A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Quantification of three DNA Lesions by Mass Spectrometry and Assessment of Their Levels in Tissues of Mice Exposed to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
We describe here methods for sensitive and accurate quantification of the lesions 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo), 1,N6-etheno-2'-deoxyadenosine (1,N6-dAdo) and 1,N2-etheno-2'-deoxyguanosine (1,N2-dGuo) in DNA. The methods were applied to the assessment of the effects of ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in tissues (lung, liver and kidney) of exposed A/J mice.
Abstract
DNA adducts and oxidized DNA bases are examples of DNA lesions that are useful biomarkers for the toxicity assessment of substances that are electrophilic, generate reactive electrophiles upon biotransformation, or induce oxidative stress. Among the oxidized nucleobases, the most studied one is 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoGua) or 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo), a biomarker of oxidatively induced base damage in DNA. Aldehydes and epoxyaldehydes resulting from the lipid peroxidation process are electrophilic molecules able to form mutagenic exocyclic DNA adducts, such as the etheno adducts 1,N2-etheno-2'-deoxyguanosine (1,N2-εdGuo) and 1,N6-etheno-2'-deoxyadenosine (1,N6-εdAdo), which have been suggested as potential biomarkers in the pathophysiology of inflammation. Selective and sensitive methods for their quantification in DNA are necessary for the development of preventive strategies to slow down cell mutation rates and chronic disease development (e.g., cancer, neurodegenerative diseases). Among the sensitive methods available for their detection (high performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrochemical or tandem mass spectrometry detectors, comet assay, immunoassays, 32P-postlabeling), the most selective are those based on high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS). Selectivity is an essential advantage when analyzing complex biological samples and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS evolved as the gold standard for quantification of modified nucleosides in biological matrices, such as DNA, urine, plasma and saliva. The use of isotopically labeled internal standards adds the advantage of corrections for molecule losses during the DNA hydrolysis and analyte enrichment steps, as well as for differences of the analyte ionization between samples. It also aids in the identification of the correct chromatographic peak when more than one peak is present.
We present here validated sensitive, accurate and precise HPLC-ESI-MS/MS methods that were successfully applied for the quantification of 8-oxodGuo, 1,N6-dAdo and 1,N2-dGuo in lung, liver and kidney DNA of A/J mice for the assessment of the effects of ambient PM2.5 exposure.
Introduction
Some reactive oxygen species (ROS) are able to oxidize carbon double bonds of DNA bases and some carbons in the deoxyribose moiety, generating oxidized bases and DNA strand breaks1. As a negatively charged molecule rich in nitrogen and oxygen atoms, DNA is also a target for electrophilic groups that covalently react with the nucleophilic sites (nitrogen and oxygen), giving products that are called DNA adducts2. So, DNA adducts and oxidized DNA bases are examples of DNA lesions that are useful biomarkers for the toxicity assessment of substances that are electrophilic, generate reactive electrophiles upon biotransformation, or induce oxidative stress1,2. Although the modified DNA bases can be removed from DNA by base or nucleotide excision repair (BER or NER), the induction of an imbalance between the generation and removal of DNA lesions in favor of the former leads to a net increase of their levels in DNA overtime3. Outcomes are the increase of DNA mutation rates, reduced gene expression, and diminished protein activity2,4,5,6,7, effects that are closely related to the development of diseases. DNA mutations may affect diverse cellular functions, such as cell signaling, cell cycle, genome integrity, telomere stability, the epigenome, chromatin structure, RNA splicing, protein homeostasis, metabolism, apoptosis, and cell differentiation8,9. Strategies to slow down cell mutation rates and chronic disease development (e.g., cancer, neurodegenerative diseases) pass through the knowledge of the mutation sources, among them, DNA lesions and their causes.
ROS generated endogenously in excess, due to pollutant exposure, persistent inflammation, disease pathophysiology (e.g., diabetes), etc., are important causes of biomolecule damage, including DNA and lipid damage1. As an example, the highly reactive hydroxyl radical (OH) formed from H2O2 reduction by transition metal ions (Fe2+, Cu+) oxidizes the DNA bases, DNA sugar moiety and polyunsaturated fatty acids at diffusion-controlled rates10. Among the 80 already characterized oxidized nucleobases3, the most studied one is 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoGua) or 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo, Figure 1), a lesion that is able to induce GT transversions in mammalian cells10,11. It is formed by the mono electronic oxidation of guanine, or by hydroxyl radical or singlet oxygen attack of guanine in DNA1. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are other important targets of highly reactive oxidants, such as •OH, which initiate the process of lipid peroxidation1,12. It gives rise to fatty acid hydroperoxides that may decompose to electrophilic aldehydes and epoxyaldehydes, such as malondialdehyde, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, 2,4-decadienal, 4,5-epoxy-(2E)-decenal, hexenal, acrolein, crotonaldehyde, which are able to form mutagenic exocyclic DNA adducts, such as malondialdehyde-, propano-, or etheno adducts1,12,13. The etheno adducts 1,N2-etheno-2'-deoxyguanosine (1,N2-εdGuo, Figure 1) and 1,N6-etheno-2'-deoxyadenosine (1,N6-εdAdo, Figure 1) have been suggested as potential biomarkers in the pathophysiology of inflammation14,15.
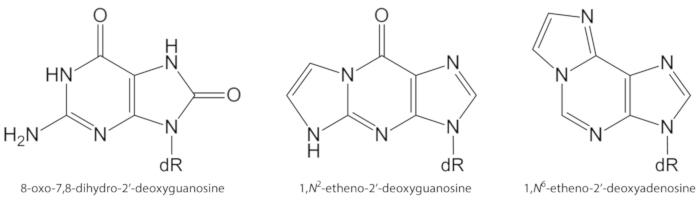
Figure 1. Chemical structures of the DNA lesions quantified in the present study. dR = 2´-deoxyribose. This figure has been modified from Oliveira et al.34. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Studies carried out in the early 1980s allowed the sensitive detection of 8-oxodGuo by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD). Quantification of 8-oxodGuo by HPLC-ECD in several biological systems subjected to oxidizing conditions led to the recognition of 8-oxodGuo as a biomarker of oxidatively induced base damage in DNA1,16. Although robust and allowing the quantification of 8-oxodGuo in the low fmol range17, HPLC-ECD measurements rely on the accuracy of the analyte retention time for analyte identification and on the chromatography resolution to avoid interferences of other sample constituents. As the electrochemical detection requires the use of salt (e.g., potassium phosphate, sodium acetate) in the mobile phase, the maintenance of adequate analytical conditions needs routine column and equipment cleaning time.
Alternatively, the use of the bacterial DNA repair enzyme formamidopyrimidine DNA glycosylase (FPG) and, afterwards, human 8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (hOGG1), for detection and removal of 8-oxoGua from DNA, emerged as a way for the induction of DNA alkali labile sites. The alkali labile sites are converted to DNA strand breaks and allow the very high sensitive indirect quantification of 8-oxoGua by alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis ("comet assay"). The high sensitivity and the accomplishment of the analyses without the need of cellular DNA extraction are the main advantages of this type of assay. It gives the lowest steady-state levels of 8-oxoGua in DNA, typically 7-10 times lower than the levels obtained by bioanalytical methods based on HPLC. However, it is an indirect measurement of 8-oxoGua and some drawbacks are the lack of specificity or the unknown efficiency of the repair enzymes used1,16,18.
Immunoassays are other set of methods used for the detection of 8-oxoGua1 and exocyclic DNA adducts, such as 1,N6-dAdo and 1,N2-dGuo12. Despite the sensitivity, a shortcoming of the use of antibodies for detection of DNA lesions is the lack of specificity due to cross-reactivity to other components of biological samples, including the normal DNA bases1,12. The exocyclic DNA adducts, including 1,N6-dAdo and 1,N2-dGuo, may also be detected and quantified by highly sensitive 32P-postlabeling assays12. The high sensitivity of 32P-postlabeling allows the use of very small amounts of DNA (e.g., 10 µg) for detection of about 1 adduct per 1010 normal bases19. However, the use of radio-chemicals, lack of chemical specificity and low accuracy are some disadvantages19,20.
A shared limitation of the methods cited above is the low selectivity or specificity for the detection of the desired molecules. In this scenario, HPLC coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS and HPLC-MS3) evolved as the gold standard for quantification of modified nucleosides in biological matrices, such as DNA, urine, plasma and saliva1,19,20. Advantages of HPLC-ESI-MS/MS methods are the sensitivity (typically in the low fmol range) and the high specificity provided by i) the chromatographic separation, ii) the characteristic and known pattern of molecule fragmentation inside the mass spectrometer collision chamber, and iii) the accurate measurement of the selected mass to charge ratio (m/z) in multiple reaction monitoring mode1,19. The use of isotopically labeled internal standards adds the advantage of corrections for molecule losses during the DNA hydrolysis and analyte enrichment steps, as well as for differences of the analyte ionization between samples. It also aids in the identification of the correct chromatographic peak when more than one peak is present1,12,19,20.
Several methods based on HPLC-ESI-MS/MS have been used for quantification of 8-oxodGuo, 1,N6-dAdo and 1,N2-dGuo in DNA extracted from different biological samples12,15,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29. Fine particles (PM2.5) carry organic and inorganic chemicals, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), nitro-PAHs, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, quinolines, metals, and water-soluble ions, which may induce inflammation and oxidative stress, conditions that favor the occurrence of biomolecule damage and disease30,31,32,33. We present here validated HPLC-ESI-MS/MS methods that were successfully applied for the quantification of 8-oxodGuo, 1,N6-dAdo and 1,N2-dGuo in lung, liver and kidney DNA of A/J mice for the assessment of the effects of ambient PM2.5 exposure34.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
Four week old male A/J mice, specific pathogen free, were obtained from the Breeding Center of Laboratory Animals of Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (FIOCRUZ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and were treated accordingly to the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, University of São Paulo (protocol no 1310/09).
1. Collection of mice tissues
- Anesthetize the animal with xylazine and ketamine. For a mouse with 30 g of body weight, inject a solution (no more than 2 mL) containing 2.63 mg of ketamine and 0.38 mg of xylazine, intraperitoneally.
- Collect blood (0.5 - 1.5 mL) for complementary analyses (e.g., antioxidant enzyme activity, malondialdehyde levels).
- Shave the abdominal hair from the pelvis to the xiphoid process. Make an incision in a vertical middle line in the hairless area. Make incisions in horizontal lateral lines in order to expose the abdominal organs.
- Cut the abdominal aorta to promote exsanguination and to euthanize the animal.
- Remove the tissues of interest (in this case, liver, kidneys and lungs).
- To remove the liver, cut the inferior cava vein and portal hepatic vein.
- To remove the kidneys, section the renal veins and arteries.
- To remove the lungs, make an incision in the diaphragm extremities and circumference close to the thoracic wall. Break the clavicles by opening a scissor in the interior of the thoracic cavity. Cut the extern bone from the xiphoid process toward the trachea, in order to expose the lungs and heart.
- Hold the lung with a forceps, section the trachea and the ligaments around the lungs. Remove carefully the block lungs plus heart. To remove the lungs out of the block, hold the heart with a forceps and cut all vessels in its base.
- Wash the isolated tissues immediately in cold saline solution (0.9% NaCl), transfer to cryogenic tubes, and immediately dip the tubes into liquid nitrogen. After completing the work, store the tubes at -80 °C.
CAUTION: Liquid nitrogen in direct contact with the skin, mucosa or eyes causes burns. Use proper individual protection to avoid contact. Work in a ventilated laboratory to avoid asphyxia due to liquid nitrogen vapor.
2. DNA extraction
Note: The DNA extraction method was modified from Loureiro et al. (2009)35 to allow the analyses of the lesions studied here.
- Transfer the tubes containing the tissues to dry ice.
- Use a culture plate placed on ice as a base to cut a piece of tissue with a scalpel. Weight 1 g for immediate use. The remaining tissue should be kept on dry ice until it returns to storage at -80 °C.
NOTE: It is important to avoid thawing of the remaining tissue to prevent the formation of artifacts if repetitions of the analyses are needed. - To each 1 g of tissue in 50 mL capped tubes, add 10 mL of the commercial cell lysis solution containing 0.5 mM deferoxamine and keep on ice.
NOTE: Add deferoxamine to the volume of solution for immediate use. For each 100 mL of solution, add 0.0328 g of the deferoxamine mesylate salt. - Homogenize the tissues using a tissue homogenizer until a homogeneous solution without tissue fragments is obtained. Keep the tube cold (on ice) during homogenization. Use a low speed to avoid heating.
- Add 150 µL of proteinase K solution (20 mg/mL) to each homogenized sample. Shake the tubes by inversion and keep them at room temperature overnight.
- Add 40 µL of ribonuclease A solution (15 mg/mL), shake by inversion, and keep the tubes at room temperature for 2 h.
NOTE: Prepare ribonuclease A solution in sodium acetate buffer 10 mM, pH 5.2 to avoid precipitation. Heat the solution at 100 °C for 15 min before use to obtain a solution free from deoxyribonuclease. - Add 5 mL of the commercial protein precipitation solution, vortex vigorously, and centrifuge at 2,000 x g, 4 °C, for 10 minutes.
- Transfer the supernatants to 50 mL capped tubes containing 10 mL of cold isopropanol. Invert the tubes gently several times until the observation of the precipitated DNA.
NOTE: The protocol can be paused here, keeping the tubes at -20 °C. - Collect the precipitated DNA using a Pasteur pipette closed at the end. Transfer it to tubes containing 4 mL of 10 mM Tris buffer, 1 mM deferoxamine, pH 7.0.
- After the DNA is completely dissolved in the above solution (do not vortex), add 4 mL of a chloroform solution containing 4% of isoamyl alcohol.
- Invert the tubes 10 times for homogenization, centrifuge at 2,000 x g, 4 °C, for 10 minutes to separate the two phases, and transfer the upper phase to a new tube.
- Repeat the steps 2.10 and 2.11 two more times.
- Add 8 mL of absolute ethanol and 0.4 mL of a 5 M NaCl solution to precipitate the DNA.
- Collect again the precipitated DNA and transfer it to 3 mL of 70% ethanol. Repeat this step one more time.
- Discard the ethanol solution with caution and invert the tubes containing the precipitated DNA on absorbent paper to remove the excess of the solution.
- Add 200 µL of 0.1 mM deferoxamine solution to dissolve the DNA. Maintain the tubes at 4 °C until the DNA is completely rehydrated (overnight).
- Determine the DNA concentration by measuring the absorbance at 260 nm and its purity by the 260/280 nm absorbance ratio.
NOTE: To determine the DNA concentration, transfer an aliquot of 10 µL of the DNA solution to 990 µL of ultrapure water (100x dilution). Multiply the absorbance at 260 nm (it should be below 1) by 50 (50 µg/mL is the concentration of double stranded DNA when the absorbance of a 1 cm path length solution at 260 nm is 1) and by the dilution used (100x) to obtain the DNA concentration in µg/mL. If the absorbance at 260 nm is above 1, additional dilutions are necessary. The 260/280 nm absorbance ratio should be equal or above 1.8 for the desired DNA purity, but ratios around 1.6 are acceptable.
3. DNA enzymatic hydrolysis
- Analysis recipe
- 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo analyses: To an aliquot containing 150 µg of DNA, add 7.5 µL of 200 mM Tris/MgCl2 buffer (pH 7.4), 1.4 µL of the internal standard solution containing 250 fmol/µL of [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo, and 15 units of deoxyribonuclease I. Adjust the final volume to 200 µL with ultrapure water, subtracting the volumes of enzymes to be used on step 3.2.1.
- 8-oxodGuo analyses: To an aliquot containing 80 µg of DNA, add 3.8 µL of 200 mM Tris/MgCl2 buffer (pH 7.4), 2 µL of the internal standard solution containing 1,000 fmol/µL of [15N5]8-oxodGuo, and 8 units of deoxyribonuclease I. Adjust the final volume to 100 µL with ultrapure water, subtracting the volumes of enzymes to be used on step 3.2.2.
NOTE: The internal standards [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo, [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo and [15N5]8-oxodGuo can be synthetized and characterized as described35,36,37. The quantities of the internal standards in the injected sample volumes should be the same as those in the injected calibration curve volumes.
- Incubate the samples at 37 °C for 1 hour.
- Samples from step 3.1: Add 0.006 units of phosphodiesterase I from Crotalus atrox and 15 units of alkaline phosphatase from bovine intestinal mucosa.
- Samples from step 3.2: Add 0.0032 units of phosphodiesterase I from Crotalus atrox and 8 units of alkaline phosphatase from bovine intestinal mucosa.
- Incubate the samples at 37 °C for 1 hour.
- Centrifuge the samples at 14,000 x g for 10 minutes.
- Samples from step 3.2.1: Separate 10 µL of each sample for quantification of the deoxynucleosides (dAdo, dGuo) by HPLC/DAD (step 9). Subject the residual volume to solid phase extraction (step 4).
- Samples from step 3.2.2: Transfer 80 µL of the supernatant to vials for injections of 50 µL (1,000 fmol of [15N5]8-oxodGuo) in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system. Reserve the remaining 20 µL for quantification of dGuo by HPLC/DAD (step 9).
4. Solid phase extraction for analyses of 1, N6-εdAdo and 1, N2-εdGuo
- Load the cartridges (SPE-C18, 30 mg/mL, 33 µm, 1 mL) with 1 mL of the following sequence of solutions: 100% methanol, deionized water, hydrolyzed DNA sample, deionized water, 10% methanol, 15% methanol, and 100% methanol (to be collected).
NOTE: Do not leave the cartridges dry between the applications of the different solutions. Add the next solution immediately after the previous solution enters the cartridge completely. - Vacuum dry the last elution fraction (100% methanol) containing the adducts.
- Resuspend the dried samples in 83.1 μL of ultrapure water immediately prior to the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis, to obtain 200 fmol of each internal standard in 50 µL of each sample.
5. Preparation of calibration curves
- Prepare at least five points in the interval of 300 to 6,000 fmol of 8-oxodGuo standard, with the fixed amount of 1,000 fmol of [15N5]8-oxodGuo in each point. Consider these amounts in the volume injected.
- Prepare at least five points in the interval of 1 to 40 fmol of 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo, with fixed amounts of 200 fmol of [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo in each point. Consider these amounts in the volume injected.
- Prepare at least five points in the interval of 0.05 - 1 nmol of dGuo and dAdo. Consider these amounts in the volume injected.
6. Preparation of DNA samples for method validation
- 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo analyses: Add varying amounts of 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo (e.g., 1.75, 8.75, 17.5, and 35 fmol) and fixed amounts of [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo (350 fmol) to 100 µg of calf thymus DNA and carry out the enzymatic hydrolysis as described in step 3. Process the samples in quadruplicate in two different days. Use the samples for method accuracy and precision assessment.
NOTE: The final volume of the DNA hydrolysates will be 200 µL (step 3), from which 10 µL will be separated for quantification of deoxynucleosides by HPLC/DAD (step 9). The remaining solution (190 µL) will be subjected to solid phase extraction (step 4), the dried fraction will be resuspended in 83.1 µL (step 4.3), from which 50 µL will be injected in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system. The amounts of 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo injected will be 1, 5, 10, and 20 fmol, with 200 fmol of [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo in each sample. - 8-oxodGuo analyses: Add varying amounts of 8-oxodGuo (e.g., 734, 1,468, 2,938, and 4,408 fmol) and a fixed amount of [15N5]8-oxodGuo (2,000 fmol) to 100 µg of calf thymus DNA and carry out the enzymatic hydrolysis as described in step 3. Process the samples in quadruplicate in two different days. Use the samples for method accuracy and precision assessment.
NOTE: The final volume of the DNA hydrolysates will be 100 µL (step 3), from which 50 µL will be injected in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system. The amounts of 8-oxodGuo injected will be 367, 734, 1469, and 2204 fmol, with 1,000 fmol of [15N5]8-oxodGuo in each sample. - Add 13.125 fmol of 1,N6-εdAdo (to obtain 7.5 fmol in the injection volume) and 35 fmol of 1,N2-εdGuo (to obtain 20 fmol in the injection volume) to eight samples of 100 µg of calf thymus DNA.
- Add the internal standards [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo (200 fmol) to four of the samples. Proceed with the DNA hydrolysis and solid phase extraction of all samples.
- Add the internal standards [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo (200 fmol) to the other four samples.
- Use the samples to calculate the recovery of the adducts from solid phase extraction.
7. HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of 8-oxodGuo
- Infusing the 8-oxodGuo standard into the equipment, set the ESI-MS/MS parameters for the best detection of its fragmentation pattern by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM): m/z 284 [M+H]+ → m/z 168 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+.
- Use the same parameters for detection of [15N5]8-oxodGuo: m/z 289 [M+H]+m/z → 173 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+.
NOTE: Use an equipment equivalent or better than the equipment used in this work (see the Table of Materials). The ESI-MS/MS parameters were set as described in Table 1.
- Use the same parameters for detection of [15N5]8-oxodGuo: m/z 289 [M+H]+m/z → 173 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+.
- Filter (using 0.22 µm porous membranes) and degasify (using a sonicator) all the water based HPLC solvents.
- Use the following chromatography conditions for the analyses, mounting the system as shown in Figure 2.
NOTE: Column A is connected to the binary pump. Its eluent is directed to UV detection and waste in the first 16 min and from 32 to 46 min of the chromatography, as shown in Figure 2A. This is the column through which the sample is eluted immediately after injection. Column B is connected to the isocratic pump and the mass spectrometer. It receives the eluent of column A only in the 16 - 32 min interval, when the valve is switched to the position shown in Figure 2B. The valve switching allows the connection between the two columns, which are eluted by the binary pump gradient. The configuration shown in Figure 2B permits further peak separation and narrowing. Additionally, only the chromatographic fraction of interest reaches the mass spectrometer, improving sensitivity and selectivity.- Elute a 50 x 2.0 mm i.d., 2.5 µm, C18 column (column A of Figure 2) coupled to a C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) with a gradient of 0.1% formic acid (solvent A) and methanol containing 0.1% formic acid (solvent B) at a flow rate of 150 µL/min and 25 °C.
- Use the following gradient program for the binary pump: from 0 to 25 min, 0 - 15% of solvent B; 25 to 28 min, 15 - 80% of solvent B; 28 to 31 min, 80% of solvent B; 31 to 33 min, 80 - 0 % of solvent B; 33 to 46 min, 0% of solvent B.
- Use the switching valve to direct the first 16 min of eluent to waste and the 16 - 32 min fraction to a second column (150 x 2.0 mm i.d., 3.0 µm, C18, column B of Figure 2) connected to the ESI source and conditioned by the isocratic pump with a solution of 15% methanol in water containing 0.1% formic acid (150 µL/min).
NOTE: Before using the switching valve program of step 7.3.1.2, check if the 8-oxodGuo standard elutes from the first column after 16 min. It is important to close the valve at 32 min to use the gradient of the binary pump to elute 8-oxodGuo from the second column and get a sharp chromatographic peak. The lesion 8-oxodGuo elutes from the second column at approximately 36 min. Variations of the retention time of the analyte may occur depending on the column and equipment used. Adaptations of the HPLC solvent gradient program may be necessary.
- Elute a 50 x 2.0 mm i.d., 2.5 µm, C18 column (column A of Figure 2) coupled to a C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) with a gradient of 0.1% formic acid (solvent A) and methanol containing 0.1% formic acid (solvent B) at a flow rate of 150 µL/min and 25 °C.
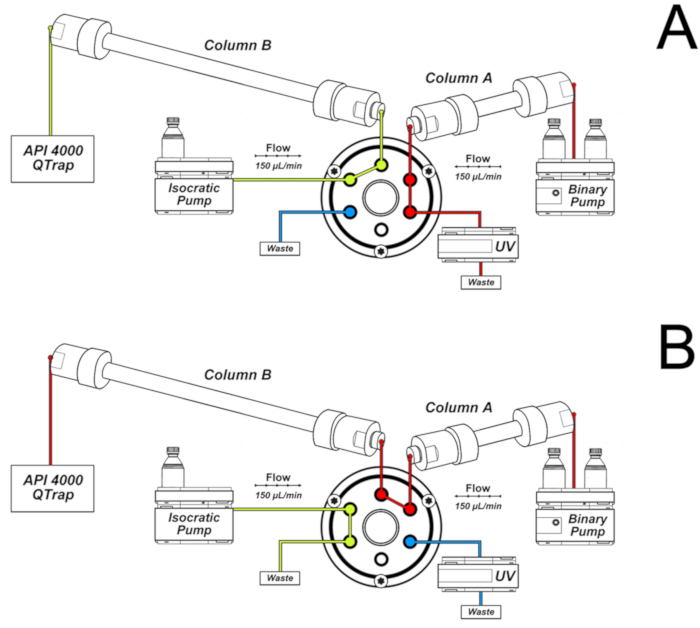
Figure 2. System of two columns used for 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-oxodGuo) analyses. A) Configuration used in the first 16 min and from 32 to 46 min of the chromatography; B) Configuration used in the interval 16 - 32 min, allowing further separation and peak narrowing in column B prior to elution to the ESI source of the mass spectrometer. This figure has been republished from Oliveira et al.34. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
8. HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of 1, N 6 -εdAdo and 1, N 2 -εdGuo
- Infusing the 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo standards into the equipment, set the ESI-MS/MS parameters for the best detection of their fragmentation patterns by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM): m/z 276 [M+H]+ → m/z 160 [M 2'-deoxyribose + H]+ for detection of 1,N6-εdAdo and m/z 292 [M+H]+ → m/z 176 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+ for detection of 1,N2-εdGuo.
- Use the same parameters for detection of [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo (m/z 281 [M+H]+ m/z → 165 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+) and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo (m/z 297 [M+H]+ → m/z 181 [M - 2'-deoxyribose + H]+). Set the ESI-MS/MS parameters as described in Table 1.
| ESI-MS/MS parameters | 8-oxodGuo | Etheno adducts |
| Curtain Gas | 20 psi | 20 psi |
| Nebulizing Gas | 55 | 50 |
| Ion Source Gas | 50 psi | 40 psi |
| Collision-induced Dissociation Gas | Medium | Medium |
| Ion Spray Voltage | 5000 | 4500 |
| ESI Probe Temperature | 450 | 450 |
| Declustering Potential | 31 V, 8-oxodGuo | 41 V, 1,N6-εdAdo |
| 31 V, [15N5]8-oxodGuo | 41 V, [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo | |
| 45 V, 1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| 45V, [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| Collision Energy | 23 eV, 8-oxodGuo | 25 eV, 1,N6-εdAdo |
| 23 eV, [15N5]8-oxodGuo | 25 eV, [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo | |
| 27 eV, 1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| 27 eV, [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| Collision Cell Exit Potential | 16 V, 8-oxodGuo, | 8 V, 1,N6-εdAdo |
| 16 V, [15N5]8-oxodGuo | 8 V, [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo | |
| 16 V, 1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| 16 V, [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo | ||
| Entrance Potential | 10 V | 10 V |
Table 1. Parameters used in the ESI-MS/MS equipment for detection of the DNA lesions. This table has been modified from Oliveira et al.34.
- Filter (using 0.22 µm porous membranes) and degasify (using a sonicator) all the water based HPLC solvents.
- Use the following chromatography conditions for the analyses.
- Elute a 150 x 2.0 mm i.d., 3.0 µm, C18 column coupled to a C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) with a gradient of 5 mM ammonium acetate, pH 6.6 (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) at a flow rate of 130 µL/min and 25 °C.
- Use the following gradient program for the binary pump: from 0 to 10 min, 0% of solvent B; 10 to 39 min, 0 - 20% of solvent B; 39 to 41 min, 20 - 75% of solvent B; 41 to 46 min, 75% of solvent B; 46 to 47 min, 75 - 0% of solvent B; 47 to 60 min, 0% of solvent B.
- Use the switching valve to direct the first 35 min of eluent to waste and the 35 - 42 min fraction to the ESI source. Be sure that the adduct standards elute from the column in the set interval (35 - 42 min). Make adjustments if necessary.
- Elute a 150 x 2.0 mm i.d., 3.0 µm, C18 column coupled to a C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) with a gradient of 5 mM ammonium acetate, pH 6.6 (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) at a flow rate of 130 µL/min and 25 °C.
9. Quantification of normal 2'-deoxyribonucleosides by HPLC-UV
- Use an equipment similar to the equipment used in this work (see the Table of Materials).
- Elute a 250 mm x 4.6 mm i.d., 5 µm, C18 column attached to a C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) with a gradient of 0.1% formic acid and methanol.
- Use the following gradient program: from 0 to 25 min, 0 to 18% methanol; from 25 to 27 min, 18 to 0% methanol; from 27 to 37 min, 0% methanol) at a flow rate of 1 mL/min and 30 °C.
- Inject 5 µL of each sample reserved for 2'-deoxynucleosides quantification.
- Set the DAD detector at 260 nm for integration of the dGuo and dAdo peaks.
10. Quantification of the DNA lesions
- Integrate the peaks of 8-oxodGuo, [15N5]8-oxodGuo, 1,N6-εdAdo, [15N5]1,N6-εdAdo, 1,N2-εdGuo, and [15N5]1,N2-εdGuo from the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS analyses.
- Calculate the area ratios of 8-oxodGuo/[15N5]8-oxodGuo, 1,N6-εdAdo/[15N5]1,N6-εdAdo, and 1,N2-εdGuo/[15N5]1,N2-εdGuo for the calibration curves and the samples.
- Plot the calibration curves using the area ratios obtained in step 10.1.1 in the y axis and the amounts of analytes present in each point in the x axis.
- Calculate the amounts (fmol) of lesions in each injected sample using the ratios calculated in step 10.1.1 and the calibration curves of step 10.1.2.
- Integrate the peaks of dGuo and dAdo from the HPLC-UV analyses.
- Plot the calibration curves using the areas obtained in step 10.2 in the y axis and the amounts of analytes present in each point in the x axis.
- Calculate the amounts (nmol) of dGuo and dAdo in each injected sample using the areas obtained in step 10.2 and the calibration curves of step 10.2.1.
- Calculate the amounts (nmol) of dGuo and dAdo present in each sample injected in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system, considering that the amounts calculated in step 10.2.2 are present in the sample volume of 5 µL, while 50 µL were injected in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system.
NOTE: To calculate the amount of dGuo in the samples used for 8-oxodGuo analysis, just multiply the amount (nmol/µL) obtained in step 10.2.2 by 50. To calculate the amounts of dAdo and dGuo in the samples used for analyses of 1,N6-εdAdo and 1,N2-εdGuo, consider the concentration step after solid phase extraction. The volume of 50 µL injected in the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system corresponds to 114.32 µL of the original sample. The amounts (nmol/µL) obtained in step 10.2.2 should be multiplied by 114.32 to obtain the correct values. - Calculate the molar fractions 8-oxodGuo/dGuo, 1,N6-εdAdo/dAdo, 1,N2-εdGuo/dGuo. The ratios (fmol lesion/nmol normal deoxynucleoside) give the number of lesions per 106 normal dGuo or dAdo.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
The average DNA concentrations (± SD) obtained from mice liver (~ 1 g tissue), lung (~ 0.2 g tissue) and kidney (~ 0.4 g tissue) were, respectively, 5,068 ± 2,615, 4,369 ± 1,021, and 3,223 ± 723 µg/mL in the final volume of 200 µL. A representative chromatogram obtained by HPLC-DAD of the purified DNA is shown in Figure 3. The presence of the four 2'-deoxynucleosides, free from the RNA ribonucleosides, which elute immediately...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
A major problem found in the 8-oxodGuo analyses by HPLC methods is the possible induction of its formation during the workup procedures of DNA extraction, DNA hydrolysis, and concentration of DNA hydrolysates22,38. In order to minimize the problem of 8-oxodGuo artifactual formation, it is recommended the addition of deferoxamine to all DNA extraction, storage and hydrolysis solutions, the use of the sodium iodide chaotropic method and avoidance of phenol in ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Proc. 2012/22190-3 and 2012/08616-8), CNPq (Proc. 454214/2014-6 and 429184/2016-6), CAPES, PRPUSP (Pró-Reitoria de Pesquisa da Universidade de São Paulo), INCT INAIRA (MCT/CNPq/FNDCT/CAPES/FAPEMIG/FAPERJ/FAPESP; Proc. 573813/2008-6), INCT Redoxoma (FAPESP/CNPq/CAPES; Proc. 573530/2008-4), NAP Redoxoma (PRPUSP; Proc. 2011.1.9352.1.8) and CEPID Redoxoma (FAPESP; Proc. 2013/07937-8). T. F. Oliveira and A. A. F. Oliveira received scholarships from FAPESP (Proc. 2012/21636-8, 2011/09891-0, 2012/08617-4) and CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior). M. H. G. Medeiros, P. Di Mascio, P. H. N. Saldiva, and A. P. M. Loureiro received fellowships from CNPq.
Some figures and tables present in this work were originally published in Oliveira A.A.F. et al. Genotoxic and epigenotoxic effects in mice exposed to concentrated ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from São Paulo city, Brazil. Particle and Fibre Toxicology. 15, 40 (2018).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| [15N5]-2’-deoxyadenosine | Cambridge Isotope Laboratories | NLM-3895-25 | |
| [15N5]-2’-deoxyguanosine | Cambridge Isotope Laboratories | NLM-3899-CA-10 | |
| acetonitrile | Carlo Erba Reagents | 412413000 | |
| alkaline phosphatase from bovine intestinal mucosa | Sigma | P5521 | |
| ammonium acetate | Merck | 101116 | |
| calf thymus DNA | Sigma | D1501 | |
| cell lysis solution | QIAGEN | 158908 | |
| chloroform | Carlo Erba Reagents | 412653 | |
| deferoxamine | Sigma | D9533 | |
| deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I) | Bio Basic Inc | DD0649 | |
| ethanol | Carlo Erba Reagents | 414542 | |
| formic acid | Sigma-Aldrich | F0507 | |
| HPLC-ESI-MS/MS system | HPLC: Agilent 1200 series ESI-MS/MS: Applied Biosystems/MDS Sciex Instruments | HPLC: binary pump (G1312B), isocratic pump (G1310A), column oven with a column switching valve (G1316B), diode array detector (G1315C), auto sampler (G1367C). ESI-MS/MS: Linear Quadrupole Ion Trap mass spectrometer, Model 4000 QTRAP. | |
| HPLC/DAD system | Shimadzu | Two pumps (LC-20AT), photo diode array detector (DAD-20AV), auto-injector (Proeminence SIL-20AC), column oven (CTO-10AS/VP) | |
| HPLC column (50 x 2.0 mm i.d., 2.5 µm, C18) | Phenomenex | 00B-4446-B0 | |
| HPLC column (150 x 2.0 mm i.d., 3.0 µm, C18) | Phenomenex | 00F-4251-B0 | |
| HPLC column (250 x 4.6 mm i.d., 5.0 µm, C18) | Phenomenex | 00G-4252-E0 | |
| HPLC C18 security guard cartridge (4.0 x 3.0 mm i.d.) | Phenomenex | AJO-4287 | |
| isoamyl alcohol | Sigma-Aldrich | M32658 | |
| isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) | Carlo Erba Reagents | A412790010 | |
| ketamine | Ceva | Commercial name: Dopalen | |
| magnesium chloride | Carlo Erba Reagents | 349377 | |
| magnesium chloride | Sigma | M2393 | |
| methanol | Carlo Erba Reagents | L022909K7 | |
| phosphodiesterase I from Crotalus atrox | Sigma | P4506 | |
| protein precipitation solution | QIAGEN | 158912 | |
| proteinase K | Sigma-Aldrich | P2308 | |
| ribonuclease A | Sigma | R5000 | |
| sodium chloride | Sigma-Aldrich | S9625 | |
| SPE-C18 (Strata-X) | Phenomenex | 8B-S100-TAK | |
| tris(hydroxymethyl)-aminomethane | Carlo Erba Reagents | 489983 | |
| xylazine | Syntec do Brasil | Commercial name: Xilazin |
References
- Cadet, J., Davies, K. J. A., Medeiros, M. H. G., Di Mascio, P., Wagner, J. R. Formation and repair of oxidatively generated damage in cellular DNA. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 107, 13-34 (2017).
- Barnes, J. L., Zubair, M., John, K., Poirier, M. C., Martin, F. L. Carcinogens and DNA damage. Biochemical Society Transactions. 46, 1213-1224 (2018).
- Cadet, J., Davies, K. J. A. Oxidative DNA damage & repair: An introduction. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 107, 2-12 (2017).
- Cao, H., Jiang, Y., Wang, Y. Stereospecific synthesis and characterization of oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing an N2-(1-carboxyethyl)-2'-deoxyguanosine. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 129, 12123-12130 (2007).
- Breyer, V., et al. Analysis and biological relevance of advanced glycation end-products of DNA in eukaryotic cells. The FEBS Journal. 275, 914-925 (2008).
- Tamae, D., Lim, P., Wuenschell, G. E., Termini, J. Mutagenesis and repair induced by the DNA advanced glycation end product N2-1-(carboxyethyl)-2'-deoxyguanosine in human cells. Biochemistry. 50, 2321-2329 (2011).
- Hecht, S. S. Lung carcinogenesis by tobacco smoke. International Journal of Cancer. 131, 2724-2732 (2012).
- Garraway, L. A., Lander, E. S. Lessons from the cancer genome. Cell. 153, 17-37 (2013).
- Ong, T. P., Loureiro, A. P. M. Nutritional interventions in age-related genetic and epigenetic instability and cancer. Anti-ageing nutrients: Evidence-based prevention of age-associated diseases. , John Wiley & Sons. UK. (2015).
- Evans, M. D., Dizdaroglu, M., Cooke, M. S. Oxidative DNA damage and disease: induction, repair and significance. Mutation Research. 567, 1-61 (2004).
- Moriya, M. Single-stranded shuttle phagemid for mutagenesis studies in mammalian cells: 8-oxoguanine in DNA induces targeted GC → TA transversions in simian kidney cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90, 1122-1126 (1993).
- Medeiros, M. H. G. Exocyclic DNA adducts as biomarkers of lipid oxidation and predictors of disease. Challenges in developing sensitive and specific methods for clinical studies. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 22, 419-425 (2009).
- Guéraud, F. 4-Hydroxynonenal metabolites and adducts in pre-carcinogenic conditions and cancer. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 111, 196-208 (2017).
- Nair, U., Bartsch, H., Nair, J. Lipid peroxidation-induced DNA damage in cancer-prone inflammatory diseases: A review of published adduct types and levels in humans. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 43, 1109-1120 (2007).
- Pang, B., et al. Lipid peroxidation dominates the chemistry of DNA adduct formation in a mouse model of inflammation. Carcinogenesis. 28, 1807-1813 (2007).
- Møller, P., et al. Harmonising measurements of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine in cellular DNA and urine. Free Radical Research. 46, 541-553 (2012).
- Hofer, T., Moller, L. Optimization of the workup procedure for the analysis of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine with electrochemicaldetection. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 15, 426-432 (2002).
- Collins, A., El Yamani, N., Dusinska, M. Sensitive detection of DNA oxidation damage induced by nanomaterials. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. , 69-76 (2017).
- Zubel, T., Buerkle, A., Mangerich, A. Mass spectrometric analysis of sulfur mustard-induced biomolecular adducts: Are DNA adducts suitable biomarkers of exposure? Toxicology Letters. 293, 21-30 (2018).
- Tretyakova, N., Goggin, M., Sangaraju, D., Janis, G. Quantitation of DNA adducts by stable isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 25, 2007-2035 (2012).
- Churchwell, M. I., Beland, F. A., Doerge, D. R. Quantification of multiple DNA adducts formed through oxidative stress using liquid chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 15, 1295-1301 (2002).
- Chao, M. R., Yen, C. C., Hu, C. W. Prevention of artifactual oxidation in determination of cellular 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine by isotope-dilution LC-MS/MS with automated solid-phase extraction. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 44, 464-473 (2008).
- Danielsen, P. H., et al. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage in rats after intratracheal instillation or oral exposure to ambient air and wood smoke particulate matter. Toxicological Sciences. 118, 574-585 (2010).
- Danielsen, P. H., et al. Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation induced by ambient air and wood smoke particulate matter in human A549 and THP-1 cell lines. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 24, 168-184 (2011).
- Garcia, C. C. M., et al. [13C2]-Acetaldehyde promotes unequivocal formation of 1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine in human cells. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 133, 9140-9143 (2011).
- Angeli, J. P. F., et al. Lipid hydroperoxide-induced and hemoglobin-enhanced oxidative damage to colon cancer cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 51, 503-515 (2011).
- Yu, Y., et al. Comprehensive assessment of oxidatively induced modifications of DNA in a rat model of human Wilson's disease. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics. 15, 810-817 (2016).
- Torres-Cuevas, I., Aupi, M., Asensi, M. A., Vento, M., Ortega, Á, Escobar, J. 7,8-Hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine/2'-deoxiguanosine ratio determined in hydrolysates of brain DNA by ultrachromatrography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta. 170, 97-102 (2017).
- Wu, D., et al. Detection of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) as a biomarker of oxidative damage in peripheral leukocyte DNA by UHPLC-MS/MS. Journal of Chromatography B. 1064, 1-6 (2017).
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Outdoor Air Pollution. 109, IARC. Lyon, France. (2016).
- De Martinis, B. S., Kado, N. Y., Carvalho, L. R. F., Okamoto, R. A., Gundel, L. A. Genotoxicity of fractionated organic material in airborne particles from São. Mutation Research. 446, 83-94 (1999).
- Karlsson, H. L., Nygren, J., Möller, L. Genotoxicity of airborne particulate matter: The role of cell-particle interaction and of substances with adduct-forming and oxidizing capacity. Mutation Research. 565, 1-10 (2004).
- Bell, M. L., Dominici, F., Ebisu, K., Zeger, S. L., Samet, J. M. Spatial and temporal variation in PM2.5 chemical composition in the United States for health effects studies. Environmental Health Perspectives. 115, 989-995 (2007).
- Oliveira, A. A. F., et al. Genotoxic and epigenotoxic effects in mice exposed to concentrated ambient fine particulate matter (PM2.5) from São Paulo city, Brazil. Particle and Fibre Toxicology. 15, 40(2018).
- Loureiro, A. P. M., Zhang, W., Kassie, F., Zhang, S., Villalta, P. W., Wang, M., Hecht, S. S. Mass spectrometric analysis of a cyclic 7,8-butanoguanine adduct of N-nitrosopyrrolidine: comparison to other N-nitrosopyrrolidine adducts in rat hepatic DNA. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 22, 1728-1735 (2009).
- Loureiro, A. P. M., Marques, S. A., Garcia, C. C. M., Di Mascio, P., Medeiros, M. H. G. Development of an on-line liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry assay to quantitatively determine 1,N2-etheno-2'-deoxyguanosine in DNA. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 15, 1302-1308 (2002).
- Mangal, D., et al. Analysis of 7,8-dihydro-8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine in cellular DNA during oxidative stress. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 22, 788-797 (2009).
- ESCODD (European Standards Committee on Oxidative DNA Damage). Comparative analysis of baseline 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine in mammalian cell DNA, by different methods in different laboratories: an approach to consensus. Carcinogenesis. 23, 2129-2133 (2002).
- Helbock, H. J., et al. DNA oxidation matters: The HPLC-electrochemical detection assay of 8-oxo-deoxyguanosine and 8-oxo-guanine. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95, 288-293 (1998).
- Risom, L., et al. Oxidative DNA damage and defence gene expression in the mouse lung after short-term exposure to diesel exhaust particles by inhalation. Carcinogenesis. 24, 1847-1852 (2003).
- Risom, L., et al. Repeated inhalations of diesel exhaust particles and oxidatively damaged DNA in young oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1) deficient mice. Free Radical Research. 41, 172-181 (2007).
- Tsurudome, Y., et al. Changes in levels of 8-hydroxyguanine in DNA, its repair and OGG1 mRNA in rat lungs after intratracheal administration of diesel exhaust particles. Carcinogenesis. 20, 1573-1576 (1999).
- Marie-Desvergne, C., Maître, A., Bouchard, M., Ravanat, J. L., Viau, C. Evaluation of DNA adducts, DNA and RNA oxidative lesions, and 3-hydroxybenzo(a)pyrene as biomarkers of DNA damage in lung following intravenous injection of the parent compound in rats. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 23, 1207-1214 (2010).
- Iwai, K., et al. Early oxidative DNA damages and late development of lung cancer in diesel exhaust-exposed rats. Environmental Research. 84, 255-264 (2000).
- Ichinose, T., et al. Lung carcinogenesis and formation of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine in mice by diesel exhaust particles. Carcinogenesis. 18, 185-192 (1997).
- Schmerold, I., Niedermu, H. Levels of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine in cellular DNA from 12 tissues of young and old Sprague Dawley rats. Experimental Gerontology. 36, 1375-1386 (2001).
- Garcia, C. C. M., Freitas, F. P., Di Mascio, P., Medeiros, M. H. G. Ultrasensitive simultaneous quantification of 1,N2-etheno-2'-deoxyguanosine and 1,N2-propano-2'-deoxyguanosine in DNA by an online liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry assay. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 23, 1245-1255 (2010).
- Godshalk, R., et al. Comparison of multiple DNA adduct types in tumor adjacent human lung tissue: effect of cigarette smoking. Carcinogenesis. 23, 2081-2086 (2002).
- Dechakhamphu, S., et al. Lipid peroxidation and etheno DNA adducts in white blood cells of liver fluke-infected patients: protection by plasma alpha-tocopherol and praziquantel. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 19, 310-318 (2010).
- Arab, K., et al. Typical signature of DNA damage in white blood cells: a pilot study on etheno adducts in Danish mother-newborn child pairs. Carcinogenesis. 30, 282-285 (2009).
- Nair, J., et al. High dietary omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids drastically increase the formation of etheno-DNA base adducts in white blood cells of female subjects. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention. 6, 597-601 (1997).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved