A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
The Synthesis of RGD-functionalized Hydrogels as a Tool for Therapeutic Applications
In This Article
Summary
We present a protocol for the synthesis of RGD-functionalized hydrogels as devices for cell and drug delivery. The procedure involves copper catalyzed alkyne-azide cycloaddition (CuAAC) between alkyne-modified polyacrylic acid (PAA) and a RGD-azide derivative. The hydrogels are formed using microwave-assisted polycondensation and their physicochemical properties are investigated.
Abstract
The use of polymers as biomaterials has provided significant advantages in therapeutic applications. In particular, the possibility to modify and functionalize polymer chains with compounds that are able to improve biocompatibility, mechanical properties, or cell viability allows the design of novel materials to meet new challenges in the biomedical field. With the polymer functionalization strategies, click chemistry is a powerful tool to improve cell-compatibility and drug delivery properties of polymeric devices. Similarly, the fundamental need of biomedicine to use sterile tools to avoid potential adverse-side effects, such as toxicity or contamination of the biological environment, gives rise to increasing interest in the microwave-assisted strategy.
The combination of click chemistry and the microwave-assisted method is suitable to produce biocompatible hydrogels with desired functionalities and improved performances in biomedical applications. This work aims to synthesize RGD-functionalized hydrogels. RGD (arginylglycylaspartic acid) is a tripeptide that can mimic cell adhesion proteins and bind to cell-surface receptors, creating a hospitable microenvironment for cells within the 3D polymeric network of the hydrogels. RGD functionalization occurs through Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition. Some PAA carboxyl groups are modified with an alkyne moiety, whereas RGD is functionalized with azido acid as the terminal residue of the peptide sequence. Finally, both products are used in a copper catalyzed click reaction to permanently link the peptide to PAA. This modified polymer is used with carbomer, agarose and polyethylene glycol (PEG) to synthesize a hydrogel matrix. The 3D structure is formed due to an esterification reaction involving carboxyl groups from PAA and carbomer and hydroxyl groups from agarose and PEG through microwave-assisted polycondensation. The efficiency of the gelation mechanism ensures a high degree of RGD functionalization. In addition, the procedure to load therapeutic compounds or biological tools within this functionalized network is very simple and reproducible.
Introduction
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks formed by hydrophilic cross-linked polymers, which are natural or synthetic, and characterized by a distinctive three-dimensional structure. These devices are increasingly attractive in the biomedical fields of drug delivery, tissue engineering, gene carriers and smart sensors1,2. Indeed, their high water content, as well as their rheological and mechanical properties make them suitable candidates to mimic soft tissue microenvironments and make them effective tools for water-soluble cytokine or growth factor delivery. One of the most promising use is as an injectable biomaterial carrying cells and bioactive compounds. Hydrogels may improve cell survival and control stem cell fate by holding and precisely delivering stem cell regulatory signals in a physiological relevant fashion, as observed in in vitro and in in vivo experiments3,4. The leading advantage of this is the possibility to maintain injected cells within the zone of inoculation (in situ), minimizing the amount of cells that leaves the area and extravasates into the circulatory torrent, migrating all over the body and losing the target goal5. The stability of the three-dimensional hydrogel networks is due to its cross-linking sites, formed by covalent bonds or cohesive forces among the polymer chains6.
In this framework, orthogonal selective chemistry applied to polymer chains is a versatile tool able to improve hydrogel performances7. Indeed, the modification of polymers with suitable chemical groups could help to provide appropriate chemical, physical and mechanical properties to enhance cell viability and their use in tissue formation. In the same way, among the techniques to load cells or growth factors within the gel matrix, the use of the RGD peptide allows improvements in cell adhesion and survival. RGD is a tripeptide composed of arginine, glycine and aspartic acid, which is by far the most effective and often employed tripeptide due to its ability to address more than one cell adhesion receptor and its biological impact on cell anchoring, behavior and survival8,9. In this work, the synthesis of RGD-functionalized hydrogels is studied with the aim of designing networks characterized by sufficient biochemical properties for a hospitable cell microenvironment.
The use of microwave radiation in hydrogel synthesis offers a simple procedure to minimize side reactions and obtain higher reaction rates and yields in a shorter period of time compared to the conventional thermal processes10. This method does not require purification steps and yields sterile hydrogels due to the interactions of the polymers and the absence of organic solvent in the reaction system11. Therefore, it ensures high percentages of RGD linked to the polymeric network because no modifications are required to the polymer chemical groups involved in gel formation. Carboxyl groups, from PAA and carbomer, and hydroxyl groups, from PEG and agarose, give rise to the hydrogel three-dimensional structure through a polycondensation reaction. The mentioned polymers are used for the synthesis of hydrogels in the spinal cord injury repair treatments12. These devices, as reported in previous works13,14, show high biocompatibility as well as mechanical and physicochemical properties that resemble those of many living tissues and in thixotropic nature. Moreover, they remain localized in situ, at the zone of injection.
In this work, PAA carboxyl groups are modified with an alkyne moiety (Figure 1), and a RGD-azide compound is synthesized exploiting the reactivity of the tripeptide terminal group -NH2 with a prepared chemical compound with structure (CH2)n-N3 (Figure 2). Subsequently, the modified PAA reacts with the RGD-azide derivative through CuAAC click reaction15-17 (Figure 3). The use of a copper(I) catalyst leads to major improvements in both the reaction rate and the regioselectivity. The CuAAC reaction is widely used in organic synthesis and in polymer science. It combines high efficiency and high tolerance to the functional groups, and it is unaffected by the use of organic solvents. A high selectivity, a fast reaction time and a simple purification procedure allow the obtainment of star polymers, block copolymers or chains grafting desired moieties18. This click strategy makes it possible to modify polymers after polymerization to customize the physicochemical properties according to the final biochemical application. The CuAAC experimental conditions are easily reproducible (the reaction is insensitive to water, whereas copper oxidation may occur minimally), and the nature of formed triazole ensures stability of the product. The use of copper metal can be considered a critical point, due to its potential toxic effect against cells and in the biological microenvironment, but dialysis is used as a purification method to allow the complete removal of catalytic residues. Finally, PAA modified RGD is used in hydrogel synthesis (Figure 4) and the physicochemical properties of the resulting networks are investigated, in order to check the potential functionality of these systems as cells or drugs carriers.
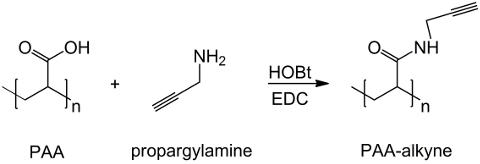
Figure 1: PAA modified alkyne synthesis. A scheme of PAA functionalization with alkyne group; "n" indicates the monomers with carboxyl group reacting with propargylamine. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 2: RGD-azide synthesis. The synthesis of RGD-azide derivative. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 3: Click reaction. Scheme of click reaction between RGD-azide derivative and alkyne-PAA. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.

Figure 4: Hydrogel synthesis. RGD functionalized hydrogel synthesis procedure. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
Note: The chemicals are used as received. Linear RGD is purchased, but it can be prepared by standard Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis16,19. Solvents are of analytical grade. The dialysis requires the use of membrane with a Mw cut-off equal to 3,500 Da. The synthesized compounds are characterized by 1H NMR spectra recorded on a 400 MHz spectrometer using chloroform (CDCl3) or deuterium oxide (D2O) as solvents, and chemical shifts are reported as δ values in parts per million. Furthermore, hydrogels are subjected to FT-IR analysis using KBr pellet technique and their physical characterization involves gelation studies assessed using the inverted test tube at 37 °C.
1. Synthesis of 4-Azidobutanoyl Chloride 1
- Dissolve 500 mg of 4-azidobutanoic acid (3.90 mmol) in 10 ml of dichloromethane and 0.5 ml of dimethylformamide.
- Cool the solution at 0 °C, using an ice bath.
- Add 505 µl of oxalyl chloride (5.85 mmol) to 5 ml of dichloromethane and slowly add dropwise to the reaction system, while stirring.
- After 1 hr at 0 °C using an ice bath, return to room temperature.
- Remove the solvent under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator.
- Characterize the obtained product by 1H-NMR spectroscopy, dissolving the sample in CDCl316.
2. Synthesis of RGD-azide Derivative 2
- Dissolve 50 mg of RGD (0.145 mmol) in 1 ml of 1 M NaOH.
- Dissolve 24 mg of 1 (0.16 mmol) in 2 ml of tetrahydrofuran.
- Add all of the RGD solution to solution 1 dropwise at 0 °C using an ice bath.
- Return to room temperature and stir overnight.
- Add 1 ml of 1 M HCl.
- Remove the solvent under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator.
- Characterize the obtained product by 1H-NMR spectroscopy, dissolving the sample in D2O16.
3. PAA Alkyne Modification 3
- Dissolve 200 mg of 35% w/w PAA solution (2.8 mmol) in 15 ml of distilled water.
- Add 15.4 mg of propargylamine hydrochloride (0.20 mmol).
- Dissolve 42.8 mg of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (HOBt, 0.28 mmol) in 14 ml of a 1:1 v/v acetonitrile:distilled water solution by heating to 50 °C.
- Add all of the HOBt solution to PAA solution at room temperature.
- Add 53.6 mg of ethyldimethylaminopropylcarbodiimide (EDC, 0.28 mmol) to the reaction mixture.
- Use 1 M HCl to adjust the pH to 5.5 and stir the reaction system overnight at room temperature.
- Dialyze the solution. Dissolve 11.2 g of sodium chloride in 2 L of distilled water and then add 0.2 ml of 37% w/w HCl. Dialyze the solution using a membrane with a Mw cut-off of 3.5 kDa.
- Perform dialysis for three days. Change the dialysis solution daily with 2 L of freshly prepared distilled water containing 0.2 ml of 37% w/w HCl.
- Store the final solution at -80 °C. Lyophilize it in a lyophilizer according to manufacturer's protocols.
- Characterize the functionalized polymer by 1H-NMR spectroscopy, dissolving the sample in D2O16.
4. Synthesis of PAA-RGD Polymer 4
- Dissolve 78 mg of PAA modified alkyne 3 (1.083 mmol) in 10 ml of distilled water.
- Dissolve 25 mg of the RGD azide 2 derivative (0.0722 mmol) in 5 ml of tetrahydrofuran.
- Add all of the RGD solution to the polymeric solution.
- Add 2.2 mg of copper iodide (0.0116 mmol) and 2.2 mg of sodium ascorbate (0.0111 mmol).
- Reflux the resulting mixture overnight at 60 °C, with stirring.
- Cool the mixture to 25 °C.
- Dialyze the solution. Dissolve 11.2 g of sodium chloride in 2 L of distilled water and then add 0.2 ml of 37% w/w HCl. Dialyze the solution using a membrane with a Mw cut-off of 3.5 kDa.
- Perform dialysis for three days. Change the dialysis solution daily with 2 L of freshly prepared distilled water containing 0.2 ml of 37% w/w HCl.
- Store the final solution at -80 °C. Lyophilize it in a lyophilizer according to manufacturer's protocols.
- Characterize the obtained product by 1H-NMR spectroscopy, dissolving the sample in D2O16.
5. RGD-functionalized Hydrogel Synthesis
- Prepare the PBS. Dissolve 645 mg of PBS salt in 50 ml of distilled water.
- Blend 40 mg of carbomer and 10 mg of functionalized PAA 4 in 9 ml of PBS (step 5.1), at room temperature, until complete dissolution (30 min).
- Add 400 mg of PEG to the solution and keep stirring for 45 min.
- Stop the stirring and allow the system to settle for 30 min.
- Use 1 N NaOH to adjust pH to 7.4.
- To 5 ml of the obtained mixture, add 25 mg of agarose powder.
- Irradiate the system with microwave radiation at 500 W until boiling, for a time usually between 30 sec and 1 min, and electromagnetically heat up to 80 °C.
- Leave the mixture exposed to room temperature until its temperature decreases to 50 °C and add 5 ml of PBS (step 5.1), in order to obtain a solution at a 1:1 volumetric ratio.
- Prepare 12 multiwell plate containing steel cylinders with a diameter of 1.1 cm.
- Take 500 µl aliquots from the solution and place them to each steel cylinders.
- Leave at rest for 45 min until complete gelification of the system.
- Remove the cylinders using a stainless steel forceps to obtain the hydrogels.
6. Loading of Therapeutic Tool (Drug or Cells)
- Repeat steps 5.1-5.7.
- When the mixture (already at sol state) reaches 37 °C, add 5 ml of the solution containing the desired drug solution or cell culture, in order to obtain a final system at a 1:1 volumetric ratio.
- Repeat steps 5.9-5.12 to obtain polymeric networks with biocompounds physically entrapped within the gel.
7. Hydrogel Characterization
- FT-IR Analysis
- After gel formation, soak one of the synthetized hydrogels in 2.5 ml of distilled water for 24 hr.
- Remove the aqueous media where hydrogel is submerged and freeze-dry with liquid N2.
- Laminate the hydrogel sample according to KBr pellet technique.
- Add a spatula full of KBr into an agate mortar. Take a small amount of hydrogel sample (about 0.1-2% of the KBr amount, or just enough to cover the tip of spatula) and mix with the KBr powder.
- Grind the mixture until the powder is fine and homogenous.
- Use the KBr pellet kit to form the IR pellet. Press the powder using a manual laboratory press: for 3 min at pressure capacity equal to 5 tons and then for 3 min at pressure capacity of 10 tons.
- Release the pressure to obtain the final pellet as homogeneous and transparent in appearance. Insert the pellet into the IR sample holder and run the spectrum16.
- Gelation Studies
- Fill 2 ml microcentrifuge tube with 900 µl of PBS and equilibrate to 37 °C.
- Add 100 µl of the prepared polymer solution to form the hydrogel and incubate at 37 °C.
- Invert the tube and observe if the gel flows at 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20 min. Record the time at which the gel does not flow as the gelation time.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The PAA alkyne derivative is efficiently synthesized from polyacrylic acid and propargylamine, as showed in Figure 1 where n labels the monomers whose carboxyl groups react with the amine. The identity of the product is confirmed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Figure 5 shows the 1H-NMR spectrum of PAA modified with triple bond.
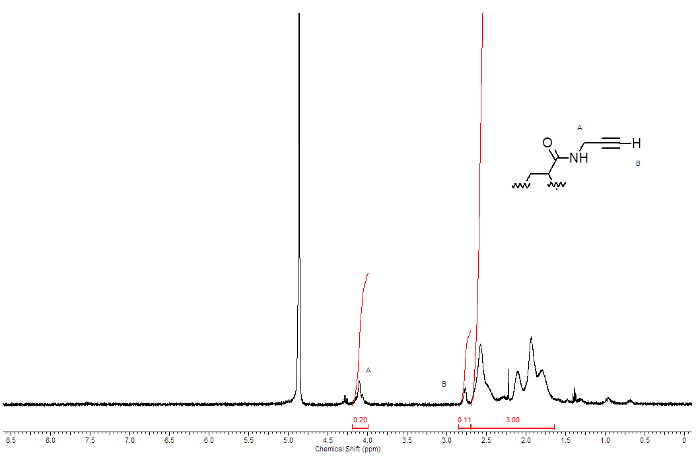
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The PAA post-polymerization modification with alkyne moieties and the RGD functionalization with the azide group guarantee the formation of a stable bond between the polymer and the peptide. Indeed, triazole serves as a rigid linking unit among the carbon atoms, attached to the 1,4 positions of the 1,2,3-triazole ring and it cannot be cleaved hydrolytically or otherwise. In addition, triazole is extremely difficult to oxidize and reduce, unlike other cyclic structures such as benzenoids and related aromatic heterocycles<...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors state no conflict of interest and they have not received any payment in preparation of this manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Prof. Maurizio Masi for fruitful discussion and Miss Chiara Allegretti for language editing. Authors' research is supported by Bando Giovani Ricercatori 2010 (Ministero della Salute GR-2010- 2312573).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Poly(acrylic acid) solution average Mw ~100,000, 35 wt% in H2O | Sigma Aldrich | 523925 | CAS 9003-01-4 |
| Poly(ethylene glycol) 2,000 | Sigma Aldrich | 84797 | CAS 25322-68-3 |
| Carbomeer 974P | Fagron | 1387083 | |
| Agarose | Invitrogen Corp. | 16500-500 | UltraPure Agarose |
| RGD peptide | abcam | ab142698 | |
| 4-azidobutanoic acid | Aurum Pharmatech | Z-2421 | CAS 54447-68-6 |
| Oxalyl chloride | Sigma Aldrich | O8801 | CAS 79-37-8 |
| Propargylamine hydrochloride 95% | Sigma Aldrich | P50919 | CAS 15430-52-1 |
| Copper(I) iodide | Sigma Aldrich | 3140 | CAS 7681-65-4 |
| Sodium ascorbate | Sigma Aldrich | Y0000039 | CAS 134-03-2 |
| Phosphate buffered saline | Sigma Aldrich | P4417 | |
| Dialysis Membrane | Spectrum Laboratories, Inc. | 132725 | Spectra/Por 3 Dialysis Membrane Standard RC Tubing MWCO: 3.5 kD |
References
- Slaughter, B. V., Khurshid, S. S., Fisher, O. Z., Khademhosseini, A., Peppas, N. A. Hydrogels in Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Mater. 21 (32-33), 3307-3329 (2009).
- Rossi, F., Perale, G., Papa, S., Forloni, G., Veglianese, P. Current options for drug delivery to the spinal cord. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 10 (3), 385-396 (2013).
- Huebsch, N., et al. Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 9 (6), 518-526 (2010).
- Mothe, A. J., Tam, R. Y., Zahir, T., Tator, C. H., Shoichet, M. S. Repair of the injured spinal cord by transplantation of neural stem cells in a hyaluronan-based hydrogel. Biomaterials. 34 (15), 3775-3783 (2013).
- Khetan, S., et al. Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 12 (5), 458-465 (2013).
- Ashley, G. W., Henise, J., Reid, R., Santi, D. V. Hydrogel drug delivery system with predictable and tunable drug release and degradation rates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 110 (6), 2318-2323 (2013).
- Rossi, F., van Griensven, M. Polymer Functionalization as a Powerful Tool to Improve Scaffold Performances. Tissue Eng. Part A. 20 (15-16), 2043-2051 (2014).
- Gould, S. T., Darling, N. J., Anseth, K. S. Small peptide functionalized thiol-ene hydrogels as culture substrates for understanding valvular interstitial cell activation and de novo tissue deposition. Acta Biomater. 8 (9), 3201-3209 (2012).
- Azagarsamy, M. A., Anseth, K. S. Wavelength-Controlled Photocleavage for the Orthogonal and Sequential Release of Multiple Proteins. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 52 (51), 13803-13807 (2013).
- Larrañeta, E., et al. Microwave-Assisted Preparation of Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays for Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 300 (6), 586-595 (2015).
- Cook, J. P., Goodall, G. W., Khutoryanskaya, O. V., Khutoryanskiy, V. V. Microwave-Assisted Hydrogel Synthesis: A New Method for Crosslinking Polymers in Aqueous Solutions. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 33 (4), 332-336 (2012).
- Perale, G., et al. Multiple drug delivery hydrogel system for spinal cord injury repair strategies. J. Control. Release. 159 (2), 271-280 (2012).
- Rossi, F., Perale, G., Storti, G., Masi, M. A Library of Tunable Agarose Carbomer-Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: The Role of Cross-Linkers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 123 (4), 2211-2221 (2012).
- Frith, J. E., et al. An injectable hydrogel incorporating mesenchymal precursor cells and pentosan polysulphate for intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomaterials. 34 (37), 9430-9440 (2013).
- Kolb, H. C., Finn, M. G., Sharpless, K. B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 40 (11), (2001).
- Sacchetti, A., Mauri, E., Sani, M., Masi, M., Rossi, F. Microwave-assisted synthesis and click chemistry as simple and efficient strategy for RGD functionalized hydrogels. Tetrahedron Lett. 55 (50), 6817-6820 (2014).
- Ossipov, D. A., Hilborn, J. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogels formed by "click chemistry". Macromolecules. 39 (5), 1709-1718 (2006).
- Truong, V., Blakey, I., Whittaker, A. K. Hydrophilic and Amphiphilic Polyethylene Glycol-Based Hydrogels with Tunable Degradability Prepared by "Click" Chemistry. Biomacromolecules. 13 (12), 4012-4021 (2012).
- Hou, R. Z., et al. New synthetic route for RGD tripeptide. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 36 (3), 243-252 (2006).
- Rossi, F., Chatzistavrou, X., Perale, G., Boccaccini, A. R. Synthesis and Degradation of Agar-Carbomer Based Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 123 (1), 398-408 (2012).
- Mauri, E., Rossi, F., Sacchetti, A. Tunable drug delivery using chemoselective functionalization of hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 61, 851-857 (2016).
- Joaquin, A., Peppas, N. A., Zoldan, J. Hydrogel Polymer Library for Developing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiac Patches. Tissue Eng. Part A. 20, S55-S55 (2014).
- Rossi, F., et al. Tunable hydrogel-Nanoparticles release system for sustained combination therapies in the spinal cord. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 108, 169-177 (2013).
- Kolb, H. C., Sharpless, K. B. The growing impact of click chemistry on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today. 8 (24), 1128-1137 (2003).
- Ossipov, D. A., Yang, X., Varghese, O., Kootala, S., Hilborn, J. Modular approach to functional hyaluronic acid hydrogels using orthogonal chemical reactions. Chem. Commun. 46 (44), 8368-8370 (2010).
- Anderson, S. B., Lin, C. C., Kuntzler, D. V., Anseth, K. S. The performance of human mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in cell-degradable polymer-peptide hydrogels. Biomaterials. 32 (14), 3564-3574 (2011).
- Caron, I., et al. A new three dimensional biomimetic hydrogel to deliver factors secreted by human mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 75, 135-147 (2016).
- Lee, J. W., Kim, H., Lee, K. Y. Effect of spacer arm length between adhesion ligand and alginate hydrogel on stem cell differentiation. Carbohyd. Polym. 139, 82-89 (2016).
- Liu, Y., Fan, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, L. Controlled Release of Low Molecular Protein Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 through Self-Assembling Peptide Hydrogel with Biotin Sandwich Approach. J.Biomed. Eng. 32 (2), 387-392 (2015).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved