24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Consider an external electric field propagating through a homogeneous medium. When the electric field crosses the surface boundary of the medium, it undergoes a discontinuity. The electric field can be resolved into normal and tangential components. The amount by which the field changes at any boundary is given by the difference between the field components above and below the surface boundary.
The surface integral of an electric field is given by Gauss's law in integral form and is related to the total enclosed charge. Consider a Gaussian pillbox on the surface boundary. The surface integral of the field is the sum of the integrals over all the surfaces of the pillbox. If the thickness of the pillbox tends to zero, then the surface integral includes only the contributions of the pillbox faces above and below the boundary. Solving this gives the discontinuity of the normal component of the electric field at any surface boundary.
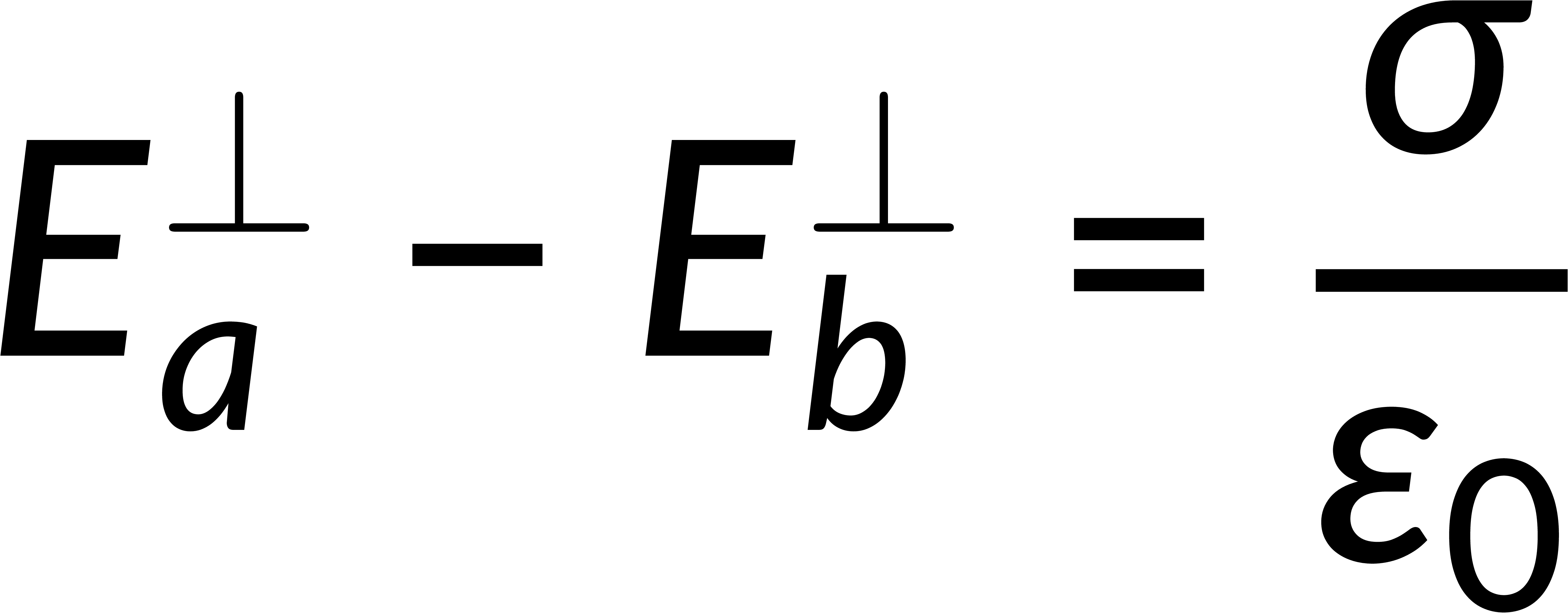
To estimate the discontinuity of the tangential component, consider a loop on the surface boundary. The integration of the electric field over this closed path is zero. Breaking this into the contributions from four parts of the loop and applying the condition that the thickness of the loop tends to zero implies that the tangential component of the electric field is continuous across the boundary.
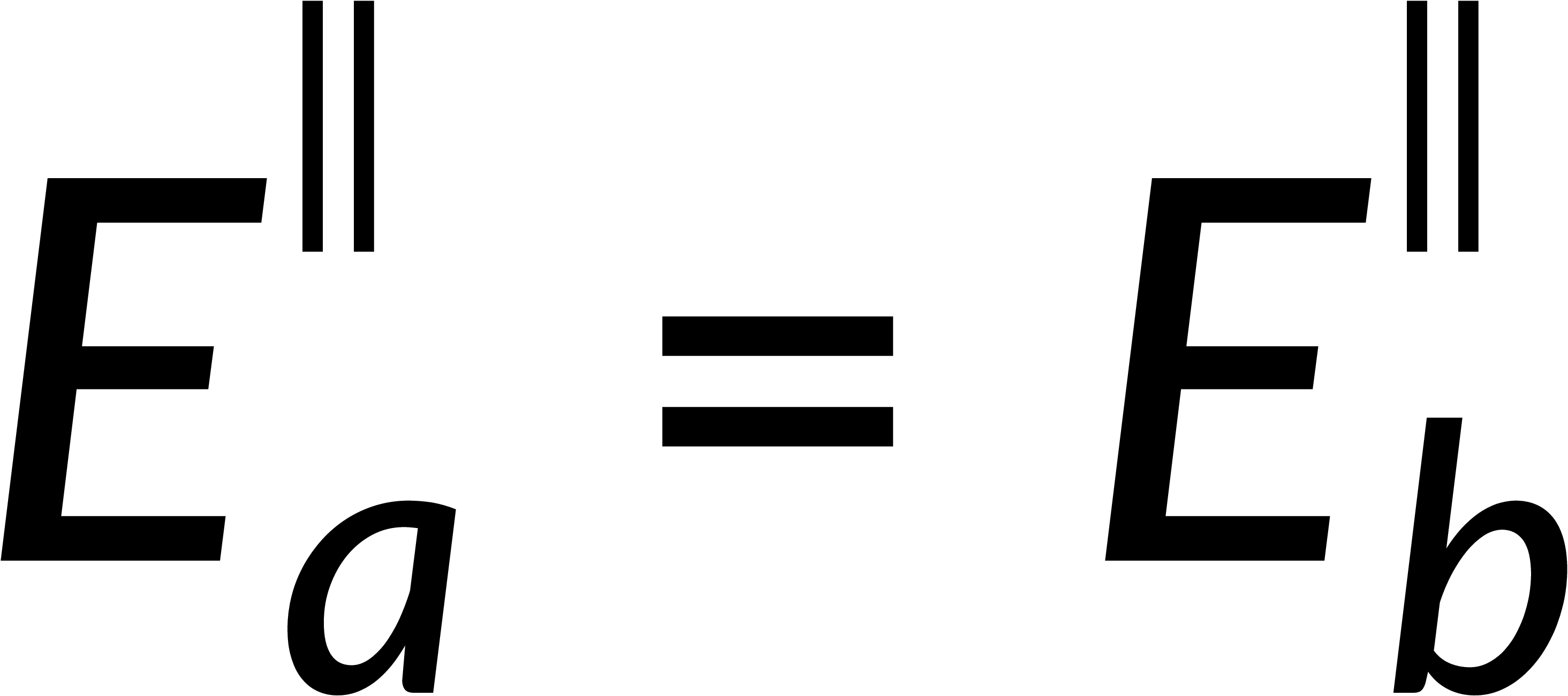
Combining the normal and tangential equations, the field at the boundary can be written by defining the unit vector perpendicular to the surface. It is known that the electric field is the negative gradient of the potential. The line integral of the field from below to above the boundary tends to zero, implying that the potential is continuous across any boundary.
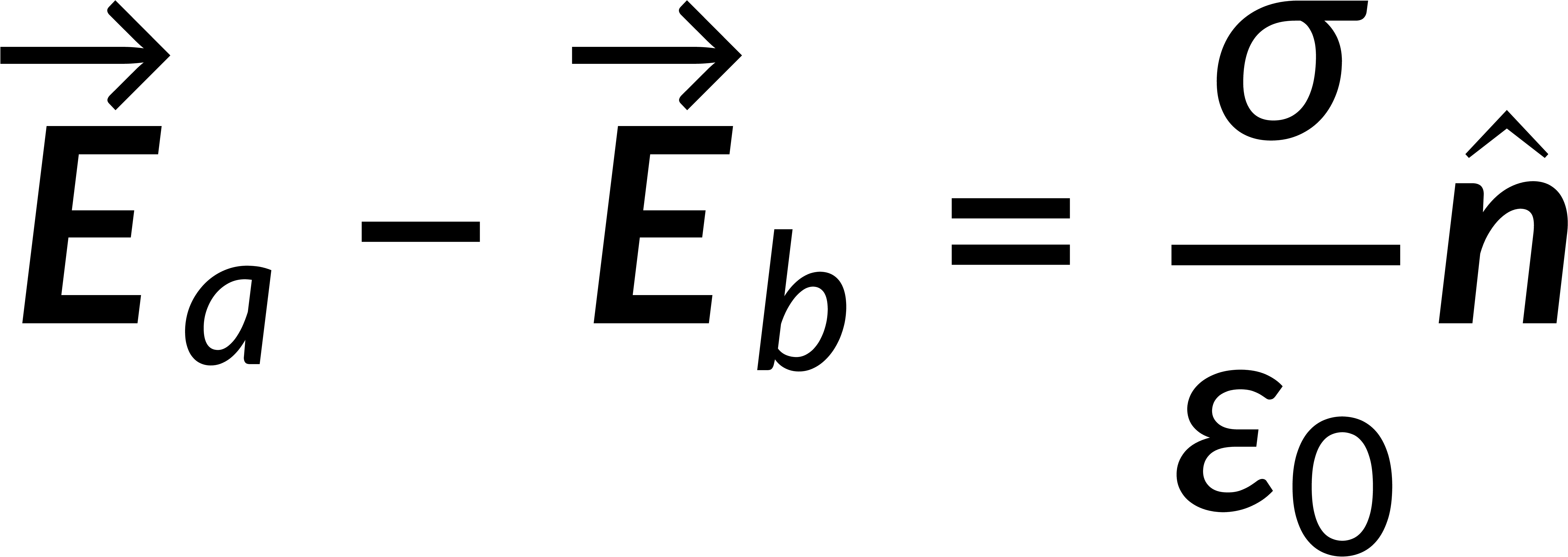
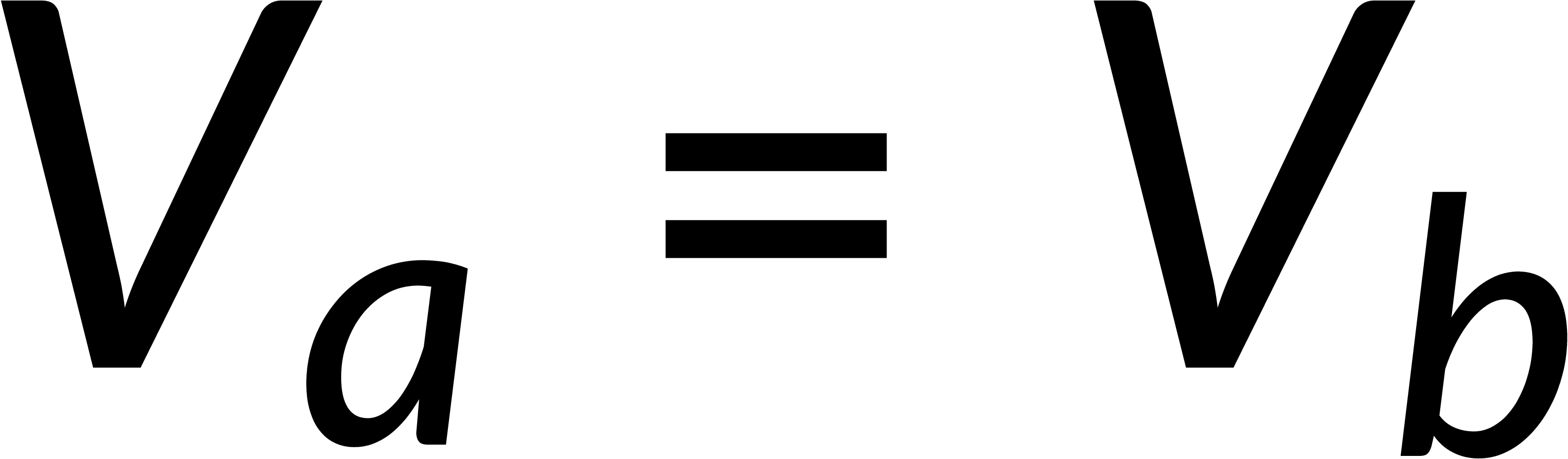
Z rozdziału 24:

Now Playing
24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Electric Potential
419 Wyświetleń

24.1 : Elektryczna energia potencjalna
Electric Potential
5.7K Wyświetleń

24.2 : Elektryczna energia potencjalna w jednorodnym polu elektrycznym
Electric Potential
4.6K Wyświetleń

24.3 : Elektryczna energia potencjalna dwóch ładunków punktowych
Electric Potential
4.5K Wyświetleń

24.4 : Potencjał elektryczny i różnica potencjałów
Electric Potential
4.3K Wyświetleń

24.5 : Znajdowanie potencjału elektrycznego z pola elektrycznego
Electric Potential
4.0K Wyświetleń

24.6 : Obliczenia potencjału elektrycznego I
Electric Potential
1.9K Wyświetleń

24.7 : Obliczenia potencjału elektrycznego II
Electric Potential
1.6K Wyświetleń

24.8 : Powierzchnie ekwipotencjalne i linie pól
Electric Potential
3.6K Wyświetleń

24.9 : Powierzchnie ekwipotencjalne i przewodniki
Electric Potential
3.3K Wyświetleń

24.10 : Wyznaczanie pola elektrycznego na podstawie potencjału elektrycznego
Electric Potential
4.4K Wyświetleń

24.11 : Równanie Poissona i Laplace'a
Electric Potential
2.6K Wyświetleń

24.12 : Generator Van de Graaffa
Electric Potential
1.7K Wyświetleń

24.13 : Energia związana z rozkładem ładunku
Electric Potential
1.5K Wyświetleń

24.15 : Drugie twierdzenie o wyjątkowości
Electric Potential
977 Wyświetleń
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. Wszelkie prawa zastrzeżone