A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
An Image Guided Transapical Mitral Valve Leaflet Puncture Model of Controlled Volume Overload from Mitral Regurgitation in the Rat
In This Article
Summary
A rodent model of left heart volume overload from mitral regurgitation is reported. Mitral regurgitation of controlled severity is induced by advancing a needle of defined dimensions into the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve, in a beating heart, with ultrasound guidance.
Abstract
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a widely prevalent heart valve lesion, which causes cardiac remodeling and leads to congestive heart failure. Though the risks of uncorrected MR and its poor prognosis are known, the longitudinal changes in cardiac function, structure and remodeling are incompletely understood. This knowledge gap has limited our understanding of the optimal timing for MR correction, and the benefit that early versus late MR correction may have on the left ventricle. To investigate the molecular mechanisms that underlie left ventricular remodeling in the setting of MR, animal models are necessary. Traditionally, the aorto-caval fistula model has been used to induce volume overload, which differs from clinically relevant lesions such as MR. MR represents a low-pressure volume overload hemodynamic stressor, which requires animal models that mimic this condition. Herein, we describe a rodent model of severe MR in which the anterior leaflet of the rat mitral valve is perforated with a 23G needle, in a beating heart, with echocardiographic image guidance. The severity of MR is assessed and confirmed with echocardiography, and the reproducibility of the model is reported.
Introduction
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a common heart valve lesion, diagnosed in 1.7% of the general US population and in 9% of the elderly population greater than 65 years of age1. In this heart valve lesion, improper closure of the mitral valve leaflets in systole, causes regurgitation of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium. MR can occur due to various etiologies; however, primary lesions of the mitral valve (primary MR) are diagnosed and treated more frequently compared to secondary MR2. Isolated primary MR is often a result of myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve, resulting in elongation of the leaflets or chordae tendineae, or rupture of some chordae, all of which contribute to the loss of systolic coaptation of the valve.
MR resulting from such valve lesions elevates the blood volume filling the left ventricle in each heartbeat, increasing the end diastolic wall stress and providing a hemodynamic stressor that incites cardiac adaptation and remodeling. Cardiac remodeling in this lesion is often characterized by significant chamber enlargement3,4, mild wall hypertrophy, with preserved contractile function for prolonged periods of time. Since the ejection fraction is often preserved, correction of MR using surgical or transcatheter means is often delayed, until the onset of symptoms such as dyspnea, heart failure, and arrhythmias. However, uncorrected MR is associated with high risks of cardiac adverse events, though currently knowledge regarding the ultrastructural changes underlying these events are unknown.
Animal models of MR provide a valuable model to investigate such ultrastructural changes in the heart, and study longitudinal progression of the disease. Previously, researchers have induced MR in large animals including pigs, dogs, and sheep, by creating an external ventriculo-atrial shunt5, intracardiac chordal rupture6, or leaflet perforation7. While surgical techniques are easier in large animals, these studies have been limited to sub-chronic follow-up in a small sample size, due to the high costs of performing such studies in large animals. Furthermore, molecular analysis of tissue from these models is often challenging due to limited species-specific antibodies and annotated genome libraries for alignment.
Small animal models of MR can provide a suitable alternative to study this valve lesion and its impact on cardiac remodeling. Historically, the rat model of aorto-caval fistula (ACF) of cardiac volume overload has been used. First described in 1973 by Stumpe et al.8, an arterio-venous fistula is surgically created to bypass high pressure arterial blood from the descending aorta into the low pressure inferior vena cava. The high flow rate in the fistula induces a drastic volume overload on both sides of the heart, causing significant right and left ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction occurring within days of creating the ACF9. Despite its success, ACF does not mimic the hemodynamics of MR, a low-pressure volume overload, which elevates preload but also reduces afterload. Due to such limitations of the ACF model, we sought to develop and characterize a model of MR that better mimics the low-pressure volume overload.
Herein, we describe the protocol for a model of mitral valve leaflet puncture to create severe MR in rats10,11. A hypodermic needle was introduced into the beating rat heart, and advanced into the anterior mitral valve leaflet under real-time echocardiographic guidance. The technique is highly reproducible and a relatively good model that mimics MR as seen in patients. MR severity is controlled by the size of the needle used to perforate the mitral leaflet and severity of MR can be assessed using transesophageal echocardiography (TEE).
Protocol
Procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Program at Emory University under the protocol number EM63Rr, approval date 06/06/2017.
1. Pre-surgical preparation
- Steam sterilize surgical instruments prior to the procedure.
- On the procedure day, transfer rats from housing to surgery, and weigh them.
- Draw pre-operative and post-operative drugs according to the weight: two doses of Carprofen (2.5 mg/kg each), one dose of Gentamycin (6 mg/kg), and one dose of Buprenorphine (0.02 mg/kg).
- Ensure adequate volume of isoflurane in the gas mixer, and oxygen in the tanks are available for the surgery. One full tank of oxygen (24 ft3) is often adequate.
2. Animal preparation
NOTE: Adult Sprague-Dawley male rats weighing 350-400 g were used in this study. The surgical techniques are amenable to slightly smaller or larger animals, if desired.
- Sedate the rat in an induction chamber with 5% isoflurane mixed in 1 LPM (liter per minute) of 100% oxygen. Determine adequate level of sedation from a slower respiratory rate under visual observation, and loss of twitch upon pinching the rat's toe.
- Intubate the rat with a 16 G angiocath, fitted for use as an endotracheal tube.
- Visualize the trachea and vocal cords using an otoscope, and use a cotton tip applicator to clear pharyngeal secretions.
- Introduce the endotracheal tube on a 0.034-inch guidewire, into the vocal cords. Once the tube is appropriately placed in the trachea, push the tube inwards and withdraw the wire (Figure1).
- Place the rat on the heated surgical pad maintained at 37 °C and connect the endotracheal tube to a mechanical ventilator. Input the weight of the rat into the ventilator control software, which calculates the ventilation rate and tidal volume. 66 breaths per minute with a tidal volume of 1 mL/100 g body weight were used in this study (Figure 1D).
- Use 100% oxygen (1 LPM) mixed with 2-2.5% isoflurane as inhalant anesthetic and confirm the level of anesthesia with loss of jaw tone and loss of response to toe pinch.
- Note that if properly intubated, chest motion should synchronize with the ventilator.
- If improperly intubated, chest motion will not synchronize with the ventilator. To test for improper intubation, compress the abdomen of rat, which creates backpressure on the ventilator, generating an over-pressure alarm. In this scenario, retract the angiocath gently, and return the rat to the induction chamber with 5% isoflurane for few minutes to ensure the rat is sufficiently anesthetized and re-intubate the rat.
- Once properly intubated, secure the endotracheal tube by suturing the proximal end of the tube to the cheek of the rat with a 4-0 silk suture to avoid extubation during the procedure.
- Insert a rectal temperature probe to monitor body temperature, and a four-terminal electrocardiogram to monitor ECG during the entire procedure.
- Use an overhead heating lamp if heat from the surgical platform is insufficient. Turn off lamp if body temperature rises above 37 °C.
- Visually assess the electrocardiogram for any arrhythmias or signs of myocardial ischemia. If none are present, record the baseline electrocardiogram.
- Perform transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) for baseline cardiac function (Figure 2A).
- Turn the rat to a supine position and shave the left side of the thorax. To obtain clear echo views, remove hair using a depilatory cream.
- Use any ultrasound system with adequate frequency for high heart rate imaging. In this study we used the Visualsonics 2100 system with a 21 MHz probe, which is appropriate for cardiac imaging in rats.
- Obtain B-mode images in the parasternal long-axis plane, to calculate the left ventricular volumes. In the same plane, obtain M-mode images to measure wall dimensions.
- Turn the probe by 90°, and obtain B-mode and M-mode parasternal short-axis views at the mid-papillary level to measure cross-sectional wall dimensions.
- Perform transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) for baseline imaging (Figure 2B).
- Place the rat in the right decubitus position and insert an 8 Fr intracardiac ultrasound probe (8 MHz) into the esophagus of the rat with a small amount of gel applied to the tip. The frequency of the ICE (intracardiac echocardiography) probe is sufficient to obtain 4-6 frames per heartbeat, which are adequate to visualize the valve motion.
NOTE: A GE Vivid I or Siemens SC2000 prime system can be used for ICE imaging. - Obtain a high esophageal view to obtain a two-chamber view of the left side of the heart. This view is ideal to visualize the left atrium, mitral valve, and left ventricle. Position the probe such that anterior and posterior leaflets are visualized and coaptation is central. This angle also allows Doppler measurements across the mitral valve, without angle correction.
- Measure left atrial area and mitral valve annulus dimensions in this view.
- Perform color Doppler imaging to confirm valve competence and lack of MR at baseline. Perform pulsed wave and continuous wave Doppler imaging to quantify mitral inflow and confirm lack of regurgitant flow.
- Perform B-mode and pulsed wave Doppler imaging of the aorta to measure the aortic root diameter and calculate aortic flow.
- Perform pulsed wave Doppler imaging of the pulmonary vein to measure pulmonary venous flow.
- Place the rat in the right decubitus position and insert an 8 Fr intracardiac ultrasound probe (8 MHz) into the esophagus of the rat with a small amount of gel applied to the tip. The frequency of the ICE (intracardiac echocardiography) probe is sufficient to obtain 4-6 frames per heartbeat, which are adequate to visualize the valve motion.
- Inject a single dose of Carprofen (2.5 mg/kg, SQ, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory), Gentamycin (6 mg/kg, SQ, antibiotic), and sterile saline (1 mL, SQ) to pre-emptively compensate for blood loss during the procedure.
- Shave the left side of the thorax as needed to remove any remaining hair from the surgical field. Shaving from the lower neck region to the xyphoid, and from the left arm down to the mid-sternum should be sufficient to ensure a field that is devoid of hair and reduce the risk of surgical site contamination.
- Scrub the surgical area with a gauze soaked in Betadine, followed by a gauze soaked in 70% ethanol. Scrub the area in circular motions on the skin, such that the gauze does not contact a previously scrubbed area.
- Repeat this step three times to achieve an adequately sterile field for surgery.
- Drape the animal with sterile covers, opening a window to access the sterile surgical area.
3. Left thoracotomy
- Perform the entire surgical procedure using aseptic techniques, with isoflurane maintained at 2-2.5% in 1 LPM of oxygen. Place all the instruments in a sterile tray, and place back in the tray after each use.
- Wear sterile gloves, a mask and a surgical cap by the surgeon for the entire procedure. A sterile surgical gown may be worn as well, but it is optional unless contamination is expected.
- Use a surgical scalpel with a No #15 blade to make a skin incision on the left side of the thorax, approximately 1 cm proximal to the xyphoid. Use a blunted dissecting tip scissors to separate the skin layer from the muscle layer and make a longitudinal incision.
- Dissect the muscle layers in the same manner until the ribs are exposed.
- Carefully make a 2-3 cm longitudinal incision in the fifth intercostal space, adequate to insert retractors and expose the heart.
- Use fine tipped forceps to lift the pericardium, and micro scissors to excise it in the region surrounding the apex of the heart. This step helps to avoid post-surgical adhesions of the heart to the chest walls and diaphragm.
NOTE: Avoid surgical incisions close to the sternum to minimize bleeding. Transecting the internal mammary arteries that run along the sternum, may cause excessive bleeding. If encountered with such bleeding, identify the bleeder and cauterize it.
4. Echo guided MR procedure (Figure 3 & Figure 4)
- Use a 6-0 prolene suture and a microneedle holder, to place a purse string suture on the apex of the left ventricle. If required, use micro forceps to stabilize the heart.
- Gently tether the apical suture to stabilize the apex and insert a 23 G needle (flushed with saline, and with a stopcock at its distal end) in the center of the purse string suture, into the left ventricular cavity.
- Use one hand to stably hold and guide the needle, and the other hand to simultaneously manipulate the transesophageal echo probe to achieve an optimal echo view to visualize the needle, as described above.
- With real time ultrasound guidance, advance the needle toward the ventricular side of the anterior mitral leaflet. Once the needle position is confirmed on ultrasound, advance the needle in one fine motion through the valve leaflet. If a resistance is felt, twist the needle as it is advanced into the leaflet to perforate it.
NOTE: Advancing the needle too far into the left atrium could result in left atrial perforation, causing excessive bleeding and animal death. The needle should be visualized on ultrasound at all times. - Retract the needle into the left ventricular chamber, away from the mitral valve, and confirm MR by turning on color Doppler imaging.
- If MR is not seen on color Doppler imaging, repeat steps 4.4 and 4.5. Adjust the echo probe if required to obtain a better view. After practice in few rats, it is possible to induce a leaflet puncture in one motion of the needle, inducing a hole that is the size of the outer diameter of the needle. This was confirmed after necropsy of the rat hearts.
- Once MR is confirmed, retract the needle out of the left ventricular cavity and gently tie the purse string suture.
- Use a sterile gauze to soak any blood on the apex and in the thoracic cavity.
NOTE: Touching the echo probe with the surgical gloves may result in contamination of the sterile environment. Spray your gloves with 70% ethanol or replace the gloves with new ones, appropriately.
5. Animal recovery and post-operative care
- After 5-10 minutes of stable cardiac function (normal ECG and heart rate), close the thoracotomy in layers with 4-0 vicryl, while reducing isoflurane in steps.
- Use an interrupted suture to approximate the ribs, with isoflurane maintained at 2%. Insert a chest tube into the sixth intercostal space and secure it to the sterile drapes to avoid inadvertent advancement of the tube into the thoracic cavity.
- Use a continuous suture to close the muscle layer with isoflurane maintained at 1.5%.
- Use a continuous suture to close the skin layer with isoflurane maintained at 1%.
- Connect a 10 mL Luer-lock valve tipped syringe to the chest tube and drain 10-12 mL of air from the chest cavity and then remove the chest tube.
- Administer a final dose of Carprofen (2.5 mg/kg, SQ) and turn off isoflurane.
- Continue mechanical ventilation while rat weans from anesthesia, monitoring vital signs (SpO2 and heart rate). At the onset of spontaneous breathing, turn off ventilation to test the ability of the rat to maintain such breathing and good SpO2.
- If SpO2 levels start to fall below 90%, turn on the ventilator. Once the rat is able to maintain SpO2 levels without ventilation, the anchoring suture to the endotracheal tube is cut, and the animal is prepared for extubation.
- Once the rat shows signs of alertness including whisker or eye movements, extubate the animal.
- Place a nose cone with 100% oxygen until the rat is ambulatory.
- Transfer rat to a clean cage with minimal bedding and continue to monitor vital signs using a handheld SpO2 monitor, placed on the rat's foot or tail, until rat is ambulatory.
NOTE: If adverse effects from the surgery are observed, animals may have a longer recovery time and may take longer to hold high SpO2 levels. If this occurs, a nose cone with 100% oxygen can be applied until SpO2 levels are stable. - To reduce the risk of injury to the surgical site and avoid the risk of infection, single house rats after surgery.
- Administer Buprenorphine within 3 h after the rat is awake and sufficiently ambulatory. Buprenorphine may cause respiratory distress when administered early in the perioperative recovery period, thus delay it until the rat is breathing without difficulty.
- After surgery, all animals receive the following medications: gentamicin (6 mg/kg, SQ, SID POD 1-3) and rimadyl (5 mg/kg, SQ, SID POD 1-3). All animals are observed once daily for five days after surgery for examination of incision sites, and once daily for the first two weeks after surgery for pain assessment.
6. Validation of MR severity with echocardiography (Figure 5)
- Repeat TEE at two weeks after surgery, using the same steps specified in section 2.7. Two weeks post-surgery is adequate time for the hemodynamics to stabilize.
- Obtain color Doppler imaging on a 2-chamber view using transesophageal ultrasound imaging, visualizing the left ventricle and left atrium. Measure the area of the left atrium and MR jet. Calculate the MR jet area fraction using
 (1)
(1)
Severe MR is defined as MR jet area ≥ 30%. - Approximate the area of the regurgitant orifice by calculating the area of 23 G needle, using the outer diameter of the needle. This equation assumes that the area of the regurgitant orifice is equal to the area of the 23G needle.
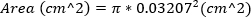 (2)
(2) - Obtain continuous-wave Doppler imaging with the Doppler gate at the orifice of the regurgitant jet. Trace the waveform to compute VTI of the regurgitant jet. MR volume can be estimated using
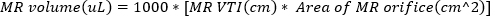 (3)
(3)
Severe MR is defined as MR volume ≥ 95 µL. - Obtain pulse wave Doppler imaging of the pulmonary vein by rotating the echo probe laterally, clockwise. Measure the systolic and diastolic wave velocities and use the following equation to calculate the ratio.
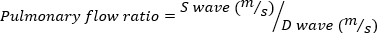 (4)
(4)
A negative pulmonary flow ratio indicates severe MR.
7. Sham surgery
- Perform sections 1-3 as described.
- Modify section 4 was modified such that the 23 G needle is inserted into the left ventricular chamber, through a purse string suture on the left ventricular apex, but not advanced into the mitral valve to create MR. Insert the needle into the left ventricular chamber and retract immediately, following by tightening and closure of the ventricular apex.
- Perform section 5 as described.
- Perform mitral valve assessment as described in section 6. However, MR should not be present in any of the animals, thus quantification as described is not necessary.
Results
Feasibility and reproducibility
The proposed MR model is highly reproducible, with a well defined hole in the mitral leaflet achieved in 100% of the rats used in this study. Figure 6A depicts the direction of the needle as it is inserted into the mitral valve. Figure 6B depicts a hole in the mitral valve leaflet from a representative rat explanted at 2 weeks after the proce...
Discussion
A reproducible rodent model of severe MR with good survival (93.75% survival after surgery) and without significant post-operative complications is reported. Real-time imaging with transesophageal echocardiography and introduction of a needle into the beating heart to puncture the mitral leaflet are feasible and can be taught. Severe MR was produced with the 23 G needle size in this study, which can be varied as desired using a smaller or larger needle. MR induced in this model creates a low-pressure volume overload on t...
Disclosures
M.P is an advisor to Heart Repair Technologies (HRT), for which he has received consulting fees. HRT did not have any role in this study, nor did it provide any funding to support this work.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by grant 19PRE34380625 and 14SDG20380081 from the American Heart Association to D. Corporan and M. Padala respectively, grants HL135145, HL133667, and HL140325 from the National Institutes of Health to M. Padala, and infrastructure funding from the Carlyle Fraser Heart Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown to M. Padala.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 23G needle | Mckesson | 16-N231 | |
| 25G needle, 5/8 inch | McKesson | 1031797 | |
| 4-0 vicryl | Ethicon | J496H | |
| 6-0 prolene | Ethicon | 8307H | |
| 70% ethanol | McKesson | 350600 | |
| ACE Light Source | Schott | A20500 | |
| ACUSON AcuNav Ultrasound probe | Biosense Webster | 10135936 | 8Fr Intracardiac echo probe |
| ACUSON PRIME Ultrasound System | Siemens | SC2000 | |
| Betadine | McKesson | 1073829 | |
| Blunted microdissecting scissors | Roboz | RS5990 | |
| Buprenorphine | Patterson Veterinary | 99628 | |
| Carprofen | Patterson Veterinary | 7847425 | |
| Chest tube (16G angiocath) | Terumo | SR-OX1651CA | |
| Disposable Surgical drapes | Med-Vet | SMS40 | |
| Electric Razor | Oster | 78400-XXX | |
| Gentamycin | Patterson Veterinary | 78057791 | |
| Heat lamp with table clamp | Braintree Scientific | HL-1 120V | |
| Hemostatic forceps, curved | Roboz | RS7341 | |
| Hemostatic forceps, straight | Roboz | RS7110 | |
| Induction chamber | Braintree Scientific | EZ-1785 | |
| Injection Plug, Cap, Luer Lock | Exel | 26539 | |
| Isoflurane | Patterson Veterinary | 6679401725 | |
| Mechanical ventilator | Harvard Apparatus | Inspira ASV | |
| Microdissecting forceps | Roboz | RS5135 | |
| Microdissecting spring scissors | Roboz | RS5603 | |
| Needle holder | Roboz | RS6417 | |
| No. 15 surgical blade | McKesson | 1642 | |
| Non-woven sponges | McKesson | 446036 | |
| Otoscope | Welch Allyn | 23862 | |
| Oxygen | Airgas Healthcare | UN1072 | |
| Pulse Oximeter | Nonin Medical | 2500A VET | |
| Retractor, Blunt 4x4 | Roboz | RS6524 | |
| Rodent Surgical Monitor | Indus Instruments | 113970 | The integrated platform allows for monitoring of vital signs and surgical warming |
| Scale | Salter Brecknell | LPS 150 | |
| Scalpel Handle | Roboz | RS9843 | |
| Silk suture 3-0 | McKesson | 220263 | |
| Small Animal Anesthesia System | Ohio Medical | AKDL03882 | |
| Sterile saline (0.9%) | Baxter | 281322 | |
| Sugical Mask | McKesson | 188696 | |
| Surgical cap | McKesson | 852952 | |
| Surgical gloves | McKesson | 854486 | |
| Syringe 10mL | McKesson | 1031801 | |
| Syringe 1mL | McKesson | 1031817 | |
| Ultra-high frequency probe | Fujifilm Visualsonics | MS250 | |
| Ultrasound gel | McKesson | 150690 | |
| VEVO Ultrasound System | Fujifilm Visualsonics | VEVO 2100 |
References
- Nkomo, V. T., et al. Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Lancet. 368 (9540), 1005-1011 (2006).
- Zamorano, J. L., et al. Mechanism and Severity of Mitral Regurgitation: Are There any Differences Between Primary and Secondary Mitral Regurgitation?. The Journal of Heart Valve Disease. 25 (6), 724-729 (2016).
- Grossman, W., Jones, D., McLaurin, L. P. Wall stress and patterns of hypertrophy in the human left ventricle. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 56 (1), 56-64 (1975).
- Carabello, B. A. Concentric versus eccentric remodeling. Journal of Cardiac Failure. 8 (6), S258-S263 (2002).
- Braunwald, E., Welch, G. H., Sarnoff, S. J. Hemodynamic effects of quantitatively varied experimental mitral regurgitation. Circulation Research. 5 (5), 539-545 (1957).
- Sasayama, S., Kubo, S., Kusukawa, R. Hemodynamic and angiocardiographic studies on cardiodynamics: experimental mitral insufficiency. Japanese Circulation Journal. 34 (6), 513-530 (1970).
- Hennein, H., Jones, M., Stone, C., Clark, R. Left ventricular function in experimental mitral regurgitation with intact chordae tendineae. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 105 (4), 624-632 (1993).
- Stumpe, K. O., Sölle, H., Klein, H., Krück, F. Mechanism of sodium and water retention in rats with experimental heart failure. Kidney International. 4 (5), 309-317 (1973).
- Abassi, Z., Goltsman, I., Karram, T., Winaver, J., Hoffman, A. Aortocaval fistula in rat: A unique model of volume-overload congestive heart failure and cardiac hypertrophy. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology. 2011 (January), 1-13 (2011).
- Corporan, D., Onohara, D., Hernandez-Merlo, R., Sielicka, A., Padala, M. Temporal changes in myocardial collagen, matrix metalloproteinases, and their tissue inhibitors in the left ventricular myocardium in experimental chronic mitral regurgitation in rodents. American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 315 (5), H1269-H1278 (2018).
- Onohara, D., Corporan, D., Hernandez-Merlo, R., Guyton, R. A., Padala, M. Mitral Regurgitation Worsens Cardiac Remodeling in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy in an Experimental Model. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. , (2019).
- Garcia, R., Diebold, S. Simple, rapid, and effective method of producing aortocaval shunts in the rat. Cardiovascular Research. 24 (5), 430-432 (1990).
- Brower, G. L., Janicki, J. S. Contribution of ventricular remodeling to pathogenesis of heart failure in rats. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 280 (2), H674-H683 (2001).
- McCutcheon, K., et al. Dynamic changes in the molecular signature of adverse left ventricular remodeling in patients with compensated and decompensated chronic primary mitral regurgitation. Circulation Heart Failure. 12 (9), (2019).
- McCutcheon, K., Manga, P. Left ventricular remodeling in chronic primary mitral regurgitation. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa. 29 (1), 51-64 (2018).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved