Method Article
הערכה של תפקוד הלב Energetics בלבבות עכבר בודדות שימוש 31 P NMR ספקטרוסקופיה
In This Article
Summary
Langendorff-mode isolated heart perfusion, in conjunction with 31P NMR spectroscopy, combines the fields of biochemistry and physiology into one experiment. The protocol allows for the dynamic measurement of high energy phosphate content and turnover in the heart while concurrently monitoring physiologic function. When performed correctly, this is a valuable technique in the assessment of cardiac energetics.
Abstract
מודלים העכבר bioengineered הפכו כלי מחקר רב עוצמה בקביעת קשרים סיבתיים בין שינויים ומודלים המולקולרי של מחלות לב וכלי דם. למרות הביולוגיה המולקולרית יש צורך בזיהוי שינויים מרכזיים מסלול איתות, זה לא פונדקאית עבור משמעות תפקודית. בעוד הפיזיולוגיה יכולה לספק תשובות לשאלה של פונקציה, תוך שילוב עם הפיזיולוגיה הערכה ביוכימיים של מטבוליטים של שלם, לב פועם מאפשר לקבל תמונה שלמה של תפקוד אנרגטיקה לב. במשך שנים במעבדה שלנו ניצלה perfusions לב מבודדים בשילוב עם ספקטרוסקופית תהודה מגנטית גרעינית (NMR) כדי לבצע משימה זו. תפקוד חדר שמאל נבחנת על ידי Langendorff מצב perfusions לב מבודדים תוך אנרגטיקה הלב נמדד על ידי ביצוע
Protocol
- בניסויים אלה, שתי מערכות נפרדות מנוצלים בעת ובעונה אחת. לרכישת ספקטרום P 31, מגנט 14T Bruker היא interfaced עם III Avance קונסולת מחשב המצויד בתוכנות טופספין v2.1. לקבלת הערכה של תפקוד הלב, זלוף אישית בנוי מערכת הלב interfaced עם PowerLab 4 / 30 רכישת נתונים, מצויד בתוכנה LabChartPro 6 לניתוח נתונים.
- ביום הניסוי, 1 ליטר של חיץ קרבס-Henseleit מוכן כדלקמן: 0.5mm EDTA, 5.3mM KCl, 1.2 מ"מ MgSO 4, 118mM NaCl, ו 25mm NaHCO 3. תערובת הוא מבעבע אז עם 5% CO 2 / 95% O 2 במשך 10-15 דקות לפני תוספת של 2 מ"מ CaCl 2. לבסוף, מצעים, בצורה של גלוקוזה 10 מ"מ pyruvate 0.5mm, מתווספים.
- ויסות טמפרטורה במהלך הניסוי הוא קריטי. Circulators מחוממת משמשים כדי לשמור על טמפרטורה בין 37.0-37.5 ° C תוך הלב בתוך המגנט. טמפרטורה היא במעקב למשך הניסוי באמצעות בדיקה סיבים אופטיים הטמפרטורה.
- לחץ זלוף והלחץ החדר השמאלי מנוטרים באמצעות מתמרים ללחץ המצורפת מערכת נתונים הרכישה מוצג באמצעות תוכנה כלולה. אלו מכוילים עם מד לחץ דם רגיל לפני הניסוי. בנוסף, קווי לחץ סמוקות כראוי על מנת להסיר את כל בועות האוויר.
- מדגם סטנדרטי של 150 מ"מ פוספט נתרן (שהוא שווה ערך כוח יוניים של למאגר KH) משמש כדי "לכייל" את החללית לקראת הכניסה של הלב. זה מקל את האות מקטין את הזמן הדרוש כדי להתחיל את תקופת רכישת פעם את הלב ממוקם בתוך החללית.
- כדי להפחית קרישת, העכבר מוזרק עם 200 יחידות של ה-IP הפרין אחרי 5 דקות, pentobarbital נתרן (175 מ"ג / ק"ג) IP נתונה.
- הלב הוא נכרת במהירות (עם הריאות התימוס שלם) ועצרו בקרח קר KH חיץ.
- אמנם שמרה על הקרח, הריאות מוסרים במהירות. אונות התימוס מזוהים קלופים בעדינות לאחור כדי לחשוף את אבי העורקים. התימוס הוא הוסר. אבי העורקים הוא מבודד אז בקפידה על ידי הסרת כל הרקמה שמסביב.
- מיקרו תפירת מלקחיים המשמשים בעדינות להחזיק בשני קירות של האאורטה לחשוף את לומן. אבי העורקים ממוקם בזהירות על צינורית עשוי צינורות פוליאתילן OD 0.965 מ"מ (PE50). אבי העורקים נערכת במקום עם מהדק כלי מיקרו בעוד התפרים קשורות במהירות סביב האאורטה. הקליפ הוסר ואת מלקחיים המשמשים לבדוק היטב כי הצינורית הוא מעל שורש האאורטה. קשרים נוספים מתווספים ככל שיידרש כדי להחזיק את הלב במקום.
- כל רקמה נוספת היא להסיר באמצעות מלקחיים microscissors. חתך קטן עשה אל החדר השמאלי. 0.61 מ"מ OD צינורות פוליאתילן (PE10) מוחדר בזהירות באמצעות אטריום שמאל, חלל LV, ועל דרך הקודקוד תוך בעדינות מחזיק את הלב. צינורות עודף חיתוך.
- בניכוי מלא מים בלון מוחדר דרך אטריום לתוך LV והוא מוחזק במקום באמצעות דבק או תפרים. מהירות המשאבה peristaltic הוא גדל בהדרגה כדי לספק זרימה מספקת ללב. עד הלב הוא המקום לתוך החללית NMR, הלב תמשיך להיות perfused עם זרם בלתי פוסק שווה ערך ל כ 2 מ"ל / דקה. הבלון מנופח LV היא עם נפח קטן באמצעות מזרק מיקרומטר כדי לוודא מתמר הלחץ LV מתפקד.
- הלב הוא מוכנס בזהירות לתוך צינור NMR 10 מ"מ. רחב נשא "טווה" משמש כדי להנחות את הצינור למקומו הנכון בתוך החללית. המנגנון כולו אז מחובר היטב "חבל הטבור" עם דבק.
- חבל הטבור הוא הוריד לאט לתוך נשא העליון של מגנט עד הצינור לב / NMR נמצא בתוך סליל של בדיקה 10 מ"מ NMR.
- לאחר הלב במקום הנכון בתוך החללית, תזרים המשאבה peristaltic מותאם על מנת להשיג בלחץ זלוף של 80mmHg. (זכור, כי עד לנקודה זו את הלב היה perfused עם תזרים קבוע של כ 2 מ"ל / דקה). הלחץ זלוף נשמר אז על ידי הפעלת "להחזיק" מנגנון בבקר המשאבה. הלב הוא מותר אז תקופה איזון 15-20 דקות. במהלך תקופה זו, בהיקף של הבלון LV מותאם להשיג הלחץ סוף דיאסטולי של 80-10 מ"מ כספית.
- במהלך התקופה איזון, יש צורך לייעל את הפרמטרים ספקטרומטר על מנת לקבל את האות זרחן הטוב ביותר האפשרי. מטרה זו מושגת על ידי הגדרת הדופק רדיו בתדר בו גרעין זרחן מהדהד ("כוונון") ועושה את השדה המגנטי אחיד ("shimming").
- לאחר תקופת איזון, מספר 31 P ספקטרום NMR ניתן להשיג. תקופת הרכישה עבור כל ספקטרום תלויה לאהוא שדה הכוח של המגנט, גודל המדגם, ואת יחס אות לרעש הדרוש לניסוי מסוים. ספקטרה מתקבלים באמצעות מגנט 14 Telsa ידי ממוצעים של האות המתקבל 256 תדירות פולסים של רדיו 20 μs עם זווית להעיף ועיכובים 60 מעלות של 2.0 שניות. ניסוי זה ידרוש כ 10 דקות.
נציג תוצאות
מתוך נתונים על רכישת חומרה ואת התוכנה LabChart, מספר פרמטרים של תפקוד הלב יכול להימדד בכל פרוטוקול הניסוי. למדוד הטיפוסי של תפקוד הלב, החדר השמאלי לחץ המפותחות (LVDevP), מתקבל על ידי הפחתת הלחץ סוף דיאסטולי (EDP) מן הלחץ הסיסטולי (איור 1). צעד זה יכול להשתנות בהתאם זן של העכבר ואת מצב הלב (כלומר, יתר לחץ). עם זאת, LVDevP לב נורמלי C57BL6 העכבר הוא בדרך כלל בין 100-110 מ"מ כספית בלחץ הדיאסטולי סוף קבוע של 80-10 מ"מ כספית. בנוסף, התוכנית מאפשרת LabChart למדידת קצב הלב המבוסס על מדידות מחזורית של גלי לחץ LV. שוב, צעד זה יכול להשתנות אבל הערכים האופייניים הם 350-400 פעימות לדקה כאשר לבבות מותר להכות בשיעורים מהותיים. עם זאת, הלב יכול להיות סטנדרטית באמצעות מערכת לצעוד בו קצב הלב נשמר על 420 פעימות לדקה. בנוסף, אמצעי contractility (+ DP / dt) והרפיה (-dP/dt) ניתן להעריך באמצעות הנגזרת הראשונה של גל הלחץ LV. במהלך פרוטוקול הניסוי קל להעריך את מנגנון סטרלינג על ידי שילוב מערכת יחסים הלחץ נפח. מטרה זו מושגת על ידי ביצוע חשיפה הדרגתית של נפח את הבלון LV ורשם LVDevP וכן EDP. ערכים אלה לאחר מכן ניתן להתוות כמתואר באיור 2. בעוד עקומת סטרלינג הוא אופטימלי, וציין את נפח הדרושים כדי להשיג EDP של 8-10 מ"מ כספית יכולה לתת מושג עקיפה מימד קאמרית LV. ניתן להשתמש במודלים של אבי העורקים banding כמו לבבות שגדלה יתר על המידה בדרך כלל ידרוש נפח בלון קטן בעוד לבבות מורחבים דורשים נפח גדול יותר בהשוואה לקבוצת הביקורת. טבלה 1 מציגה נתונים נציג תפקוד הלב רכשה במהלך הפרוטוקול זלוף.
31 P NMR הספקטרומטר יספק אותות של phosphocreatine (PCR) ושלושה פוספטים מן ה-ATP (γ-ATP, α-ATP, ו - β-ATP) וכן פוספטים אנאורגניים (PI) כפי שמוצג באיור 2. ניתוח של כל אחת מן הפסגות האלה מספק ערך עבור האזור מתחת לעקומה. כמות ה-ATP מוערך על ידי חישוב ממוצע γ-ATP ו - β-ATP אזורים. (Α-ATP אינו משמש כי מולקולות NAD לתרום חלק לא ידוע של האות סה"כ). המצב האנרגטי של הלב נקבע על ידי מנה של PCR אזורי ה-ATP (PCR: יחס ATP). ערך זה הוא בדרך כלל 1.5-1.7 בלב עכבר מסופק עם גלוקוז כמו המצע הראשוני. למרות 31 P התמ"ג אינו מספק אמצעי ישיר של ה-ATP או PCR, באזור של פסגות היא פרופורציונלית לסכום של זרחן המכיל תרכובות במדגם. ערכים עבור אותות אלה יכולים להיות מוערך על ידי שימוש בשיטות אחרות. לדוגמה, אמצעים ישירה של ה-ATP על ידי כרומטוגרפיה ביצועים גבוהים נוזלי (HPLC) במדגם של לבבות יכול להניב הריכוז הממוצע. ערך זה לאחר מכן ניתן להשתמש כדי לכייל את האזורים הממוצע ATP שנצפתה הספקטרום. ריכוז ה-PCR יכול להיות מחושב על בסיס אזור PCR יחסית לאזור ה-ATP. אפשר גם להעריך את רמת החומציות על ידי ניתוח שינוי כימי יחסית של פוספטים אנאורגניים (PI) אות לאות PCR. 1 שימוש אחר הדופק רדיו רצפים, מהירות התגובה קריאטין קינאז או את מהירות התגובה סינתזה ATP ניתן גם למדוד 2.
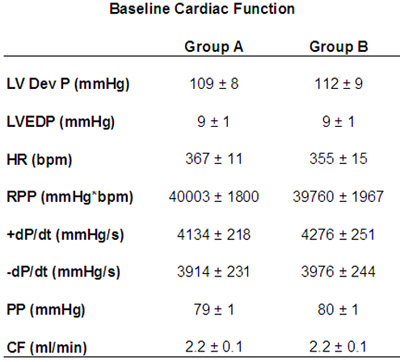
1. Baseline טבלה תפקוד הלב מן הלבבות perfused מבודדים. LVDevP: הלחץ החדר השמאלי מפותח; LVEDP: החדר השמאלי בסוף הלחץ הדיאסטולי, HR: קצב הלב, RPP: הלחץ מוצר קצב; + DP / dt: לחץ first נגזרות LV חיובית; -dP/dt: לחץ first נגזרות LV שלילי; PP : לחץ זלוף: ק"פ: זרימה כלילית.
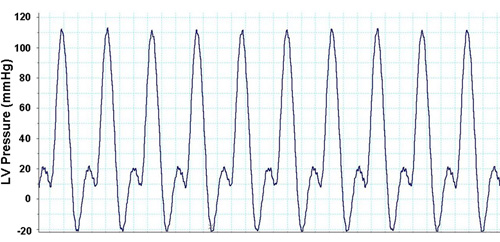
1. איור נציג הלחץ LV גלים מפני תוכנות LabChart Pro.
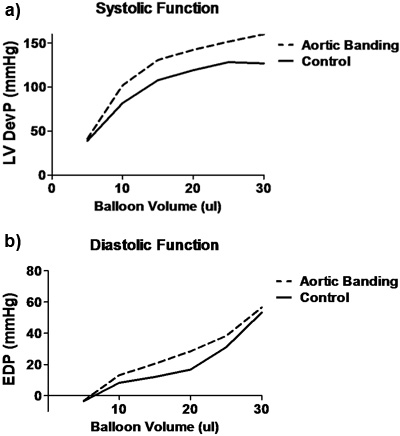
איור 2. עקומות נציג זרזיר מהשלט (קו מוצק) ואת אבי העורקים התאגדו (קו מקווקו) בעכברים. א) פונקציה הסיסטולי כפי שהוא מיוצג על ידי הגדלת נפח LV LVDevP כפי שנקבע על ידי היקף הבלון LV. ב) פונקציה הדיאסטולי כמו מיוצג על ידי EDP על הגדלת נפח LV כפי שנקבע על ידי עוצמת הקול של הבלון LV. LVDevP: הלחץ החדר השמאלי מפותח (סיסטולי ודיאסטולי מינוס pressure); EDP: סוף דיאסטולי לחץ.
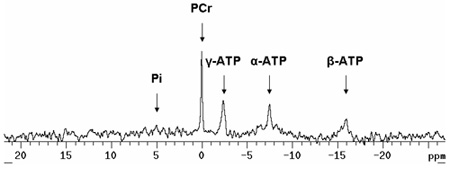
3. איור 31 נציג P ספקטרום NMR של הלב מבודד עכבר perfused. שימו לב לשיא קטן יחסית Pi. בלב perfused aerobically מסופק עם חומצות שומן או pyruvate בנוסף גלוקוז, שיא זה צריך להיות מינימלי. בתקופות של איסכמיה, זה מגביר את השיא בזמן שיא PCR פוחתת. שימו לב כתף ימין של שיא α-ATP. זוהי תרומתו של מולקולות NAD. Pi: פוספטים אנאורגניים; PCR: phosphocreatine; ה-ATP: אדנוזין טריפוספט.
Discussion
31P NMR spectroscopy in the Langendorff-perfused isolated mouse heart provides reliable and reproducible data.3, 4 However, it is imperative that cannulation of the aorta and insertion of the LV balloon are done properly such to allow stable cardiac performance while inside the NMR tube. In addition, temperature regulation is paramount in order to achieve proper baseline function. One important factor in obtaining good, analyzable NMR spectra is increasing the signal to noise ratio. This can be achieved by ensuring optimal "tuning" and "shimming" on the sample. As mentioned in the protocol text, the use of a standard sample prior to the insertion of the heart can facilitate this. It is also helpful to have an adequate sized "sample". Hearts weighing less than 100 mg typically provide lower PCr and ATP signals so increases in acquisition time will be necessary to obtain good phosphorous spectra.
There are several ways to modify the existing protocol to garner additional information regarding cardiac function and energetics. In our laboratory, we have perfused hearts with mixed substrate buffers which can include the presence of different combinations of fatty acids (in low and high concentrations), lactate, ketones, and insulin. With the use of stable isotopes in the perfusion buffer (i.e., 13C labeled substrates), we possess the ability to estimate substrate utilization by the relative contribution of labeled acetyl CoA to the TCA cycle.5-7 For this application, we perform isotopomer analysis of 13C3- and 13C4- glutamate with 13C NMR spectroscopy. This requires freeze-clamping the heart at the end of the perfusion protocol and performing an extraction of the frozen tissue. This will be an additional experiment as the analysis requires the use of a different probe with separate setup parameters. Other applications include the substitution of glucose with deoxyglucose in the buffer while monitoring the time-dependent accumulation of 2-deoxyglucose phosphate in the heart using 31P NMR spectroscopy. This method allows for the measurement of myocardial glucose uptake.7, 8 In addition, our laboratory has analyzed cardiac function and energetics in perfusion protocols consisting of ischemia/reperfusion and high workload challenge.6, 8-10
In summary, 31P NMR spectroscopy in isolated mouse hearts is a technically challenging procedure requiring the use of sophisticated equipment. However, the data that it yields is invaluable to the researcher who wishes to analyze the function and energetics of bioengineered mouse models. For our laboratory, these techniques have been vital in our understanding of the consequences of a variety of stressors on cardiac function, energetics, and metabolism.1, 11, 12
Disclosures
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Lynne Spencer for her support during the NMR spectroscopy portion of the experiment. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health fund R01 HL059246, R01 HL067970, R01 HL088634 (to Dr. Tian) and F32 HL096284 (to Dr. Kolwicz).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments | |
| Magnesium Sulfate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | M7506 | |
| EDTA | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | E1644 | |
| Potassium chloride | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | P4505 | |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | S6297 | |
| Sodium chloride | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | S7653 | |
| Calcium chloride dihydrate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | C5080 | |
| D-Glucose | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | G7528 | |
| Sodium Pyruvate | Reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | P2256 | |
| Bruker Ultrashield 600WB Plus | Equipment | Bruker Corporation | ||
| PowerLab 4/30 | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | ML866/P | |
| LabChart 6 Pro | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | MLS260/6 | |
| Quad Bridge Amp | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | ML224 | |
| STH Pump Controller | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | ML175 | |
| Minipuls 3 Peristaltic Pump | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | ML172 | |
| Disposable BP Transducer | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | MLT0699 | |
| 10mm NMR Sample Tube | Equipment | Wilmad LabGlass | 513-7PP-7 | |
| Polyethylene tubing PE10 | Equipment | BD Biosciences | 427401 | |
| Physiological Pressure Transducer | Equipment |  ADInstruments ADInstruments | MLT844 | |
| Polyethylene tubing PE50 | Equipment | BD Biosciences | 427411 | |
| Micrometer syringe | Equipment | Gilmont Instruments | GS-1101 | |
| McPherson Forceps | Equipment | Miltex Inc. | 18-949 | |
| Castraviejo microscissors | Equipment | Roboz Surgical Instruments Co. | RS-5650 | |
| Neoptix Signal Conditioner | Equipment | Neoptix, Inc. | Reflex - 1 |
References
- Nascimben, L., Ingwall, J. S., Lorell, B. H., Pinz, I., Schultz, V., Tornheim, K., Tian, R. Mechanisms for increased glycolysis in the hypertrophied rat heart. Hypertension. 44, 662-667 (2004).
- Spindler, M., Saupe, K. W., Tian, R., Ahmed, S., Matlib, M. A., Ingwall, J. S. Altered creatine kinase enzyme kinetics in diabetic cardiomyopathy. A(31)P NMR magnetization transfer study of the intact beating rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31, 2175-2189 (1999).
- Ingwall, J. S. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of cardiac and skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 242, H729-H744 (1982).
- Ingwall, J. S., Javadpour, M. M., Miao, W., Hoit, B. D., Walsh, R. A. 31P NMR spectroscopy of the mouse heart. Cardiovascular physiology in the genetically engineered. , 151-163 (2002).
- Luptak, I., Balschi, J. A., Xing, Y., Leone, T. C., Kelly, D. P., Tian, R. Decreased contractile and metabolic reserve in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha-null hearts can be rescued by increasing glucose transport and utilization. Circulation. 112, 2339-2346 (2005).
- Yan, J., Young, M. E., Cui, L., Lopaschuk, G. D., Liao, R., Tian, R. Increased glucose uptake and oxidation in mouse hearts prevent high fatty acid oxidation but cause cardiac dysfunction in diet-induced obesity. Circulation. 119, 2818-2828 (2009).
- Luptak, I., Shen, M., He, H., Hirshman, M. F., Musi, N., Goodyear, L. J., Yan, J., Wakimoto, H., Morita, H., Arad, M., Seidman, C. E., Seidman, J. G., Ingwall, J. S., Balschi, J. A., Tian, R. Aberrant activation of AMP-activated protein kinase remodels metabolic network in favor of cardiac glycogen storage. J Clin Invest. 117, 1432-1439 (2007).
- Xing, Y., Musi, N., Fujii, N., Zou, L., Luptak, I., Hirshman, M. F., Goodyear, L. J., Tian, R. Glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis in mouse hearts overexpressing dominant negative alpha2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 278, 28372-28377 (2003).
- Luptak, I., Yan, J., Cui, L., Jain, M., Liao, R., Tian, R. Long-term effects of increased glucose entry on mouse hearts during normal aging and ischemic stress. Circulation. 116, 901-909 (2007).
- Tian, R., Abel, E. D. Responses of GLUT4-deficient hearts to ischemia underscore the importance of glycolysis. Circulation. 103, 2961-2966 (2001).
- Liao, R., Jain, M., Cui, L., D'Agostino, J., Aiello, F., Luptak, I., Ngoy, S., Mortensen, R. M., Tian, R. Cardiac-specific overexpression of GLUT1 prevents the development of heart failure attributable to pressure overload in mice. Circulation. 106, 2125-2131 (2002).
- Tian, R., Musi, N., D'Agostino, J., Hirshman, M. F., Goodyear, L. J. Increased adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity in rat hearts with pressure-overload hypertrophy. Circulation. 104, 1664-1669 (2001).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved