Clark Y-14 Tragflächenleistung: Einsatz von Hochauftriebsvorrichtungen (Klappen und Vorflügel)
Überblick
Quelle: David Guo, College of Engineering, Technology, and Aeronautics (CETA), Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), Manchester, New Hampshire
Ein Flügel ist das haupthebe-erzeugungserzeugende Gerät in einem Flugzeug. Die Flügelleistung kann durch den Einsatz von Hochhubgeräten wie Klappen (an der Hinterkante) und Lamellen (an der Vorderkante) während des Starts oder der Landung weiter verbessert werden.
In diesem Experiment wird ein Windkanal verwendet, um bestimmte Luftgeschwindigkeiten zu erzeugen, und ein Clark Y-14 Flügel mit Klappe und Latte wird verwendet, um Daten zu sammeln und zu berechnen, wie z. B. den Hebe-, Luftwiderstands- und Pitching-Moment-Koeffizienten. Eine Clark Y-14 Tragfläche ist in Abbildung 1 dargestellt und hat eine Dicke von 14% und ist auf der unteren Oberfläche von 30% des Akkords nach hinten flach. Hier wird anhand von Windkanaltests demonstriert, wie die aerodynamische Leistung eines Clark Y-14-Flügels durch Hochhubgeräte wie Klappen und Latten beeinflusst wird.
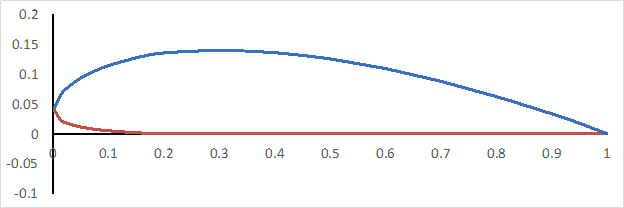
Abbildung 1. Clark Y-14 Tragflächenprofil.
Verfahren
- Verwenden Sie für dieses Verfahren einen aerodynamischen Windkanal mit einem Testabschnitt von 1 ft x 1 ft und einer maximalen Betriebsgeschwindigkeit von 140 mph. Der Windkanal muss mit einem Datenerfassungssystem (in der Lage, Angriffswinkel, normale Kraft, Axialkraft und Pitching-Moment) und einem Stichgleichgewicht ausgestattet sein.
- Öffnen Sie den Testabschnitt, und installieren Sie den Flügel auf der Stichbalance. Beginnen Sie mit der Konfiguration des sauberen Flügels.
- Legen Sie ein Hand-Clinometer auf den Sti
Ergebnisse
Die Ergebnisse der Clean Wing-Konfiguration sind in Tabelle 1 dargestellt. Die Abbildungen 6 - 8 zeigen alle drei Koeffizienten vs. Angriffswinkel, b, für alle vier Konfigurationen. In Abbildung 6 verbesserten sowohl die Klappe als auch die Latte den Hubkoeffizienten, jedoch auf unterschiedliche Weise. Vergleicht man den sauberen Flügel und die Lattenliftkurve, so überlappen sich die beiden Kurven bei niedrigen Angriffswinkeln fast. Die saubere Flügelliftkurve erreicht einen Spitzenwe...
Anwendung und Zusammenfassung
Die Aufzugserzeugung kann durch den Einsatz von Hochhubgeräten wie Klappen und Lamellen verbessert werden. Die meisten Flugzeuge sind mit Klappen ausgestattet, und alle kommerziellen Transportflugzeuge haben sowohl Klappen als auch Lamellen. Es ist wichtig, die Leistung eines Flügels mit Klappen und Lamellen während der Flugzeugentwicklung zu charakterisieren.
Bei dieser Demonstration wurde ein Clark Y-14 Flügel mit einer Klappe und einer Latte in einem Windkanal bewertet. Die Kräfte und ...
Referenzen
- John D. Anderson (2017), Fundamentals of Aerodynamics, 6th Edition, ISBN: 978-1-259-12991-9, McGraw-Hill
pringen zu...
Videos aus dieser Sammlung:

Now Playing
Clark Y-14 Tragflächenleistung: Einsatz von Hochauftriebsvorrichtungen (Klappen und Vorflügel)
Aeronautical Engineering
13.4K Ansichten

Aerodynamisches Verhalten eines Modellflugzeugs: Die DC-6B
Aeronautical Engineering
8.3K Ansichten

Charakterisierung von Propellern: Variationen von Pitch, Durchmesser und Blattzahl, und deren Einfluss auf die Leistung
Aeronautical Engineering
26.5K Ansichten

Verhalten der Tragflächen: Druckverteilung über einem Clark Y-14-Flügel
Aeronautical Engineering
21.2K Ansichten

Turbulence Sphere-Methode: Bewertung der Strömungsqualität im Windkanal
Aeronautical Engineering
8.7K Ansichten

Querzylindrische Strömung: Messung der Druckverteilung und Einschätzung des Strömungswiderstandskoeffizient
Aeronautical Engineering
16.2K Ansichten

Analyse einer Düse: Variationen in Machzahl und Druck entlang einer konvergierenden und einer konvergierend-divergierenden Düse
Aeronautical Engineering
38.0K Ansichten

Schlieren-Imaging: Eine Technik zur Visualisierung der Eigenschaften von Überschallströmungen
Aeronautical Engineering
11.7K Ansichten

Strömungsvisualisierung in einem Wassertunnel: Beobachtung des Vorderkantenwirbels über einem Deltaflügel
Aeronautical Engineering
8.2K Ansichten

Surface Dye Flow Visualisierung: Eine qualitative Methode zur Beobachtung von Stromlinien in Überschallströmungen
Aeronautical Engineering
4.9K Ansichten

Pitotrohr: Ein Gerät zur Messung der Luftströmungsgeschwindigkeit
Aeronautical Engineering
49.2K Ansichten

Konstant-Temperatur-Anemometrie: Ein Werkzeug zur Untersuchung der turbulenten Grenzschichtströmung
Aeronautical Engineering
7.3K Ansichten

Druckwandler: Kalibrierung mit einem Pitotrohr
Aeronautical Engineering
8.5K Ansichten

Echtzeit-Flugsteuerung: Eingebettete Sensorkalibrierung und Datenerfassung
Aeronautical Engineering
10.3K Ansichten

Multicopter-Aerodynamik: Charakterisierung der Schubkraft bei einem Hexacopter
Aeronautical Engineering
9.2K Ansichten
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Alle Rechte vorbehalten