24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Consider an external electric field propagating through a homogeneous medium. When the electric field crosses the surface boundary of the medium, it undergoes a discontinuity. The electric field can be resolved into normal and tangential components. The amount by which the field changes at any boundary is given by the difference between the field components above and below the surface boundary.
The surface integral of an electric field is given by Gauss's law in integral form and is related to the total enclosed charge. Consider a Gaussian pillbox on the surface boundary. The surface integral of the field is the sum of the integrals over all the surfaces of the pillbox. If the thickness of the pillbox tends to zero, then the surface integral includes only the contributions of the pillbox faces above and below the boundary. Solving this gives the discontinuity of the normal component of the electric field at any surface boundary.
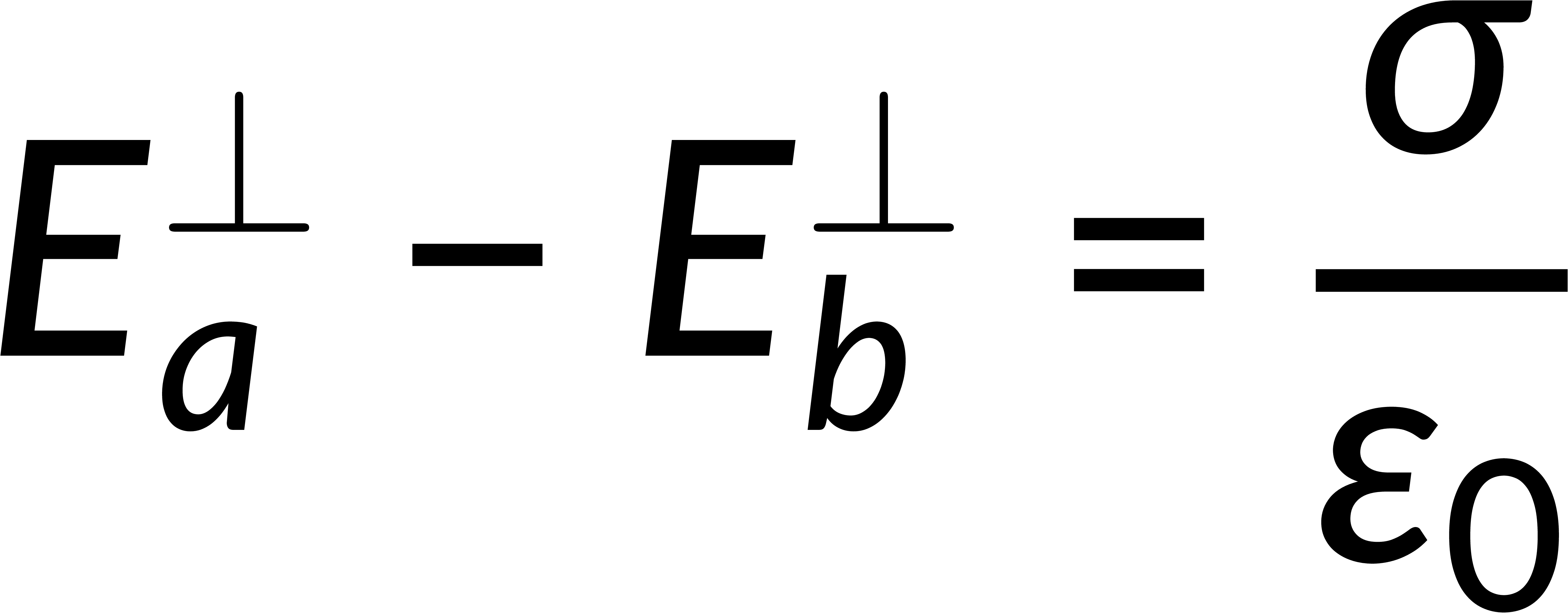
To estimate the discontinuity of the tangential component, consider a loop on the surface boundary. The integration of the electric field over this closed path is zero. Breaking this into the contributions from four parts of the loop and applying the condition that the thickness of the loop tends to zero implies that the tangential component of the electric field is continuous across the boundary.
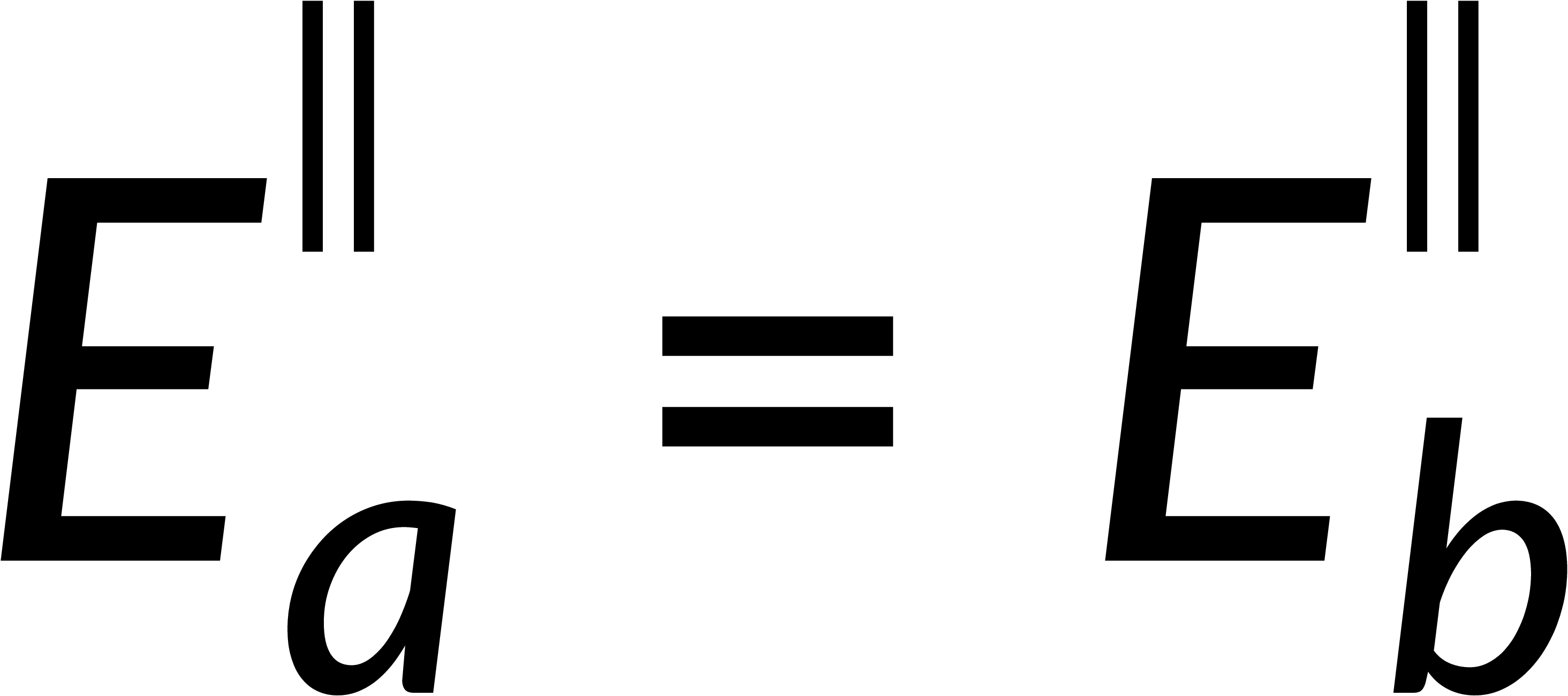
Combining the normal and tangential equations, the field at the boundary can be written by defining the unit vector perpendicular to the surface. It is known that the electric field is the negative gradient of the potential. The line integral of the field from below to above the boundary tends to zero, implying that the potential is continuous across any boundary.
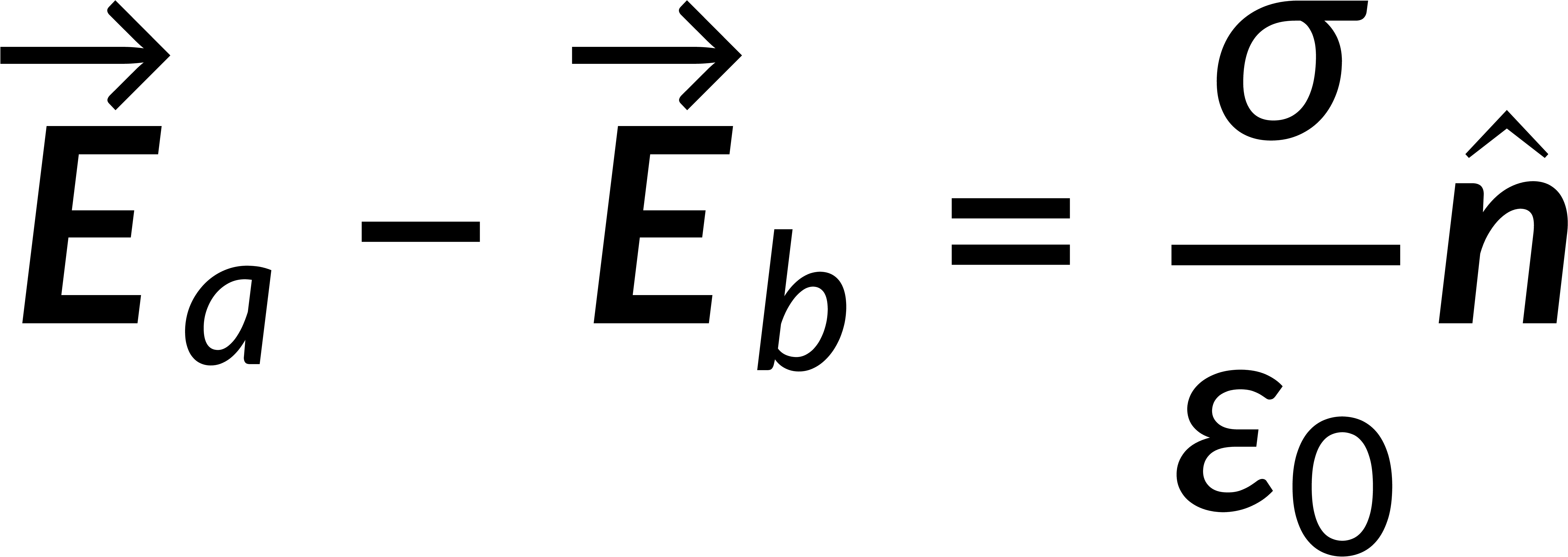
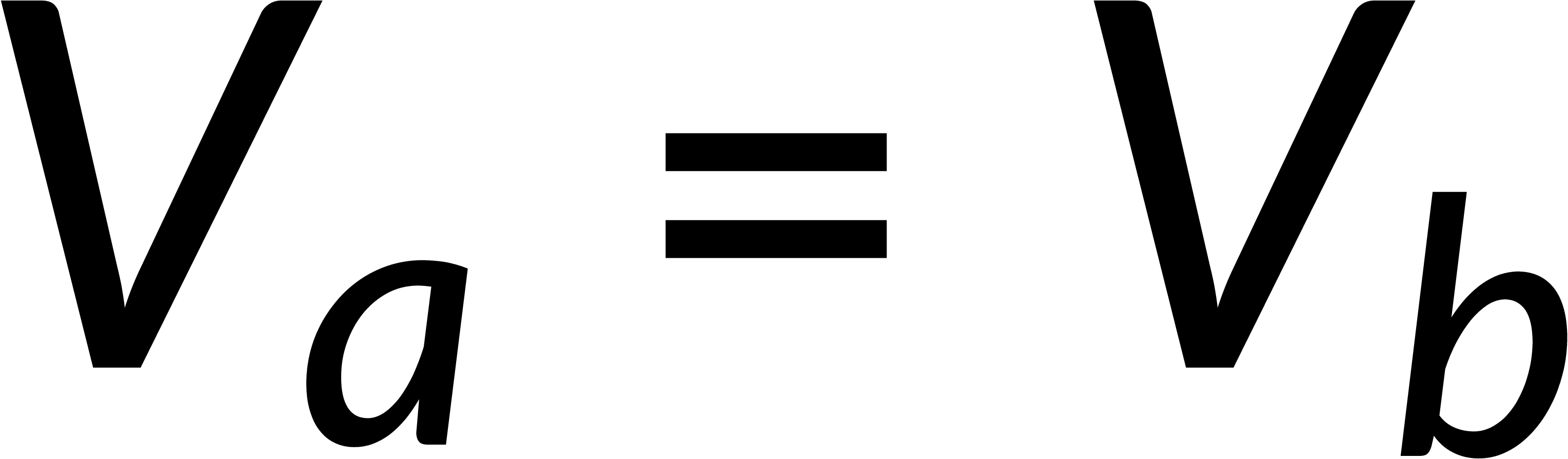
章から 24:

Now Playing
24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
電気ポテンシャル
415 閲覧数

24.1 : 電位エネルギー
電気ポテンシャル
5.7K 閲覧数

24.2 : 一様電界における電位エネルギー
電気ポテンシャル
4.6K 閲覧数

24.3 : 2点電荷の電気ポテンシャルエネルギー
電気ポテンシャル
4.5K 閲覧数

24.4 : 電位と電位差
電気ポテンシャル
4.3K 閲覧数

24.5 : 電界から電位を求める
電気ポテンシャル
4.0K 閲覧数

24.6 : 電位の計算I
電気ポテンシャル
1.9K 閲覧数

24.7 : 電位計算 II
電気ポテンシャル
1.6K 閲覧数

24.8 : 等電位サーフェスと磁力線
電気ポテンシャル
3.6K 閲覧数

24.9 : 等電位表面と導体
電気ポテンシャル
3.3K 閲覧数

24.10 : 電位からの電界の決定
電気ポテンシャル
4.3K 閲覧数

24.11 : ポアソン方程式とラプラス方程式
電気ポテンシャル
2.6K 閲覧数

24.12 : Van de Graaffジェネレーター
電気ポテンシャル
1.7K 閲覧数

24.13 : 電荷分布に関連付けられたエネルギー
電気ポテンシャル
1.5K 閲覧数

24.15 : 第二一意性定理
電気ポテンシャル
975 閲覧数
Copyright © 2023 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved