Compared with pure water, the solubility of an ionic compound is less in aqueous solutions containing a common ion (one also produced by dissolution of the ionic compound). This is an example of a phenomenon known as the common ion effect, which is a consequence of the law of mass action that may be explained using Le Châtelier’s principle. Consider the dissolution of silver iodide:
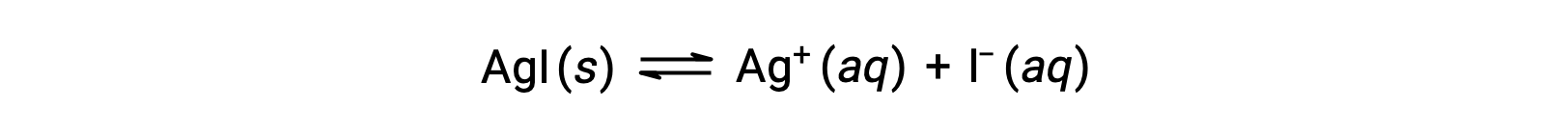
This solubility equilibrium may be shifted left by the addition of either silver(I) or iodide ions, resulting in the precipitation of AgI and lowered concentrations of dissolved Ag+ and I–. In solutions that already contain either of these ions, less AgI may be dissolved than in solutions without these ions.
This effect may also be explained in terms of mass action as represented in the solubility product expression:
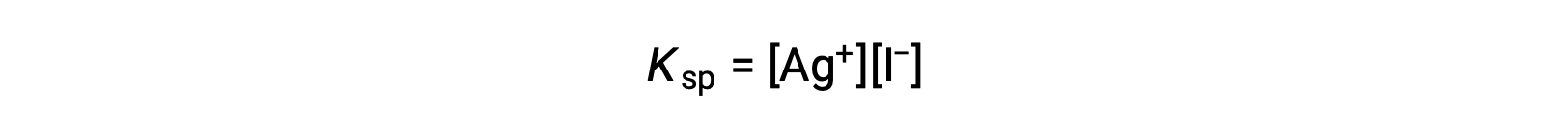
The mathematical product of silver(I) and iodide ion molarities is constant in an equilibrium mixture regardless of the source of the ions, and so an increase in one ion’s concentration must be balanced by a proportional decrease in the other.
Common Ion Effect on Solubility
The common ion affects the solubility of the compound in a solution. For example, solid Mg(OH)2 dissociate into Mg2+ and OH− ions as follows;
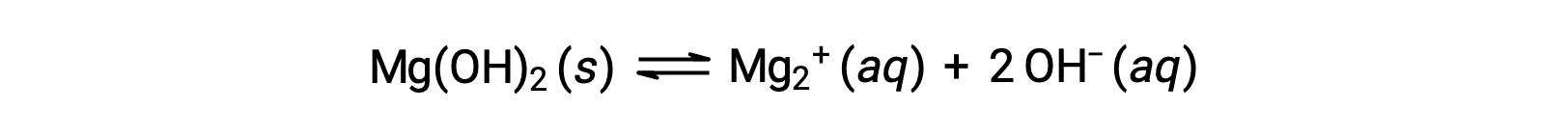
If MgCl2 is added to a saturated solution of Mg(OH)2, the reaction shifts to the left to relieve the stress produced by the additional Mg2+ ion, in accordance with Le Châtelier’s principle. In quantitative terms, the added Mg2+ causes the reaction quotient to be larger than the solubility product (Q > Ksp), and Mg(OH)2 forms until the reaction quotient again equals Ksp. At the new equilibrium, [OH–] is less and [Mg2+] is greater than in the solution of Mg(OH)2 in pure water.
If KOH is added to a saturated solution of Mg(OH)2, the reaction shifts to the left to relieve the stress of the additional OH– ion. Mg(OH)2 forms until the reaction quotient again equals Ksp. At the new equilibrium, [OH–] is greater and [Mg2+] is less than in the solution of Mg(OH)2 in pure water.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 15.1: Precipitation and Dissolution.
Z rozdziału 16:

Now Playing
16.1 : Common Ion Effect
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
40.7K Wyświetleń

16.2 : Buffers
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
163.1K Wyświetleń

16.3 : Równanie Hendersona-Hasselbalcha
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
67.8K Wyświetleń

16.4 : Obliczanie zmian pH w roztworze buforowym
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.3K Wyświetleń

16.5 : Skuteczność bufora
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
48.3K Wyświetleń

16.6 : Obliczenia miareczkowania: mocny kwas - mocna zasada
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
28.8K Wyświetleń

16.7 : Obliczenia miareczkowania: słaby kwas - mocna zasada
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
43.6K Wyświetleń

16.8 : Wskaźniki
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
47.6K Wyświetleń

16.9 : Miareczkowanie kwasu poliprotonowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
95.5K Wyświetleń

16.10 : Równowaga rozpuszczalności
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
51.4K Wyświetleń

16.11 : Czynniki wpływające na rozpuszczalność
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
32.8K Wyświetleń

16.12 : Powstawanie jonów złożonych
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
23.0K Wyświetleń

16.13 : Wytrącanie jonów
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
27.3K Wyświetleń

16.14 : Analiza jakościowa
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
19.9K Wyświetleń

16.15 : Krzywe miareczkowania kwasowo-zasadowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
125.8K Wyświetleń
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone