16.6 : Titration Calculations: Strong Acid - Strong Base
Calculating pH for Titration Solutions: Strong Acid/Strong Base
A titration is carried out for 25.00 mL of 0.100 M HCl (strong acid) with 0.100 M of a strong base NaOH. The pH at different volumes of added base solution can be calculated as follows:
(a) Titrant volume = 0 mL. The solution pH is due to the acid ionization of HCl. Because this is a strong acid, the ionization is complete and the hydronium ion molarity is 0.100 M. The pH of the solution is then:

(b) Titrant volume = 12.50 mL. Since the acid sample and the base titrant are both monoprotic and equally concentrated, this titrant addition involves less than a stoichiometric amount of base, and so it is completely consumed by reaction with the excess acid in the sample. The concentration of acid remaining is computed by subtracting the consumed amount from the initial amount and then dividing by the solution volume:
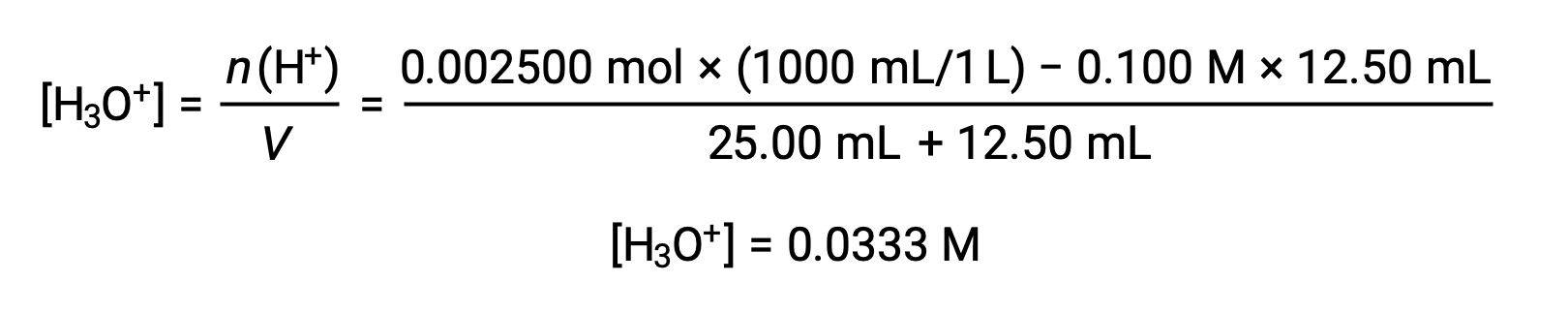
(c) Titrant volume = 25.00 mL. This titrant addition involves a stoichiometric amount of base (the equivalence point), and so only products of the neutralization reaction are in solution (water and NaCl). Neither the cation nor the anion of this salt undergo acid-base ionization; the only process generating hydronium ions is the autoprotolysis of water. The solution is neutral, having a pH = 7.00.
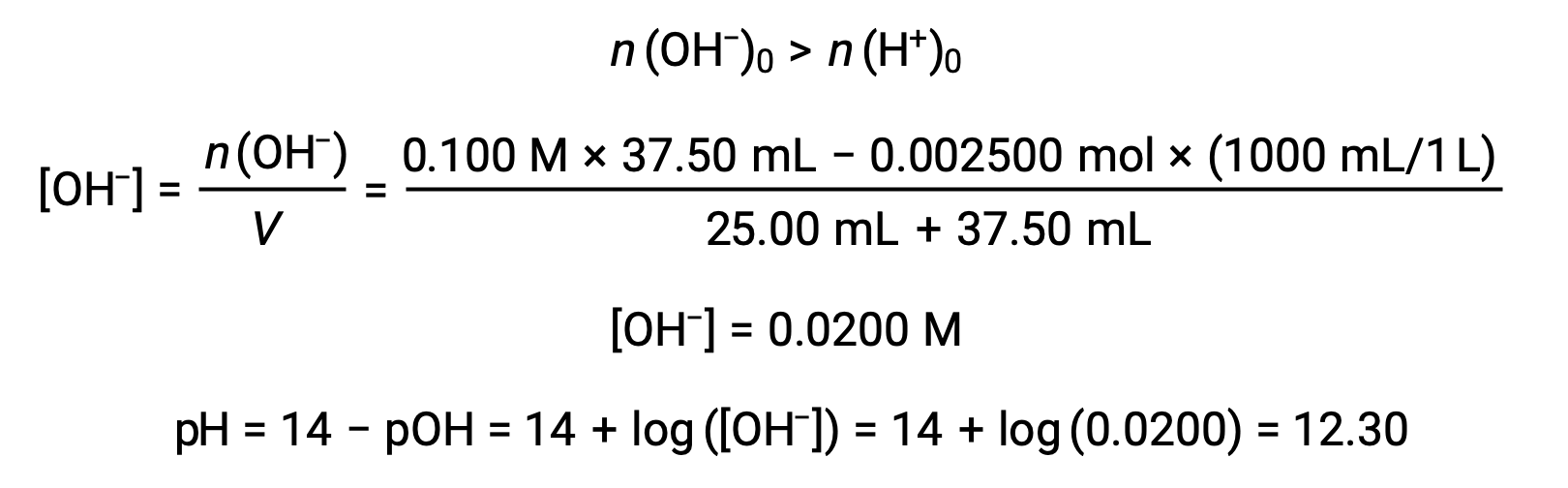
(d) Titrant volume = 37.50 mL. This involves the addition of titrant in excess of the equivalence point. The solution pH is then calculated using the concentration of hydroxide ion:
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.7: Acid-base Titrations.
Z rozdziału 16:

Now Playing
16.6 : Titration Calculations: Strong Acid - Strong Base
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
28.9K Wyświetleń

16.1 : Wspólny efekt jonowy
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
40.8K Wyświetleń

16.2 : Buffers
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
163.2K Wyświetleń

16.3 : Równanie Hendersona-Hasselbalcha
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
67.9K Wyświetleń

16.4 : Obliczanie zmian pH w roztworze buforowym
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.5K Wyświetleń

16.5 : Skuteczność bufora
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
48.3K Wyświetleń

16.7 : Obliczenia miareczkowania: słaby kwas - mocna zasada
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
43.7K Wyświetleń

16.8 : Wskaźniki
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
47.7K Wyświetleń

16.9 : Miareczkowanie kwasu poliprotonowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
95.6K Wyświetleń

16.10 : Równowaga rozpuszczalności
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
51.8K Wyświetleń

16.11 : Czynniki wpływające na rozpuszczalność
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
32.9K Wyświetleń

16.12 : Powstawanie jonów złożonych
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
23.1K Wyświetleń

16.13 : Wytrącanie jonów
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
27.4K Wyświetleń

16.14 : Analiza jakościowa
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
20.0K Wyświetleń

16.15 : Krzywe miareczkowania kwasowo-zasadowego
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
126.1K Wyświetleń
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone