalliques et vitraux sont généralement stérilisés par l'autoclacage avant et après l'utilisation, les soumettant à une vapeur saturée à haute pression à environ 121 oC qui élimine efficacement les cellules persistantes. L'espace de travail est généralement désinfecté à l'aide d'éthanol avant et après l'utilisation. Le manteau de laboratoire et les gants sont toujours portés pendant le travail avec des agents infectieux.
Procédure
1. Mise en place
- Tous les microbes doivent être traités comme s'ils étaient dangereux. Portez toujours une blouse de laboratoire et des gants, attachez les cheveux longs et assurez-vous que les plaies sont particulièrement bien protégées.
- Préparez l'espace de travail en le stérilisant à l'aide de 70 % d'éthanol.
- Assurez-vous que les plaques d'agar, les solutions d'échantillon et une boîte de boucles d'inoculation en plastique pré-stérilisées ou une boucle métallique plus une
Résultats
La plaque de stries initialepeut contenir des colonies provenant de cellules ayant une composition génétique différente ou (selon la pureté de l'échantillon) de différentes espèces bactériennes (figure 2A).
Par l'isolement ultérieur d'une seule colonie, où toutes les unités sont dérivées d'une cellule mère commune, la deuxième procédure de stries génère une populat...
Applications et Résumé
La capacité d'obtenir et de cultiver une colonie bactérienne pure est essentielle, tant en milieu clinique qu'universitaire. Le placage de strie permet l'isolement d'une population de cellules relativement clonale, provenant d'un CFU partagé, qui peut être d'un intérêt particulier lors du diagnostic ou pour la caractérisation supplémentaire de l'isolat. Un échantillon est strié sur un milieu nutritif à base d'agar approprié et incubé jusqu'à ce que les colonies deviennent visibles. Une colonie isolée est e...
References
- The Human Microbiome Project C. Structure, Function and Diversity of the Healthy Human Microbiome. Nature. 486:207-214. (2012)
- Locey KJ, Lennon JT. Scaling laws predict global microbial diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (21) 5970-5975 (2016)
- Skouloubris S, Thiberge JM, Labigne A, De Reuse H. The Helicobacter pylori UreI protein is not involved in urease activity but is essential for bacterial survival in vivo. Infection and Immunity. 66:4517-21. (1998)
- Mikucki JA, Auken E, Tulaczyk S, Virginia RA, Schamper C, Sørensen KI, Doran PT, Dugan H, Foley N. Deep groundwater and potential subsurface habitats beneath an Antarctic dry valley. Nature Communications. 6:6831. (2015)
- Mullineaux-Sanders C, Suez J, Elinav E, Frankel G. Sieving through gut models of colonization resistance. Nature Microbiology. 3:132-140. (2018)
- Fournier PE, Drancourt M, Raoult D. Bacterial genome sequencing and its use in infectious diseases. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 7:711-23 (2007)
- Yao Z, Li W, Lin Y, Wu Q, Yu F, Lin W, Lin X. Proteomic Analysis Reveals That Metabolic Flows Affect the Susceptibility of Aeromonas hydrophila to Antibiotics. Scientific Reports. 6:39413 (2016)
- Medina D, Walke JB, Gajewski Z, Becker MH, Swartwout MC, Belden LK. Culture Media and Individual Hosts Affect the Recovery of Culturable Bacterial Diversity from Amphibian Skin. Frontiers in Microbiology. 8:1574 (2017)
Tags
Passer à...
Vidéos de cette collection:

Now Playing
Cultures pures et ensemencement des géloses : isolement des colonies bactériennes pures à partir d'un échantillon mixte
Microbiology
166.3K Vues

Création d'une colonne de Winogradsky : une méthode pour enrichir les espèces microbiennes dans un échantillon de sédiments.
Microbiology
129.7K Vues

Dilutions en série et ensemencement des géloses : numération des micro-organismes
Microbiology
316.6K Vues

Cultures enrichies : Cultiver des micro-organismes aérobies et anaérobies dans des milieux sélectifs et différentiels
Microbiology
132.1K Vues

Séquençage de l'ARNr 16S : une technique basée sur la PCR pour l'identification d'espèces bactériennes
Microbiology
189.3K Vues

Courbes de croissance : Générer des courbes de croissance en comptant les unités formant colonies (UFC) et en mesurant l'absorbance
Microbiology
297.1K Vues

Tests de sensibilité aux antibiotiques : Utilisation du ETEST pour déterminer la CMI de deux antibiotiques et évaluer la synergie des antibiotiques
Microbiology
93.9K Vues

Microscopie et coloration : Gram, Capsule et endospores.
Microbiology
363.7K Vues

Test de la plaque : méthode de détermination de la charge virale exprimée en unités formant des plaques
Microbiology
186.4K Vues

Transformation des cellules E. coli en utilisant le chlorure de calcium
Microbiology
87.0K Vues

Conjugaison : méthode de transfert de la résistance à l'ampicilline du donneur à l'hôte E. coli
Microbiology
38.3K Vues

Transduction via bactériophage : méthode de transfert de la résistance à l'ampicilline du donneur au receveur E. coli
Microbiology
29.1K Vues