A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
Neutron Spin Echo Spectroscopy as a Unique Probe for Lipid Membrane Dynamics and Membrane-Protein Interactions
In This Article
Erratum Notice
Summary
This paper describes the protocols for sample preparation, data reduction, and data analysis in neutron spin echo (NSE) studies of lipid membranes. Judicious deuterium labeling of lipids enables access to different membrane dynamics on mesoscopic length and time scales, over which vital biological processes occur.
Abstract
Lipid bilayers form the main matrix of cell membranes and are the primary platform for nutrient exchange, protein-membrane interactions, and viral budding, among other vital cellular processes. For efficient biological activity, cell membranes should be rigid enough to maintain the integrity of the cell and its compartments yet fluid enough to allow membrane components, such as proteins and functional domains, to diffuse and interact. This delicate balance of elastic and fluid membrane properties, and their impact on biological function, necessitate a better understanding of collective membrane dynamics over mesoscopic length and time scales of key biological processes, e.g., membrane deformations and protein binding events. Among the techniques that can effectively probe this dynamic range is neutron spin echo (NSE) spectroscopy. Combined with deuterium labeling, NSE can be used to directly access bending and thickness fluctuations as well as mesoscopic dynamics of select membrane features. This paper provides a brief description of the NSE technique and outlines the procedures for performing NSE experiments on liposomal membranes, including details of sample preparation and deuteration schemes, along with instructions for data collection and reduction. The paper also introduces data analysis methods used to extract key membrane parameters, such as the bending rigidity modulus, area compressibility modulus, and in-plane viscosity. To illustrate the biological importance of NSE studies, select examples of membrane phenomena probed by NSE are discussed, namely, the effect of additives on membrane bending rigidity, the impact of domain formation on membrane fluctuations, and the dynamic signature of membrane-protein interactions.
Introduction
The understanding of cell membranes and their function has remarkably evolved over the last few decades. The former view of cell membranes as passive lipid bilayers that define cell boundaries and house membrane proteins1 has gradually transformed into a dynamic model in which lipid bilayers play an important role in regulating vital biological processes, including cellular signaling, molecular exchange, and protein function — to name a few2,3,4,5,6. This realization that cell membranes are highly dynamic, constantly undergoing remodeling and molecular redistribution, has urged scientific explorations beyond equilibrium structures of membranes7,8,9. Accordingly, multiple approaches have been developed to study the various dynamic modes in biological and bioinspired lipid membranes. To date, the majority of these studies have primarily focused on diffusive molecular motions10,11,12,13 and macroscopic shape fluctuations14,15,16, leaving a significant gap in understanding intermediate membrane dynamics, i.e., collective fluctuations of lipid assemblies consisting of few 10-100s of lipid molecules. These dynamics occur over length scales of few tens to few 100 Å and over time scales of sub-ns to few hundred ns (see Figure 1), referred to here as mesoscopic scales. It is indeed on these scales that key biological activity takes place at the membrane level17. This includes viral budding18, channel gating19, and membrane-protein interactions20. It is also important to point out that the energy landscape of membrane proteins21,22 shows that conformational changes in proteins — necessary for their regulatory role — happen over the ns time scales23 of collective membrane fluctuations, further emphasizing the importance of mesoscopic dynamics in the biological function of cell membranes and their bioinspired analogs20. This paper focuses on the two primary mesoscopic dynamic modes in lipid membranes, namely, bending fluctuations and thickness fluctuations.
The main challenge in directly probing these fluctuation modes is the difficulty in simultaneously accessing their spatial and temporal scales using standard spectroscopy methods. The other challenge is that direct contact techniques could impact the same fluctuations they are meant to measure16. This is further exacerbated by the compositional and structural complexity of biological membranes24,25, which results in non-homogeneous membrane features, including lipid domain formation26,27,28,29,30 and membrane asymmetry31,32,33— demanding selective probes to understand the dynamics of different membrane features. Fortunately, these challenges can be overcome with non-invasive neutron spectroscopy methods, such as neutron spin echo (NSE), which inherently access the required length and time scales, and further enable studies of selective membrane features without changing their physicochemical environment34. Indeed, over the last few years NSE spectroscopy has evolved into a unique and powerful probe of collective membrane dynamics35. Results from NSE studies on lipid membranes have produced new insights into mechanical36,37 and viscoelastic38,39 properties of lipid membranes and have shed new light on their potential role in biological function40,41.
The NSE spectroscopy technique is based on an interferometric instrument design, first proposed by Mezei42, using a series of spin-flippers and magnetic coils to control the precession of the neutron spin as neutrons traverse the instrument. The design rests on magnetic mirroring of the magnetic field elements with respect to the sample position (Figure 1A). This implies that in the absence of energy exchange between the neutron and the sample, the neutron performs the same number of spin precessions, in opposite directions, in the first and second half of the instrument (notice the π-flipper between the two precession coils). As a result, the final spin state of the neutron remains unchanged relative to the initial state - a phenomenon referred to as spin-echo (see transparent neutron in Figure 1A). However, when the neutron energetically interacts with the sample, the energy exchange modifies the number of spin precessions in the second half of the instrument, leading to a different final spin state (see Figure 1A). This is experimentally detected as a loss in polarization, as will be shown later in this paper. For more details on the NSE technique, the reader is referred to dedicated technical papers42,43,44,45.
Here, a simplified description is presented to provide a rough estimate of the length and time scales accessible with NSE. The length scales are determined by the range of achievable wavevector transfers, Q = 4π sin θ/λ, where 2θ is the scattering angle and λ is the neutron wavelength. One can see that Q is set by the wavelength range and the extent of rotation of the second arm of the spectrometer (see Figure 1A). A typical Q-range on NSE spectrometers is ~0.02-2 Å-1 46,47, and up to 0.01-4 Å-1 with recent upgrades48,49, corresponding to spatial scales of ~1-600 Å. On the other hand, the accessible time scale is calculated from the total precession angle (or phase) acquired by the neutron within the magnetic precession coils, and is found to be50: 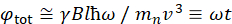 . In this expression, t is the Fourier time defined as
. In this expression, t is the Fourier time defined as 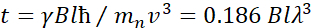 , where
, where 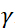 is the neutron gyromagnetic ratio,
is the neutron gyromagnetic ratio,  is the coil length, and
is the coil length, and 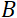 is the strength of the coil's magnetic field. It is worth pointing out that the Fourier time is a quantity that is strictly dependent on the instrument geometry, magnetic field strength, and neutron wavelength. For instance, using neutrons of wavelength
is the strength of the coil's magnetic field. It is worth pointing out that the Fourier time is a quantity that is strictly dependent on the instrument geometry, magnetic field strength, and neutron wavelength. For instance, using neutrons of wavelength 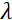 = 8 Å and instrument settings of
= 8 Å and instrument settings of  = 1.2 m and
= 1.2 m and 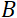 = 0.4 T, the Fourier time is calculated to be t ~ 50 ns. Experimentally, the Fourier time is tuned by changing the current in the precession coils (i.e., magnetic field strength) or using different neutron wavelengths, resulting in typical NSE time scales of ~ 1 ps to 100 ns. However, recent upgrades in NSE spectrometers have enabled access to longer Fourier times, up to ~400 ns on the J-NSE-Phoenix spectrometer at the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum51 and the SNS-NSE spectrometer at Oak Ridge National Lab48, and up to ~1,000 ns at the IN15 NSE spectrometer at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL)49.
= 0.4 T, the Fourier time is calculated to be t ~ 50 ns. Experimentally, the Fourier time is tuned by changing the current in the precession coils (i.e., magnetic field strength) or using different neutron wavelengths, resulting in typical NSE time scales of ~ 1 ps to 100 ns. However, recent upgrades in NSE spectrometers have enabled access to longer Fourier times, up to ~400 ns on the J-NSE-Phoenix spectrometer at the Heinz Maier-Leibnitz Zentrum51 and the SNS-NSE spectrometer at Oak Ridge National Lab48, and up to ~1,000 ns at the IN15 NSE spectrometer at the Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL)49.
Besides direct access to the length and time scale of membrane dynamics, NSE has the inherent capabilities of neutron isotope sensitivity52. Specifically, the ability of neutrons to interact differently with the isotopes of hydrogen, the most abundant element in biological systems, results in a different neutron scattering length density,34 or NSLD (the equivalent of the optical index of refraction50), when protium is substituted by deuterium. This enables an approach known as contrast variation, which is commonly used to highlight specific membrane features or conceal others — the latter scenario is referred to as contrast matching. A frequent application of contrast variation/matching is the substitution of water (NSLD = -0.56 × 10-6 Å-2) by heavy water or D2O (NSLD = 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) to amplify the neutron signal from protiated lipid membranes (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2). This approach is highly effective in studies of membrane structure because the penetration of D2O into the headgroup region of the membrane allows accurate determination of the membrane thicknesses (see Figure 2A, left panel) and of the location of different lipid subgroups when more sophisticated models are applied53,54. This paper highlights some examples on the use of contrast variation for studies of collective dynamics in biomimetic membranes and select membrane features.
Here, the effectiveness of NSE in providing unique insights into dynamical and functional membrane properties is illustrated through tangible examples of NSE studies on model and biologically relevant lipid membrane systems with emphasis on mesoscale dynamics in free-standing membranes, in the form of liposomal suspensions. For NSE measurements of in-plane membrane dynamics, the reader is referred to dedicated publications on grazing-incidence neutron spin-echo spectroscopy (GINSES)55,56 and other studies of aligned multilamellar membrane stacks57,58,59,60.
For simplicity, this paper highlights three different schemes of membrane deuteration illustrated on a well-studied domain-forming, or phase separating, lipid bilayer system of 1,2-dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DMPC) and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DSPC) mixtures61,62. The two lipids are characterized by a mismatch in their hydrocarbon chain length (14 carbons/tail in DMPC vs 18 carbons/tail in DSPC) and their gel-fluid transition temperature (Tm, DMPC = 23 °C vs Tm, DSPC = 55 °C). This results in lateral phase-separation in DMPC:DSPC membranes at temperatures between the upper and lower transition temperatures of the mixture63. The deuteration schemes considered here are chosen to demonstrate the different dynamic modes accessible in NSE measurements on liposomal membranes, namely, bending fluctuations, thickness fluctuations, and selective bending/thickness fluctuations of lateral domains. All lipid compositions are reported for DMPC:DSPC bilayers prepared at a mole fraction of 70:30, using commercially available protiated and perdeuterated variants of DMPC and DSPC. All sample preparation steps are based on 4 mL of liposomal suspension, in D2O, with a lipid concentration of 50 mg/mL, for a total lipid mass of Mtot = 200 mg per sample.
Protocol
1. Deuteration scheme required for the experiment
- For bending fluctuation measurements, make fully protiated liposomes in D2O (D 99.9%) or D2O-buffer (e.g., phosphate buffer prepared with D2O instead of H2O). Use fully protiated DMPC (C36H72NO8P) and DSPC (C44H88NO8P) with
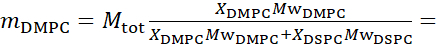 133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel).
133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel). - To measure the bending dynamics of select lateral membrane features, e.g., matrix dynamics in phase-separating DMPC:DSPC membranes, use protiated DMPC (C36H72NO8P) and deuterated, DSPC-d83 (C44H5NO8PD83, Mw 873.7 g/mol), such that mDMPC = 128.8 mg and mDSPC-d83 = 71.2 mg. This deuteration scheme minimizes the scattering from the undesired DSPC-rich domains, enabling selective measurements of bending fluctuations from the DMPC-rich matrix (see Figure 2B middle).
NOTE: To find the optimal lipid deuteration required for a specific contrast matching scheme, utilize available web-based scattering length density (SLD) calculators, such as the one developed by the NIST Center for Neutron Research64. These web-based interfaces are equipped with user-friendly tools for easy calculation of the SLD of lipids with various degrees of deuteration, as well as that of lipid mixtures. - For NSE measurements of average membrane thickness fluctuations (with no lateral contrast), use tail-deuterated variants of the constituent lipids, i.e., DMPC-d54 (C36H18NO8PD54, 732.3 g/mol) and DSPC-d70 (C44H18NO8PD70, 860.1 g/mol)35,38, such that mDMPC-d54 = 133.0 mg and mDSPC-d70 = 67.0 mg. This contrast scheme (Figure 2A, right panel) amplifies the scattering signal from the lipid headgroups (NSLD ~ 4.5 × 10-6 Å-2) by contrast-matching the tail-group (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) to the deuterated buffer enabling the detection of fluctuations in membrane thickness.
- For thickness fluctuation studies of select membrane compartments, e.g., DMPC-rich matrix, use the same strategy described in step 1.2 by substituting protiated DMPC lipids with their tail-deuterated analogs, i.e., DMPC-d54, such that the DSPC-rich domains are contrast-matched to the deuterated buffer and the primary scattering signal is from the headgroup region of the tail-deuterated DMPC-rich matrix.
2. Preparation of lipid suspension for extrusion
- Calculate the mass of each constituent in the sample, depending on sample composition. As a rule of thumb, for samples with multiple molecular components, the mass of a component is given by its molar mass, Mwi, weighted by its mole fraction, Xi, and normalized over all components such that:
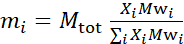 where Mtot is the total mass, set here to 200 mg. See the example above for DMPC-DSPC lipid bilayers with different deuteration schemes.
where Mtot is the total mass, set here to 200 mg. See the example above for DMPC-DSPC lipid bilayers with different deuteration schemes. - Using a digital semi-microbalance, weigh the calculated masses of lipids (and other sample constituents, e.g., proteins, nanoparticles, etc.) and add them to a vial or round-bottom flask – remember to weigh the vial or flask beforehand. Add 1 mL of solvent to dissolve the weighed components by manually mixing inside a hood. For pure lipid samples, use chloroform or ethanol. For samples with additional, non-lipid components (e.g., nanoparticles), choose a common solvent that disperses all components.
- For small lipid amounts (<10 mg), prepare a stock solution and pipette the required volume into the mixture.
NOTE: Do not add excessive amounts of solvent as it will significantly slow down the solvent drying step described below.
- For small lipid amounts (<10 mg), prepare a stock solution and pipette the required volume into the mixture.
- Dry the lipid solution, inside a hood, by gently streaming an inert gas (e.g., nitrogen, argon) in the vial while slowly rotating the vial at an angle. Keep the vials in tilted position to create a thin film of dried lipid on the vial walls, which will allow for even drying. Intermittently place the vial in a water bath at 35 °C to circumvent evaporation-mediated cooling, which will slow down the solvent evaporation.
- Place the vials overnight in a vacuum oven at ~35 °C to fully remove the residual solvent. For unsaturated lipids, purge vacuum with an inert gas to minimize oxidation.
- To ensure full solvent removal, weigh the vial after lipid drying and confirm that there is no excess mass beyond the measured amounts of materials. Do this by subtracting the mass of the vial from the measured mass after drying. If there is excess mass, dry the sample under vacuum for another 6 h. Repeat this process as needed.
- Hydrate the lipid film with 4 mL of D2O or D2O-buffer to obtain a lipid concentration of 50 mg/mL. For lipids with high transition temperatures, such as DMPC-DSPC mixtures, heat the buffer to above the transition temperature (60 °C) to ensure even mixing.
NOTE: Since NSE experiments require relatively large sample volumes (~4 mL), consider hydrating the sample using half of the required buffer, i.e., 2 mL, to minimize the number of extrusions per sample (see section 3). In this case, add the remaining half of the buffer post extrusion. Notice that the capacity of syringes used in extrusion is limited to 1 mL. Thus, hydrating with 4 mL of buffer would require four sets of extrusion. - Vortex-mix the hydrated lipid solution until the lipid film is fully dissolved and is no longer visible on the walls of the vial. At this stage, the hydrated lipids form multilamellar vesicles and micron sized multilamellar stacks and the suspension appears milky white.
- To facilitate the breaking of the lipid stacks and to reduce multilamellarity, perform five freeze/thaw cycles by placing the vial of hydrated lipid solution in a lab grade freezer (preferably -80 °C freezer) until fully frozen and then transferring the vial to a 35 °C water bath until the lipid solution is fully thawed. Vortex the thawed solution until homogenous. Repeat four more times.
NOTE: Alternatively, a dry ice bath can be prepared for rapid freezing by combining acetone and dry ice.
3. Extrusion of the hydrated lipid solution
- Assemble the extruder setup using a polycarbonate membrane between two membrane supports and adding two paper filters on each side to provide additional support. Use a polycarbonate membrane with a pore size that matches the target liposomal size (common pore sizes for NSE experiments are 50 nm and 100 nm – typically, 100 nm-diameter liposomes allow for less constrained membrane fluctuations, but smaller 50 nm liposomes could be used for curvature studies). Ensure that the polycarbonate membrane is fully stretched before completing the assembly and tightening the external extruder casing.
- Hydrate the polycarbonate membrane by passing ~0.3 mL of D2O or D2O-buffer a few times through the membrane assembly using airtight glass syringes. Utilize the same buffer used in sample preparation. Leave it for at least 10 min, then completely suck the buffer out before introducing the sample.
- Fill a 1 mL gas-tight syringe with the prepared lipid solution and insert into one end of the extruder apparatus. Then, insert an empty syringe into the opposite end. Once the syringes are connected to the extruder assembly, place it into the extruder block.
- If elevated temperatures are needed for extrusion, as in the case of saturated lipids with high transition temperatures (e.g., DSPC, Tm = 55 °C), preheat the extruder heating block above the lipid transition temperature (e.g., 60 °C), by placing the heating block on a hot plate or by using a circulation bath as shown in Figure 3A.
NOTE: This step is crucial to ensure homogeneous mixing of lipids and to avoid exerting extreme pressure during extrusion, which could rupture the polycarbonate membrane. For lipid samples with low transition temperatures (<25 °C), perform the extrusion at room temperature. - To extrude the lipid solution, attach the extruder set to a programmable syringe pump with an aluminum/steel frame as shown in Figure 3A. For temperature-controlled extrusions, add a custom-built extruder base with a fluid channel and attach to a circulating water bath.
- Program the syringe pump to perform 15-20 extrusion cycles following the manufacturer's manual. When extruded, the color of the lipid solution changes from milky white to transparent opal blue (Figure 3B,C), indicating a final liposomal size that is smaller than the wavelength of visible light, as expected. For the type of syringe pump shown in Figure 3A, follow the steps below.
- Start by adjusting the pump settings. Hold down the Rate button and enter the extrusion rate (50.99 mL/h), then press the Diameter button and enter the syringe diameter (4.606 mm). Use the up arrows under each digit on the screen to change that digit value.
- Place the extruder set with the sample syringe to the right (see Figure 3A). Press the Withdraw button until the withdraw light turns on. Press Start and wait for the sample to dispense into the left (empty) syringe.
- Hit the Stop button just before the sample (right) syringe is fully empty. Record the dispensed volume and use it to program the extrusion cycle. Hold down the Rate button until phase 1 (PH:01) appears on the screen. Press the Volume button to enter the dispensed volume recorded earlier. In this phase, make sure that the Withdraw light is off – this dispenses the sample in the right direction.
- Press the Rate button again and use the rightmost up arrow to access phase 2 (PH:02). Press Volume to enter the same value of the dispensed volume recorded earlier. In this phase, press the Withdraw button until the Withdraw light is on – this dispenses the sample to the left.
- To repeat this cycle, press the Rate button again and use the rightmost up arrow to access phase 3 (PH:03). Press the Volume button until LP:SE appears on the screen and set it to 20. This is the number of loops or repeats that the pump will perform. Finally, press the Rate button, access phase 4 (PH:04), and hit the Volume button to get to the Stop function. The pump is now set up for automated extrusion.
- Press Start to start the extrusion cycle.
- Empty the syringe containing the extruded lipid suspension in a clean vial and prepare for storage or measurements. For lipid samples with high melting temperature, store the sample above the fluid phase transition until measured. Otherwise, keep samples at room temperature.
- Do not freeze extruded samples as freezing will cause the vesicles to burst (the suspension will turn milky white again).
4. NSE measurements for the sample(s) and reduction of the collected data
- Prior to the NSE experiment, characterize the extruded liposomal sample from step 3.7 using available methods to ensure adequate sample quality. A list of potential charcaterization methods that can be used to assess the quality of liposomal suspensions for NSE experiments, e.g., size distribution, multilamellarity, lateral membrane structure, is included in the discussion section.
- Determine the Q-range and corresponding instrument settings required for the experiment. For bending rigidity measurements of lipid bilayers, use a Q-range of ~(0.04 - 0.2) Å-1. For studies of membrane thickness fluctuations, use a Q-range of ~(0.04 - 0.2) Å-1 corresponding to the membrane thickness35,66,67.
NOTE: Discuss the experimental setup with the instrument scientist before the start of the experiment. As mentioned earlier, SANS characterization of the sample is necessary, especially if prior information of the scattering signal is not available, as in selectively deuterated membranes. Alternatively, run static (also known as diffraction) measurements over a limited Q-range on the NSE instrument, with the caveat that such measurements take much longer compared to SANS. - Using a syringe or a transfer pipette, load the extruded liposomal suspension(s) in the designated sample cells available at NSE beamlines. Note that standard NSE sample cells come in thicknesses of 1, 2, 3, and 4 mm. Choose the cell thickness in such a way to optimize the scattering signal while keeping the incoherent background signal to a reasonable intensity.
NOTE: As a rule of thumb, use sample cells with 1 or 2 mm pathlength for protiated liposomes in deuterated buffer – thicker cells could result in multiple scattering effects that are difficult to correct for. For liposomes with higher levels of deuterations (e.g., tail contrast-matched liposomes or asymemetric liposomes with single protiated leaflets), consider using a thicker sample cell (e.g., 3 or 4 mm pathlength) to enhance the counting statistics if the sample is available in larger quantities – sometimes this can be cost prohibitive. - Prepare an identical sample cell for the buffer. Use the same buffer as in the liposomal suspension. Measurements on the buffer are necessary for intensity normalization and background (BKG) corrections.
- Place the sample cell(s) in the sample holder of the NSE spectrometer, program the measurement runs, and collect echo data. Consult with the instrument scientist about programming the measurements if a first-time NSE user.
- Perform two additional sets of measurements needed for the data reduction: Resolution (R) and transmission (T) measurements.
- Perform Resolution (R) measurement on an elastic scattering reference (e.g., carbon) — to be run under the same settings; i.e. same wavevector and Fourier times as the sample and buffer measurements.
- Perform transmission (T) measurements on the sample and buffer to calculate the intensity of the transmitted neutron beam (see step 4.9. below). The transmission is calculated as the the ratio of neutron counts from the sample or buffer divided by the neutron counts for an open beam (i.e., with an empty sample position).
- Use the dedicated data reduction software for the NSE spectrometer on which the measurements are performed to reduce the collected data.
NOTE: Different spectrometers might utilize different software or user interfaces. Below is an example of NSE data reduction using the Data Analysis and Visualization Environment (DAVE)68 software specifically written for the NSE spectrometer at the NIST Center for Neutron Research.- Open the DAVE software and select Reduce NSE Data from the data reduction menu. Several pop-up windows will appear.
- Upload the data files over different Q-values using the Open .echo Files from the file menu. These files correspond to the raw data files with the spin echo signals and have the extension .echo in the file name. Once the file upload is complete, the files will show under the available data sets.
- Right-click on the selected file and label it according to the measurement it corresponds to; i.e., Sample, Cell (for empty cell or buffer), or Resolution.
- Group the detector pixles in 2 x 2 to improve the signal-to-noise ratio using the Data Set tab. Apply the same binning to all files; i.e., Resolution, Cell, and Sample.
- Inspect the data over all pixel groups and mask those with poor signals (see Figure 4B) by pressing the m key on the keyboard. Press Enter to access a pop up window to apply the same mask to all Fourier times or subsequent Fourier times. This can also be applied to individual pixels at any point during data reduction. Masked pixels will turn green.
- Ensure that the collected data is in the form of an echo signal, i.e., cosine function in terms of the phase current, over each detector pixel (see Figure 4A).
NOTE: The phase current is proportional to the precession angle of the neutron spin; hence, it is common to represent the phase current as a phase angle as shown in Figure 4A. For measurements on pulsed sources, additional time of flight calculations are applied to the data to obtain the echo signals as a function of incident neutron wavelength within a neutron pulse. - Start by fitting the resolution file. Select a resolution file from the uploaded file list and right-click on the file. Select Fit Operations: Fit Echoes (Resolution) from the pop-up menu.
- Ensure that the fits of the echo signals yield a number of fitting parameters, including the parameter, A, required in step 4.8. The fits are automatically performed using following expression.
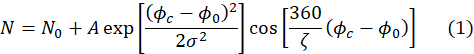
Here, ζ is the period of the echo signal (i.e., cosine function in Figure 4A), σ is the width of the Gaussian envelope determined by the mean wavelength and wavelength spread of the incident neutron beam, Φc is the phase current, and Φ0 is the echo point which depends on the field path experienced by neutrons50. Physical information about the sample is encoded in the amplitude, A, of the cosine function in equation (1).
NOTE: The width of the Gaussian envelope is based on values predetermined by the instrument scientist and should not be changed. The other paramters are variables that are fitted to the specific echo signal over each pixel. - Inspect the fit results by clicking on each pixel to show the resulting fitting parameters, the quality of the fit, and the mean square deviation of the fit. To inspect the error associated with each fitting parameter over the entire detector, select Image Options and then select the fitting parameter of interest. This will generate a map with the value of the fitting paramter over each pixel. Right-click on the detector image. A pop up window will appear showing an error bar map of the selected fitting parameter.
- If the fit over a specific pixel is unsatisfactory (e.g., fit parameeters with large error bars), refit the signal over that specific pixel. Select that pixel, press the Fitting tab, and then press Fit Pixel. Input new starting parameters for the phase (Φ0) and period (ζ) in the Fitting tab to obtain a more satisfactory fit.
NOTE: It is useful to plot the fitted phase as a function of Fourier Time. To do so, go to the main plot window and select Fit Phase v. Fourier Time. This plot should be smooth and continuous. Inspect discontinuities in this plot and refit the pixels that they correspond to.
- Reduce the Sample or Cell file by selecting the corresponding file from the uploaded and labeled file list.
- Inspect all pixels and mask the ones with bad statistics as described in step 4.7.5.
- Right-click on the file and select Fit Operations: Import Phases (Sample, Cell). This imports the phases and the applied mask from the Resolution file.
- Fit the echo signals using the same procedure described before for the Resolution file (steps 4.7.8-4.7.10). In fitting the Sample and Cell files, do not change the values of the period and echo phase point imported from the Resolution fits. These parameters depend on the instrumental settings and should not vary with samples.
- Before proceeding to data reduction, input the beam center for all data files. Select the data file, go to the General tab and enter X and Y beam center values. These values are recorded during the experiment.
- Once the fits to the Sample, Cell, and Resolution files are complete, calculate the normalized intermediate scattering function to be used later in data analysis and interpretation. To do that, right click on the Sample file to be reduced from the list of fitted files, and select Calculate I(Q) from the pop up menu. A window will appear with entry choices for the Resolution and Cell (i.e., buffer) files, and the number of Q-arcs (see step 4.9). After entering all the required informaiton, press the OK button. The results will appear in a new window.
NOTE: The data reduction is performed according to the following equation to obtain the normalized intermediate scattering function69.
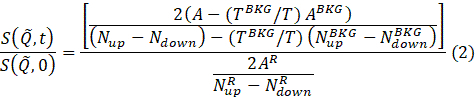
where t is Fourier time, Nup and Ndown are the neutron counts in the non-spin-flip and spin-flip configurations (measured with the π/2-flippers off and the π-flipper off and on, respectively), and the superscripts, BKG and R, correspond to the background and resolution measurements, respectively, as defined in steps 4.4 and 4.6. Note that the beam polarization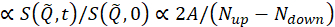 , thus changes in the spin state due to energy exchange between the neutron and the sample is detected as a drop in the polarization (from unity).
, thus changes in the spin state due to energy exchange between the neutron and the sample is detected as a drop in the polarization (from unity).
- Finally, group the detector pixels into Q-arcs as shown in Figure 4B to obtain the Q-dependence of the normalized intermediate scattering function, S(Q,t) / S(Q,0). This is technically referred to as data binning and should be done judiciously, i.e., taking into account the counting statistics from the sample and the expected standard deviation of the data over the grouped pixels.
- For strongly scattering samples, divide the detector into more Q-arcs while maintaining reasonable error bars on the resultant intermediate scattering function, S(Q,t) / S(Q,0). This yields more Q data points and is important for the data analysis procedure described below. Be aware that for weakly scattering samples, excessive binning results in poor decay signals, i.e., large error bars on S(Q,t) / S(Q,0), which could result in large uncertainties.
5. Data analysis and interpretation
- Fit the normalized intermediate scattering functions, S(Q,t) / S(Q,0), obtained from the data reduction above to a stretched exponential function with a stretching exponent of 2/370.
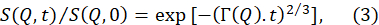
NOTE: An example of these fits is provided in Figure 5B. Fits of S(Q,t) / S(Q,0) to equation (3) yield the Q-dependent relaxation rates Γ(Q). - Plot Γ(Q) as a function of Q and fit to a suitable model to extract relevant membrane parameters.
Results
NSE studies accessing bending fluctuations are typically performed over a Q-range of ~ (0.04 - 0.2) Å-1. This Q-range corresponds to intermediate length scales between the membrane thickness and the liposomal radius, where bending dynamics dominate. Measurement over an extended Q-range can give access to additional dynamic modes, including liposomal diffusion and intramembrane dynamics. For more details on the cross-over in membrane dynamics accessed by NSE, check these relevant publications
Discussion
NSE is a powerful and unique technique in measuring mesoscopic dynamics of lipid membranes under various conditions. The effective utilization of NSE depends on sample quality, neutron contrast, and the range of accessible dynamics that can be probed for a given sample. Thus, several critical steps are required for performing successful NSE experiments and collecting high-quality data. A key step in ensuring the effective use of neutron beam time during an NSE experiment is to characterize the liposomal suspensions with ...
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
R. Ashkar thanks M. Nagao, L.-R. Stingaciu, and P. Zolnierczuk for many useful discussions and for their frequent assistance with NSE experiments on their respective beamlines. The authors acknowledge the use of neutron spin echo spectrometers at NIST and ORNL. The NSE spectrometer at NIST is supported by the Center for High Resolution Neutron Scattering, a partnership between the National Institute of Standards and Technology and the National Science Foundation under agreement no. DMR-1508249. The NSE spectrometer at ORNL's Spallation Neutron Source is supported by the Scientific User Facilities Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, US Department of Energy. Oak Ridge National Laboratory is managed by UT-Battelle, LLC under US DOE Contract No. DE-AC05-00OR22725.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Chloroform (biotech grade) | Sigma Aldrich | 496189 | Biotech. grade, ≥99.8%, contains 0.5-1.0% ethanol as stabilizer |
| Circulating water bath | Julabo | SE-12 | Heating Circulator with smart pump, programmable temperature settings, and external sensor connection for measurement and control |
| Deuterium Oxide | Cambridge Isotopes Laboratories | DLM-4 | Deuterated water; Heavy water (D2O) (D, 99.9%) |
| Digital Semi-Microbalance | Mettler Toledo | MS105 | Semi-micro balance with 120 g capacity, 0.01 mg readability, high resolution weighing cell, ergonomic doors, and pipette-check application |
| Ethanol (molecular biology grade) | Sigma Aldrich | E7023 | 200 proof ethanol for molecular biology applications |
| Glass Pipets | VWR | 36360-536 | Disposable Soda Lime glass Pasteur pipets |
| Glass Vials | Thermo Scientific | B7990-1 | Borosilicate glass vials with PTFE/Silione septum caps |
| Lab grade freezer | Fisher Scientific | IU2886D | Ultra-low temprature freezer (-86 to -50 C) for long-term storage of lipids and proteins |
| Lipids (protaited or perdeuterated) | Avanti Polar Lipids | varies by lipid | Lipids can be purchased from Avanti in powder form or in a chloroform solution with the required amounts and deuteration schemes. |
| Millipore water purifier | Millipore Sigma | ZRQSVP3US | Direct-Q® 3 UV Water Purification System which deliver both pure and ultrapure water with a built-in UV lamp to reduce the levels of organics for biological applications |
| Mini Extruder Set | Avanti Polar Lipids | 610020 | Mini-extruder set includes mini-extruder, heating block, 2 GasTight Syringes, and 2 O-rings, Polycarbonate Membranes, and Filter Supports |
| Quick Connect Fittings | Grainger | 2YDA1 and 2YDA7 | Push-button tube fittings for QuickConnect water circulation applications, e.g. high temperature vesicle extrusion |
| Syringe Pump | SyringePump.com | New Era-1000 | Fully programmable syringe pump for infusion and withdrawal; programs up to 41 pumping phases with adjustable pumping rates, dispensed volumes, and extrusion cycles |
| Ultrasonic bath | Fisher Scientific | CPX2800 | Temperature controlled ultra sonic bath with programmable functionality for degassing and ultrasonic applications |
| Vacuum Oven | Thermo Scientific | 3608 | 0.7 cu ft vaccum oven with built-in-high-limit thermostat guards against overheating |
| Vortex Mixer | Fisher Scientific | 02-215-414 | Variable speed, analog control that allows low rpm start-up for gentle shaking or high-speed mixing for vigorous vortexing of samples |
References
- Singer, S. J., Nicolson, G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 175 (4023), 720-731 (1972).
- Andersen, O. S., Koeppe, R. E. Bilayer thickness and membrane protein function: an energetic perspective. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 36, 107-130 (2007).
- Lundbæk, J. A., Collingwood, S. A., Ingólfsson, H. I., Kapoor, R., Andersen, O. S. Lipid bilayer regulation of membrane protein function: gramicidin channels as molecular force probes. Journal of The Royal Society Interface. 7 (44), 373-395 (2010).
- Bradley, R. P., Radhakrishnan, R. Curvature-undulation coupling as a basis for curvature sensing and generation in bilayer membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 113 (35), 117-124 (2016).
- Perozo, E., Cortes, D. M., Sompornpisut, P., Kloda, A., Martinac, B. Open channel structure of MscL and the gating mechanism of mechanosensitive channels. Nature. 418 (6901), 942-948 (2002).
- Jensen, M. &. #. 2. 1. 6. ;., Mouritsen, O. G. Lipids do influence protein function-the hydrophobic matching hypothesis revisited. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1666 (1-2), 205-226 (2004).
- Rajendran, L., Simons, K. Lipid rafts and membrane dynamics. Journal of Cell Science. 118 (6), 1099-1102 (2005).
- Katchalsky, A., Spangler, R. Dynamics of membrane processes. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. 1 (2), 127-175 (1968).
- Rheinstädter, M. C. Collective molecular dynamics in proteins and membranes (Review). Biointerphases. 3 (2), 83-90 (2008).
- Fujiwara, T., Ritchie, K., Murakoshi, H., Jacobson, K., Kusumi, A. Phospholipids undergo hop diffusion in compartmentalized cell membrane. The Journal of Cell Biology. 157 (6), 1071-1082 (2002).
- Hac, A. E., Seeger, H. M., Fidorra, M., Heimburg, T. Diffusion in two-component lipid membranes--a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and monte carlo simulation study. Biophysical Journal. 88 (1), 317-333 (2005).
- Heinrich, M., Tian, A., Esposito, C., Baumgart, T. Dynamic sorting of lipids and proteins in membrane tubes with a moving phase boundary. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (16), 7208-7213 (2010).
- Hormel, T. T., Kurihara, S. Q., Brennan, M. K., Wozniak, M. C., Parthasarathy, R. Measuring lipid membrane viscosity using rotational and translational probe diffusion. Physical Review Letters. 112 (18), 188101 (2014).
- Dimova, R. Recent developments in the field of bending rigidity measurements on membranes. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 208, 225-234 (2014).
- Bassereau, P., Sorre, B., Lévy, A. Bending lipid membranes: Experiments after W. Helfrich's model. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 208, 47-57 (2014).
- Monzel, C., Sengupta, K. Measuring shape fluctuations in biological membranes. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 49 (24), 243002 (2016).
- Deserno, M. Mesoscopic membrane physics: concepts, simulations, and selected applications. Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 30 (9-10), 752-771 (2009).
- Reynwar, B. J., et al. Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated interactions. Nature. 447 (7143), 461-464 (2007).
- Haswell, E. S., Phillips, R., Rees, D. C. Mechanosensitive channels: what can they do and how do they do it. Structure. 19 (10), 1356-1369 (2011).
- Phillips, R., Ursell, T., Wiggins, P., Sens, P. Emerging roles for lipids in shaping membrane-protein function. Nature. 459 (7245), 379-385 (2009).
- Dill, K. A., Chan, H. S. From Levinthal to pathways to funnels. Nature Structural Biology. 4 (1), 10-19 (1997).
- Henzler-Wildman, K., Kern, D. Dynamic personalities of proteins. Nature. 450 (7172), 964-972 (2007).
- Grimaldo, M., Roosen-Runge, F., Zhang, F., Schreiber, F., Seydel, T. Dynamics of proteins in solution. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. 52, 7 (2019).
- Lyman, E., Hsieh, C. -. L., Eggeling, C. From dynamics to membrane organization: experimental breakthroughs occasion a "modeling manifesto". Biophysical Journal. 115 (4), 595-604 (2018).
- Arriaga, L. R., et al. Dissipative curvature fluctuations in bilayer vesicles: Coexistence of pure-bending and hybrid curvature-compression modes. The European Physical Journal. E, Soft Matter. 31 (1), 105-113 (2010).
- Honerkamp-Smith, A. R., Veatch, S. L., Keller, S. L. An introduction to critical points for biophysicists; observations of compositional heterogeneity in lipid membranes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1788 (1), 53-63 (2009).
- Veatch, S. L., Keller, S. L. Organization in lipid membranes containing cholesterol. Physical Review Letters. 89 (26), 268101 (2002).
- Heberle, F. A., et al. Bilayer thickness mismatch controls domain size in model membranes. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 135 (18), 6853-6859 (2013).
- Nickels, J. D., et al. The in vivo structure of biological membranes and evidence for lipid domains. PLOS Biology. 15 (5), 2002214 (2017).
- Simons, K., Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 387 (6633), 569-572 (1997).
- van Meer, G., Voelker, D. R., Feigenson, G. W. Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 9 (2), 112-124 (2008).
- Liu, S. -. L., et al. Orthogonal lipid sensors identify transbilayer asymmetry of plasma membrane cholesterol. Nature Chemical Biology. 13, 268 (2016).
- Rothman, J., Lenard, J. Membrane asymmetry. Science. 195 (4280), 743-753 (1977).
- Ashkar, R., et al. Neutron scattering in the biological sciences: progress and prospects. Acta Crystallographica Section D. 74 (12), 1129-1168 (2018).
- Woodka, A. C., Butler, P. D., Porcar, L., Farago, B., Nagao, M. Lipid bilayers and membrane dynamics: insight into thickness fluctuations. Physical Review Letters. 109 (5), 058102 (2012).
- Chakraborty, S., et al. How cholesterol stiffens unsaturated lipid membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (36), 21896-21905 (2020).
- Arriaga, L. R., et al. Stiffening effect of cholesterol on disordered lipid phases: a combined neutron spin echo + dynamic light scattering analysis of the bending elasticity of large unilamellar vesicles. Biophysical Journal. 96 (9), 3629-3637 (2009).
- Nagao, M., Kelley, E. G., Ashkar, R., Bradbury, R., Butler, P. D. Probing elastic and viscous properties of phospholipid bilayers using neutron spin echo spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 8 (19), 4679-4684 (2017).
- Kelley, E. G., Butler, P. D., Ashkar, R., Bradbury, R., Nagao, M. Scaling relationships for the elastic moduli and viscosity of mixed lipid membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (38), 23365-23373 (2020).
- Rickeard, B. W., et al. Transverse lipid organization dictates bending fluctuations in model plasma membranes. Nanoscale. 12 (3), 1438-1447 (2020).
- Nickels, J. D., et al. Mechanical properties of nanoscopic lipid domains. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (50), 15772-15780 (2015).
- Mezei, F. Neutron spin echo: A new concept in polarized thermal neutron techniques. Zeitschrift für Physik A Hadrons and Nuclei. 255 (2), 146-160 (1972).
- Hayter, J. B., Penfold, J. Neutron spin-echo integral transform spectroscopy. Zeitschrift für Physik B Condensed Matter. 35 (2), 199-205 (1979).
- Monkenbusch, M., Richter, D., Imae, T., Kanaya, T., Furusaka, M., Torikai, N. . Neutrons in Soft Matter. , 147-182 (2011).
- Pynn, R., Mezei, F., Pappas, C., Gutberlet, T. . Neutron Spin Echo. , 159-177 (2003).
- Holderer, O., et al. The JCNS neutron spin-echo spectrometer J-NSE at the FRM II. Measurement Science and Technology. 19 (3), 034022 (2008).
- Schleger, P., et al. The long-wavelength neutron spin-echo spectrometer IN15 at the Institut Laue-Langevin. Physica B: Condensed Matter. 241-243, 164-165 (1997).
- Holderer, O., Zolnierczuk, P., Pasini, S., Stingaciu, L., Monkenbusch, M. A better view through new glasses: Developments at the Jülich neutron spin echo spectrometers. Physica B: Condensed Matter. 562, 9-12 (2019).
- Farago, B., et al. The IN15 upgrade. Neutron News. 26 (3), 15-17 (2015).
- Ashkar, R. Selective dynamics in polymeric materials: Insights from quasi-elastic neutron scattering spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Physics. 127 (15), 151101 (2020).
- Pasini, S., Holderer, O., Kozielewski, T., Richter, D., Phoenix Monkenbusch, M. J-NSE- Phoenix, a neutron spin-echo spectrometer with optimized superconducting precession coils at the MLZ in Garching. Review of Scientific Instruments. 90 (4), 043107 (2019).
- Svergun, D. I., Koch, M. H. J., Timmins, P. A., May, R. P. . Small Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering from Solutions of Biological Macromolecules. , (2013).
- Eicher, B., et al. Joint small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering data analysis of asymmetric lipid vesicles. Journal of Applied Crystallography. 50 (2), 419-429 (2017).
- Heberle, F. A., et al. Model-based approaches for the determination of lipid bilayer structure from small-angle neutron and X-ray scattering data. European Biophysics Journal. 41 (10), 875-890 (2012).
- Jaksch, S., Koutsioubas, A., Mattauch, S., Holderer, O., Frielinghaus, H. Long-range excitations in phospholipid membranes. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids. 225, 104788 (2019).
- Jaksch, S., et al. Influence of ibuprofen on phospholipid membranes. Physical Review E. 91 (2), 022716 (2015).
- Armstrong, C. L., et al. Effect of cholesterol on the lateral nanoscale dynamics of fluid membranes. European Biophysics Journal. 41 (10), 901-913 (2012).
- Rheinstädter, M. C., Häußler, W., Salditt, T. Dispersion relation of lipid membrane shape fluctuations by neutron spin-echo spectrometry. Physical Review Letters. 97 (4), 048103 (2006).
- Armstrong, C. L., Häußler, W., Seydel, T., Katsaras, J., Rheinstädter, M. C. Nanosecond lipid dynamics in membranes containing cholesterol. Soft Matter. 10 (15), 2600-2611 (2014).
- Nickels, J. D., et al. Lipid rafts: buffers of cell membrane physical properties. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 123 (9), 2050-2056 (2019).
- Michonova-Alexova, E. I., Sugár, I. P. Component and state separation in DMPC/DSPC lipid bilayers: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Biophysical Journal. 83 (4), 1820-1833 (2002).
- Sugár, I. P., Thompson, T. E., Biltonen, R. L. Monte Carlo simulation of two-component bilayers: DMPC/DSPC mixtures. Biophysical Journal. 76 (4), 2099-2110 (1999).
- Mabrey, S., Sturtevant, J. M. Investigation of phase transitions of lipids and lipid mixtures by sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 73 (11), 3862-3866 (1976).
- . Neutron activation and scattering calculator Available from: https://www.ncnr.nist.gov/resources/activation/ (2021)
- Scott, H. L., et al. On the mechanism of bilayer separation by extrusion, or why your LUVs are not really unilamellar. Biophysical Journal. 117 (8), 1381-1386 (2019).
- Ashkar, R., et al. Tuning membrane thickness fluctuations in model lipid bilayers. Biophysical Journal. 109 (1), 106-112 (2015).
- Carrillo, J. -. M. Y., Katsaras, J., Sumpter, B. G., Ashkar, R. A computational approach for modeling neutron scattering data from lipid bilayers. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 13 (2), 916-925 (2017).
- Azuah, R. T. DAVE: a comprehensive software suite for the reduction, visualization, and analysis of low energy neutron spectroscopic data. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology. 114 (6), 341-358 (2009).
- Van Hove, L. Correlations in space and time and born approximation scattering in systems of interacting particles. Physical Review. 95 (1), 249-262 (1954).
- Zilman, A. G., Granek, R. Undulations and dynamic structure factor of membranes. Physical Review Letters. 77 (23), 4788-4791 (1996).
- Kelley, E. G., Butler, P. D., Nagao, M. . Collective dynamics in model biological membranes measured by neutron spin echo spectroscopy. , 131-176 (2019).
- Zheng, Y., Michihiro, N., Dobrin, P. B. Bending elasticity of saturated and monounsaturated phospholipid membranes studied by the neutron spin echo technique. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 21 (15), 155104 (2009).
- Sharma, V. K., Qian, S. Effect of an antimicrobial peptide on lateral segregation of lipids: a structure and dynamics study by neutron scattering. Langmuir. 35 (11), 4152-4160 (2019).
- Boggara, M. B., Faraone, A., Krishnamoorti, R. Effect of pH and Ibuprofen on the Phospholipid Bilayer Bending Modulus. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 114 (24), 8061-8066 (2010).
- Lee, J. -. H., et al. Thermal fluctuation and elasticity of lipid vesicles interacting with pore-forming peptides. Physical Review Letters. 105 (3), 038101 (2010).
- Chakraborty, S., Abbasi, A., Bothun, G. D., Nagao, M., Kitchens, C. L. Phospholipid bilayer softening due to hydrophobic gold nanoparticle inclusions. Langmuir. 34 (44), 13416-13425 (2018).
- Hoffmann, I., et al. Softening of phospholipid membranes by the adhesion of silica nanoparticles - as seen by neutron spin-echo (NSE). Nanoscale. 6 (12), 6945-6952 (2014).
- Watson, M. C., Brown, F. L. H. Interpreting membrane scattering experiments at the mesoscale: the contribution of dissipation within the bilayer. Biophysical Journal. 98 (6), 9-11 (2010).
- Seifert, U., Langer, S. A. Viscous modes of fluid bilayer membranes. Europhysics Letters (EPL). 23 (1), 71-76 (1993).
- Bingham, R. J., Smye, S. W., Olmsted, P. D. Dynamics of an asymmetric bilayer lipid membrane in a viscous solvent. EPL (Europhysics Letters). 111 (1), 18004 (2015).
- Rawicz, W., Olbrich, K. C., McIntosh, T., Needham, D., Evans, E. Effect of chain length and unsaturation on elasticity of lipid bilayers. Biophysical Journal. 79 (1), 328-339 (2000).
- Doktorova, M., LeVine, M. V., Khelashvili, G., Weinstein, H. A new computational method for membrane compressibility: bilayer mechanical thickness revisited. Biophysical Journal. 116 (3), 487-502 (2019).
- Evans, E., Needham, D. Physical properties of surfactant bilayer membranes: thermal transitions, elasticity, rigidity, cohesion and colloidal interactions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 91 (16), 4219-4228 (1987).
- Lesieur, S., Grabielle-Madelmont, C., Paternostre, M. T., Ollivon, M. Size analysis and stability study of lipid vesicles by high-performance gel exclusion chromatography, turbidity, and dynamic light scattering. Analytical Biochemistry. 192 (2), 334-343 (1991).
- Heberle, F. A., et al. Direct label-free imaging of nanodomains in biomimetic and biological membranes by cryogenic electron microscopy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (33), 19943-19952 (2020).
- Cornell, C. E., Mileant, A., Thakkar, N., Lee, K. K., Keller, S. L. Direct imaging of liquid domains in membranes by cryo-electron tomography. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (33), 19713-19719 (2020).
- Yao, X., Fan, X., Yan, N. Cryo-EM analysis of a membrane protein embedded in the liposome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 117 (31), 18497-18503 (2020).
- Kučerka, N., Nieh, M. -. P., Katsaras, J. Fluid phase lipid areas and bilayer thicknesses of commonly used phosphatidylcholines as a function of temperature. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1808 (11), 2761-2771 (2011).
- Nielsen, J. E., Bjørnestad, V. A., Lund, R. Resolving the structural interactions between antimicrobial peptides and lipid membranes using small-angle scattering methods: the case of indolicidin. Soft Matter. 14 (43), 8750-8763 (2018).
- Kučerka, N., et al. Lipid bilayer structure determined by the simultaneous analysis of neutron and X-ray scattering data. Biophysical Journal. 95 (5), 2356-2367 (2008).
- Kelley, E. G., Butler, P. D., Nagao, M. Scaling of lipid membrane rigidity with domain area fraction. Soft Matter. 15 (13), 2762-2767 (2019).
- Brüning, B. -. A., et al. Bilayer undulation dynamics in unilamellar phospholipid vesicles: Effect of temperature, cholesterol and trehalose. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1838 (10), 2412-2419 (2014).
- Kučerka, N., et al. Areas of monounsaturated diacylphosphatidylcholines. Biophysical Journal. 97 (7), 1926-1932 (2009).
- Sharma, V. K., Mamontov, E., Anunciado, D. B., O'Neill, H., Urban, V. S. Effect of antimicrobial peptide on the dynamics of phosphocholine membrane: role of cholesterol and physical state of bilayer. Soft Matter. 11 (34), 6755-6767 (2015).
- Kelley, E. G., Butler, P. D., Nagao, M. Collective dynamics in lipid membranes containing transmembrane peptides. Soft Matter. , (2021).
- Yu, J., et al. Structure and dynamics of lipid membranes interacting with antivirulence end-phosphorylated polyethylene glycol block copolymers. Soft Matter. 16 (4), 983-989 (2020).
- Stingaciu, L. -. R., et al. Revealing the dynamics of thylakoid membranes in living cyanobacterial cells. Scientific Reports. 6 (1), 19627 (2016).
- Stingaciu, L. -. R., O'Neill, H. M., Liberton, M., Pakrasi, H. B., Urban, V. S. Influence of chemically disrupted photosynthesis on cyanobacterial thylakoid dynamics in synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Scientific Reports. 9 (1), 5711 (2019).
- Miller, I. R. Energetics of fluctuation in lipid bilayer thickness. Biophysical Journal. 45 (3), 643-644 (1984).
- Nagao, M. Observation of local thickness fluctuations in surfactant membranes using neutron spin echo. Physical Review E. 80 (3), 031606 (2009).
Erratum
Formal Correction: Erratum: Neutron Spin Echo Spectroscopy as a Unique Probe for Lipid Membrane Dynamics and Membrane-Protein Interactions
Posted by JoVE Editors on 8/06/2021. Citeable Link.
An erratum was issued for: Neutron Spin Echo Spectroscopy as a Unique Probe for Lipid Membrane Dynamics and Membrane-Protein Interactions. The Introduction, Protocol, and Representative Results sections have been updated.
In the Introduction, the fith pargraph was updated from:
Besides direct access to the length and time scale of membrane dynamics, NSE has the inherent capabilities of neutron isotope sensitivity52. Specifically, the ability of neutrons to interact differently with the isotopes of hydrogen, the most abundant element in biological systems, results in a different neutron scattering length density,34 or NSLD (the equivalent of the optical index of refraction50), when protium is substituted by deuterium. This enables an approach known as contrast variation, which is commonly used to highlight specific membrane features or conceal others — the latter scenario is referred to as contrast matching. A frequent application of contrast variation/matching is the substitution of water (NSLD = -0.56 × 10-6 Å-2) by heavy water or D2O (NSLD = 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) to amplify the neutron signal from protiated lipid membranes (NSLD ~ 2 × 10-6 Å-2). This approach is highly effective in studies of membrane structure because the penetration of D2O into the headgroup region of the membrane allows accurate determination of the membrane thicknesses (see Figure 2A, left panel) and of the location of different lipid subgroups when more sophisticated models are applied53,54. This paper highlights some examples on the use of contrast variation for studies of collective dynamics in biomimetic membranes and select membrane features.
to:
Besides direct access to the length and time scale of membrane dynamics, NSE has the inherent capabilities of neutron isotope sensitivity52. Specifically, the ability of neutrons to interact differently with the isotopes of hydrogen, the most abundant element in biological systems, results in a different neutron scattering length density,34 or NSLD (the equivalent of the optical index of refraction50), when protium is substituted by deuterium. This enables an approach known as contrast variation, which is commonly used to highlight specific membrane features or conceal others — the latter scenario is referred to as contrast matching. A frequent application of contrast variation/matching is the substitution of water (NSLD = -0.56 × 10-6 Å-2) by heavy water or D2O (NSLD = 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) to amplify the neutron signal from protiated lipid membranes (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2). This approach is highly effective in studies of membrane structure because the penetration of D2O into the headgroup region of the membrane allows accurate determination of the membrane thicknesses (see Figure 2A, left panel) and of the location of different lipid subgroups when more sophisticated models are applied53,54. This paper highlights some examples on the use of contrast variation for studies of collective dynamics in biomimetic membranes and select membrane features.
In the Protocol, step 1.1 was updated from:
For bending fluctuation measurements, make fully protiated liposomes in D2O (D 99.9%) or D2O-buffer (e.g., phosphate buffer prepared with D2O instead of H2O). Use fully protiated DMPC (C36H72NO8P) and DSPC (C44H88NO8P) with 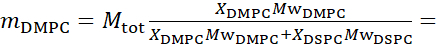 133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 2 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel).
133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 2 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel).
to:
For bending fluctuation measurements, make fully protiated liposomes in D2O (D 99.9%) or D2O-buffer (e.g., phosphate buffer prepared with D2O instead of H2O). Use fully protiated DMPC (C36H72NO8P) and DSPC (C44H88NO8P) with 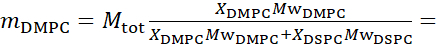 133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel).
133.4 mg, where XDMPC and XDSPC are the mole fractions of DMPC and DSPC, here set to 0.7 and 0.3, respectively, and MwDMPC and MwDSPC are the molar weights given by 677.9 g/mol and 790.1 g/mol, respectively. Similarly, mDSPC = 66.6 mg. This deuteration scheme increases the scattering contrast between the membrane (NSLD ~ 0 × 10-6 Å-2) and the deuterated buffer (NSLD ~ 6.4 × 10-6 Å-2) and amplifies the signal from membrane undulations (see Figure 2A left panel).
In the Representative Results, the fist pagargaph was updted from:
NSE studies accessing bending fluctuations are typically performed over a Q-range of ~ (0.04 - 0.2) Å-1. This Q-range corresponds to intermediate length scales between the membrane thickness and the liposomal radius, where bending dynamics dominate. Measurement over an extended Q-range can give access to additional dynamic modes, including liposomal diffusion and intramembrane dynamics. For more details on the cross-over in membrane dynamics accessed by NSE, check these relevant publications25,71. It is important to emphasize that NSE signals are proportional to: 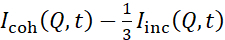 , where Icoh and Iinc are, respectively, the coherent and incoherent scattering intensity from the sample. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare NSE liposomal samples in deuterated buffers (i.e., buffers prepared with D2O instead of H2O) to minimize the incoherent scattering signal, mainly contributed by the hydrogen content of the sample. However, in some cases intermediate deuteration schemes (i.e., using mixtures of D2O and H2O) might be necessary to obtain optimal contrast conditions. Typically, NSE measurements of membrane bending fluctuations are performed on fully protiated liposomes in deuterated buffer, referred to as fully contrasted liposomes in Figure 5. This deuteration scheme results in a large NSLD difference between the membrane core (~2 × 10-6 Å-2) and its deuterated fluid environment (~6.4 × 10-6 Å-2), which significantly enhances the scattering signal from the liposomal membranes and improves the measurement statistics of bending dynamics. This contrast scheme (Figure 2A left panel) is frequently utilized in studies of bending rigidity of lipid membranes with single38,72 and multiple39,66 lipid components and in studies of membrane softening/stiffening by biological inclusions (e.g., cholesterol, drug molecules, peptides/proteins)36,37,73,74,75, and synthetic additives (e.g., nanoparticles)76,77.
, where Icoh and Iinc are, respectively, the coherent and incoherent scattering intensity from the sample. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare NSE liposomal samples in deuterated buffers (i.e., buffers prepared with D2O instead of H2O) to minimize the incoherent scattering signal, mainly contributed by the hydrogen content of the sample. However, in some cases intermediate deuteration schemes (i.e., using mixtures of D2O and H2O) might be necessary to obtain optimal contrast conditions. Typically, NSE measurements of membrane bending fluctuations are performed on fully protiated liposomes in deuterated buffer, referred to as fully contrasted liposomes in Figure 5. This deuteration scheme results in a large NSLD difference between the membrane core (~2 × 10-6 Å-2) and its deuterated fluid environment (~6.4 × 10-6 Å-2), which significantly enhances the scattering signal from the liposomal membranes and improves the measurement statistics of bending dynamics. This contrast scheme (Figure 2A left panel) is frequently utilized in studies of bending rigidity of lipid membranes with single38,72 and multiple39,66 lipid components and in studies of membrane softening/stiffening by biological inclusions (e.g., cholesterol, drug molecules, peptides/proteins)36,37,73,74,75, and synthetic additives (e.g., nanoparticles)76,77.
to:
NSE studies accessing bending fluctuations are typically performed over a Q-range of ~ (0.04 - 0.2) Å-1. This Q-range corresponds to intermediate length scales between the membrane thickness and the liposomal radius, where bending dynamics dominate. Measurement over an extended Q-range can give access to additional dynamic modes, including liposomal diffusion and intramembrane dynamics. For more details on the cross-over in membrane dynamics accessed by NSE, check these relevant publications25,71. It is important to emphasize that NSE signals are proportional to: 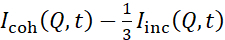 , where Icoh and Iinc are, respectively, the coherent and incoherent scattering intensity from the sample. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare NSE liposomal samples in deuterated buffers (i.e., buffers prepared with D2O instead of H2O) to minimize the incoherent scattering signal, mainly contributed by the hydrogen content of the sample. However, in some cases intermediate deuteration schemes (i.e., using mixtures of D2O and H2O) might be necessary to obtain optimal contrast conditions. Typically, NSE measurements of membrane bending fluctuations are performed on fully protiated liposomes in deuterated buffer, referred to as fully contrasted liposomes in Figure 5. This deuteration scheme results in a large NSLD difference between the membrane core (~0 × 10-6 Å-2) and its deuterated fluid environment (~6.4 × 10-6 Å-2), which significantly enhances the scattering signal from the liposomal membranes and improves the measurement statistics of bending dynamics. This contrast scheme (Figure 2A left panel) is frequently utilized in studies of bending rigidity of lipid membranes with single38,72 and multiple39,66 lipid components and in studies of membrane softening/stiffening by biological inclusions (e.g., cholesterol, drug molecules, peptides/proteins)36,37,73,74,75, and synthetic additives (e.g., nanoparticles)76,77.
, where Icoh and Iinc are, respectively, the coherent and incoherent scattering intensity from the sample. Therefore, it is advisable to prepare NSE liposomal samples in deuterated buffers (i.e., buffers prepared with D2O instead of H2O) to minimize the incoherent scattering signal, mainly contributed by the hydrogen content of the sample. However, in some cases intermediate deuteration schemes (i.e., using mixtures of D2O and H2O) might be necessary to obtain optimal contrast conditions. Typically, NSE measurements of membrane bending fluctuations are performed on fully protiated liposomes in deuterated buffer, referred to as fully contrasted liposomes in Figure 5. This deuteration scheme results in a large NSLD difference between the membrane core (~0 × 10-6 Å-2) and its deuterated fluid environment (~6.4 × 10-6 Å-2), which significantly enhances the scattering signal from the liposomal membranes and improves the measurement statistics of bending dynamics. This contrast scheme (Figure 2A left panel) is frequently utilized in studies of bending rigidity of lipid membranes with single38,72 and multiple39,66 lipid components and in studies of membrane softening/stiffening by biological inclusions (e.g., cholesterol, drug molecules, peptides/proteins)36,37,73,74,75, and synthetic additives (e.g., nanoparticles)76,77.
In the Representative Reults, Figure 2 was updated from:
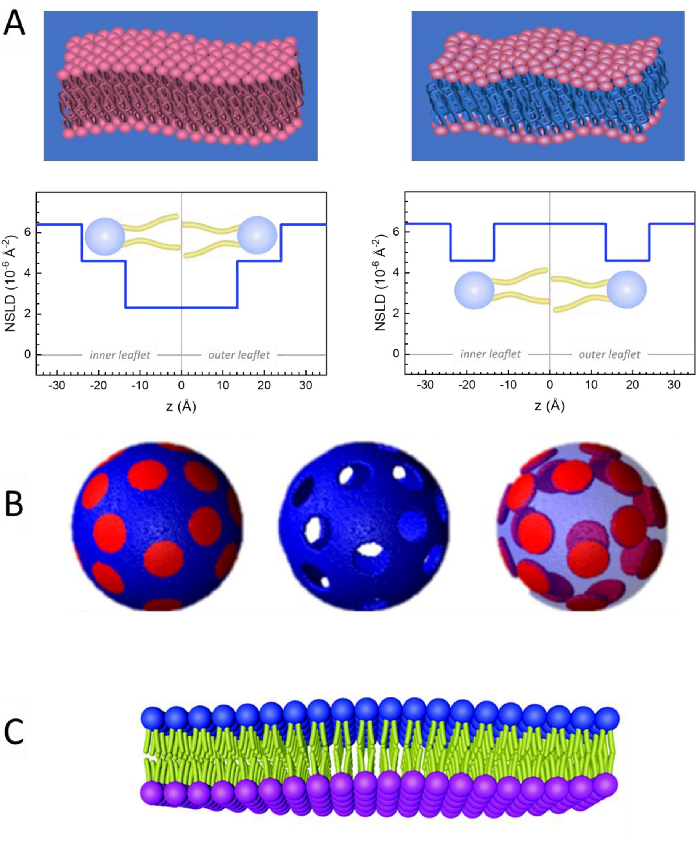
Figure 2: Examples of possible deuteration schemes in NSE experiments on lipid membranes. (A) Left: Fully contrasted membranes, e.g., protiated membranes in deuterated buffer, showing the NSLD profile along the normal to the membrane surface. The difference in the NSLD between the headgroup (~2 × 10-2 Å-2) and tail region (~4.5 × 10-6 Å-2) of the membrane is due to the headgroup hydration with deuterated buffer. Right: Tail-contrast matched membranes such that the hydrocarbon tail region of the membrane has the same NSLD as the buffer, as shown in the corresponding NSLD profile along the membrane normal. (B) Domain-forming membranes with two neutron contrast schemes where the domains (center) or the matrix (left) are contrast-matched to the buffer, enabling selective studies of matrix or domain dynamics, respectively. This figure has been modified from Nickels et al., JACS 201541. (C) Asymmetric membranes prepared by cyclodextrin exchange between protiated and deuterated lipid vesicles, resulting in the deuteration of one membrane leaflet while keeping the other leaflet protiated. This allows studies of the bending dynamics of the protiated leaflet and provides insights into the mechanical coupling between opposing leaflets in asymmetric membranes. This figure has been modified from Rickeard et al., Nanoscale 202040. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
to:
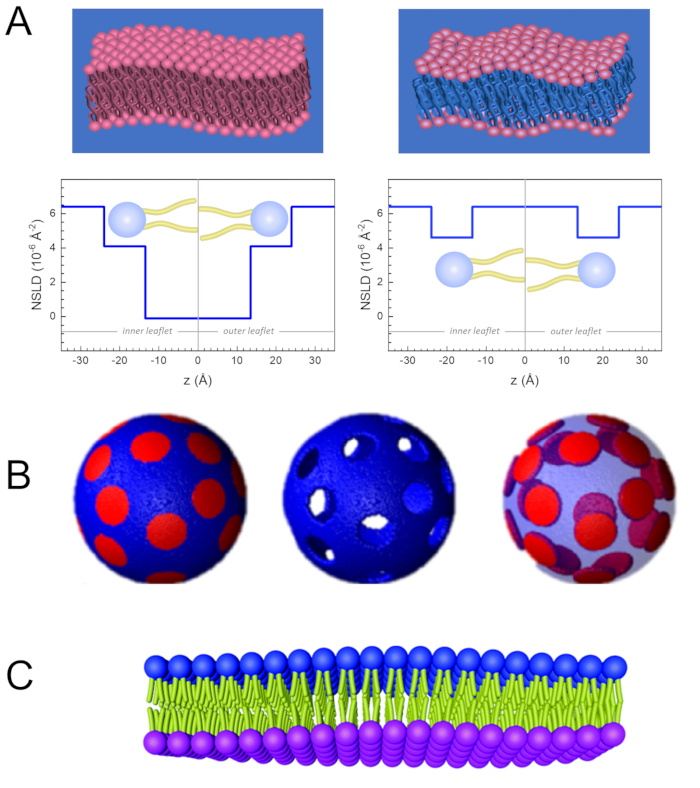
Figure 2: Examples of possible deuteration schemes in NSE experiments on lipid membranes. (A) Left: Fully contrasted membranes, e.g., protiated membranes in deuterated buffer, showing the NSLD profile along the normal to the membrane surface. The difference in the NSLD between the tail region (~0 × 10-2 Å-2) and headgroup region (~4.5 × 10-6 Å-2) of the membrane is due to the headgroup hydration with deuterated buffer. Right: Tail-contrast matched membranes such that the hydrocarbon tail region of the membrane has the same NSLD as the buffer, as shown in the corresponding NSLD profile along the membrane normal. (B) Domain-forming membranes with two neutron contrast schemes where the domains (center) or the matrix (left) are contrast-matched to the buffer, enabling selective studies of matrix or domain dynamics, respectively. This figure has been modified from Nickels et al., JACS 201541. (C) Asymmetric membranes prepared by cyclodextrin exchange between protiated and deuterated lipid vesicles, resulting in the deuteration of one membrane leaflet while keeping the other leaflet protiated. This allows studies of the bending dynamics of the protiated leaflet and provides insights into the mechanical coupling between opposing leaflets in asymmetric membranes. This figure has been modified from Rickeard et al., Nanoscale 202040. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionExplore More Articles
This article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved