A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Choice and No-Choice Bioassays to Study the Pupation Preference and Emergence Success of Ectropis grisescens
In This Article
Summary
Here, we present a protocol to investigate the pupation preference of mature larvae of Ectropis grisescens in response to soil factors (e.g., substrate type and moisture content) using choice bioassays. We also present a protocol of no-choice bioassays to determine the factors that affect the pupation behaviors and survivorship of E. grisescens.
Abstract
Many insects live above the ground as larvae and adults and as pupate below the ground. Compared to the above-ground stages of their life cycles, less attention has been paid on how environmental factors affect these insects when they pupate within the soil. The tea looper, Ectropis grisescens Warren (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), is a severe pest of tea plants and has caused huge economic losses in South China. The protocols described here aim to investigate, through multiple-choice bioassays, whether mature last-instar E. grisescens larvae can discriminate soil variables such as the substrate type and moisture content, and determine, through no-choice bioassays, the impact of the substrate type and moisture content on pupation behaviors and the emergence success of E. grisescens. The results would enhance the understanding of the pupation ecology of E. grisescens and may bring insights into soil-management tactics for suppressing E. grisescens populations. In addition, these bioassays can be modified to study the influences of various factors on the pupation behaviors and survivorship of soil-pupating pests.
Introduction
Compared to the larval and adult stages of insects, the pupal stage is highly vulnerable due to the limited mobile ability of pupae, which cannot rapidly escape from dangerous situations. Pupating below the ground is a common strategy used by diverse groups of insects (e.g., in the orders Diptera1,2,3,4, Coleoptera5, Hymenoptera6, Thysanoptera7, and Lepidoptera8,9,10,11,12) to protect them from above-ground predators and environmental hazards. Many of them are severe agricultural and forestry pests1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12. The mature larvae of these soil-pupating insects usually leave their hosts, fall on the ground, wander to find a proper site, burrow into the soil, and construct a pupal chamber for pupating8,10.
The tea looper, Ectropis grisescens Warren (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), is one of the most significant defoliator pests of the tea plant Camellia sinensis L.13. Although this species was first described in 1894, it has been mistakenly identified as Ectropis obliqua Prout (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in the past decades14,15. The differences in morphology, biology, and geographic distribution between the two sibling species have been described in some recent studies14,15,16. For example, Zhang et al.15 reported that E. oblique mainly occurred on the borders of three provinces (Anhui, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang) of China, whereas E. grisescens has a much wider distribution compared to E. oblique. Therefore, the economic losses caused by E. grisescens are largely overlooked, and the knowledge of this pest needs to be extensively revised and renewed16,17,18,19. Our previous studies showed that E. grisescens prefer to pupate within soil but could also pupate when soil is not available (no-pupation-substrate conditions)11,12.
This paper provides a step-by-step procedure to (1) determine the pupation preference of E. grisescens in response to factors such as substrate type and moisture content by using multiple-choice bioassays, and (2) determine the impact of abiotic factors on the pupation behaviors and emergence success of E. grisescens by using no-choice bioassays. All of these bioassays are conducted under well-controlled laboratory conditions. Also, these bioassays are adapted to evaluate the influence of other factors on the pupation behaviors and survivorship of diverse soil-pupating insects.
Protocol
1. Moisture-choice Bioassays to Determine Pupation Preference of E. grisescens
- Obtaining mature last-instar larvae of E. grisescens
- Cut fresh shoots (30 - 40 cm in length) of tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Insert 25 - 30 shoots into a 250 mL triangular flask. Fill the flask with tap water. Put 3 - 4 flasks (with tea shoots) in a plastic basin (upper side: 51 cm in diameter; bottom side: 40 cm in diameter; height: 16 cm).
- Release 1,000 - 2,000 larvae (second to fifth instar) of the laboratory colony of E. grisescens onto the leaves of the tea shoots in each basin. Maintain these larvae at controlled laboratory conditions [a photoperiod of 14 h of light followed by 10 h of dark (14:10 L:D), 60 - 90% relative humidity (RH), and 24 - 28 °C]. Carefully transfer the larvae onto fresh leaves by hand every 1 - 2 d. Each day remove feces and debris from the bottom of the basins.
- Select mature last-instar larvae that fall from the leaves of the tea shoots and actively wander on the bottom of the basin. Obtain at least 240 mature larvae to ensure that enough larvae are available for the bioassays.
NOTE: Only select actively wandering larvae for the experiments. Do not select larvae that stay on the leaves, because these are not ready to pupate. Also, do not select prepupae with limited mobile activities because they will not actively search for the proper conditions after being released into the bioassay arenas.
- Substrate Preparation
- Collect and identify 4 types of substrate (e.g., sand, sandy loam 1, sandy loam 2, and silt loam) using the hydrometer method20. Sterilize the soil and the sand at an 80 °C oven dryer for > 3 d, and then completely dry the soil and the sand at 50 °C for several weeks until the dry weight of the substrate samples does not change anymore over time.
- Ground the dry soil with wooden pestles and mortars. Sift the sand and the grounded soil through a 3 mm sieve and store them in sealable plastic bags.
- Calculate the different moisture contents of each substrate (sand, sandy loam 1, sandy loam 2, or silt loam) as follows2:
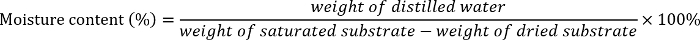
- Add the required amount of distilled water into the sealable plastic bags containing the dry soil or sand to prepare 5%-, 20%-, 35%-, 50%-, 65%-, and 80%-moisture substrate. Thoroughly mix the distilled water and the soil or sand.
- Bioassay arena preparation
- Equally divide the polypropylene containers (upper side: 20.0 cm in length x 13.5 cm in width, bottom side: 17.0 cm in length x 10.0 cm in width, height: 6.5 cm) into 6 chambers with waterproof polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheets (height: 3.5 cm). Fix the PVC sheets and seal the cracks using hot glue.
NOTE: Completely seal any crack to prevent water permeation. - For each test, fill the 6 chambers using the same type of substrate with different moisture contents (5%-, 20%-, 35%-, 50%-, 65%-, and 80%-moisture) (Figure 1a).
NOTE: Only use 1 type of substrate of different moisture contents in each test. Randomly assign the order of chambers that contain the substrate with the 6 moisture contents. - Paste 4 - 6 pieces of fresh tea leaves using small pieces of tape to cover the inner surface of the lids of the polypropylene containers (Figure 1b).
- Equally divide the polypropylene containers (upper side: 20.0 cm in length x 13.5 cm in width, bottom side: 17.0 cm in length x 10.0 cm in width, height: 6.5 cm) into 6 chambers with waterproof polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheets (height: 3.5 cm). Fix the PVC sheets and seal the cracks using hot glue.
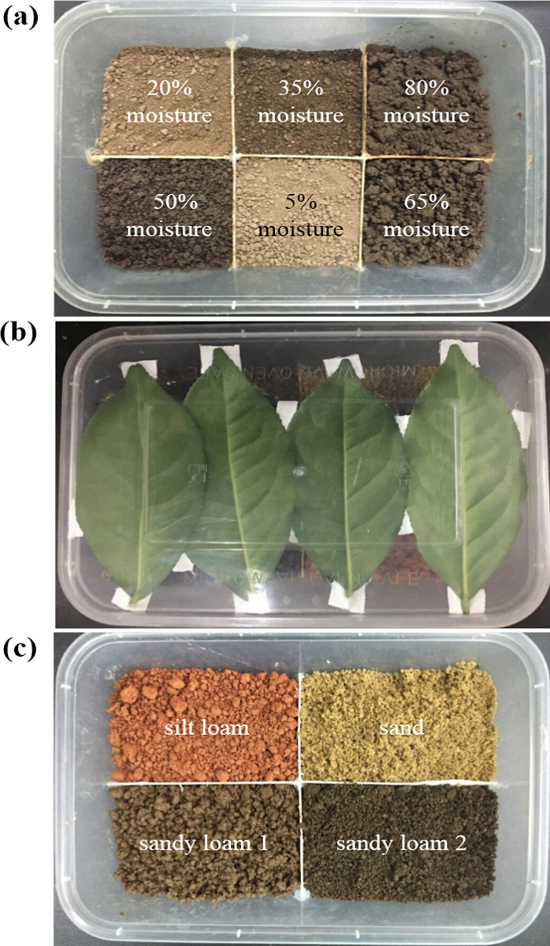

Figure 1: Examples of bioassay arenas for the choice tests. (a) Waterproof polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheets are used to equally divide the polypropylene containers into 6 chambers. PVC sheets are fixed with hot glue, and any cracks are carefully sealed. In this example, sandy loam 2 with different moisture contents (5%, 20%, 35%, 50%, 65%, and 80% moisture) are used to fill the chambers in the randomly assigned orders. (b) Fresh tea leaves are pasted on the inner side of the lids where the mature Ectropis grisescens larvae will be released. (c) PVC sheets are used to equally divide the polypropylene containers into 4 chambers, which are filled with 4 types of substrates (sand, sandy loam 1, sandy loam 2, and silt loam) at 50% moisture. This figure has been modified from Wang et al.11. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- Bioassay setting and data recording
- Release 30 mature last-instar larvae (obtained in step 1.1.3) onto the fresh tea leaves pasted on the lid of the polypropylene container. Carefully overturn the lid and tightly cover the polypropylene container.
- Repeat each test 8x. Maintain the bioassay arenas in an environmental chamber setting at a 14:10 (L:D) photoperiod and 26 °C.
- On day 5, count the number of pupae on the surface of the soil in each chamber. Also, dismantle the bioassays and count the number of pupae within the substrate.
NOTE: Only count the live pupae on or within the substrate. Check the pupae viability by observing abdominal motions after touching the pupae using forceps.
- Data analyses
- For each test, calculate the percentage of pupae found in each chamber of each replicate. Transfer the percentage data to the log-ratio using the method provided by Kucera and Malmgren21.
- Compare the percentage of pupae (transformed data) in each chamber using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Set the significance levels at α = 0.05 for each test.
2. Substrate-Choice Bioassays to Determine the Pupation Preference of E. grisescens
- Repeat step 1.1 to obtain mature last-instar larvae, and step 1.2 to prepare the substrate with different moisture contents. This time, only 20%, 50%, and 80%-moisture substrate are needed.
- Preparation of the bioassay arenas
- Similar to step 1.3.1, equally divide the polypropylene containers into 4 chambers using PVC sheets. Fix the PVC sheets and seal the cracks using hot glue.
- For each test, fill the chambers with the 4 types of substrates (sand, sandy loam 1, sandy loam 2, and silt loam) that have the same moisture content (20%, 50%, or 80% moisture) with randomly assigned orders (Figure 1c). Repeat step 1.3.3 to prepare the lids.
- Repeat step 1.4 to set the bioassays and record the data and step 1.5 to analyze the data.
3. No-choice Bioassays to Determine the Soil-burrowing Behavior and Emergence Success of E. grisescens
- Repeat step 1.1 to obtain the mature last-instar larvae, and step 1.2 to prepare the 4 substrates (sand, sandy loam 1, sandy loam 2, and silt loam) at 3 moisture contents (20%, 50%, and 80% moisture).
- Bioassay setting
- Add the substrate into a plastic container (upper side: 11.5 cm in diameter; bottom side: 8.5 cm in diameter; height: 6.5 cm) to a depth of 3 cm. In total, ensure that there will be 12 treatments (the combinations of 4 substrate types and 3 moisture contents). Repeat each treatment 7x.
- Release 15 mature last-instar larvae onto the substrate of each bioassay arena. Seal the containers by tightly covering the lids. Maintain the bioassays in an environmental chamber setting at a 14:10 (L:D) photoperiod and 26 °C.
NOTE: There will be no need to paste fresh tea leaves on the lids as mentioned in the choice bioassays.
- Data recording and analyses
- On day 3, count the number of pupae and any dead larvae on the surface of the substrate of each replicate. Calculate the percentage of E. grisescens individuals that burrowed into the substrate as follows:
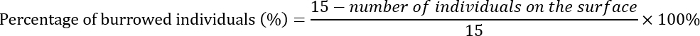
- Record the number of emerging adults each day until no more adult emerged for 15 d. Calculate the emergence success as follows:
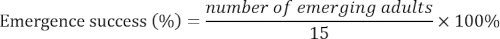
- Compare the percentage of burrowed individuals and the emergence success among the treatments using one-way ANOVA. Set the significance levels at α = 0.05.
- On day 3, count the number of pupae and any dead larvae on the surface of the substrate of each replicate. Calculate the percentage of E. grisescens individuals that burrowed into the substrate as follows:
Results
The moisture-choice bioassays showed that significantly more E. grisescens individuals pupated on or within the 5%- and 35%-moisture sand compared to the 80%-moisture sand (Figure 2a). However, significantly more individuals preferred to pupate on or within the soil (sandy loam 1 and 2 and silt loam) that had an intermediate moisture content (Figures 2b - 2d).
Discussion
Pupation preferences responding to different soil variables have been studied in a few pests6,9,22,23. For example, to study the preference of mature larvae of Bactrocera tryoni (Froggatt) (Diptera: Tephritidae) among different soil moisture conditions, Hulthen and Clarke22 set a 3 x 3 Latin-square design containing 9 containers filled with soil at either 0%, 75...
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuzhen Wen, Shiping Liang, Shengzhe Jian, and Yanjun Li (College of Forestry and Landscape Architecture, South China Agricultural University) for their help in the insect rearing and experimental set-up. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31600516), the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2016A030310445), and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2015A020208010).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Triangular flask | Bomex Chemical (Shanghai) Co., LTD | 99 | 250 mL |
| Plastic basin | Chahua, Fuzhou, China | 100 | upper side: 51 cm in diameter; bottom side: 40 cm in diameter; height: 16 cm |
| Zip lock bags | Glad, Guangzhou, China | 126/133 | |
| Polypropylene containers | Youyou Plastic Factory, Taian, China | 139/155/160/161/190 | upper side: 20.0 cm [L] × 13.5 cm [W], bottom side: 17.0 cm [L] × 10.0 cm [W], height: 6.5 cm |
| Waterproof polyviny chloride sheet | Yidimei, Shanghai, China | 141 | |
| Tape | V-tech, Guangzhou, China | VT-710 | |
| Oven drier | Kexi, Shanghai, China | KXH-202-3A | |
| Environmental chamber | Life Apparatus, Ningbo, China | PSX-280H |
References
- Dimou, I., Koutsikopoulos, C., Economopoulos, A. P., Lykakis, J. Depth of pupation of the wild olive fruit fly, Bactrocera (Dacus) oleae (Gmel.) (Dipt., Tephritidae), as affected by soil abiotic factors. Journal of Applied Entomology. 127 (1), 12-17 (2003).
- Chen, M., Shelton, A. M. Impact of soil type, moisture, and depth on swede midge (Diptera: Cecidomyiidae) pupation and emergence. Environmental Entomology. 36 (6), 1349-1355 (2007).
- Holmes, L. A., Vanlaerhoven, S. L., Tomberlin, J. K. Substrate effects on pupation and adult emergence of Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Environmental Entomology. 42 (2), 370-374 (2013).
- Renkema, J. M., Cutler, G. C., Lynch, D. H., MacKenzie, K., Walde, S. J. Mulch type and moisture level affect pupation depth of Rhagoletis mendax Curran (Diptera: Tephritidae) in the laboratory. Journal of Pest Science. 84 (3), 281 (2011).
- Ellis, J. D., Hepburn, R., Luckman, B., Elzen, P. J. Effects of soil type, moisture, and density on pupation success of Aethina tumida (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae). Environmental Entomology. 33 (4), 794-798 (2004).
- Pietrantuono, A. L., Enriquez, A. S., Fernández-Arhex, V., Bruzzone, O. A. Substrates preference for pupation on sawfly Notofenusa surosa (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae). Journal of Insect Behavior. 28 (3), 257-267 (2015).
- Buitenhuis, R., Shipp, J. L. Influence of plant species and plant growth stage on Frankliniella occidentalis pupation behaviour in greenhouse ornamentals. Journal of Applied Entomology. 132 (1), 86-88 (2008).
- Zheng, X. L., Cong, X. P., Wang, X. P., Lei, C. L. Pupation behaviour, depth, and site of Spodoptera exigua. Bulletin of Insectology. 64 (2), 209-214 (2011).
- Wen, Y., et al. Effect of substrate type and moisture on pupation and emergence of Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae): choice and no-choice studies. Journal of Insect Behavior. 29 (4), 473-489 (2016).
- Wen, Y., et al. Soil moisture effects on pupation behavior, physiology, and morphology of Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Journal of Entomological Science. 52 (3), 229-238 (2017).
- Wang, H., et al. Pupation behaviors and emergence successes of Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in response to different substrate types and moisture contents. Environmental Entomology. 46 (6), 1365-1373 (2017).
- Wang, H., et al. No-substrate and low-moisture conditions during pupating adversely affect Ectropis grisescens (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) adults. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology. 21 (2), 657-662 (2018).
- Ge, C. M., Yin, K. S., Tang, M. J., Xiao, Q. Biological characteristics of Ectropis grisescens Warren. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis. 28 (3), 464-468 (2016).
- Xi, Y., Yin, K. S., Tang, M. J., Xiao, Q. Geographic populations of the tea geometrid, Ectropis obliqua (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) in Zhejiang, eastern China have differentiated into different species. Acta Entomologica Sinica. 57, 1117-1122 (2014).
- Zhang, G. H., et al. Detecting deep divergence in seventeen populations of tea geometrid (Ectropis obliqua Prout) in China by COI mtDNA and cross-breeding. PloS One. 9 (6), e99373 (2014).
- Ma, T., et al. Analysis of tea geometrid (Ectropis grisescens) pheromone gland extracts using GC-EAD and GC× GC/TOFMS. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 64 (16), 3161-3166 (2016).
- Zhang, G. H., et al. Asymmetrical reproductive interference between two sibling species of tea looper: Ectropis grisescens and Ectropis obliqua. Bulletin of Entomological Research. , (2016).
- Luo, Z. X., Li, Z. Q., Cai, X. M., Bian, L., Chen, Z. M. Evidence of premating isolation between two sibling moths: Ectropis grisescens and Ectropis obliqua (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Journal of Economic Entomology. 110 (6), 2364-2370 (2017).
- Li, Z. Q., et al. Chemosensory gene families in Ectropis grisescens and candidates for detection of Type-II sex pheromones. Frontiers in Physiology. 8, (2017).
- Chen, L. Q. Research on structure of soil particle by hydrometer method. Environmental Science Survey. 29 (4), 97-99 (2010).
- Kucera, M., Malmgren, B. A. Logratio transformation of compositional data: a resolution of the constant sum constraint. Marine Micropaleontology. 34 (1-2), 117-120 (1998).
- Hulthen, A. D., Clarke, A. R. The influence of soil type and moisture on pupal survival of Bactrocera tryoni (Froggatt) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Australian Journal of Entomology. 45 (1), 16-19 (2006).
- Alyokhin, A. V., Mille, C., Messing, R. H., Duan, J. J. Selection of pupation habitats by oriental fruit fly larvae in the laboratory. Journal of Insect Behavior. 14 (1), 57-67 (2001).
- Torres-Muros, L., Hódar, J. A., Zamora, R. Effect of habitat type and soil moisture on pupal stage of a Mediterranean forest pest (Thaumetopoea pityocampa). Agricultural and Forest Entomology. 19 (2), 130-138 (2017).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved