A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Development of Efficient OLEDs from Solution Deposition
In This Article
Summary
Presented here is a protocol for the fabrication of efficient, simple, solution-deposited organic light-emitting diodes with low roll-off.
Abstract
The use of highly efficient organic emitters based on the thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) concept is interesting due to their 100% internal quantum efficiency. Presented here is a solution deposition method for the fabrication of efficient organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) based on a TADF emitter in a simple device structure. This fast, low-cost, and efficient process can be used for all OLED emissive layers that follow the host-guest concept. The fundamental steps are described along with necessary information for further reproduction. The goal to establish a general protocol that can be easily adapted for principal organic emitters currently under study and development.
Introduction
The increase in organic electronics used in daily life has become an unsurpassed reality. Among several organic electronic applications, OLEDs are perhaps the most attractive. Their image quality, resolution, and color purity have made OLEDs a primary choice for displays. Moreover, the possibility to achieve large area emission in extremely thin, flexible, lightweight, and easy color-tunable OLEDs has applications in lighting. However, some technological issues associated with the fabrication process in large area emitters have postponed further application.
With the first OLED working at low applied voltages1, new paradigms for solid-state lighting have been designed, though with low external quantum efficiency (EQE). The OLED EQE is obtained by the ratio of emitted photons (light) to injected electrical carriers (electrical current). A simple theoretical estimate for the maximum expected EQE is equal to ηout x ηint 2. The internal efficiency (ηint) can be approximated by ηint = γ x 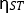 x ΦPL, where γ corresponds to the charge balance factor, ΦPL is the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY), and
x ΦPL, where γ corresponds to the charge balance factor, ΦPL is the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY), and 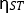 is the efficiency of emissive exciton (electron hole pair) generation. Finally, ηout is the outcoupling efficiency2. If outcoupling is not considered, attention is focused on three topics: (1) how efficient the material is in creating excitons that radiatively recombine, (2) how efficient the emissive layers are, and (3) how efficient the device structure is in promoting a well-balanced electrical system3.
is the efficiency of emissive exciton (electron hole pair) generation. Finally, ηout is the outcoupling efficiency2. If outcoupling is not considered, attention is focused on three topics: (1) how efficient the material is in creating excitons that radiatively recombine, (2) how efficient the emissive layers are, and (3) how efficient the device structure is in promoting a well-balanced electrical system3.
A purely fluorescent organic emitter has only 25% internal quantum efficiency (IQE). According to spin rules, the radiative transition from a triplet to a singlet (T→S) is forbidden4. Therefore, 75% of excited electrical carriers do not contribute to the emission of photons5. This issue was first overcome using transition metals in organic emitter phosphorescence OLEDs6,7,8,9,10, where the IQE was reportedly close to 100%11,12,13,14,15,16. This is due to the spin-orbit coupling between the organic compound and heavy transition metal. The disadvantage in such emitters is their high cost and poor stability. Recently, reports on the chemical synthesis of a pure organic compound with low energy separation between the excited triplet and singlet states (∆EST) by Adachi17,18 have given rise to a new framework. Although not new19, the successful employment of the TADF process in OLEDs have made it possible to obtain high efficiencies without using transition metal complexes.
In such metal-free organic emitters, there is a high probability for the excited carriers in a triplet state to populate to the singlet state; therefore, the IQE can achieve a theoretical limit of 100%5,20,21,22. These TADF materials provide excitons that can radiatively recombine. However, these emitters require dispersion in a matrix host to avoid emission quenching3,20,21,23,24 in a host-guest concept. Additionally, its efficiency depends on how the host (organic matrix) is appropriated to the guest (TADF) material25. Also, it is necessary to idealize the device structure (i.e., thin layers, materials, and thickness) to achieve an electrically balanced device (equilibrium between holes and electrons to avoid loss)26. Achieving the best host-guest system for an electrically balanced device is fundamental to increase the EQE. In TADF-based systems, this is not simple, due to the changes in the electrical carrier mobilities in EML that are not easily tuned.
With TADF emitters, EQE values greater than 20% are easy to obtain26,27,28,29. However, the device structure is typically comprised of three to five organic layers (hole transport/blocking and electron transport/blocking layers, HTL/HBL and ETL/EBL, respectively). Additionally, it is fabricated using a thermal evaporation process that is high in cost, technologically complex, and almost only for display applications. Depending on the HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) and LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) levels, electrical mobility of carriers, and thickness, each layer can inject, transport, and block electrical carriers and guarantee recombination in the emissive layer (EML).
Reducing the device complexity (e.g., a simple, two layer structure) usually results in a noticeable decrease of EQE, sometimes to less than 5%. This happens due to the different electron and hole mobility in the EML, and the device becomes electrically unbalanced. Thus, instead of the high efficiency of exciton creation, the efficiency of emission in the EML becomes low. Moreover, a noticeable roll-off occurs with a strong decrease of the EQE as the brightness increases, due to the high concentration of excitons at a high applied voltage and long excited lifetimes24,30,31. Overcoming such issues requires a strong capability to manipulate electrical properties of the emissive layer. For a simple OLED architecture using solution-deposited methods, electrical properties of the EML can be tuned by the solution preparation and deposition parameters32.
Solution deposition methods for organic-based devices have been previously used31. OLED fabrication, compared to the thermal evaporation process, is of great interest due to their simplified structure, low cost, and large area production. With high success in transition metal complexes OLEDs, the main goal is to increase the emitting area but keep device structure as simple as possible33. Methods such as roll-to-roll (R2R)34,35,36, inkjet printing37,38,39 and slot-die40 have been successfully applied in multilayer fabrication of OLEDs, which is a possible industrial approach.
Despite solution deposition methods for organic layers serving as a good choice for device architecture simplification, not all desired materials can be easily deposited. Two types of materials are used: small molecules and polymers. In solution deposition methods, small molecules have some drawbacks, such as poor thin film uniformity, crystallization, and stability. Thus, polymers are mostly used due to the ability to form uniform thin films with low surface roughness and on large, flexible substrates. Moreover, the materials should have good solubility in the appropriate solvent (mainly organic ones like chloroform, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, etc.), water, or alcohol derivatives.
Besides the problem of solubility, it is necessary to guarantee that a solvent used in one layer should not act as one for the preceding layer. This allows a multi-layer structure deposited by the wet process; however, there are limitations41. The most typical device structure uses some solution-deposited layers (i.e., the emissive one) and one thermally evaporated layer (ETL). Additionally, thin film homogeneity and morphology strongly depend on the deposition methods and parameters. Electrical charge transport through these layers is completely governed by such morphology. Nevertheless, a tradeoff between the desired final device and compatibilities of the fabrication process should be judiciously established. Adjusting the deposition parameters is a key to success, despite being time-consuming work. For instance, the spin coating is not a straightforward technique. Although it seems simple, there are several aspects of thin film formation from a solution on top of a spinning substrate that require attention.
Besides film thickness optimization, manipulation of spinning velocity, and time (thickness is an exponential decay of both parameters), the experimenter’s actions must also be adjusted to obtain good results. Correct parameters also depend on the solution viscosity, deposition area, and wettability/contact angle of solution on the substrate. There are no unique sets of parameters. Only basic assumptions with specific adjustments to the solution/substrate yield the desired results. Moreover, the electrical properties that depend on the layer molecular conformation and morphology can be optimized for desired results, following the protocol described here. Once completed, the process is simple and feasible.
Nevertheless, decreasing the device structure complexity leads to a maximum EQE decrease; although, a compromise can be achieved in terms of efficiency vs. brightness. As such a compromise allows practical applications, the surplus of a simple, large area compatible, and low cost process can become a reality. This article describes these requirements and how to develop a recipe to handle the required issues.
The protocol focuses on a green TADF emitter 2PXZ-OXD [2,5-bis(4-(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole]42 as a guest in a host matrix composed by PVK [poly(N-vinylcarbazole)] and OXD-7 [1,3-Bis[2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazo-5-yl]benzene], which corresponds to the EML. An electron transport layer (ETL) of TmPyPb [1,3,5-Tri(m-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)benzene] is used. Both the anode’s and cathode’s work functions are optimized. The anode is comprised of ITO (indium tin oxide) with a high conductive polymer PEDOT:PSS [poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate)], and the cathode is comprised of a double layer of aluminum and LiF (lithium fluoride).
Finally, both the PEDOT:PSS and EML (PVK: OXD-7: 2PXZ-OXD) are deposited by spin coating, whereas TmPyPb, LiF, and Al are thermally evaporated. Considering the conductive metal-like nature of PEDOT:PSS, the device is a typical “two organic layer” in the simplest structure possible. In the EML, TADF guest (10% wt.) is dispersed in the host (90% wt.) composed of PVK0.6+OXD-70.4.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocol
CAUTION: The following steps involve the use of different solvents and organic materials, so proper care must be taken when handling. Use the fume hood and protective equipment such as lab glasses, face masks, gloves, and lab coats. Weighing of the materials should be done precisely using a high precision scale machine. To ensure cleanliness of the substrates, solution deposition of thin films, and evaporation, it is recommended that all the procedures be performed in a controlled environment or glovebox. Before the use of a spin-coater, micropipettes, thermal evaporators, organic materials, and solvents, all safety data sheets must be consulted.
1. Preparation of host-guest solution
- In two small vials (volume between 4–6 mL, cleaned with isopropanol and dried with nitrogen), weigh host matrix composed of 12 mg of PVK and 8 mg of OXD-7. Start with weighing the OXD-7. Compensate any deviation in the weight using PVK to achieve a final ratio of 6:4 (PVK:OXD-7). In the second vial, weigh 10 mg of 2PXZ-OXD TADF emitter.
- Add 2 mL of chlorobenzene to the vial with host matrix, and 1 mL to the vial with TADF material. If the weights of any vials are not exactly the values described above, adjust the chlorobenzene volume in both vials to achieve a solution with final concentration of 10 mg/mL.
- Leave the solutions stirring with small, cleaned magnetic stir bars for at least 3 h to ensure complete dissolution of the materials. Ensure that the vials are safely covered with respective caps and tightly sealed with organic chemical safe film to avoid any evaporation of solvents.
2. Substrate cleaning
NOTE: To handle the substrates, use a pair of tweezers, touching only in a corner (never touch the middle of the substrates). The substrates used here have six pre-patterned ITO pixels (Figure 1A).
- Obtain pre-patterned ITO substrates. Clean substrates in an ultrasonic bath containing 1% v/v Hellmanex solution in water, acetone, and 2-propanol (IPA), sequentially, for 15 min in each bath. Perform the first bath at approximately 95 °C and the remaining at room temperature (RT). Finally, dry the substrates using nitrogen flux to remove any cleaning solvent residue.
- Before fabrication, expose the substrates (ITO film facing upwards) to UV ozone treatment for 5 min. Carefully extract the gases and ensure that the ITO patterned face is exposed to the UV. Here, use an ozone cleaner (100 W, 40 kHz). Set the emission wavelength of the UV lamps to 185 nm and 254 nm with a high intensity, low pressure, mercury vapor discharge lamp.
3. Spin coating
This is the most important step of this protocol. To ensure uniformity, homogeneity, and absence of pinholes in the thin films, all solvents must be filtered with their respective filter papers. Complete removal of excess solvents from substrates should be ensured to avoid any short in the final device. For the substrates used here, the removal of excess materials from the patterned ITO and cathode is also important to fix the final pixel, and it should be performed with high precision, without disturbing the active area of the pixel. The steps described below should be followed for spin coating of the thin films. The final thickness of the thin film will vary if using a spin coater different than the one used here.
- Prepare the spin coater equipment.
NOTE: Before using the spin coater, it is necessary to make a curve calibration with the deposition parameters and final thickness obtained for the films. This should be done for each solution employed. The procedure involves making several depositions for the same solution but with different parameters, and the final thickness is measured with a profilometer. Figure 2 shows a typical calibration curve for an active layer. - Deposit PEDOT:PSS as the first layer on top of ITO. Filter the PEDOT:PSS with a 0.45 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) filter. Fill a micropipet with 100 μL of PEDOT:PSS.
- Carefully place the substrate on the spin coater chuck and activate the vacuum system to fix the substrate (Figure 1B,C). Rotate the ITO face-up and adjust to center the substrate area as much as possible. Set the parameters for the spin coating to 5,000 rpm for 30 s. Set an initial step using the spin coater of ~2–3 s at low rotation (200–500 rpm). A thickness of 30 nm is expected.
- Keeping the micropipet perpendicular to the substrate (Figure 1D), drop the solution (100 μL) in the middle of the substrate (Figure 1D) and start the spin coater (Figure 1E).
NOTE: Do not drop the solution too quickly or slowly to avoid the risk of nonhomogeneous spread of the solution (depending on the viscosity, the contact angle can be nonideal). Usually, dropping the solution in ~1 s is ideal. Do not touch the substrate with the micropipette, and try to synchronize between starting the spin coater and dropping the solution. If a two-step deposition setting (as explained in step 3.3) is not available, consider a static deposition: drop the solution first, then start the spin coater immediately after. Dropping of the solution should be done carefully. All solutions should be dropped at the center of the rotation axis and form a uniform spot to avoid nonuniformities during the process. Be advised that, although these rules are ideal for good film deposition, the spin coating technique is hard to optimize (i.e., requires several preoptimization steps). Furthermore, it depends on solution viscosity, deposition desired area, how the solution is dropped on the substrate, and the start of spinning. An example of good film formation at a microscopic scale can be seen in Figure 3 as an AFM image. - Complete the spin coater step (Figure 1F). Turn off the vacuum, and with a tweezer, remove the substrate. With the help of small cotton bud soaked in water (i.e., the PEDOT:PSS solvent; Figure 1G), remove the excess deposited film around the cathode and corner areas from the substrate, keeping the central pixeled area untouched.
- Keep the substrate in an oven or on a hot plate at 120 °C for 15 min to remove the PEDOT:PSS solvent (water). Remove from the oven or hot plate, move to a glovebox, and leave to cool down to RT (Figure 1H).
- Prepare the solution for the EML. In a new clean vial (see step 1.1), using a micropipette, prepare a new solution composed of 1.8 mL of host solution and 0.2 mL of TADF solution. Before using the solution, filter it with a 0.1 μm PTFE filter.
- Leave the new solution stirring for 15 min at RT.
- Following steps 3.3–3.5, make the deposition of this second solution in a spin coater in the glovebox. Spin at 2,000 rpm for 60 s. The expected film thickness should be 50 nm. To remove any excess of the second film, use cotton buds soaked in chlorobenzene.
- Leave the substrates on a hot plate inside the glove box at 70 °C for 30 min to completely remove the excess chlorobenzene.
- Remove the substrates from the hot plate and leave to cool to RT.
- For additional precautions, consider some temperature/time (indirectly, evaporation rate) tests for different solvents. The morphology of the final film is strongly dependent on these parameters. A simple AFM test can be useful to confirm that the solvent evaporation rate is adequate. The final structure of the deposited thin films should be more or less similar to the scheme in Figure 1I.
4. Evaporation of materials
NOTE: For better evaporation, the minimum vacuum required is typically a pressure lower than 5 x 10-5 mbar. For all organic materials, the evaporation rate should be kept under 2 Å/s to reduce the roughness and uniformity of the layers. For LiF, the evaporation rate should be less than 0.2 Å/s. Failure to adhere to this may result in nonuniform emissions. If not already done, program the piezoelectric sensor system (which measures the deposition thickness and evaporation rate) with the required parameters, such as 1) material density, 2) Z-factor: an acoustic coupling of material to the sensor, and 3) tooling factor: geometric calibration of the evaporation crucible vs. sample holder. Before using the evaporator, refer to the equipment specifications on how to perform such calibrations, and consult the materials datasheet for the density and Z-factor values for a specific material. Once programmed, and without any evaporation chamber geometry change (tooling factor), the data can be stored for future use with the same materials.
- Insert the substrates (films face-down and after step 3.11 is completed) into the sample holder with the desired evaporation mask (Figure 4A).
- Include the necessary crucibles (the geometry depends on the specific evaporator system) and fill each with the necessary materials (LiF, TmPyPb, and Al). A detailed explanation of the thermal evaporation process in OLEDs development can be found in the literature43 and is discussed further in this report.
- Place the substrate holder with samples in the evaporator sample holder (Figure 4B). Close the chamber and pump down the evaporator chamber. Follow the respective instructions for the evaporator system.
- Evaporate a film of TmPyPb with a thickness of 40 nm. Evaporate 2 nm of LiF and 100 nm of Al, sequentially. For the evaporation, follow the published procedure43.
NOTE: The final structure is represented in Figure 4C. In the current work, devices are not encapsulated. For long-term experiments, encapsulation should be performed, which is not the focus here.
5. Device characterization
NOTE: To characterize the final device, use a highly sensitive voltage meter, luminance meter, and spectrometer. If there is an integrating sphere, use it. Otherwise, place the luminance meter perpendicularly to the OLED surface emission at a distance indicated by the manufacturer and dependent on the focus lens. If not using an integrating sphere, it can be assumed that the OLED device emission follows a Lambertian profile for the efficiency calculation. Here, the plotted brightness does not correspond to the measured under an integrating sphere (thus, it will be at least π times less).
- Insert the fabricated OLED device in the testing holder and make the electrical contacts for the desired pixel. Measure the current (I), applied voltage (V), and brightness (L). Complete details about the experimental setup have been explained previously43.
- With a spectrometer, measure the electroluminescence spectra (EL) at different applied voltages in a range corresponding to the dynamic range of the OLED operation44. Take at least three to four spectra. Here, applied voltages of 5 V, 10 V, and 15 V are used.
- Using the necessary software, calculate the current density (J), current efficiency (μc candela/Ampere), power efficiency (ηp, lumen/Watt), and external efficiency (EQE). With the electroluminescence spectra, determine the CIE color coordinates. Suitable information on how to calculate all these figures of merit have been described previously44.
- Plot the indicated data. Perform a critical analysis of the results in terms of efficiencies and brightness. See the electroluminescence spectra and attempt to establish a model to understand the results.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Results
Figure 5 shows the main results for the fabricated device. The turn-on voltage was extremely low (~3 V), which is an interesting result for a two organic layer device. The maximum brightness was around 8,000 cd/m2 without using an integrating sphere. The maximum values for ηc, ηp, and EQE were around 16 cd/A, 10 lm/W, and 8%, respectively. Although the results are not the best figures of merits for this TADF emitter, they were the best found in such...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
The protocol used here to fabricate an efficient OLED in a simple device structure is relatively simple. The electrical mobility is not only modulated by the material composition of a device layer but also critically depends on film morphology. Preparation of the solutions and a suitable choice of solvent and concentration are important. No material aggregation can occur, implying complete solubility at the nanometric scale. It is also important to observe the viscosity of the solution. A high viscosity leads to a high c...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the “EXCILIGHT” Project from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 674990. This work was also developed within the scope of the project i3N, UIDB/50025/2020 & UIDP/50025/2020, financed by national funds through the FCT/MEC.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2PXZ-OXD (2,5-bis(4-(10H-phenoxazin-10-yl)phenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole) | Lumtec ltd | 1447998-13-1 | |
| Aluminum (99.999%) | Alfa Aesar | 7429-90-5 | |
| Acetone (99.9%) | Sigma Aldrich | 67-64-1 | |
| Hellmanex | Ossila | 7778-53-2 | |
| Isopropyl alcohol | Sigma Aldrich | 67-63-0 | |
| ITO patterned substrates | Ossila | 65997-17-3 | |
| Lithium Fluoride (99.99%) | Sigma Aldrich | 7789-24-4 | |
| OXD-7 (1,3-Bis[2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazo-5-yl]benzene) | Ossila | 138372-67-5 | |
| PEDOT: PSS (Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate) | Ossila | 155090-83-8 | |
| PVK (Polyvinlycarbazole) (average Mn 25,000-50,000) | Sigma Aldrich | 25067-59-8 | |
| TmPyPb (1,3,5-Tri(m-pyridin-3-ylphenyl)benzene) | Ossila | 138372-67-5 |
References
- Tang, C. W., VanSlyke, S. A. Organic electroluminescent diodes. Applied Physics Letters. 51 (12), 913-915 (1987).
- Pereira, D. D. S., Monkman, A. P. Methods of Analysis of Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Display and Imaging. 2, 323-337 (2017).
- Kumar, M., Ribeiro, M., Pereira, L. New Generation of High Efficient OLED Using Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Materials. Light-Emitting Diode-An Outlook On the Empirical Features and Its Recent Technological Advancements. , IntechOpen. (2018).
- Baldo, M. A., et al. Highly efficient phosphorescent emission from organic electroluminescent devices. Nature. 395 (6698), 151(1998).
- Uoyama, H., Goushi, K., Shizu, K., Nomura, H., Adachi, C. Highly efficient organic light-emitting diodes from delayed fluorescence. Nature. 492 (7428), 234(2012).
- Baldo, M., Lamansky, S., Burrows, P., Thompson, M., Forrest, S. Very high-efficiency green organic light-emitting devices based on electrophosphorescence. Applied Physics Letters. 75 (1), 4-6 (1999).
- Adachi, C., Baldo, M. A., Thompson, M. E., Forrest, S. R. Nearly 100% internal phosphorescence efficiency in an organic light-emitting device. Journal of Applied Physics. 90 (10), 5048-5051 (2001).
- Tsuzuki, T., Nakayama, Y., Nakamura, J., Iwata, T., Tokito, S. Efficient organic light-emitting devices using an iridium complex as a phosphorescent host and a platinum complex as a red phosphorescent guest. Applied Physics Letters. 88 (24), 243511(2006).
- Kwong, R. C., et al. Efficient, saturated red organic light emitting devices based on phosphorescent platinum (II) porphyrins. Chemistry of Materials. 11 (12), 3709-3713 (1999).
- Kalinowski, J., Fattori, V., Cocchi, M., Williams, J. G. Light-emitting devices based on organometallic platinum complexes as emitters. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 255 (21-22), 2401-2425 (2011).
- Tanaka, D., et al. Ultra high efficiency green organic light-emitting devices. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. 46 (1), 10(2006).
- Sun, Y., et al. Management of singlet and triplet excitons for efficient white organic light-emitting devices. Nature. 440 (7086), 908(2006).
- Reineke, S., et al. White organic light-emitting diodes with fluorescent tube efficiency. Nature. 459 (7244), 234(2009).
- Helander, M., et al. Chlorinated indium tin oxide electrodes with high work function for organic device compatibility. Science. 332 (6032), 944-947 (2011).
- Tao, Y., et al. Multifunctional Triphenylamine/Oxadiazole Hybrid as Host and Exciton-Blocking Material: High Efficiency Green Phosphorescent OLEDs Using Easily Available and Common Materials. Advanced Functional Materials. 20 (17), 2923-2929 (2010).
- Lee, C. W., Lee, J. Y. Above 30% external quantum efficiency in blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes using pyrido [2, 3-b] indole derivatives as host materials. Advanced Materials. 25 (38), 5450-5454 (2013).
- Endo, A., et al. Efficient up-conversion of triplet excitons into a singlet state and its application for organic light emitting diodes. Applied Physics Letters. 98 (8), 42(2011).
- Endo, A., et al. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence from Sn4+–porphyrin complexes and their application to organic light emitting diodes-A novel mechanism for electroluminescence. Advanced Materials. 21 (47), 4802-4806 (2009).
- Baleizão, C., Berberan-Santos, M. N. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence as a cycling process between excited singlet and triplet states: Application to the fullerenes. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 126 (20), 204510(2007).
- Dias, F. B., et al. Triplet harvesting with 100% efficiency by way of thermally activated delayed fluorescence in charge transfer OLED emitters. Advanced Materials. 25 (27), 3707-3714 (2013).
- Dias, F. B., Penfold, T. J., Monkman, A. P. Photophysics of thermally activated delayed fluorescence molecules. Methods and Applications in Fluorescence. 5 (1), 012001(2015).
- Yersin, H. Highly efficient OLEDs: Materials based on thermally activated delayed fluorescence. , Wiley-VCH. (2018).
- dos Santos, P. L., Ward, J. S., Bryce, M. R., Monkman, A. P. Using guest-host interactions to optimize the efficiency of TADF Oleds. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 7 (17), 3341-3346 (2016).
- Kumar, M., Pereira, L. Effect of the Host on Deep-Blue Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Based on a TADF Emitter for Roll-Off Suppressing. Nanomaterials. 9 (9), 1307(2019).
- Méhes, G., Goushi, K., Potscavage, W. J., Adachi, C. Influence of host matrix on thermally-activated delayed fluorescence: Effects on emission lifetime, photoluminescence quantum yield, and device performance. Organic Electronics. 15 (9), 2027-2037 (2014).
- Yang, Z., et al. Recent advances in organic thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials. Chemical Society Reviews. 46 (3), 915(2017).
- Wong, M. Y., Zysman-Colman, E. Purely organic thermally activated delayed fluorescence materials for organic light-emitting diodes. Advanced Materials. 29 (22), 1605444(2017).
- Tsai, K. W., Hung, M. K., Mao, Y. H., Chen, S. A. Solution-Processed Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent OLED with High EQE as 31% Using High Triplet Energy Crosslinkable Hole Transport Materials. Advanced Functional Materials. , 1901025(2019).
- Lin, T. A., et al. Sky-blue organic light emitting diode with 37% external quantum efficiency using thermally activated delayed fluorescence from spiroacridine-triazine hybrid. Advanced Materials. 28 (32), 6976-6983 (2016).
- Cho, Y. J., Yook, K. S., Lee, J. Y. High efficiency in a solution-processed thermally activated delayed-fluorescence device using a delayed-fluorescence emitting material with improved solubility. Advanced Materials. 26 (38), 6642-6646 (2014).
- Huang, T., Jiang, W., Duan, L. Recent progress in solution processable TADF materials for organic light-emitting diodes. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. 6 (21), 5577-5596 (2018).
- Kumar, M., Pereira, L. Towards Highly Efficient TADF Yellow-Red OLEDs Fabricated by Solution Deposition Methods: Critical Influence of the Active Layer Morphology. Nanomaterials. 10 (1), 101(2020).
- Cai, M., et al. High-efficiency solution-processed small molecule electrophosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes. Advanced Materials. 23 (31), 3590-3596 (2011).
- Amruth, C., Szymański, M. Z., Łuszczyńska, B., Ulański, J. Inkjet printing of super Yellow: Ink Formulation, Film optimization, oLeDs Fabrication, and transient electroluminescence. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 1-10 (2019).
- Abbel, R., et al. Toward high volume solution based roll-to-roll processing of OLEDs. Journal of Materials Research. 32 (12), 2219-2229 (2017).
- Hast, J., et al. 18.1: Invited Paper: Roll-to-Roll Manufacturing of Printed OLEDs, SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. Wiley Online Library. , 192-195 (2013).
- Chang, S. C., et al. Multicolor organic light-emitting diodes processed by hybrid inkjet printing. Advanced Materials. 11 (9), 734-737 (1999).
- Singh, M., Haverinen, H. M., Dhagat, P., Jabbour, G. E. Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Advanced Materials. 22 (6), 673-685 (2010).
- Villani, F., et al. Inkjet printed polymer layer on flexible substrate for OLED applications. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 113 (30), 13398-13402 (2009).
- Choi, K. -J., Lee, J. -Y., Shin, D. -K., Park, J. Investigation on slot-die coating of hybrid material structure for OLED lightings. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 95, 119-128 (2016).
- Geffroy, B., Le Roy, P., Prat, C. Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) technology: materials, devices and display technologies. Polymer International. 55 (6), 572-582 (2006).
- Lee, J., et al. Oxadiazole-and triazole-based highly-efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters for organic light-emitting diodes. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. 1 (30), 4599-4604 (2013).
- Monkman, A., Data, P. Production and Characterization of Vacuum Deposited Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Journal of Visualized Experiments. (141), (2018).
- Pereira, L. F. Organic light emitting diodes: The use of rare earth and transition metals. , Pan Stanford. (2012).
- Kumar, M., Pereira, L. Mixed-Host Systems with a Simple Device Structure for Efficient Solution-Processed Organic Light-Emitting Diodes of a Red-Orange TADF Emitter. ACS Omega. 5 (5), 2196-2204 (2020).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved