A subscription to JoVE is required to view this content. Sign in or start your free trial.
Method Article
CD Spectroscopy to Study DNA-Protein Interactions
In This Article
Summary
The interaction of an ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler with a DNA ligand is described using CD spectroscopy. The induced conformational changes on a gene promoter analyzed by the peaks generated can be used to understand the mechanism of transcriptional regulation.
Abstract
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy is a simple and convenient method to investigate the secondary structure and interactions of biomolecules. Recent advancements in CD spectroscopy have enabled the study of DNA-protein interactions and conformational dynamics of DNA in different microenvironments in detail for a better understanding of transcriptional regulation in vivo. The area around a potential transcription zone needs to be unwound for transcription to occur. This is a complex process requiring the coordination of histone modifications, binding of the transcription factor to DNA, and other chromatin remodeling activities. Using CD spectroscopy, it is possible to study conformational changes in the promoter region caused by regulatory proteins, such as ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers, to promote transcription. The conformational changes occurring in the protein can also be monitored. In addition, queries regarding the affinity of the protein towards its target DNA and sequence specificity can be addressed by incorporating mutations in the target DNA. In short, the unique understanding of this sensitive and inexpensive method can predict changes in chromatin dynamics, thereby improving the understanding of transcriptional regulation.
Introduction
Circular dichroism (CD) is a spectroscopic technique that relies on the inherent chirality of biological macromolecules that leads to differential absorption of right-handed and left-handed circularly polarized light. This differential absorption is known as circular dichroism. The technique, therefore, can be used to delineate the conformation of biological macromolecules, such as proteins and DNA, both of which contain chiral centers1,2.
Electromagnetic waves contain both electric and magnetic components. Both the electrical and the magnetic fields oscillate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. In the case of unpolarized light, these fields oscillate in many directions. When the light is circularly polarized, two electromagnetic fields are obtained at 90° phase difference to each other. Chiral molecules show circular optical rotation (birefringence) such that they will absorb the right-handed circularly polarized light and the left-handed circularly polarized light to different extents3. The resulting electrical field will be traced as an ellipse, a function of the wavelength. The CD spectrum is, thus, recorded as ellipticity (q), and the data are presented as Mean Residue Ellipticity as a function of wavelength.
In the case of proteins, the Cα of amino acids (except glycine) is chiral, and this is exploited by CD spectroscopy to determine the secondary structure of this macromolecule4. The CD spectra of protein molecules are typically recorded in the Far UV range. α-helical proteins have two negative bands at 222 nm and 208 nm and one positive peak at 193 nm4. Proteins with anti-parallel β-sheet secondary structure show a negative peak at 218 nm and a positive peak at 195 nm4. Proteins with disordered structures show low ellipticity near 210 nm and a negative peak at 195 nm4. Thus, the well-defined peak/bands for different secondary structures make CD a convenient tool to elucidate the conformational changes occurring in the secondary structure of the proteins during denaturation as well as ligand binding.
Nucleic acids have three sources of chirality: the sugar molecule, the helicity of the secondary structure, and the long-range tertiary ordering of DNA in the environment5,6. The CD spectra of nucleic acids are typically recorded in the 190 to 300 nm range5,6. Each conformation of DNA, just like proteins, gives a characteristic spectrum, although the peaks/bands can vary by some degrees due to solvent conditions and differences in DNA sequences7. B-DNA, the most common form, is characterized by a positive peak around 260-280 nm and a negative peak around 245 nm6. The peaks/bands of B-form DNA are generally small because the base pairs are perpendicular to the double helix, conferring weak chirality to the molecule. A-DNA gives a dominant positive peak at 260 nm and a negative peak around 210 nm6. Z-DNA, the left-handed helix, gives a negative band at 290 nm and a positive peak around 260 nm6. This DNA also gives an extremely negative peak at 205 nm6.
In addition to these conformations, DNA can also form triplexes, quadruplexes, and hairpins, all of which can be distinguished by CD spectroscopy. The parallel G-quadruplex give a dominant positive band at 260 nm, while the anti-parallel G-quadruplex gives a negative band at 260 nm and a positive peak at 290 nm, making it easy to distinguish between the two forms of quadruplex structures6. Triplexes do not give a characteristic spectrum8. For example, the spectra of a 36 nucleotide-long DNA with the potential to form an intramolecular triple helix containing G.G.C and T.A.T base pairs in the presence of Na+ show a strong negative band at 240 nm and a broad positive peak. The broad positive peak shows contributions at 266, 273, and 286 nm. The same oligonucleotide in the presence of Na+ and Zn+ shows four negative bands (213, 238, 266, and 282 nm) and a positive peak at 258 nm. Thus, the spectra of triplex DNA can vary depending upon salt conditions8.
In addition to these conformations, CD spectra have enabled the identification of another form of DNA called X-DNA. X-DNA is formed when the DNA sequence contains alternate adenine and thymine residues. The CD spectra of X-DNA contain two negative peaks at 250 and 280 nm. Very little information is available about X-DNA, although it has been speculated to function as a sink for positive supercoiling6,9. Changes in CD spectra can also reveal details about ligand-protein interactions and, therefore, have been added to the arsenal of molecular methods for detecting drug-protein interactions10,11,12,13,14. CD spectra have also been used to monitor the changes in the secondary structure of proteins during the folding process15. Similarly, CD spectra can also be used for probing ligand-DNA interactions16,17.
CD spectroscopy, thus, is an easy, inexpensive method to distinguish between the different forms of DNA conformation, provided there is access to not-so-inexpensive equipment and software. The method is exceedingly sensitive and quick. It only requires a small amount of DNA, giving it an edge over the alternate technique of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. Titrations with ligands and substrates are also easy to perform. The major constraint is that the DNA should be highly pure. It is advisable to use polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE)-purified DNA.
The information obtained by CD spectra has been mainly used to deduce protein structural features and to identify distinct DNA conformers. In this study, CD spectra have been used to integrate the results obtained from an in vivo Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiment to delineate whether the protein of interest/predicted transcription factor can bring about a conformational change in the promoter region of its effector genes. This collaboration aids in the progress of traditional CD spectroscopic techniques by predicting the mechanism of transcription regulation by the predicted transcription factor on and around the transcription start site (TSS) of a promoter.
Chromatin remodeling is a well-defined mechanism known to regulate DNA metabolic processes by making the tightly packed chromatin accessible to various regulatory factors such as transcription factors, components of DNA replication, or damage repair proteins. The ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers, also known as the SWI/SNF family of proteins, are key remodeler proteins present in eukaryotic cells18,19. Phylogenetic clustering has categorized the SWI/SNF family of proteins into 6 sub-groups20: Snf2-like, Swr1-like, SSO1653-like, Rad54-like, Rad5/16-like, and distant. SMARCAL1, the protein of interest in this study, belongs to the distant sub-group20. This protein has been used to investigate its mode of transcriptional regulation using CD spectroscopy.
Most of the members of the ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling proteins have been shown to either reposition or evict nucleosomes or mediate histone variant exchange in an ATP-dependent manner21,22. However, some members of this family have not been shown to remodel nucleosomes, e.g., SMARCAL1. Even though studies have shown that SMARCAL1 associates with polytene chromosomes, experimental evidence regarding its ability to remodel nucleosomes is lacking23. Therefore, it was postulated that SMARCAL1 may regulate transcription by altering the conformation of DNA24. CD spectroscopy provided an easy and accessible method to validate this hypothesis.
SMARCAL1 is an ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling protein that primarily functions as an annealing helicase25,26,27. It has been postulated to modulate transcription by remodeling the DNA conformation24. To test this hypothesis, the role of SMARCAL1 in regulating gene transcription during doxorubicin-induced DNA damage was studied. In these studies, SMARCAL1 was used for in vivo analysis and ADAAD for in vitro assays28,29. Previous studies have shown that ADAAD can recognize DNA in a structure-dependent but sequence-independent manner30,31. The protein binds optimally to DNA molecules possessing double-strand to single-strand transition regions, similar to stem-loop DNA, and hydrolyzes ATP 30,31.
In vivo experiments showed that SMARCAL1 regulates the expression of MYC, DROSHA, DGCR8, and DICER by binding to the promoter regions28,29. The region of interaction was identified by ChIP experiments28,29. The ChIP technique is used to analyze the interaction of a protein with its cognate DNA within the cell. Its goal is to determine whether specific proteins, such as transcription factors on promoters or other DNA binding sites, are bound to specific genomic areas. The protein bound to DNA is first cross-linked using formaldehyde. This is followed by isolation of the chromatin. The isolated chromatin is sheared to 500 bp fragments either by sonication or nuclease digestion, and the protein bound to DNA is immunoprecipitated using antibodies specific to the protein. The cross-linking is reversed, and the DNA is analyzed using either polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or quantitative real-time PCR.
The ChIP results led to the hypothesis that SMARCAL1 possibly mediates transcriptional regulation by inducing a conformational change in the promoter regions of these genes. QGRS mapper and Mfold software were used to identify the potential of these promoter regions to form secondary structures28,29. QGRS mapper is used for predicting G-quadruplexes32, while Mfold33 analyzes the ability of a sequence to form secondary structures such as stem-loops.
After secondary structure analysis, further in vitro experiments were performed with recombinant 6X His-tagged Active DNA-dependent ATPase A Domain (ADAAD), the bovine homolog of SMARCAL1, purified from Escherichia coli34. ATPase assays were performed using ADAAD to establish that the identified DNA sequences could act as effectors28,29. Finally, CD spectroscopy was performed to monitor the conformational changes induced in the DNA molecule by ADAAD28,29.
To prove that the ATPase activity of the protein was essential for inducing a conformational change in the DNA molecule, either ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) was added to chelate Mg+2 or Active DNA-dependent ATPase A Domain Inhibitor Neomycin (ADAADiN), a specific inhibitor of the SWI/SNF protein, was added35,36. This CD spectroscopic technique can be utilized with any purified protein that has been demonstrated by ChIP or any other relevant assay to bind to a predicted genomic region of a promoter.
Protocol
1. Working concentration of the reaction components
- Prepare the working concentrations of buffers for CD and other reaction components freshly (see Table 1) and keep them at 4 °C before setting up the reactions.
NOTE: For the CD reactions described in this paper, the working concentrations of components are as follows: Sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) 1 mM, ATP 2 mM, DNA 500 nM, Protein 1 µM, MgCl2 10 mM, EDTA 50 mM, ADAADiN 5 µM.
2. ATPase activity
- Before CD spectroscopy, establish the ATPase activity of the protein in the presence of the DNA molecules to ensure that the protein used in the CD spectroscopy is active and to identify the DNA molecules that are optimally effective in eliciting ATP hydrolysis.
- Measure the ATPase activity of the protein in the presence of different DNA molecules by an NADH-coupled oxidation assay consisting of the following two reactions.
- Mix 0.1 µM ADAAD, 2 mM ATP, 10 nM DNA, and 1x REG buffer in a 96-well plate to a final volume of 250 µL.
NOTE: The pyruvate kinase enzyme uses the ADP and Pi to convert phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate, thus regenerating ATP. This ensures that ATP is always in a saturating concentration in the reaction. In the second reaction, the pyruvate formed by the action of pyruvate kinase is converted by lactate dehydrogenase to lactate. In this reaction, one NADH molecule is oxidized to NAD+. The consumption of NADH is measured by measuring the absorbance of the molecule at 340 nm. - Incubate for 30 min at 37 °C in an incubator.
- Measure the amount of NAD+ at 340 nm using a microplate reader.
- To measure the amount of NAD+, use the software provided along with the microplate reader.
- Click on the NADH assay to measure the absorbance at 340 nm.
- Place the 96-well plate on the plate holder in the instrument. Click on the Read Plate button to record the absorbance.
NOTE: The concentration of NAD+ is calculated using the molar extinction coefficient of NADH as 6.3 mM−1 by using eq (1).
A = εcl (1)
Here, A = Absorbance
ε = Molar extinction coefficient
c = Molar concentration
l = Optical path length in cm
- Mix 0.1 µM ADAAD, 2 mM ATP, 10 nM DNA, and 1x REG buffer in a 96-well plate to a final volume of 250 µL.
3. Choosing and preparation of CD cuvettes
- Collect CD spectra in high-transparency quartz cuvettes. Use rectangular or cylindrical cuvettes.
NOTE: A CD quartz cuvette (nominal volume of 0.4 mL, path-length of 1 mm) was used for all the reactions described in this paper. - Use a cuvette cleaning solution to clean the cuvette. Add 1% cuvette cleaning solution in water to make 400 µL of the solution, pour it in the cuvette, and incubate it at 37 °C for 1 h.
- Wash the cuvette with water several times to clean the cuvette. Take a scan of the water or buffer in the cuvette to check whether it is clean.
NOTE: The water or buffer must give a reading in the 0 to 1 mdeg range.
4. Preparation of proteins and DNA oligonucleotide
- Keep the volume of the protein below 50 µL in the reaction to minimize the amounts of the buffer components that sometimes cause the formation of ambiguous peaks. Keep the protein on the ice throughout the experiment to avoid any degradation.
- Use PAGE-purified DNA oligonucleotides in the reactions.
NOTE: In the reactions described here, DNA was used both in native as well as heat-cooled forms (fast-cooled (FC) and slow-cooled (SC)). Fast cooling promotes intramolecular bonding in the DNA, yielding more secondary structures. In contrast, slow cooling promotes intermolecular bonding in the DNA, resulting in fewer secondary structures. - For fast-cooling, heat DNA at 94 °C for 3 min on the heating block and immediately cool it on ice. For slow-cooling, heat DNA at 94 °C for 3 min and allow it to cool to room temperature at a rate of 1 °C per minute.
5. Setting up control experiments to record the baseline spectra
- Keep the reaction volume at 300 µL in all the reactions. Set up a total of 5 baseline reactions in 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes, one by one, as follows: i) Buffer + Water; ii) Buffer + MgCl2 + ATP + Water; iii) Buffer + MgCl2 + ATP + Protein + Water; iv) iii + EDTA or ADAADiN; v) Buffer + Protein +Water.
6. Setting up the experiments to record CD spectra
- Set up a total of 5 reactions, one by one, in 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes as follows: i) Buffer + DNA + Water; ii) Buffer + DNA + MgCl2 + ATP + Water; iii) Buffer + DNA + MgCl2 + ATP + Protein + Water; iv) iii + EDTA or ADAADiN; v) Buffer + DNA + Protein +Water.
7. Recording scan
- Turn on the gas and switch on the CD spectrometer.
- Switch on the lamp after 10-15 min. Switch on the water bath and set the holder temperature at 37 °C.
- Open the CD spectrum software.
- Set the temperature to 37 °C.
- Set the wavelength range at 180 - 300 nm.
- Set the time per point to 0.5 s.
- Set the scan number to 5.
- Click on Pro-Data Viewer, make a new file, and rename it with details about the experiment and date.
- Keep all the reaction components on ice to avoid any degradation. Make the baselines and reactions, one by one, in centrifuge tubes and mix them by pipetting. Transfer the reaction mix to the cuvette carefully, ensuring that there are no air bubbles.
- If performing a time-course experiment, incubate the reactions at 37 °C for the required time and take the scan. Add EDTA to the buffer containing the DNA, ATP, Mg+2, and protein to stop ATP hydrolysis.
- Increase the concentration of EDTA and its incubation time to inhibit ATPase activity completely.
- Subtract the baselines from the corresponding reactions in the software (e.g., subtract reaction 1 from baseline 1). Smoothen the data either in the CD spectrum software or in the data plotting software. Plot the data in the data plotting software.
NOTE: Subtracting the baselines from the corresponding reactions will give the net CD spectra of only DNA.
8. Data analysis and interpretation
- Use the formula given by eq (2) to convert the values obtained in millidegrees to mean residue ellipticity.
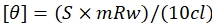 (2)
(2)
Here, S is the CD signal in millidegrees, c is the DNA concentration in mg/mL, mRw is the mean residue mass, and l is the path length in cm. - Plot a graph against wavelength and mean residue ellipticity using the data plotting software and analyze the peaks.
- To plot the graph, select the mean residue ellipticity on the Y-axis and wavelength on the X-axis and plot a straight line graph.
NOTE: This graph will provide the characteristics peaks of different forms of DNA. The forms of DNA corresponding to the peaks can be identified using existing literature6.
Results
ADAAD stabilizes a stem-loop like structure on the MYC promoter
Previous experimental evidence showed that SMARCAL1 is a negative regulator of MYC29. Analysis of the 159 bp long promoter region of the MYC gene by QGRS mapper showed that the forward strand had the potential to form a G-quadruplex (Table 2). Mfold showed that both strands of the MYC DNA could form a stem-loop-like structure ...
Discussion
The purpose of this article is to introduce the CD spectroscopy technique as an approach to study the conformational changes occurring in the DNA in the presence of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling proteins and to link these conformational changes to gene expression. CD spectroscopy provides a fast and easily accessible method to study the conformational changes in DNA.
A crucial point to be considered for this technique is the purity of the DNA and protein. It is advisable to ensure...
Disclosures
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility, JNU, for the CD spectrophotometer. V.J. and A.D. were supported by a fellowship from CSIR.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2-Mercaptoethanol | Fisher scientific | O3446I-100 | |
| Adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate | Sigmaaldrich | A2383 | |
| CD Quartz Cuvette | STARNA | 21-Q-1 | |
| Chirascan V100 CD spectrometer | Applied Photophysics | Not available | |
| EDTA Disodium Salt Dihydrate | SRL | 43272 | |
| Glutathione Sepharose 4B | GE Healthcare | 17-0756-01 | Glutathione affinity chromatography |
| Hellmanex III cleaning solution | Hellma | 9-307-011-4-507 | |
| L-Lactic Dehydrogenase | Sigmaaldrich | L2625 | |
| Magnesium Acetate Tetrahydrate | Fisher scientific | BP215-500 | |
| Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate | Fisher scientific | M33-500 | |
| NADH disodium salt | Sigmaaldrich | 10107735001 | |
| Phosphoenolpyruvate Monocyclohexylammonium Salt | SRL | 40083 | |
| Potassium Acetate | Fisher scientific | P178-3 | |
| Pyruvate Kinase | Sigmaaldrich | P1506 | |
| Sodium Phosphate Dibasic Anhydrous | Fisher scientific | S374-500 | |
| Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate | Fisher scientific | S369-500 | |
| Synergy HT microplate reader | BioTek | Not available | |
| Tris Base | Fisher scientific | BP152-500 |
References
- Woody, R. W. Circular dichroism. Methods in Enzymology. 246, 34-71 (1995).
- Kelly, S., Price, N. The Use of Circular Dichroism in the Investigation of Protein Structure and Function. Current Protein & Peptide Science. 1 (4), 349-384 (2000).
- Rodger, A., Marshall, D. Beginners guide to circular dichroism. The Biochemist. 43 (2), 58-64 (2021).
- Greenfield, N. J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nature Protocols. 1 (6), 2876-2890 (2006).
- Kypr, J., Kejnovská, I., Bednářová, K., Vorlíčková, M. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy of Nucleic Acids. Comprehensive Chiroptical Spectroscopy. , 575-586 (2012).
- Kypr, J., Kejnovska, I., Renciuk, D., Vorlickova, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (6), 1713-1725 (2009).
- Miyahara, T., Nakatsuji, H., Sugiyama, H. Helical Structure and Circular Dichroism Spectra of DNA: A Theoretical Study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 117 (1), 42-55 (2013).
- Khomyakova, E. B. Parallel intramolecular DNA triple helix with G and T bases in the third strand stabilized by Zn2+ ions. Nucleic Acids Research. 28 (18), 3511-3516 (2000).
- Kypr, J., et al. The unusual X-form DNA in oligodeoxynucleotides: dependence of stability on the base sequence and length. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 13 (6), 999-1006 (1996).
- Zohoorian-Abootorabi, T., Sanee, H., Iranfar, H., Saberi, M. R., Chamani, J. Separate and simultaneous binding effects through a non-cooperative behavior between cyclophosphamide hydrochloride and fluoxymesterone upon interaction with human serum albumin: multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling approaches. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy. 88, 177-191 (2012).
- Sharifi-Rad, A., Mehrzad, J., Darroudi, M., Saberi, M. R., Chamani, J. Oil-in-water nanoemulsions comprising Berberine in olive oil: biological activities, binding mechanisms to human serum albumin or holo-transferrin and QMMD simulations. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 39 (3), 1029-1043 (2021).
- Mokaberi, P., Babayan-Mashhadi, F., Amiri Tehrani Zadeh, Z., Saberi, M. R., Chamani, J. Analysis of the interaction behavior between Nano-Curcumin and two human serum proteins: combining spectroscopy and molecular stimulation to understand protein-protein interaction. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 39 (9), 3358-3377 (2021).
- Danesh, N., et al. Determining the binding site and binding affinity of estradiol to human serum albumin and holo-transferrin: fluorescence spectroscopic, isothermal titration calorimetry and molecular modeling approaches. Journal of Biomolecular Structure & Dynamics. 36 (7), 1747-1763 (2018).
- Sadeghzadeh, F., et al. Characterizing the binding of angiotensin converting enzyme I inhibitory peptide to human hemoglobin: influence of electromagnetic fields. Protein and Peptide Letters. 27 (10), 1007-1021 (2020).
- Chamani, J., et al. Cooperative alpha-helix formation of beta-lactoglobulin induced by sodium n-alkyl sulfates. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science. 293 (1), 52-60 (2006).
- Dareini, M., et al. A novel view of the separate and simultaneous binding effects of docetaxel and anastrozole with calf thymus DNA: Experimental and in silico approaches. Spectrochimica Acta. Part A, Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy. 228, 117528 (2020).
- Dehghani Sani, F., et al. Changes in binding affinity between ofloxacin and calf thymus DNA in the presence of histone H1: Spectroscopic and molecular modeling investigations. Journal of Luminescence. 203, 599-608 (2018).
- Hargreaves, D. C., Crabtree, G. R. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling: genetics, genomics and mechanisms. Cell Research. 21 (3), 396-420 (2011).
- Morettini, S., Podhraski, V., Lusser, A. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes and their various roles in cell cycle control. Frontiers in Bioscience: A Journal and Virtual Library. 13, 5522-5532 (2008).
- Flaus, A., Martin, D. M. A., Barton, G. J., Owen-Hughes, T. Identification of multiple distinct Snf2 subfamilies with conserved structural motifs. Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (10), 2887-2905 (2006).
- Flaus, A., Owen-Hughes, T. Mechanisms for ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling: the means to the end. The FEBS Journal. 278 (19), 3579-3595 (2011).
- Mizuguchi, G., et al. ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science. 303 (5656), 343-348 (2004).
- Elizondo, L. I., et al. Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia: SMARCAL1 loss-of-function and phenotypic correlation. Journal of Medical Genetics. 46 (1), 49-59 (2009).
- Baradaran-Heravi, A., et al. SMARCAL1 deficiency predisposes to non-Hodgkin lymphoma and hypersensitivity to genotoxic agents in vivo. American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A. 158 (9), 2204-2213 (2012).
- Bansal, R., et al. SMARCAL1, the annealing helicase and the transcriptional co-regulator. IUBMB life. 72 (10), 2080-2096 (2020).
- Yusufzai, T., Kadonaga, J. T. HARP is an ATP-driven annealing helicase. Science. 322 (5902), 748-750 (2008).
- Yusufzai, T., Kong, X., Yokomori, K., Kadonaga, J. T. The annealing helicase HARP is recruited to DNA repair sites via an interaction with RPA. Genes & Development. 23 (20), 2400-2404 (2009).
- Patne, K., et al. BRG1 and SMARCAL1 transcriptionally co-regulate DROSHA, DGCR8 and DICER in response to doxorubicin-induced DNA damage. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1860 (9), 936-951 (2017).
- Sharma, T., Bansal, R., Haokip, D. T., Goel, I., Muthuswami, R. SMARCAL1 negatively regulates c-Myc transcription by altering the conformation of the promoter region. Scientific Reports. 5, 17910 (2015).
- Muthuswami, R., Truman, P. A., Mesner, L. D., Hockensmith, J. W. A eukaryotic SWI2/SNF2 domain, an exquisite detector of double-stranded to single-stranded DNA transition elements. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (11), 7648-7655 (2000).
- Nongkhlaw, M., Dutta, P., Hockensmith, J. W., Komath, S. S., Muthuswami, R. Elucidating the mechanism of DNA-dependent ATP hydrolysis mediated by DNA-dependent ATPase A, a member of the SWI2/SNF2 protein family. Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (10), 3332-3341 (2009).
- Kikin, O., D'Antonio, L., Bagga, P. S. QGRS Mapper: a web-based server for predicting G-quadruplexes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Research. 34, 676-682 (2006).
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (13), 3406-3415 (2003).
- Gupta, M., et al. Ligand-induced conformation changes drive ATP hydrolysis and function in SMARCAL1. The FEBS Journal. 282 (19), 3841-3859 (2015).
- Dutta, P., et al. Global epigenetic changes induced by SWI2/SNF2 inhibitors characterize neomycin-resistant mammalian cells. PloS One. 7 (11), 49822 (2012).
- Muthuswami, R., et al. Phosphoaminoglycosides inhibit SWI2/SNF2 family DNA-dependent molecular motor domains. Biochemistry. 39 (15), 4358-4365 (2000).
- Gondeau, C. Circular dichroism and UV melting studies on formation of an intramolecular triplex containing parallel T*A:T and G*G:C triplets: netropsin complexation with the triplex. Nucleic Acids Research. 26 (21), 4996-5003 (1998).
- Nongkhlaw, M., Gupta, M., Komath, S. S., Muthuswami, R. Motifs Q and I are required for ATP hydrolysis but not for ATP binding in SWI2/SNF2 proteins. Biochemistry. 51 (18), 3711-3722 (2012).
- Luchnik, A. N. DNA conformational transitions induced by supercoiling control transcription in chromatin. Gene Regulation and Systems Biology. 8, 89-96 (2014).
- Siddiqui-Jain, A., Grand, C. L., Bearss, D. J., Hurley, L. H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (18), 11593-11598 (2002).
- Uribe, D. J., Guo, K., Shin, Y. -. J., Sun, D. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K and nucleolin as transcriptional activators of the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter through interaction with secondary DNA structures. Biochemistry. 50 (18), 3796-3806 (2011).
- Young, S. L., Krawczyk, S. H., Matteucci, M. D., Toole, J. J. Triple helix formation inhibits transcription elongation in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 88 (22), 10023-10026 (1991).
- Dürr, H., Flaus, A., Owen-Hughes, T., Hopfner, K. -. P. Snf2 family ATPases and DExx box helicases: differences and unifying concepts from high-resolution crystal structures. Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (15), 4160-4167 (2006).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved