Method Article
Determination of Immune Cell Identity and Purity Using Epigenetic-Based Quantitative PCR
In This Article
Summary
Here we describe a robust method of determining immune cell identity and purity through epigenetic signatures detected using quantitative PCR (qPCR). DNA demethylation at a specific locus serves as a unique identifier for a particular cell type and allows for identification of CD8+, regulatory, or Th17 T cells.
Abstract
Immune cell subtype population frequencies can have a large effect on the efficacy of T cell therapies. Current methods, like flow cytometry, have specific sample requirements, high sample input, are low throughput, and are difficult to standardize, all of which are detrimental to characterization of cell therapy products during their development and manufacturing.
The assays described herein accurately identify and quantify immune cell types in a heterogeneous mixture of cells using isolated genomic DNA (gDNA). DNA methylation patterns are revealed through bisulfite conversion, a process in which unmethylated cytosines are converted to uracils. Unmethylated DNA regions are detected through qPCR amplification using primers targeting converted areas. One unique locus per assay is measured and serves as an accurate identifier for a specific cell type. The assays are robust and identify CD8+, regulatory, and Th17 T cells in a high throughput manner. These optimized assays can potentially be used for in-process and product release testing for cell therapy process.
Introduction
The use of T cells in cellular immunotherapy has increased significantly over the last decade, especially with the advent of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell technology1. While T cell-based therapies have been met with great clinical success, they are heterogeneous and cell characteristics and identities can vary significantly between donors2. The heterogeneity of T cell populations can have major impacts on therapeutic efficacy and complicate conclusions from clinical trials. For this reason, it is crucial to understand T cell heterogeneity during product manufacturing and formulation to determine the optimal formulations of T cell immunotherapies.
In a broad sense, T cells can be divided into two groups: CD4+ helper T cells, which secrete immunomodulatory cytokines, and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, which directly lyse cells presenting the cognate antigen on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I molecules. CD4+ helper T cells can differentiate into a myriad of specific subsets that produce a unique set of cytokines. Some suggest that a defined ratio of CD4+ to CD8+ T cells in the final cell product maximize in vivo efficacy and persistence but could complicate cell manufacturing3. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), a subset of CD4+ T cells, are immunosuppressive and diminish the activation of immune cells. Regulatory T cells have been implicated in mediating tumor tolerance and, if present during CAR T cell manufacturing, can inhibit the antitumor immune response of CAR T cells4,5,6. Other CD4+ subsets such as T helper 17 (Th17) T cells promote tumor clearance and can be leveraged to increase the efficacy of T cell therapies. Thus, increasing Th17 CD4+ T cells is of special interest in solid tumor settings where increased production of interleukin 17 (IL-17) promotes antitumor immune response5,7,8,9. Understanding the importance of Th17 cells in tumor responses has prompted more investigation into strategies to generate these cells in vitro7,9. Therefore, methods for detecting these T cell subsets are crucial for optimizing T cell therapies and should be robust, easy, scalable, and reproducible.
Flow cytometry is the most common method to determine the identity of an immune cell. However, flow cytometry requires live, intact cells that must be analyzed on the same day they are harvested. For intracellular cytokine staining (ICS), protein secretion inhibition is required to retain cytokines within the T cells. However, different inhibitor compounds have differential effects on the secretion of specific cytokines, forcing users to create specialized cocktails for the detection of the cytokine of interest10,11. Additionally, the fidelity of flow cytometry relies on antibody clones that bind specifically and potently to their target. The use of different antibody clones can cause varying results and lead to imprecise conclusions, making the method difficult to standardize12. Further, analysis of data collected via flow cytometry, and thus conclusions drawn from the data, can vary greatly between users based on how gates are set13,14. For these reasons, flow cytometry is not ideal for precise quality control during cell therapy development.
The assessment of genomic methylation at specific gene loci is an alternative method of determining cell identity. The rationale for using DNA methylation to identify specific cell types has been described in multiple articles and relies on specific methylation patterns present in a given cell population15,16,17. In target cells, certain sites contain unmethylated nucleotides, while in non-target cells these sites are methylated. This pattern can be detected through bisulfite conversion, a process that exclusively converts unmethylated cytosine nucleotides (C) to uracil (U). Primers and probes can be designed against the converted sites, then amplified and detected through qPCR16.
The assay described herein measures the frequency of immune cell subtypes within heterogeneous populations by quantifying the number of specific unmethylated loci compared to a housekeeping gene. Copies of the unmethylated regulatory elements for the CD8 B gene are measured in the CD8 assay, FoxP3 in Treg, and IL-17 in Th17 in this assay. These loci were identified by isolating the specific cell population of interest (e.g., CD8+ T cells) and performing bisulfite sequencing to identify loci that are unmethylated in only that cell type15. Primers and probes are developed against the uniquely unmethylated loci and samples are analyzed via qPCR. A standard curve of known copy numbers is created from dilutions of a high copy number standard plasmid, allowing for the conversion of a Ct value to a transcript copy number.
To evaluate assay performance, control samples are required, including a reference gDNA and a calibrator plasmid. The reference genomic material is a pooled blood sample from multiple donors with known immune cell frequencies and is used for a quality control (QC) assay performance check. The calibrator sample is a synthesized plasmid that contains the CD8, FoxP3, and GAPDH gene sequences in an equimolar ratio. It is used as a measure of the bisulfite conversion efficiency, because bisulfite conversions within different genomic regions will vary in efficiency. The ratio of the target to GAPDH within the calibrator is 1, but due to differences of the bisulfite conversion efficiency, the ratio can vary. This calibration factor is applied to the CD8 and Treg assays. FoxP3, the gene used in the Treg assay, is located on the X chromosome. Because this assay measures only unmethylated copies of FoxP3, and only one copy of FoxP3 is unmethylated in Tregs, this assay is sex agnostic and can be used with both male and female samples18. The Th17 assay does not utilize a calibrator sample or GAPDH as a housekeeping gene. Instead, another primer set targeting the methylated loci present in non-Th17 cells is included and the total number of cells is reflected by the sum of the methylated and unmethylated copies of IL-17. The data obtained from the qPCR is entered into a preset analysis template that performs quality control checks on the data and calculates the percentage of the target cell within the starting population. This provides automated and unbiased data analysis, thereby removing user subjectivity and improving standardization capabilities.
This assay uses gDNA, which can be isolated by a leukapheresis procedure using cultured or fixed cells, or frozen cell pellets. The low sample requirement, flexibility in sample starting material, high accuracy, and standardized analysis address the limitations associated with flow cytometry and are ideal for quality control purposes during cell therapy process development.
Protocol
All human samples were obtained from a commercial source following their guidelines for human research ethics.
1. Genomic DNA isolation
NOTE: Genomic DNA isolation is performed using a commercially available kit (see Table of Materials) from any hematopoietic cells, such as peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), purified T cells, or any other hematopoietic cell type. In this experiment, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and T cells from three different human donors were used.
- Place 1-2 x 106 hematopoietic cells in a conical tube and centrifuge at 400 x g for 10 min.
- Aspirate the supernatant completely.
- Add 350 µL of lysis/binding buffer to the sample and incubate for 10 min at 55 °C.
- Add 50 µL of proteinase K (20 mg/mL) to 350 µL of cell suspension and vortex for 30 s.
- Add 50 µL of DNA binding paramagnetic beads and 400 µL of 100% isopropanol and incubate for 3 min at room temperature (RT).
- Place the tube on a magnetic rack for 2 min and remove the supernatant, taking care not to disturb the beads. The DNA is bound to the magnetic beads at this step.
- Add 950 µL of wash buffer 1. Vortex for 30 s and repeat step 1.6.
- Repeat step 1.7.
- Add 950 µL of wash buffer 2. Vortex for 30 s and repeat step 1.6.
- Add 100 µL of elution buffer and vortex for 2 min. Place the tube on a magnetic stand for 1 min and transfer the supernatant containing the gDNA to a new tube.
- Use 1 µL of the gDNA isolated from the hematopoietic cells to measure the purity of the gDNA by spectrophotometry using a fluorimeter by obtaining the OD at 260 nm, 280 nm, and 230 nm. Ensure that the ratio of optical density (OD ratio) at 260 and 280 nm is between 1.7-2.0 and the OD ratio at 260 and 230 nm is between 1.5-2.4.
2. Sample preparation
- Preheat a thermomixer to 56 °C.
- Label 2 mL tubes for all samples, calibrator, and reference material.
- Dilute the samples and calibrator with the elution buffer (available with the kit used for step 1) at RT.
- For all experimental samples, dilute the gDNA to a total volume of 142 µL. For example, dilute 4 µL of gDNA at 100 ng/µL into 138 µL of elution buffer.
NOTE: 400-1,200 ng of gDNA can be used for the assay. - Dilute 75 µL of the calibrator to a total volume of 142 µL.
- Check the reference gDNA concentration with a spectrophotometer, using TE (pH = 8.0) as a blank.
- Dilute 1,000-1,200 ng of the reference gDNA to a total volume of 142 µL. For example, dilute 10 µL of reference gDNA at 100 ng/µL into 132 µL of elution buffer.
- For all experimental samples, dilute the gDNA to a total volume of 142 µL. For example, dilute 4 µL of gDNA at 100 ng/µL into 138 µL of elution buffer.
- Incubate the tubes at 56 °C for 5 min at 900 rpm in a thermomixer. Briefly spin down the tubes to collect the samples.
3. Bisulfite conversion
NOTE: Ensure that the incubation times during the bisulfite conversion follow the recommended times. Over-incubation or under-incubation will affect the results of the assay.
- Set a thermomixer to 80 °C.
- Add 270 µL of ammonium bisulfite and 90 µL of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFA) to all the tubes. Vortex to mix completely and briefly spin down the samples to gather the liquid at the bottom.
- Incubate the tubes in a thermomixer at 80 °C for 45 min at 900 rpm. If using a heat block, vortex the tubes for 1-2 s every 4.5 min during incubation.
- Briefly spin down the samples and allow to cool to RT for 3-5 min before continuing with step 4 or 5. The final volume should be ~500 µL.
4. CD8 and Treg assays
- DNA purification following bisulfite conversion
NOTE: This step is performed using a commercially available DNA purification kit (see Table of Materials) on bisulfite-converted DNA. Ensure that the reagents are warmed to RT before use.- Before starting the purification, create a homogeneous mixture of the DNA isolation paramagnetic beads by vortexing for 30 s. Add ethanol and isopropanol to the wash buffers, following the volumes listed on the bottles, and set a heat block to 65 °C.
- At RT, add 870 µL of lysis/binding buffer and 105 µL of DNA binding paramagnetic beads to each tube from step 3.4. Vortex to mix completely and briefly spin down the tubes.
- Add 570 µL of 2-propanol and vortex to mix completely.
- Incubate the tubes at RT for 7 min at 50 rpm in a thermomixer or a standard rotating mixer.
- Briefly spin down the tubes. Place the tubes on the magnetic rack and incubate for 5 min.
- With the samples still on the magnetic rack, remove the supernatant without disturbing the beads.
NOTE: The DNA is bound to the beads. - Remove the tubes from the magnetic rack and add 900 µL of wash buffer 1. Vortex the tubes to completely resuspend the beads and then briefly spin down the tubes.
- Return the tubes to the magnetic rack and incubate for 3 min.
- With the samples still on the magnetic rack, remove the supernatant without disturbing the beads.
- Repeat the washes (4.1.7-4.1.9), once with wash buffer 1, then twice with wash buffer 2.
- After removing the supernatant, briefly spin down the tubes and return to the magnetic rack for 3 min.
- Remove all residual wash buffer 2 and remove the tubes from the magnetic rack.
- Dry the beads with the tube lids open at 65 °C for 15 min.
- Add 60 µL of elution buffer to each tube and incubate at RT for 7 min at 1,400 rpm. Alternatively, vortex at a moderate speed using a foam adaptor.
- Briefly spin down the tubes and place on the magnetic rack for 2 min.
- Transfer 55 µL of eluate to a new tube without disturbing the beads. The eluate contains the bisulfite-converted DNA. Measuring the DNA concentration is not required.
- Set up and run qPCR
- Turn on the qPCR machine and the computer that operates its software.
- On the software user interface create a new experiment and select which block is being used to run the experiment.
- Select Standard Curve as the type of experiment.
- If applicable, select which detection chemistry you want to use. This assay uses the TaqMan reagents. Otherwise, select ROX as the passive reference.
- If applicable, select the properties of the instrument run as Standard.
- Define your experimental design by assigning targets (e.g., GAPDH or CD8 with FAM as the reporter), and a non-fluorescent quencher.
- Assign sample names for the standards, samples, and controls.
- Next, assign each well position according to the qPCR plate. Each well requires a target, such as CD8 or GAPDH, and a sample name. Each sample is run in triplicate and must be reflected on the plate layout for the instrument.
- Assign each standard the task Standard and specify the final copy numbers according to Table 1.
- Assign samples, calibrator, and reference the task Unknown.
- Designate wells for no template control as NTC or N.
- Prepare the serial dilutions of lambda DNA (10 ng/µL) to be used as the standard (see Table 1).
- Prepare qPCR master mix cocktails, one for the target cell type and one for GAPDH (see Table 2). Run all the samples, standards, and the NTC control in triplicate.
NOTE: GAPDH is used to quantify the total number of cells and is run in parallel with the target amplification. Copies of unmethylated regulatory elements for the CD8 B gene are measured in the CD8 assay, FoxP3 in Treg, and IL-17 in Th17. - Use a 96 well plate for qPCR. Load 3 µL of template DNA into the wells first. Next, load 7 µL of the master mix.
- Seal the plate with a qPCR film and briefly spin down the plate before placing it into the qPCR instrument.
- Run the qPCR as shown in Table 3.
- After the run completion, export the qPCR data as a .txt or .xlsx file.
- Analyze the data using the Analysis Templates for the CD8 assay and the Treg assay (see Table of Materials) to calculate the Ct Average, Ct Standard Deviation, and Copy Number.
| Initial plasmid Copy Number/3 µL | Volume | Diluent DNA [1] | Final Copy Number per 3 µL | Label |
| 31250 | 1000 µL | - | 31250 | STD#1 |
| 31250 | 200 µL | 800 µL | 6250 | STD#2 |
| 6250 | 200 µL | 800 µL | 1250 | STD#3 |
| 1250 | 200 µL | 800 µL | 250 | STD#4 |
| 250 | 200 µL | 800 µL | 50 | STD#5 |
| 1250 | 30 µL | 1200 µL | 30 | STD#6 [2] |
| [1] 10 ng/µL Lambda DNA in TE (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, pH 8.0) | ||||
| [2] Use STD#3 to prepare STD#6 | ||||
Table 1: Preparation of standard dilutions. A 4-log dilution standards spanning 31250-30 copies were prepared according to the table using TE/lambda DNA as the diluent. The same standard dilutions were used for both CD8 and GAPDH. The standards were stored at -20 °C.
| Reagents | Amount |
| Lambda DNA (50 ng/µL in TE, pH8.0) | 1 µL |
| TaqMan assay | 0.5 µL |
| Water, Nuclease-free | 0.5 µL |
| Master Mix | 5 µL |
| TOTAL | 7 µL |
Table 2: Preparation of qPCR cocktail. Prepare the qPCR master mix in two separate tubes, one each for CD8 and GAPDH, excluding the template DNA according to the table.
| Step | Time | Temp | Cycles |
| Pre-incubation | 35 min | 95°C | 1X |
| Amplification | 15 sec | 95°C | 50X |
| 1 min | 61°C | ||
| Cooldown | 5 sec | 42°C | 1X |
Table 3: qPCR run parameters for the CD8 and Treg assay. The qPCR was run according to the parameters specified in the table.
5. Th17 assay
- DNA purification following bisulfite conversion
- Perform the purification steps as described in section 4.1.
- To elute the samples, add 25 µL of elution buffer to each tube and incubate at RT for 7 min at 1,400 rpm. Alternatively, vortex at a moderate speed using a foam adaptor.
- Briefly spin down the tubes and place on a magnetic rack for 2 min.
- Transfer 20 µL of eluate to a new tube without disturbing the beads. The eluate contains the bisulfite-converted DNA.
- DNA preamplification
NOTE: DNA preamplification is recommended for low abundance targets for accurate quantification via qPCR19. The Th17 methylation assay was designed to require preamplification for this reason.- Transfer 2 µL of bisulfite-converted DNA into the PCR strip tubes. Create an NTC tube with 2 µL of water.
- Create the preamplification master mix for all samples (see Table 4).
- Add 23 µL of the master mix to each tube. Cap the tubes, vortex, and briefly spin down the tubes.
- Run the preamplification protocol on a thermocycler using a heated lid. (Table 5). After the run is complete, briefly spin down the tubes.
- Transfer 2 µL of the amplified DNA to new tubes and add 78 µL of water, diluting the samples 1:40.
- qPCR set up and run
- Follow section 4.2 to set up and run the qPCR.
- Analyze data using the analysis template for the Th17 assay (see Table of Materials) to calculate the Ct Average, Ct Standard Deviation, and Copy Number.
| Reagent | Amount |
| Water, Nuclease-free | 9.5 µL |
| Hot Start PCR Master Mix | 12.5 µL |
| Th17 PCR Primer | 1 µL |
| TOTAL | 23 µL |
Table 4: Pre-amplify the DNA for the Th17 assay. The pre-amplification reaction master mix was prepared according to the table.
| Step | Time | Temp | Cycles |
| Pre-incubation | 35 min | 95°C | 1X |
| Denaturation | 1 min | 95°C | 12X |
| Annealing | 45 sec | 55°C | |
| Elongation | 30 sec | 72°C | |
| Final elongation | 10 min | 72°C | 1X |
| Hold | Indefinite | 4°C |
Table 5: Preamplify Th17 DNA. Th17 DNA was pre-amplified for 12 cycles before the actual qPCR.
Results
All three methylation assays begin with an input of gDNA and result in a percentage of CD8+ T cells, Treg, or Th17 cells within the entire cell population. The data generated from the qPCR following bisulfite conversion was analyzed using the provided analysis template. This template used the standard curves obtained from the standard samples to estimate the copy number of the targets and total cell counts in the test samples. The percent cell type was then calculated using the formulas integrated in the analysis templates. Figure 1 shows representative data from the CD8+ assay, obtained from analyzing both peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and T cells from three different donors using both flow cytometry and the described methylation assay. The trends between the two methods across all donors in both cell types were similar. Figure 2 shows representative data from the Treg assay. Three purified Treg donors were analyzed using both methylation-based qPCR and flow cytometry and the results were plotted on the graph shown. Results for both methods were relatively similar. However, in all cases flow cytometry yielded higher values. Figure 3 shows the comparison of Th17 cells detected via flow cytometry and methylation. In this graph, there are stimulated and unstimulated conditions for the experimental methods. Cells require stimulation with PMA and ionomycin and treatment with a protein transport inhibitor to increase the amount of IL-17A present within each cell so that it can be detected via flow cytometry20. Methylation status can be detected regardless of the stimulation status. Flow cytometry yielded lower levels of Th17 cells when compared to methylation. The sensitivity and specificity of the assay was demonstrated by the limit of blank (LOB), limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantitation (LOQ) values displayed in Table 6.

Figure 1: Flow and methylation comparison of CD8+ percentages for both PBMCs and T cells for three different donors. PBMCs and T cells from three different donors were assayed for the percentage of CD8+ T cells in the entire population using either flow cytometry or methylation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
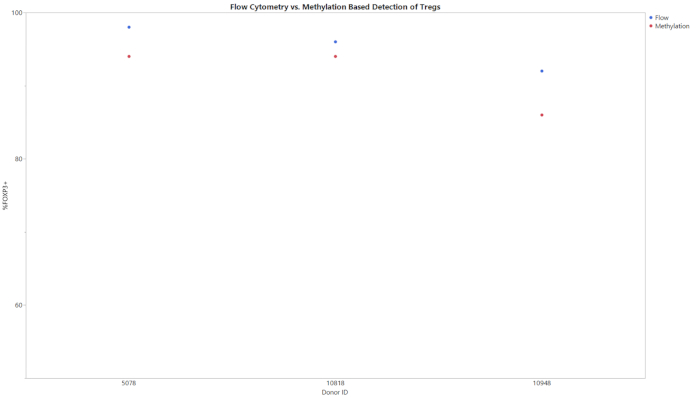
Figure 2: Flow and methylation comparison of Treg percentages for purified Treg for three different donors. Purified Treg cells were assayed for the percentage of Treg cells in the entire population using either flow cytometry or methylation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
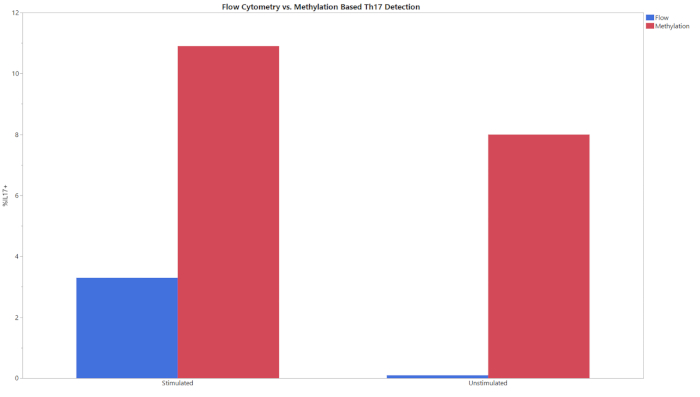
Figure 3: Flow and methylation comparison of Th17 percentages for stimulated and unstimulated experimental groups. Stimulated and unstimulated T cells were analyzed using both flow cytometry and methylation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Assay | LoB | LoD | LoQ |
| CD8 | 0 | 19 | 52 |
| Gapdh | 0 | 7 | 21 |
| FoxP3 | 0 | 3 | 12 |
| Th17 TpG | 0 | 35 | 73 |
| Th17 CpG | 0 | 38 | 73 |
Table 6: LoB, LoD, LoQ of copy numbers for methylation-based assays. Sensitivity and specificity of the assay is detailed by the LoB, LoD, and LoQ values obtained by MIQE guidelines21,22. In general, as few as 40 copies can be accurately detected by these assays.
Discussion
With the advent of new immunotherapeutics, there is a need for standardized methods of detecting immune cell identity and purity. Assessment methods for in-process and release testing that are robust, validated, and scalable remain to be established and pose a major challenge to the commercialization of cell-based therapies. While flow cytometry is currently the most common method for immune cell phenotyping, high sample quality and quantity requirements make it difficult for regular use. Further, implementing flow cytometry in a good manufacturing practice (GMP) environment is limited by operator-dependent gating strategies and the requirement of reference standards for each marker used13,14. Although automated gating has been shown to improve assay robustness, it is not yet a well-established quality control strategy. While gene expression profiling may also be used to characterize cell therapy product identity and purity, the data are semiquantitative and labor intensive. Additionally, RNA and microRNA are relatively less stable than DNA and can contribute to the lack of robust and reproducible results. Thus, utilizing the epigenetic DNA methylation status of a specific locus provides a stable, easy to perform, robust, and scalable method of identifying and quantifying a cell type of interest.
The detection of methylation patterns to phenotype cells relies on three critical steps: First, the assay requires the use of gDNA, which is isolated according to the described methods. High quality DNA is required and if not used, bisulfite conversion may be affected23,24. If low quality DNA is obtained, further purification is recommended to ensure the assay reliability. Second, successful bisulfite conversion of the unmethylated cytosine to uracil is required. The most critical step in bisulfite conversion is DNA denaturation23,25. High temperature denaturation using ammonium bisulfite, as opposed to sodium bisulfite, increases the conversion efficiency and consistency and is the recommended process for these assays25,26. Users must ensure that the reaction occurs at 80 °C and that sample mixing is done frequently. For these reasons, a digital thermomixer is recommended (see Table of Materials). Third, proper pipetting technique must be followed during the qPCR preparation. Three technical replicates are required during the qPCR reaction to adhere to the minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments (MIQE) guidelines27. The inclusion of more technical replicates is acceptable but not required. Improper pipetting technique and/or not including technical replicates will lead to unreliable qPCR results.
If the critical steps are followed and desired results are still not obtained, multiple controls within the assay can be leveraged to pinpoint the issue. Proper bisulfite conversion is the most crucial step in this assay. Improper bisulfite conversion would be highlighted by a failed calibration factor and/or reference values calculated by the analysis template. If the bisulfite conversion was performed incorrectly (e.g., if the reaction was carried out at RT), there would be no amplification during qPCR. Also, no amplification would be seen if an error was made during the qPCR reaction preparation (e.g., if the qPCR master mix was not added). These two issues can be separated by investigating the standard samples. Amplification in the standard samples, but not the reference, calibrator, and experimental samples, would indicate that the bisulfite conversion was not performed correctly. No amplification in any of the samples would indicate that the qPCR was not performed correctly.
While this assay addresses the stringent sample requirement and analysis variability associated with other phenotyping methods, specifically flow cytometry, there are limitations that must be noted. This assay targets a single locus that is used as a unique identifier for the target cell, which prohibits the multiplexed analysis that is commonly performed with flow cytometry. This makes identifying complex cell types like Th17 difficult. However, the use of methylation patterns at a single locus has been shown to be an accurate phenotypic marker of multiple cells and has been used in multiple clinical trials15,16. This is true especially in Tregs where assessing FOXP3 methylation signatures is an accurate and unambiguous method for detecting true Tregs from transiently FOXP3 expressing cells28. The loss of multiplexed analysis is compensated by the accuracy of the loci interrogated. Future iterations of the assay could include multiple qPCR dyes and quenchers to allow for the detection of multiple loci in one qPCR reaction.
This assay can be used as an alternative method for flow cytometry in determining cell phenotype and identity. It should be noted that this assay does not yield the exact values that flow cytometry does (Figures 1-3). This is due in part to the variability of data analysis associated with flow cytometry. Depending on the gating strategy, results from flow cytometry can vary significantly. This is especially the case when using complex staining protocols to look at intracellular targets, such as IL-17, where the coefficient of variation (CV) can be as high as 15%14. Between multiple users, the assay presented consistently had a CV of <15%, supporting the robustness of the assay and improved standardization capabilities. The largest differences between epigenetic and flow cytometry-based phenotyping is seen when cell stimulation is required (Figure 3). The detection of Th17 cells via flow cytometry was accomplished using a common protocol for T cell stimulation and intracellular cytokine staining29,30,31. The differences seen in Th17 phenotyping between epigenetic measurement and flow cytometry could be due to the kinetics of IL-17 production. While methylation signatures are steady, protein production takes time and must be present in sufficient quantities to be detected by fluorescent antibodies20,32. The 6 h incubation with protein transport inhibitor and cell stimulation cocktail may need to be extended to see the level of Th17 cells detected via epigenetic-based phenotyping methods. More studies are needed to determine the precise reason why the values do not match and determine the most accurate phenotyping method.
In this report, we detail how to identify and quantify immune cell types in a heterogeneous mixture of cells in a simple and robust manner. The assays are designed and optimized for potential use for in-process and release testing of cell-based therapeutics. The described assays meet the requirement for highly qualified raw materials to be used in cell therapy applications. By addressing the shortcomings of flow cytometry and other molecular methods such as stability, sample requirements, prior stimulation, cellular permeabilization for intracellular staining, and subjectivity of data analysis, the described assays are in line with the goals of commercialization of cell-based therapies.
Disclosures
Suman K. Pradhan, Jerry Guzman, Carl Dargitz, Mark Landon, and Uma Lakshmipathy are employed by Thermo Fisher Scientific. Sven Olek, Bjoern Samans, and Ulrich Hoffmueller are a founder and employees of the company Epiontis, respectively. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The project was funded by Thermo Fisher Scientific Intramural grant.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2.0 ml Eppendorf Safe-Lock Tubes | Eppendorf | 22363344 | |
| Analysis template for CD8 assay | Click Here | ||
| Analysis template for Th17 assay | Click Here | ||
| Analysis template for Treg assay | Click Here | ||
| Attune NxT Acoustic Focusing Cytometer, blue/red/violet6/yellow | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A29004 | |
| CTS PureQuant CD8+ T-Cell Assay | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A43674 | |
| CTS PureQuant Th17 Assay | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A43676 | |
| CTS PureQuant Treg Assay | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A43675 | |
| Dynabeads SILANE Genomic DNA Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 37012D | Used for genomic DNA isolation and purification after bisulfite conversion. Contains elution buffer to dilute samples. |
| DynaMag-2 Magnet | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 12321D | Used as a magnetic rack during DNA isolation and purification |
| eBioscience Essential Human T cell Phenotyping Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A42923 | |
| eBioscience Essential Human Th1/Th17 Phenotyping Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A42927 | |
| eBioscience Essential Human Treg Phenotyping Kit | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A42925 | |
| Eppendorf SmartBlock 2 mL | Eppendorf | 5362000035 | |
| Eppendorf ThermoMixer C | Eppendorf | 5382000023 | |
| HulaMixer Sample Mixer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 15920D | Recommended sample mixer |
| NanoDrop | Thermo Fisher Scientific | ND 1000 | |
| Nonstick, RNase-free Microfuge Tubes, 1.5 mL | Applied Biosystems | AM12450 | |
| QuantStudio 12S Flex | Applied Biosystems | 4470661 | |
| TE, pH 8.0, RNase-free | Thermo Fisher Scientific | AM9849 | |
| Vortex Mixer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | H2KT17113 |
References
- Hartmann, J., Schüßler-Lenz, M., Bondanza, A., Buchholz, C. J. Clinical development of CAR T cells-challenges and opportunities in translating innovative treatment concepts. EMBO Molecular Medicine. 9, 1183-1197 (2017).
- Graham, C., Jozwik, A., Pepper, A., Benjamin, R. Allogeneic CAR-T Cells: More than Ease of Access? Cells. 7, E155(2018).
- Turtle, C. J., et al. CD19 CAR-T cells of defined CD4+:CD8+ composition in adult B cell ALL patients. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 126, 2123-2138 (2016).
- Akalin, I., et al. Effects of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Expression on Regulatory T Cells. Molecular Therapy. 17, S25(2009).
- Knochelmann, H. M., et al. CAR T Cells in Solid Tumors: Blueprints for Building Effective Therapies. Frontiers in Immunology. 9, (2018).
- Chen, M. L., et al. Regulatory T cells suppress tumor-specific CD8 T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-β signals in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102, 419-424 (2005).
- Muranski, P., et al. Tumor-specific Th17-polarized cells eradicate large established melanoma. Blood. 112, 362-373 (2008).
- Majchrzak, K., et al. Exploiting IL-17-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to improve cancer immunotherapy in the clinic. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy. 65, 247-259 (2016).
- Guedan, S., et al. ICOS-based chimeric antigen receptors program bipolar TH17/TH1 cells. Blood. 124, 1070-1080 (2014).
- Vicetti Miguel, R. D., Maryak, S. A., Cherpes, T. L. Brefeldin A, but not monensin, enables flow cytometric detection of interleukin-4 within peripheral T cells responding to ex vivo stimulation with Chlamydia trachomatis. Journal of Immunological Methods. 384, 191-195 (2012).
- Lovelace, P., Maecker, H. T. Multiparameter Intracellular Cytokine Staining. Methods in Molecular Biology. 699, 165-178 (2011).
- Presicce, P., Moreno-Fernandez, M. E., Lages, C. S., Orsborn, K. I., Chougnet, C. A. Association of two clones allows for optimal detection of human FOXP3. Cytometry A. 77, 571-579 (2010).
- Pachón, G., Caragol, I., Petriz, J. Subjectivity and flow cytometric variability. Nature Reviews Immunology. 12, 396(2012).
- Westera, L., et al. Centrally Determined Standardization of Flow Cytometry Methods Reduces Interlaboratory Variation in a Prospective Multicenter Study. Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology. 8, e126(2017).
- Baron, U., et al. Epigenetic immune cell counting in human blood samples for immunodiagnostics. Science Translational Medicine. 10, (2018).
- Kleen, T. O., Yuan, J. Quantitative real-time PCR assisted cell counting (qPACC) for epigenetic - based immune cell quantification in blood and tissue. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer. 3, 46(2015).
- Rapko, S., et al. DNA methylation analysis as novel tool for quality control in regenerative medicine. Tissue Engineering. 13, 2271-2280 (2007).
- Wieczorek, G., et al. Quantitative DNA Methylation Analysis of FOXP3 as a New Method for Counting Regulatory T Cells in Peripheral Blood and Solid Tissue. Cancer Research. 69, 599-608 (2009).
- Andersson, D., et al. Properties of targeted preamplification in DNA and cDNA quantification. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnosis. 15, 1085-1100 (2015).
- Jung, T., Schauer, U., Heusser, C., Neumann, C., Rieger, C. Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. Journal of Immunological Methods. 159, 197-207 (1993).
- Armbruster, D. A., Pry, T. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation. Clinical Biochemistry Reviews. 29, S49-S52 (2008).
- Bustin, S. A., et al. The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clinical Chemistry. 55, 611-622 (2009).
- Li, Y., Tollefsbol, T. O. DNA methylation detection: Bisulfite genomic sequencing analysis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 791, 11-21 (2011).
- Warnecke, P. M., et al. Identification and resolution of artifacts in bisulfite sequencing. Methods. 27, 101-107 (2002).
- Genereux, D. P., Johnson, W. C., Burden, A. F., Stöger, R., Laird, C. D. Errors in the bisulfite conversion of DNA: modulating inappropriate- and failed-conversion frequencies. Nucleic Acids Research. 36, e150(2008).
- Darst, R. P., Pardo, C. E., Ai, L., Brown, K. D., Kladde, M. P. Bisulfite Sequencing of DNA. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. 91, 7.9.1-7.9.7 (2010).
- Taylor, S., Wakem, M., Dijkman, G., Alsarraj, M., Nguyen, M. A practical approach to RT-qPCR-Publishing data that conform to the MIQE guidelines. Methods. 50, S1-S5 (2010).
- Baron, U., et al. DNA demethylation in the human FOXP3 locus discriminates regulatory T cells from activated FOXP3(+) conventional T cells. European Journal of Immunology. 37, 2378-2389 (2007).
- Yao, Z., et al. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. Journal of Immunology. 155, 5483-5486 (1995).
- Lockhart, E., Green, A. M., Flynn, J. L. IL-17 production is dominated by gammadelta T cells rather than CD4 T cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Journal of Immunology. 177, 4662-4669 (2006).
- Liang, S. C., et al. Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 203, 2271-2279 (2006).
- Olsen, I., Sollid, L. M. Pitfalls in determining the cytokine profile of human T cells. Journal of Immunological Methods. 390, 106-112 (2013).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved