14.15 : Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion
In the early 17th century, German astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler postulated three laws for the motion of planets in the solar system. He formulated his first two laws based on the observations of his forebears, Nikolaus Copernicus and Tycho Brahe.
Polish astronomer Nikolaus Copernicus put forth a theory that stated a heliocentric model for the solar system. According to this heliocentric theory, all the planets, including Earth, orbit the Sun in circular orbits.
On the other hand, Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe, the employer of Johannes Kepler, had meticulously recorded the position of every planet in detail. For most visible planets, these observations were in accordance with the Copernican heliocentric theory, except for the planet Mars.
While analyzing the Mars data of Tycho Brahe, Johannes Kepler realized that the Copernican theory was accurate except that planets revolve around the Sun in an elliptical orbit rather than circular orbits. This led him to his first law of planetary motion, which states that every planet travels along an ellipse, with the Sun located at one of the ellipse's foci.
An ellipse is an elongated circle. The degree of elongation of an ellipse is expressed using a parameter called eccentricity.

An axis of an ellipse along the elongation is called the major axis a, and the one perpendicular to it is the minor axis b. Therefore, the eccentricity of an ellipse is expressed as
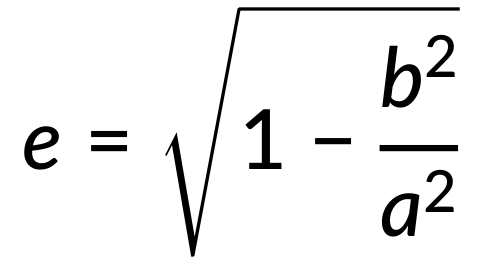
Since b < a, the eccentricity of an ellipse is always less than unity. For a circle, a = b, hence the eccentricity of a circle is zero.
The eccentricity of Martian orbit is 0.0935. It is considered to have the most eccentric orbit after Mercury, whose eccentricity is 0.21. Earth's orbit has an eccentricity of 0.0167.
Since planets are in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one of the foci, their radial distances change throughout the year. Their closest distance from the Sun is known as the perigee, while the farther distance is called the apogee.
This text is adapted from Openstax, University Physics Volume 1, Section 13.5 Kepler's Laws of Motion.
Dal capitolo 14:

Now Playing
14.15 : Kepler's First Law of Planetary Motion
Gravitation
3.9K Visualizzazioni

14.1 : Gravitazione
Gravitation
6.2K Visualizzazioni

14.2 : Legge di Gravitazione di Newton
Gravitation
12.5K Visualizzazioni

14.3 : Gravitazione tra masse sfericamente simmetriche
Gravitation
852 Visualizzazioni

14.4 : Gravità tra corpi sferici
Gravitation
8.3K Visualizzazioni

14.5 : Coordinate di massa ridotte: problema isolato a due corpi
Gravitation
1.2K Visualizzazioni

14.6 : Accelerazione dovuta alla gravità sulla Terra
Gravitation
10.6K Visualizzazioni

14.7 : Accelerazione dovuta alla gravità su altri pianeti
Gravitation
4.1K Visualizzazioni

14.8 : Peso apparente e rotazione terrestre
Gravitation
3.5K Visualizzazioni

14.9 : Variazione dell'accelerazione dovuta alla gravità vicino alla superficie terrestre
Gravitation
2.4K Visualizzazioni

14.10 : Energia potenziale dovuta alla gravitazione
Gravitation
5.4K Visualizzazioni

14.11 : Il principio di sovrapposizione e il campo gravitazionale
Gravitation
1.3K Visualizzazioni

14.12 : Velocità di fuga
Gravitation
5.6K Visualizzazioni

14.13 : Orbite circolari e velocità critica per i satelliti
Gravitation
2.9K Visualizzazioni

14.14 : Energia di un satellite in orbita circolare
Gravitation
2.2K Visualizzazioni
See More