Method Article
Rapid Isolation of Wild Nematodes by Baermann Funnel
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
This protocol outlines a method for efficiently extracting live nematodes from natural substrates in the field.
Abstract
Beyond being robust experimental model organisms, Caenorhabditis elegans and its relatives are also real animals that live in nature. Studies of wild nematodes in their natural environments are valuable for understanding many aspects of biology, including the selective regimes in which distinctive genomic and phenotypic characters evolve, the genetic basis for complex trait variation, and the natural genetic diversity fundamental to all animal populations. This manuscript describes a simple and efficient method for extracting nematodes from their natural substrates, including rotting fruits, flowers, fungi, leaf litter, and soil. The Baermann funnel method, a classical nematology technique, selectively isolates active nematodes from their substrates. Because it recovers nearly all active worms from the sample, the Baermann funnel technique allows for the recovery of rare and slow-growing genotypes that co-occur with abundant and fast-growing genotypes, which might be missed in extraction methods that involve multiple generations of reproduction. The technique is also well suited to addressing metagenetic, population-genetic, and ecological questions. It captures the entire population in a sample simultaneously, allowing an unbiased view of the natural distribution of ages, sexes, and genotypes. The protocol allows for deployment at scale in the field, rapidly converting substrates into worm plates, and the authors have validated it through fieldwork on multiple continents.
Introduction
Valuable biological insights are emerging as researchers who study C. elegans in the lab expand their focus to C. elegans and related rhabditid nematodes in the wild. Studies of wild nematodes place genes and genomes in their natural context, revealing functions potentially obscured by laboratory conditions1,2,3,4,5. These studies generate insights into the prerequisite for evolution itself, genetic variation6,7,8,9,10. The natural genetic variation captured by wild samples also provides inroads into the genetic basis of many complex traits11,12,13.
When designing studies that require the isolation of natural populations of nematodes, particularly when performing remote fieldwork, practical considerations come to the fore. This protocol aims to cleanly isolate entire populations of active nematodes that can be cultured on OP50 from bait or wild substrates. The method is well suited for extracting free-living rhabditid and diplogasterid nematodes, including Caenorhabditis, Oscheius, and Pristionchus.
There are many techniques for isolating nematodes from their substrates14,15. The most basic approach is to place the substrate directly onto a nematode-medium plate, picking animals as they crawl out8,15. This method requires large amounts of time and labor if the goal is to isolate all nematodes from a sample. More sophisticated techniques take advantage of the animals' weight, size, mobility, or some combination of these14. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages in terms of setup and throughput. They also differ in their sampling biases and may select for certain nematodes if the animals in the sample vary along the axis of the method's separation principle.
The Baermann funnel method was first described in 1917 by Dutch Physician G. K. T. F. Baermann, who invented the device on Java while studying soil-dwelling nematodes, including the parasitic hookworm16. The Baermann funnel functions based on the principle of mobility. The substrate is placed in a funnel lined with a cloth or paper filter (a "Kimwipe" is used for this study, referred to as "lint-free wipe" in the current protocol) and sealed shut at the bottom. The funnel is then filled with water, submerging the sample while the filter separates it from the sealed outlet. Active nematodes in the sample release themselves into the water and swim through the filter, eventually settling at the bottom of the funnel. The funnel outlet is opened, and a drop of nematodes is expelled onto a plate (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Summary of the Baermann funnel technique. (A) Collecting a bacteria-rich sample from a site of interest. (B) Submerging the sample in a Baermann funnel and waiting for worms to wriggle out and sink. (C) Releasing a single drop from the funnel. (D) Moving single hermaphrodites or mated females to separate plates. Illustration created by Ramin Rahni. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
The Baermann funnel will not work for every kind of nematode (see Discussion section for specific alternatives) and is best suited to those that are active forms in the size range of Caenorhabditis or smaller14. However, if a study can use the Baermann funnel, there are many advantages. The method is practical in the field, requiring limited setup, hands-on time, and cost. The researcher is left with a clean sample without the obstruction of the substrate on the plate, which makes picking easy. Using a filter also prevents contamination of the plate by insect larvae or mites, which chew up plates or prey on nematodes in the sample. Most importantly, the Baermann funnel efficiently extracts nearly the whole population from the substrate14, which may be required depending on the study's design. For example, researchers interested in counting wild populations' stage or sex distribution, finding slow-growing or rare genotypes, or sampling nematodes not attracted to OP50 might benefit from this method. This is appropriate for researchers studying ecological17, population genetic18, or metagenetic19 questions as the sampling scheme takes a snapshot of the population at the sampling time.
The present manuscript describes a complete protocol for isolating populations of nematodes using the Baermann funnel and establishing isofemale and isohermaphrodite lines in the field, using equipment chosen for easy transport. For researchers conducting fieldwork near their labs, many of these steps can be omitted or simplified.
Protocol
1. Preparation of seeded NGM plates in the field
- Before travel, weigh 23.005 g of Nematode Growth Medium (NGM) (see Table of Materials) powder and pre-pack in a sealable plastic bag. Make one bag for each liter of media desired.
NOTE: Pre-packaging before travel bypasses the need for a functional balance in the field. - Prior to travel, prepare 1 mL of 1M MgSO4, 1 mL of 1M CaCl2, and 25 mL of 1M potassium phosphate buffer for each liter of media desired. To make 1 L of potassium phosphate buffer, dissolve 108.3 g of KH2PO4 and 35.6 g of K2HPO4 in water, as described in WormBook20.
- Before travel, make an overnight culture of OP50 (see Table of Materials) grown in LB at 37 °C, as described in WormBook20. Aliquot the culture into 50 mL conical tubes and wrap the tops with paraffin film to prevent leakage.
- In the field, dissolve the contents of the NGM packet into 973 mL of double-distilled water (ddH20) or the purest, most sterile water available in a 1 L flask or bottle.
- Place the media flask or bottle, with a loose cap or aluminum foil cover, in a boiling hot water bath on a hot plate or stove. Stir occasionally until all the powder is dissolved and is clear (this takes ~30 min).
NOTE: If a magnetic hot plate is available, a stir bar is an excellent option to limit the amount of manual stirring. - Remove the media from the water bath and cool to ~58 °C with occasional shaking or with a stir bar. Once the media is cooled to 58° C, use serological or standard pipettes to add 25 mL of 1M potassium phosphate buffer, 1 mL of 1M MgSO4, and 1 mL of 1M CaCl2, mixing well between each step.
- In the most sterile environment available, pipette or pour the media into plates of the desired size and allow to cool and solidify overnight. Pour one 60 mm plate (~10 mL) for each substrate sample. Pour one 35 mm plate (~3.5 mL) for each isofemale line; the number of small plates needed is difficult to predict in advance.
- Pipette 50 µL of OP50 culture onto each plate and allow it to dry and grow overnight before use.
2. Collection of the nematode substrates
- Identify a bacteria-rich substrate in the field. Some examples include rotting fruit, flowers, fungi, and stems of herbaceous plants. Soil and leaf litter are also suitable, though they rarely contain Caenorhabditis.
- With a gloved hand, place a sample of this substrate (1-15 cm3) into a sealable plastic bag (see Table of Materials) labeled with a unique sample ID (Figure 1A).
- Record the sample ID, latitude, longitude, date, description of the substrate, and any other local environmental measurements relevant to the experiment, including ambient and substrate temperature, time of collection, condition of substrate, presence of substrate-associated macroinvertebrates, and so on. A smartphone app is available to streamline this process21.
3. Preparation of an array of Baermann funnels
- For each funnel, use scissors to cut a segment of rubber tubing (see Table of Materials) ~3 cm long.
- Fit the tubing segment over the end of a plastic funnel (see Table of Materials). This may take some effort as the fit is very tight.
- Slide a tubing clamp over the rubber tubing and clamp it shut.
- To make a funnel holder, use a scalpel to cut circular holes of 35 mm diameter in the bottom of a cardboard fly-vial tray (see Table of Materials) that has not been folded together from its flat shipping orientation. A standard tray can accommodate 12 of these holes in a 3 x 4 array.
- Invert the cardboard, fold down the sides once (not twice, as one would to make a fly-vial tray), and tape the sides together to elevate the inverted cardboard tray (Figure 2).
- Place funnels in the holes, first making sure that the tubing clamps are in the closed position.
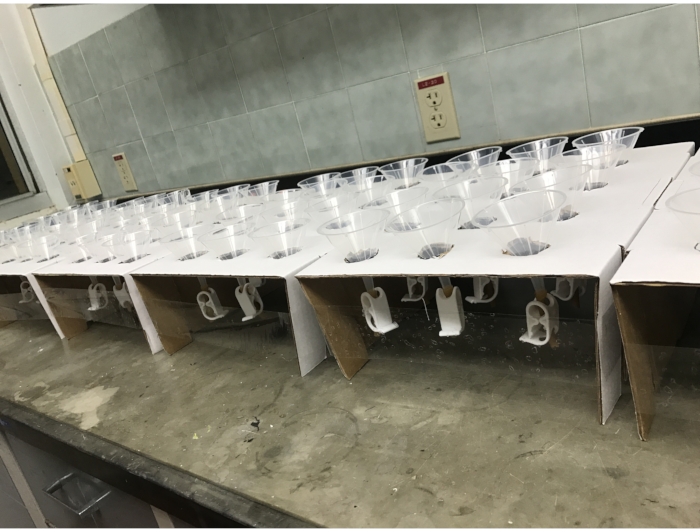

Figure 2: Repurposed cardboard fly vial trays, folded and cut to support 12 Baermann funnels each. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
4. Transfering of samples into the funnels
- Pour water (as sterile as available) into each funnel, filling it about 3 cm below the rim. If air bubbles are trapped in the tubing, tap the funnel to release them.
- With gloved hands, place a lint-free wipe or specifically a Kimwipe (folded in half to make a square) over the funnel, and press down on the center so that it is submerged in the water.
- Manually break large solid pieces of natural substrates (fruit, flower, soil, leaf litter, etc.) into smaller fragments to minimize the distance worms must travel to fall out of the substrate.
NOTE: Leaf litter and awkwardly shaped samples can be preprocessed in a food processor or blender. - Gently place a sample of the natural substrate (1-15 cm3) onto the tissue/lint-free wipe in a funnel without puncturing the tissue and without the sample protruding above the rim.
- Label the funnel, or the cardboard next to the funnel, with the sample ID corresponding to field collection notes.
- Fold the corners of the tissue/lint-free wipe over the sample (Figure 1B). Be careful to keep the sample contained within the tissue/lint-free wipe so that no soil or debris can pass to the bottom of the funnel.
NOTE: This step is to prevent the corners from draping over the edge of the funnel, where they would wick the water from the funnel over the sides. - With hands, a spatula, or a pipette tip, pick out any active insects, millipedes, or other animals that may travel from funnel to funnel, cross-contaminating samples. Wrap the tissue/lint-free wipe entirely around the sample or lay a second tissue across the top of the sample to prevent cross-contamination.
- Add more water to funnels so that the entire sample is submerged (Figure 3).
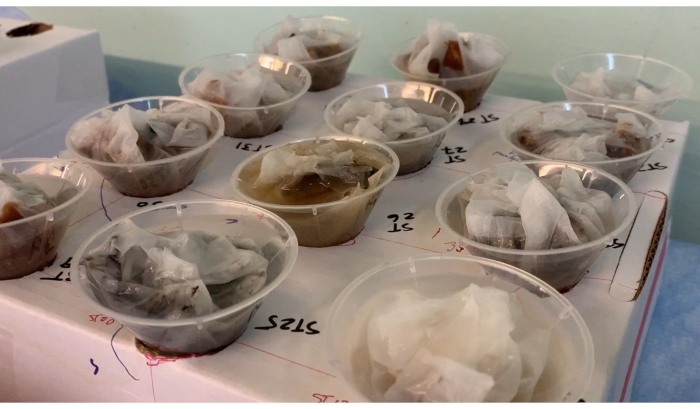

Figure 3: Assembled Baermann funnels. Each sample is wrapped in tissue/lint-free wipe and submerged under water in the funnel, which is clamped shut. Over a period of ~12 h, the nematodes will migrate through the tissue and to the bottom of the funnel. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
5. Extraction of nematodes from the funnels
- Wait for ~12 h or overnight. During this time, active worms will wriggle out of the substrate, through the tissue/lint-free wipe and down to the bottom of the clamped funnel.
NOTE: Waiting much longer than 12 h risks worm mortality due to hypoxia or pathogenic infection, which may also be a risk at shorter durations for samples that are particularly crowded with worms and bacteria. - Write the sample ID of a funnel on the bottom of a 60 mm NGM worm plate seeded with a spot of OP50 E. coli bacteria. Remove the lid from the plate.
- Remove the funnel containing that sample from the funnel stand. Using one hand to hold the funnel upright above the open worm plate, use the other hand to release pressure on the tubing clamp, allowing one drop of water to fall from the tubing onto the worm plate (Figure 1C). As soon as water drops from the funnel, quickly clamp it shut again to prevent flooding the NGM plate.
NOTE: To select worms attracted to OP50, including Caenorhabditis species, release the drop away from the bacterial lawn. When the water soaks into the plate or evaporates, Caenorhabditis nematodes will crawl into the bacterial lawn. - Clean up: Throw out the contents of the funnels. Wash the funnels with hot water for subsequent reuse.
6. Establishing the cultures
- Observe the isolated nematodes under the stereomicroscope at a magnification of 5x-50x. The plates should include nematodes, and at much lower frequencies, small oligochaete annelids, tardigrades, rotifers, and small crustaceans (Figure 4).
NOTE: If the funnel has been set up correctly, no mites, insects, or visible non-living material will have made it through the funnel.
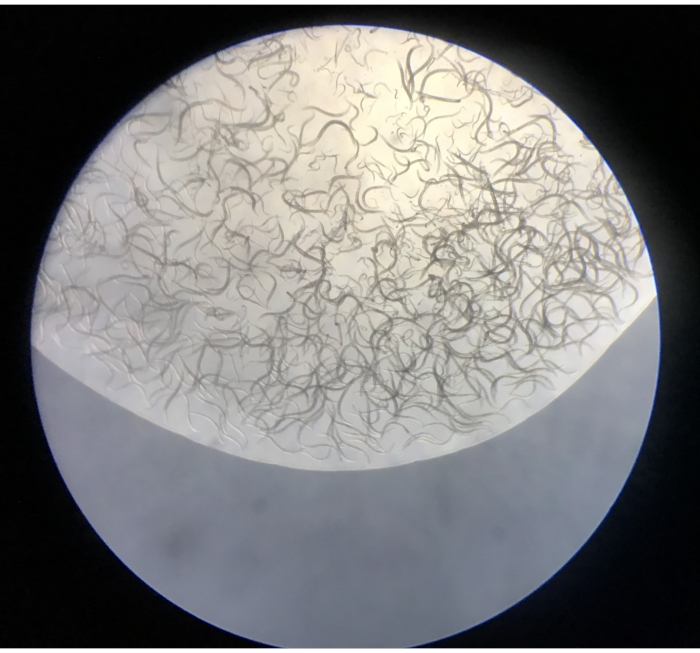
Figure 4: Contents of the first droplet released from a Baermann funnel onto an NGM plate. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
- To establish isohermaphrodite or isofemale lines, use a worm pick to transfer each L4 hermaphrodite or mated adult female (recognizable by their larger body size and lack of the distinct male tail22) to a separate 35 mm NGM plate seeded with OP50 (Figure 1D). Use a lighter to sterilize the worm pick before and after transferring worms.
- Use paraffin film to wrap plates thoroughly for travel.
Results
This protocol was used to isolate nematodes from fruit, flowers, fungi, soil, and stems on Barro Colorado Island, Panamá, at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute field station in August of 2018. Of 131 substrates processed by a single investigator over four days, 130 substrates (99.2%) yielded nematodes. Forty-four of the substrates (33.6%) yielded Caenorhabditis nematodes (Figure 5). Subsequent analysis of cultures established from these forty-four substrates, by PCR and mating tests23, revealed the presence of six different Caenorhabditis species – C. becei, C. tropicalis, C. briggsae, C. sp. 24, C. sp. 57, and C. panamensis.
This protocol was used again to isolate nematodes from various substrates in the Chernobyl Exclusion Zone, Ukraine, over four days in August of 2019. Live worms were recovered from 62 out of 63 soil samples, 1 out of 17 invertebrate samples, 31 out of 75 fruit samples, 1 out of 12 bait samples (see Discussion section), and no worms were recovered from mushroom, river reed, or wolf feces samples (one sample collected of each). Subsequent sequencing of 18S ribosomal DNA15 identified these nematodes as Oscheius, Panagrolaimus, Acrobeloides, Mesorhabditis, Panagrellus, Pristionchus, and Pelodera, but no Caenorhabditis were identified (Figure 5).
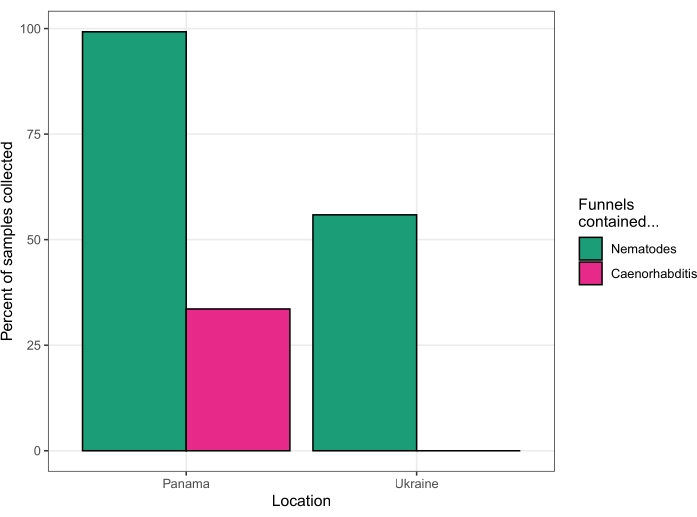
Figure 5: Success rates of two collection trips. Panama in 2018 (left) and Ukraine in 2019 (right). Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
Discussion
The central principle of this method is that nematodes will pass through the tissue submerged in water, while their substrate and larger invertebrate contaminants will not. The critical steps of the protocol are (1) collecting an appropriate substrate, (2) submerging the substrate, wrapped in a filtering material, in water, (3) collecting worms that have passed through the filter and sunk to the bottom of the water, and (4) isolating individual worms to create isofemale or isohermaphrodite lines. All other parts of the method are amenable to modification as necessary according to the resources available, the nature of the substrates, or the fieldwork goals. Some modifications worth considering are as follows.
Baiting the worms by planting fruit
If there is not an ample supply of bacteria-rich rotting material to be found in the field site, one may wish to bring a sample, such as a piece of apple or tomato, to leave to rot. Pin the bait down well with a few stakes so that larger animals do not remove them and so it can easily be found later for collection. Avoid direct sunlight, where the bait might dry before it rots.
Constructing funnel apparatus out of whatever materials are available
Any structure with holes large enough to accommodate the tubing clamp and stable enough to support a top-heavy funnel will work. For a single funnel, a drinking glass is a suitable holder. Any kind of tissue – facial tissue, toilet paper, or paper towels – can be used.
Putting less material in funnels, or adjusting the wait time, to prevent hypoxia or infection
If the sample has a very high concentration of worms or bacteria, nematodes may begin dying from hypoxia or infection before the 12 h incubation is complete. If this is a concern, the researcher may check funnels earlier or prepare an additional funnel with a very small subsample of the highly populated substrate.
Adjusting the NGM plate preparation to experimental needs and constraints
NGM plates can be prepared with whatever media and food source is appropriate to the experiment. The field protocol described above is designed to minimize baggage weight. Depending on baggage limitations and the fieldwork timing, bringing already-poured NGM plates – either prepared in the lab or purchased commercially – may be preferable rather than pouring plates in the field.
Performing the funnel isolations in the laboratory
The protocol describes carrying out the complete procedure under field conditions to capture the nematode population as it occurs in nature. For some research goals, it may be sufficient to isolate nematodes later, after traveling back to the lab with samples in sealed bags. Even then, the Baermann funnel method provides a cleaner and complete sample of the surviving nematodes than other isolation methods. However, samples in sealed bags may experience selection during travel, as they are exposed to potential extremes of temperature and hypoxia. This can be minimized by performing isolations as soon as possible after sample collection.
A common alternative method to the Baermann funnel involves placing the substrate directly onto an NGM plate and waiting for worms to crawl out, which is either highly labor-intensive or results in the incomplete collection of the population. It also yields plates contaminated with mites and insect larvae. The Baermann funnel method is a low-cost, low-tech, low-labor strategy for quickly separating the entire population of active worms from their substrate.
The Baermann funnel method is not universally applicable for collecting all types of wild nematodes. Some plant-dwelling nematodes take much longer than 12 h to emerge from their substrate and will be absent from a droplet released too early, while some insect parasites will crawl to the top of the funnel rather than the bottom, also evading collection14. Alternatives to the Baermann funnel either require more specialized equipment or more labor to recover the worms. However, they may still be preferred if the caveats above are a problem for the experiment. Alternative options, reviewed by van Bezooijen14, include the funnel spray method, which provides a constant mist of water to funnels, adding oxygen and allowing the overflow of bacteria in suspension. This allows for a more extended extraction period of nematodes from plants. The blender centrifugal flotation method recovers slow-moving, inactive, or upward-crawling nematodes by separating them by their specific gravity, the Oostenbrink elutriator applies an undercurrent to separate settling sediment from suspended nematodes, and Cobb's Method uses a series of sieves to isolate nematodes by their size, shape, and sedimentation rate14. To collect rhabditids, though, the Baermann funnel effectively produces clean samples quickly and with minimal effort.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH grants R35GM141906 and R21ES031364 and Damon Runyon Fellowship DRG-2371-19.
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 1 L glass bottle | NA | NA | Step 1 - vessel for making plate media |
| 1 mL pipette tips | any | NA | Step 1 - dispense worm media additives and seed plates |
| 1 mL pipetter | any | NA | Step 1 - dispense worm media additives and seed plates |
| 35 mm worm plates | Tritech | T3500 | Step 1 - worm plates |
| 4mm ID rubber tubing | Fisher | 14178A | Step 3 - part of the funnel |
| 60 mm worm plates | Greiner | 628161 | Step 1 - worm plates |
| 65 mm Funnel | Fisher | 22170156 | Step 3 - part of the funnel |
| Calcium chloride | Fisher | C79-500 | Step 1 - worm plate medium |
| Cooking pot | NA | NA | Step 1 - a water bath for melting the agar to pour plates |
| E. coli strain OP50 | Caenorhabditis Genetics Center | OP50 | Step 1 - worm food |
| Field microscope | OMAX | G223CS | Step 6 - for viewing worms in the field |
| Fly vial storage tray | Azer Scientific | ES-260T | Step 3 - to build a platform to hold 12 funnels |
| Hot plate or stove | NA | NA | Step 1 - to heat the water bath |
| Kimwipes | KimberlyClark | 34120 | Step 4 - filter for the funnels |
| LB media | Gibco | 10855021 | Step 1 - for growing OP50 |
| Lighter | NA | NA | Step 6 - sterilize the worm pick |
| Magnesium sulfate | Fisher | M63-500 | Step 1 - worm plate medium |
| NGM-lite agar | USBiological | N1000 | Step 1 - worm plate medium |
| Parafilm M wrapping film | Fisher | 13-374-10 | Step 6 - pack worm plates for travel |
| Potassium phosphate dibasic | Fisher | BP363-500 | Step 1 - worm plate medium |
| Potassium phosphate monobasic | Fisher | P285-3 | Step 1 - worm plate medium |
| scalpel | NA | NA | Step 3 - cut holes for the funnels |
| scissors | NA | NA | Step 3 - cut the rubber tubing |
| Tape | NA | NA | Step 3 - tape the funnel holder together |
| Tubing clamps | Fisher | 5869 | Step 3 - part of the funnel |
| Worm pick | NA | NA | Step 6 - for isolating individual worms |
| Ziplock-style storage bags | NA | NA | Step 2 - to bag a substrate sample |
References
- Frezal, L., Felix, M. A. C. elegans outside the Petri dish. Elife. 4, 05849 (2015).
- Greene, J. S., et al. Balancing selection shapes density-dependent foraging behaviour. Nature. 539 (7628), 254-258 (2016).
- Reddy, K. C., et al. Antagonistic paralogs control a switch between growth and pathogen resistance in C. elegans. PLOS Pathogens. 15 (1), 1007528 (2019).
- Schulenburg, H., Felix, M. A. The natural biotic environment of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 206 (1), 55-86 (2017).
- Zhang, F., et al. Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for microbiome research. Frontiers in Microbiology. 8, 485 (2017).
- Andersen, E. C., et al. Chromosome-scale selective sweeps shape Caenorhabditis elegans genomic diversity. Nature Genetics. 44 (3), 285-290 (2012).
- Cook, D. E., Zdraljevic, S., Roberts, J. P., Andersen, E. C. CeNDR, the Caenorhabditis elegans natural diversity resource. Nucleic Acids Research. 45, 650-657 (2017).
- Crombie, T. A., et al. Deep sampling of Hawaiian Caenorhabditis elegans reveals high genetic diversity and admixture with global populations. Elife. 8, 50465 (2019).
- Lee, D., et al. Balancing selection maintains hyper-divergent haplotypes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature Ecology & Evolution. 5 (6), 794-807 (2021).
- Rockman, M. V., Kruglyak, L. Recombinational landscape and population genomics of Caenorhabditis elegans. PLOS Genetics. 5 (3), 1000419 (2009).
- Evans, K. S., van Wijk, M. H., McGrath, P. T., Andersen, E. C., Sterken, M. G. From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation. Trends in Genetics. 37, 933-947 (2021).
- Gaertner, B. E., Phillips, P. C. Caenorhabditis elegans as a platform for molecular quantitative genetics and the systems biology of natural variation. Genetics Research (Cambridge Core). 92 (5-6), 331-348 (2010).
- Noble, L. M., Rockman, M. V., Teotonio, H. Gene-level quantitative trait mapping in Caenorhabditis elegans. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics. 11 (2), 061 (2021).
- Van Bezooijen, J. . Methods and techniques for nematology. , (2006).
- Barrièrre, A., Félix, M. -. A. Isolation of C. elegans. and related nematodes. Wormbook. , (2014).
- Baermann, G. Eine einfache Methode zur Auffindung von Anklostomum (Nematoden) Larven in Erdproben. Geneeskundig tijdschrift voor Nederlandsch-Indië. 57, 131-137 (1917).
- Gray, N. F. Ecology of nematophagous fungi Panagrellus redivivus as the target organism. Plant and Soil. 297, 293-297 (1983).
- Mallez, S., Castagnone, C., Espada, M., Viera, P., Eisenback, J., Mota, M., Guillemaud, T., Castagnone-Sereno, P. First insights into the genetic diversity of the pinewood nematode in its native area using new polymorphic microsatellite loci. PLOS ONE. 8 (3), 4-11 (2013).
- Kerfahi, D., Tripathi, M. B., Porazinska, L. D., Park, J., Go, R., Adams, M. J. Do tropical rain forest soils have greater nematode diversity than High Arctic tundra? A metagenetic comparison of Malaysia and Svalbard. Global Ecology and Biogeography. 25, 716-728 (2016).
- Stiernagle, T. Maintenance of C. elegans. WormBook. , 1-11 (2006).
- Di Bernardo, M., Crombie, T. A., Cook, D. E., Andersen, E. C. easyFulcrum: An R package to process and analyze ecological sampling data generated using the Fulcrum mobile application. PLOS ONE. 16, 0254293 (2021).
- Lints, R., Hall, D. H. Handbook of C. elegans male anatomy. WormAtlas. , (2005).
- Kiontke, K., Félix, M. -. A., Ailion, M., Rockman, M. V., Braendle, C., Pénigault, J. -. B., Fitch, D. H. A phylogeny and molecular barcodes for Caenorhabditis, with numerous new species from rotting fruits. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 11, 339 (2011).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved