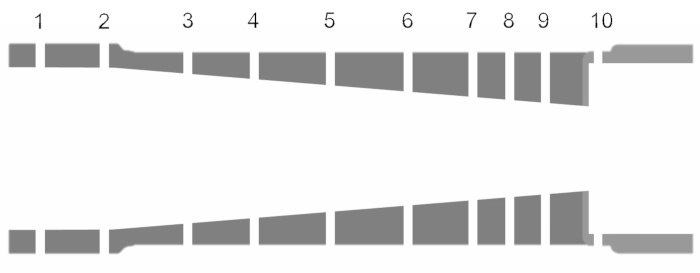
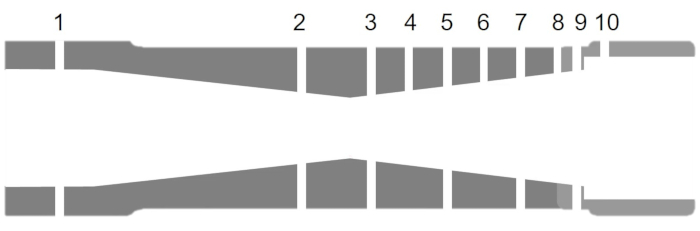
Análise de bocais: variações no número de Mach e na pressão ao longo de um bocal convergente e convergente-divergente
Visão Geral
Fonte: Shreyas Narsipur, Engenharia Mecânica e Aeroespacial, Universidade Estadual da Carolina do Norte, Raleigh, NC
Um bocal é um dispositivo que é comumente usado para acelerar ou desacelerar o fluxo em virtude de sua seção transversal variada. Bicos são amplamente utilizados em sistemas de propulsão aeroespacial. Em foguetes, o propulsor que é ejetado da câmara é acelerado através de um bico para criar uma força de reação que impulsiona o sistema. Em motores a jato, um bico é usado para transformar energia de uma fonte de alta pressão em energia cinética do escapamento para produzir impulso. O modelo isentrópico ao longo do bocal é suficiente para uma análise de primeira ordem, pois o fluxo em um bocal é muito rápido (e, portanto, adiabático a uma primeira aproximação) com muito pouca perda de atrito (porque o fluxo é quase unidimensional com um gradiente de pressão favorável, exceto se as ondas de choque se formam e os bicos são relativamente curtos).
Neste experimento, dois tipos de bicos são montados em uma plataforma de teste de bocal, e um fluxo de pressão é criado usando uma fonte de ar comprimido. Os bicos são executados para diferentes configurações de pressão traseira para analisar o fluxo interno nos bocais em condições de fluxo variadas, identificar os vários regimes de fluxo e comparar os dados com previsões teóricas.
Procedimento
Nesta demonstração, foi utilizada uma plataforma de teste de bocal, que consistia em uma fonte de ar comprimido que canaliza o ar de alta pressão através dos bocais que estão sendo testados, como mostrado na Figura 5. A pressão de fluxo varia de 0 a 120 psi e é controlada usando uma válvula mecânica. Enquanto as pressões são medidas usando um sensor externo, as taxas de fluxo de massa no bocal são medidas por um par de rotametros colocados logo antes do escape da plataforma de teste do bocal
Resultados
Na análise foram utilizadas as seguintes constantes: calor específico do ar seco, γ: 1,4; área do bocal de referência, Ai = 0,0491 em2, e pressão atmosférica padrão, Patm = 14,1 psi. As figuras 8 e 9 mostram a variação na relação de pressão e o número de Mach em todo o comprimento do bocal (normalizado com base no comprimento total do bocal) para várias configurações de pressão traseira para os bicos convergentes e convergentes, respectivamen...
Aplicação e Resumo
Os bicos são comumente usados em sistemas de propulsão de aeronaves e foguetes, pois oferecem um método simples e eficaz para acelerar o fluxo em distâncias restritas. A fim de projetar bicos para se adequar a uma determinada aplicação, uma compreensão do comportamento de fluxo e fatores que afetam o comportamento para uma série de condições de fluxo é essencial para projetar sistemas eficientes de propulsão. Nesta demonstração, os bicos convergentes e convergentes - dois dos tipos de bico mais comuns usado...
Pular para...
Vídeos desta coleção:

Now Playing
Análise de bocais: variações no número de Mach e na pressão ao longo de um bocal convergente e convergente-divergente
Aeronautical Engineering
38.0K Visualizações

Desempenho Aerodinâmico de um Aeromodelo: O DC-6B
Aeronautical Engineering
8.3K Visualizações

Caracterização da hélice: variações no passo, diâmetro e número de pás no desempenho
Aeronautical Engineering
26.5K Visualizações

Comportamento do aerofólio: Distribuição de pressão sobre uma asa Clark Y-14
Aeronautical Engineering
21.2K Visualizações

Desempenho da asa Clark Y-14: Implantação de dispositivos de alta sustentação (Flaps e Slats)
Aeronautical Engineering
13.4K Visualizações

Método da esfera de turbulência: avaliando a qualidade do fluxo do túnel de vento
Aeronautical Engineering
8.7K Visualizações

Fluxo Cilíndrico Cruzado: Medição da Distribuição de Pressão e Estimando os Coeficientes de Arrasto
Aeronautical Engineering
16.2K Visualizações

Imageamento de Schlieren: uma técnica para visualizar recursos de fluxo supersônico
Aeronautical Engineering
11.7K Visualizações

Visualização de fluxo em um túnel de água: observando o vórtice de ponta sobre uma asa delta
Aeronautical Engineering
8.2K Visualizações

Visualização de fluxo com corante de superfície: um método qualitativo para observar padrões de estrias em fluxo supersônico
Aeronautical Engineering
4.9K Visualizações

Tubo Pitot-estático: um dispositivo para medir a velocidade do fluxo de ar
Aeronautical Engineering
49.2K Visualizações

Anemometria de temperatura constante: uma ferramenta para estudar o fluxo em camada limite turbulenta
Aeronautical Engineering
7.3K Visualizações

Transdutor de Pressão: Calibração Usando um Tubo Pitot-estático
Aeronautical Engineering
8.5K Visualizações

Controle de Voo em Tempo Real: Calibração de Sensor Incorporado e Aquisição de Dados
Aeronautical Engineering
10.3K Visualizações

Aerodinâmica de Multicópteros: Caracterizando o Empuxo em um Hexacóptero
Aeronautical Engineering
9.2K Visualizações
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos os direitos reservados