The equilibrium binding constant (Kb) quantifies the strength of a protein-ligand interaction. Kb can be calculated as follows when the reaction is at equilibrium:
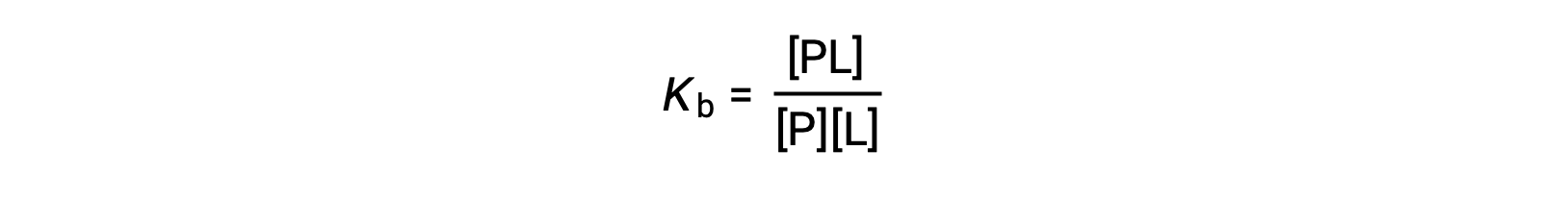
where P and L are the unbound protein and ligand, respectively, and PL is the protein-ligand complex.
As the amount of bound ligand is also related to the rate of ligand binding, experiments can also determine Kb by examining the rates of protein-ligand association (kon) and dissociation (koff) using the following ratio:
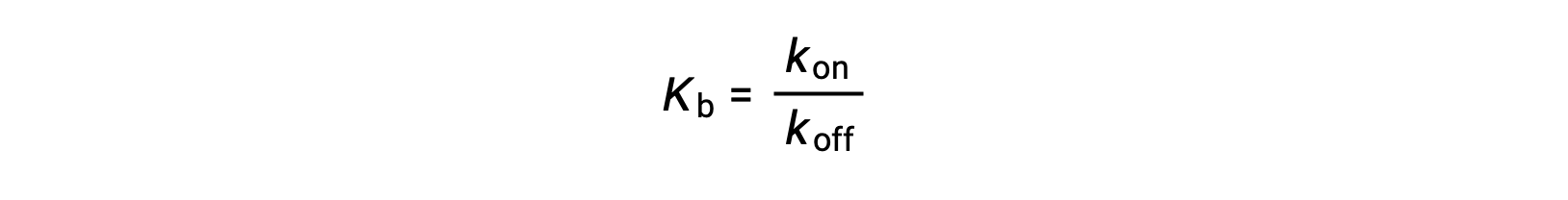
Thus, two categories of binding assays are used to determine the equilibrium binding constant – those that measure equilibrium concentrations and those that measure a reaction’s kinetics. In case, the reaction must be at equilibrium at the time of measurement.
The method of determining the equilibrium concentrations depends on the desired sensitivity and ease of signal detection. For these reasons, spectroscopic assays are most widely used. In these experiments, the reaction produces an absorbance change of a reactant or a product at a given wavelength, detectable by a UV-Vis spectrophotometer. Alternatively, the reactant or product can be tagged with a fluorescent probe or may contain an intrinsic fluorophore. Then, the reaction progress can be measured from the change in fluorescence. These assays are performed by varying one reactant’s concentrations while the rest of the experiment is held constant. The results can then be graphed and analyzed with various curve fitting methods.
Interactions between proteins and ligands are also studied using a variety of biochemical and spectroscopic techniques. Structural analysis, using X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy, aids in predicting protein-ligand interactions through molecular simulations. Theoretical and computational approaches, such as protein-ligand docking studies, are used extensively to characterize the position and interactions of small molecule ligands, including drug candidates. Computer-aided drug design is a fast and low-cost alternative to accelerate the pace of conventional trial and error drug testing.
장에서 4:

Now Playing
4.4 : 평형 결합 상수와 평형 결합 강도
Protein Function
12.5K Views

4.1 : 리간드 결합 자리
Protein Function
12.5K Views

4.2 : 단백질-단백질 접점
Protein Function
12.4K Views

4.3 : 보존된 결합 자리
Protein Function
4.1K Views

4.5 : 보조인자와 보조효소
Protein Function
7.2K Views

4.6 : 다른자리입체성 조절
Protein Function
13.8K Views

4.7 : 리간드 결합
Protein Function
4.7K Views

4.8 : 협동적 다른자리입체성 전이
Protein Function
7.8K Views

4.9 : 인산화
Protein Function
5.8K Views

4.10 : 단백질 인산화효소와 인산가수분해효소
Protein Function
12.8K Views

4.11 : GTP가수분해효소와 효소의 조절
Protein Function
8.1K Views

4.12 : 공유결합 단백질 조절자
Protein Function
6.6K Views

4.13 : 단백질 복합체와 교체 가능한 부위
Protein Function
2.5K Views

4.14 : 기계 단백질 기능
Protein Function
4.8K Views

4.15 : 구조 단백질 기능
Protein Function
27.0K Views
See More
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. 판권 소유