24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Consider an external electric field propagating through a homogeneous medium. When the electric field crosses the surface boundary of the medium, it undergoes a discontinuity. The electric field can be resolved into normal and tangential components. The amount by which the field changes at any boundary is given by the difference between the field components above and below the surface boundary.
The surface integral of an electric field is given by Gauss's law in integral form and is related to the total enclosed charge. Consider a Gaussian pillbox on the surface boundary. The surface integral of the field is the sum of the integrals over all the surfaces of the pillbox. If the thickness of the pillbox tends to zero, then the surface integral includes only the contributions of the pillbox faces above and below the boundary. Solving this gives the discontinuity of the normal component of the electric field at any surface boundary.
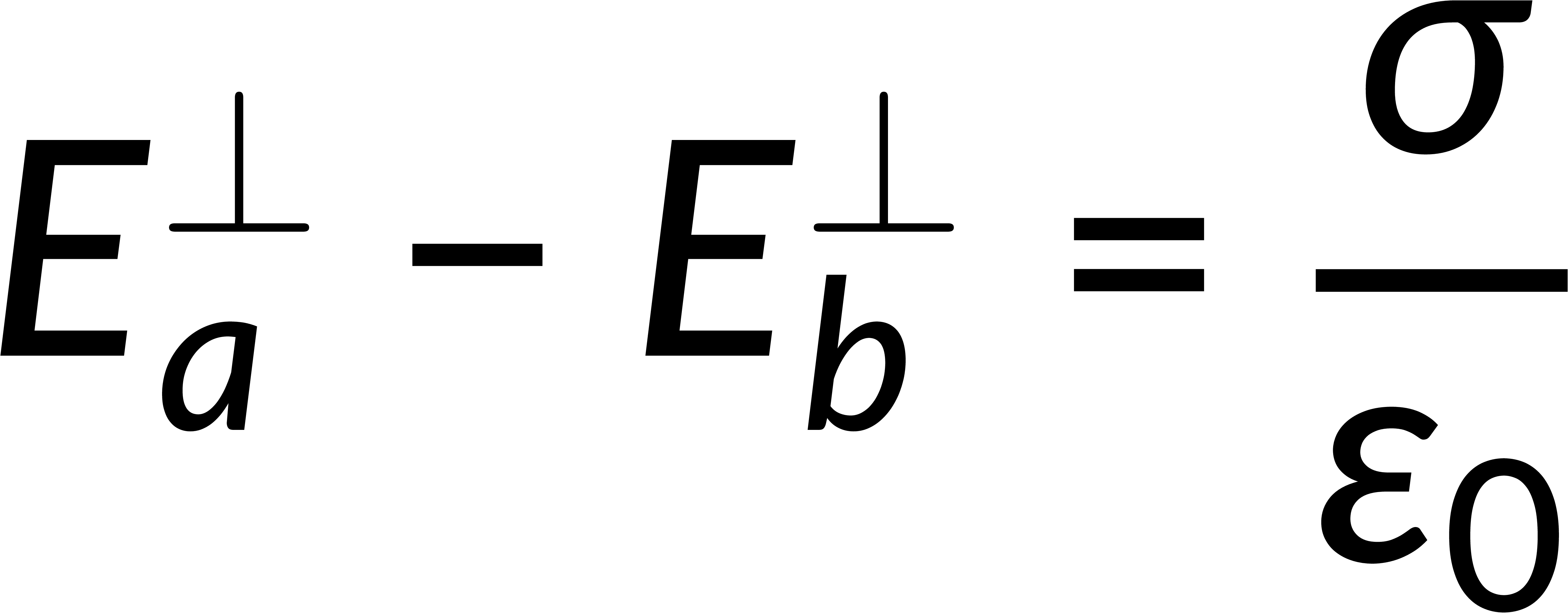
To estimate the discontinuity of the tangential component, consider a loop on the surface boundary. The integration of the electric field over this closed path is zero. Breaking this into the contributions from four parts of the loop and applying the condition that the thickness of the loop tends to zero implies that the tangential component of the electric field is continuous across the boundary.
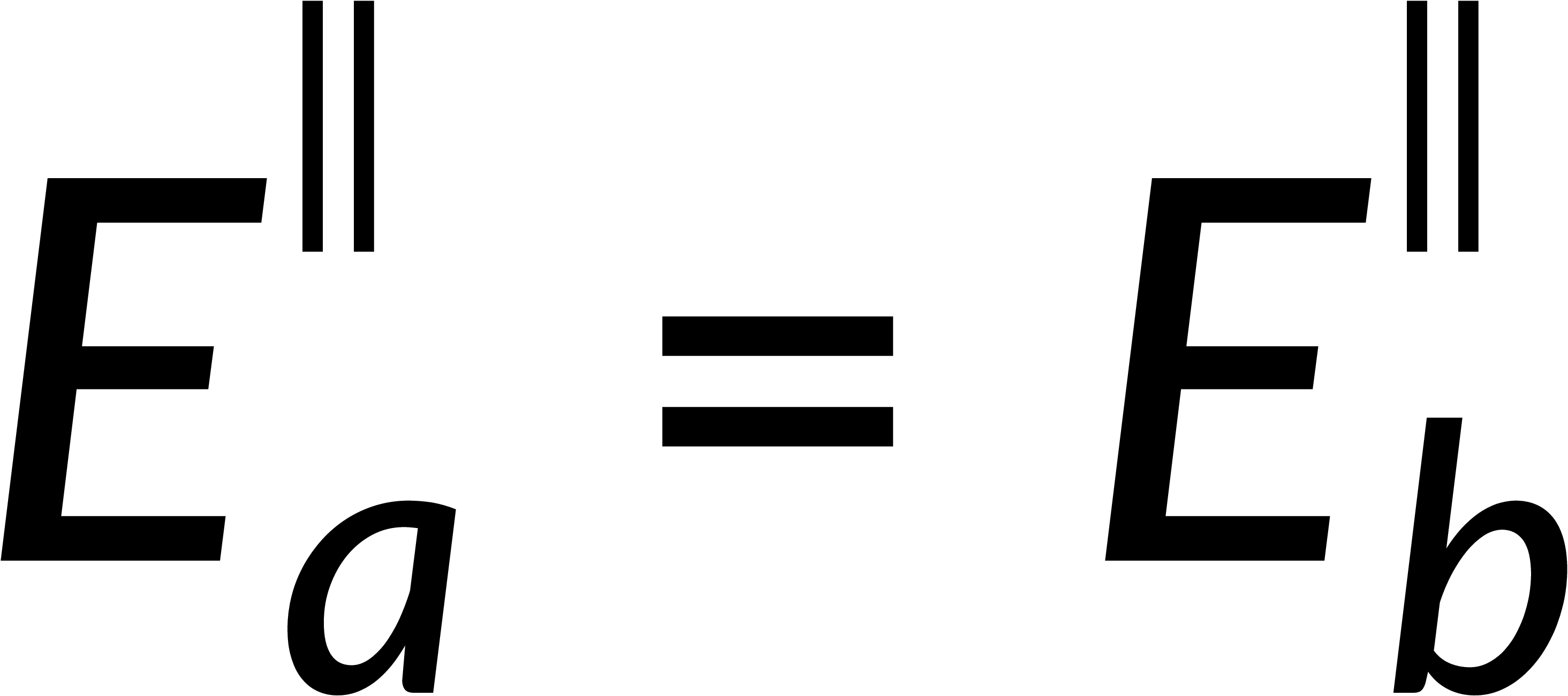
Combining the normal and tangential equations, the field at the boundary can be written by defining the unit vector perpendicular to the surface. It is known that the electric field is the negative gradient of the potential. The line integral of the field from below to above the boundary tends to zero, implying that the potential is continuous across any boundary.
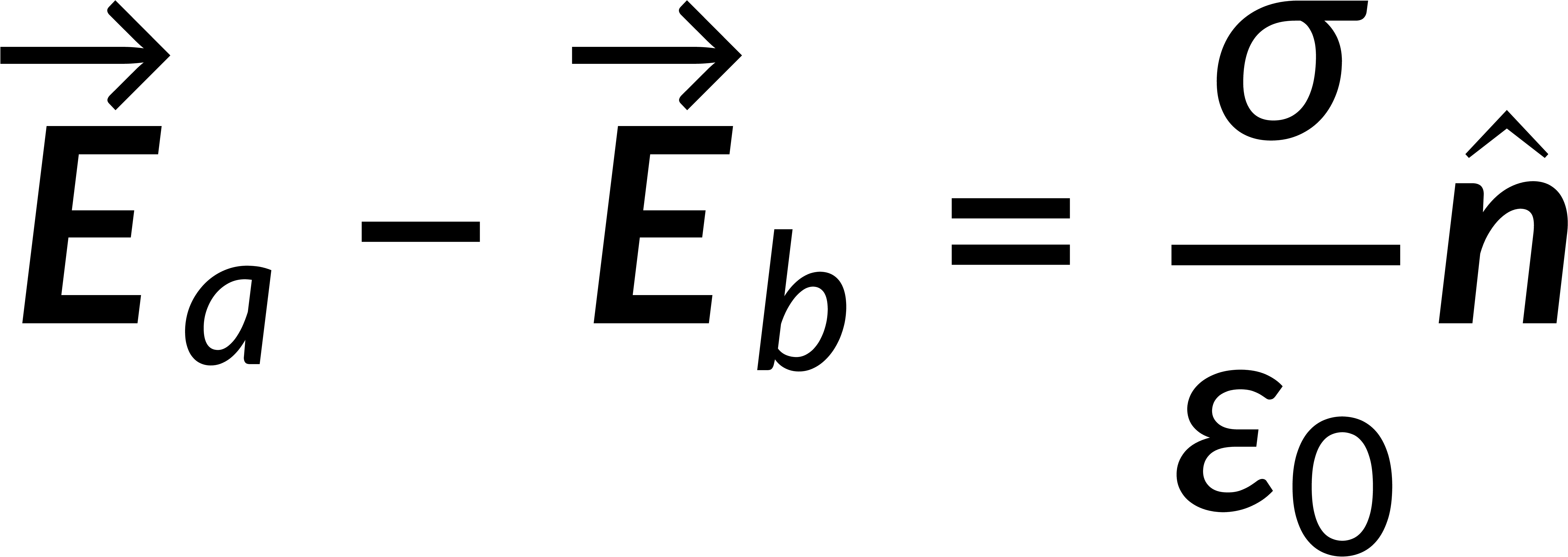
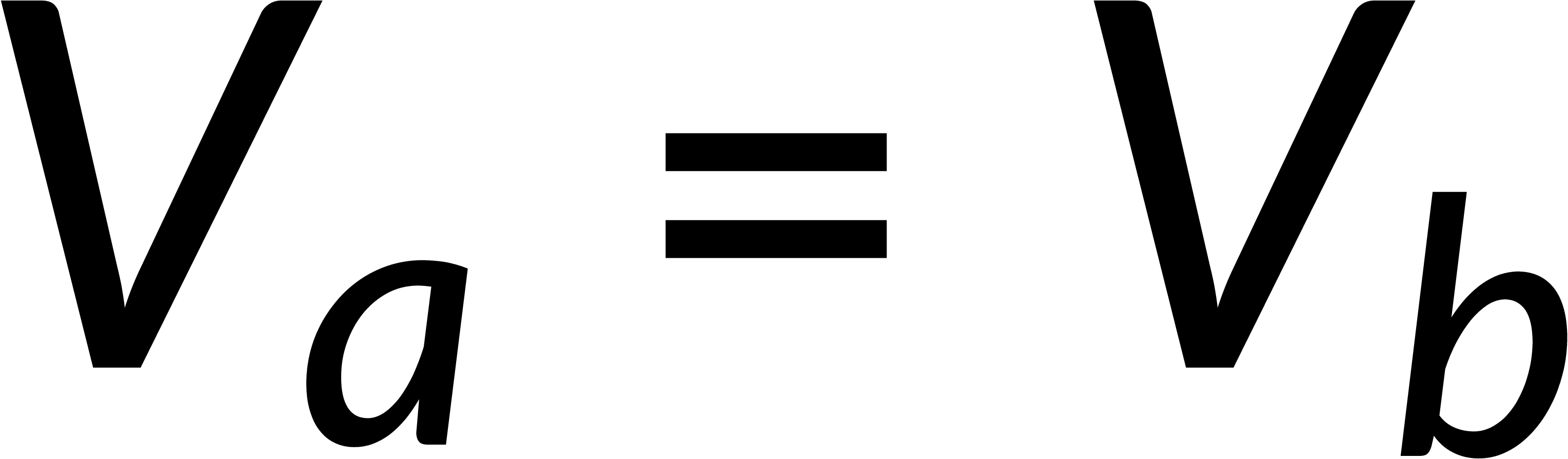
Del capítulo 24:

Now Playing
24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Electric Potential
413 Vistas

24.1 : Energía Potencial Eléctrica
Electric Potential
5.7K Vistas

24.2 : Energía potencial eléctrica en un campo eléctrico uniforme
Electric Potential
4.6K Vistas

24.3 : Energía potencial eléctrica de dos cargas puntuales
Electric Potential
4.4K Vistas

24.4 : Potencial eléctrico y diferencia de potencial
Electric Potential
4.3K Vistas

24.5 : Encontrar el potencial eléctrico del campo eléctrico
Electric Potential
4.0K Vistas

24.6 : Cálculos de Potencial Eléctrico I
Electric Potential
1.9K Vistas

24.7 : Cálculos de Potencial Eléctrico II
Electric Potential
1.6K Vistas

24.8 : Superficies equipotenciales y líneas de campo
Electric Potential
3.6K Vistas

24.9 : Superficies equipotenciales y conductores
Electric Potential
3.3K Vistas

24.10 : Determinación del campo eléctrico a partir del potencial eléctrico
Electric Potential
4.3K Vistas

24.11 : Ecuación de Poisson y Laplace
Electric Potential
2.6K Vistas

24.12 : Generador Van de Graaff
Electric Potential
1.7K Vistas

24.13 : Energía asociada a una distribución de carga
Electric Potential
1.5K Vistas

24.15 : Segundo teorema de unicidad
Electric Potential
972 Vistas
ACERCA DE JoVE
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Todos los derechos reservados