Consider an external electric field propagating through a homogeneous medium. When the electric field crosses the surface boundary of the medium, it undergoes a discontinuity. The electric field can be resolved into normal and tangential components. The amount by which the field changes at any boundary is given by the difference between the field components above and below the surface boundary.
The surface integral of an electric field is given by Gauss's law in integral form and is related to the total enclosed charge. Consider a Gaussian pillbox on the surface boundary. The surface integral of the field is the sum of the integrals over all the surfaces of the pillbox. If the thickness of the pillbox tends to zero, then the surface integral includes only the contributions of the pillbox faces above and below the boundary. Solving this gives the discontinuity of the normal component of the electric field at any surface boundary.
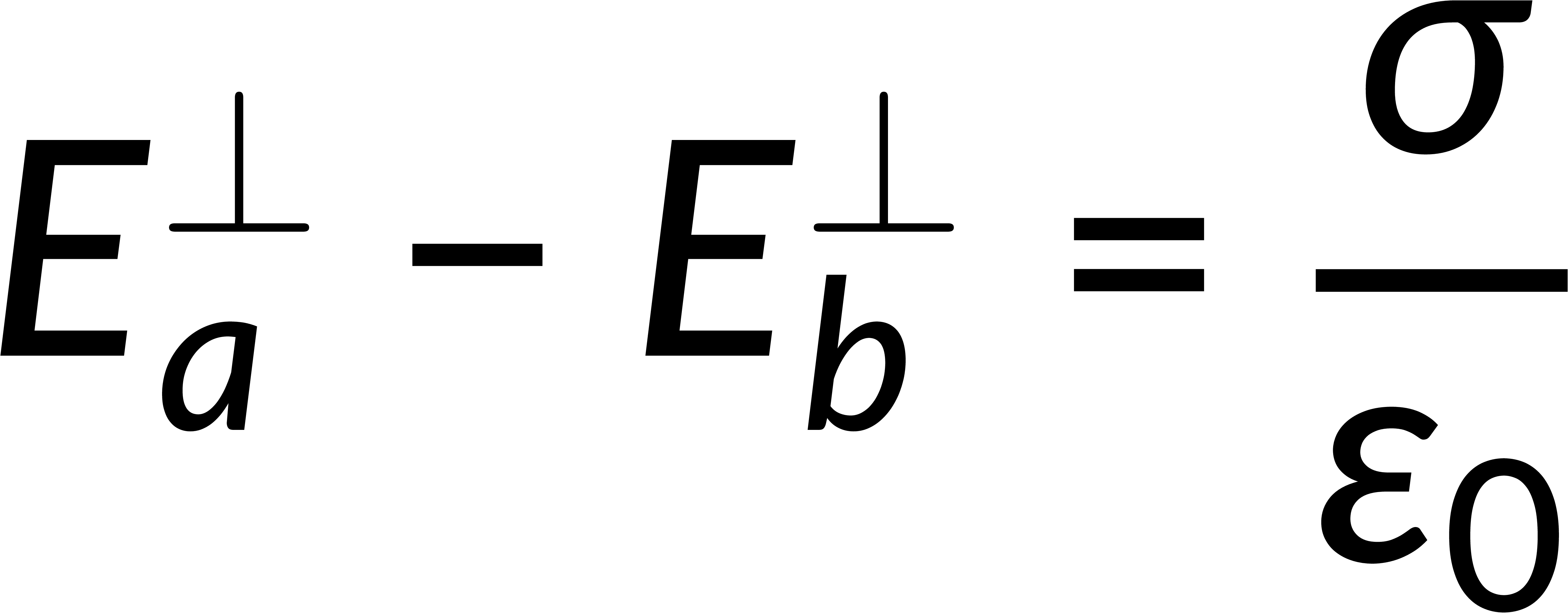
To estimate the discontinuity of the tangential component, consider a loop on the surface boundary. The integration of the electric field over this closed path is zero. Breaking this into the contributions from four parts of the loop and applying the condition that the thickness of the loop tends to zero implies that the tangential component of the electric field is continuous across the boundary.
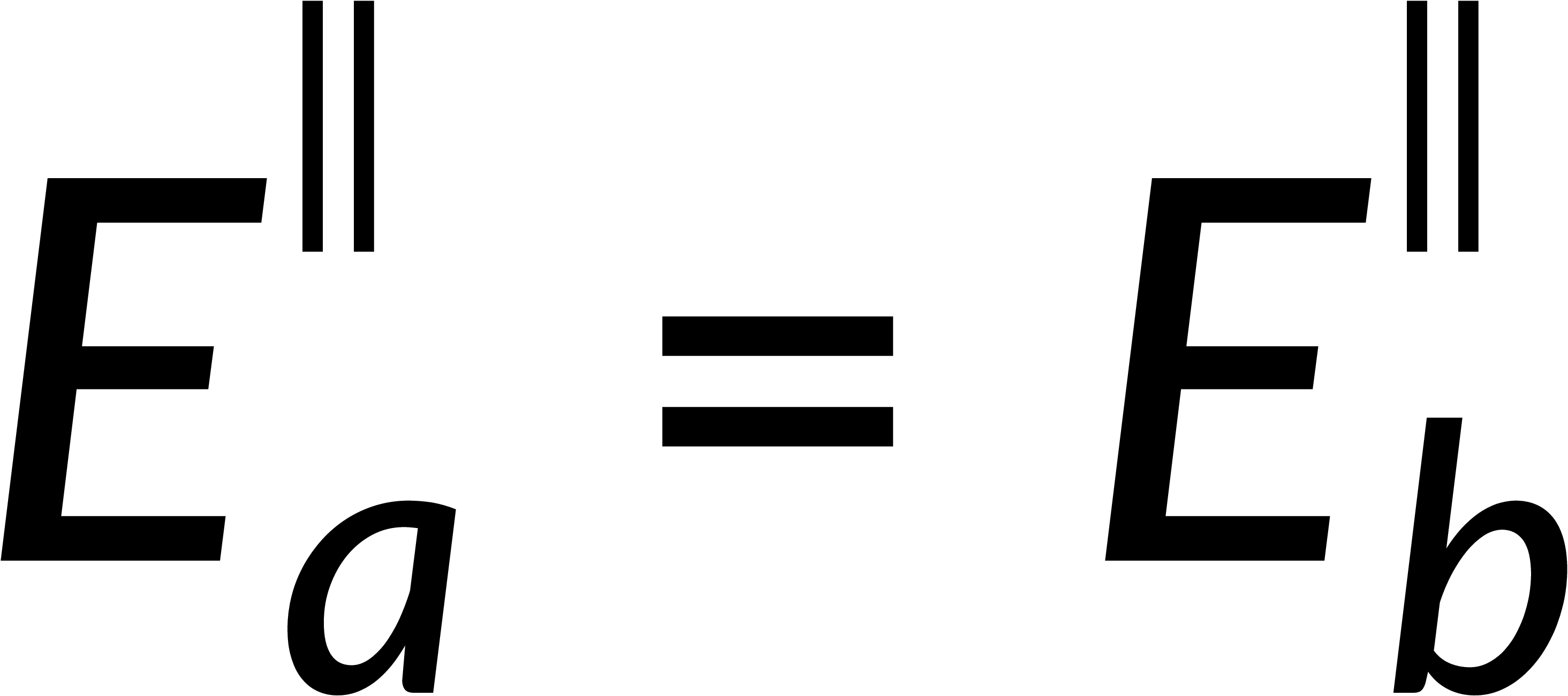
Combining the normal and tangential equations, the field at the boundary can be written by defining the unit vector perpendicular to the surface. It is known that the electric field is the negative gradient of the potential. The line integral of the field from below to above the boundary tends to zero, implying that the potential is continuous across any boundary.
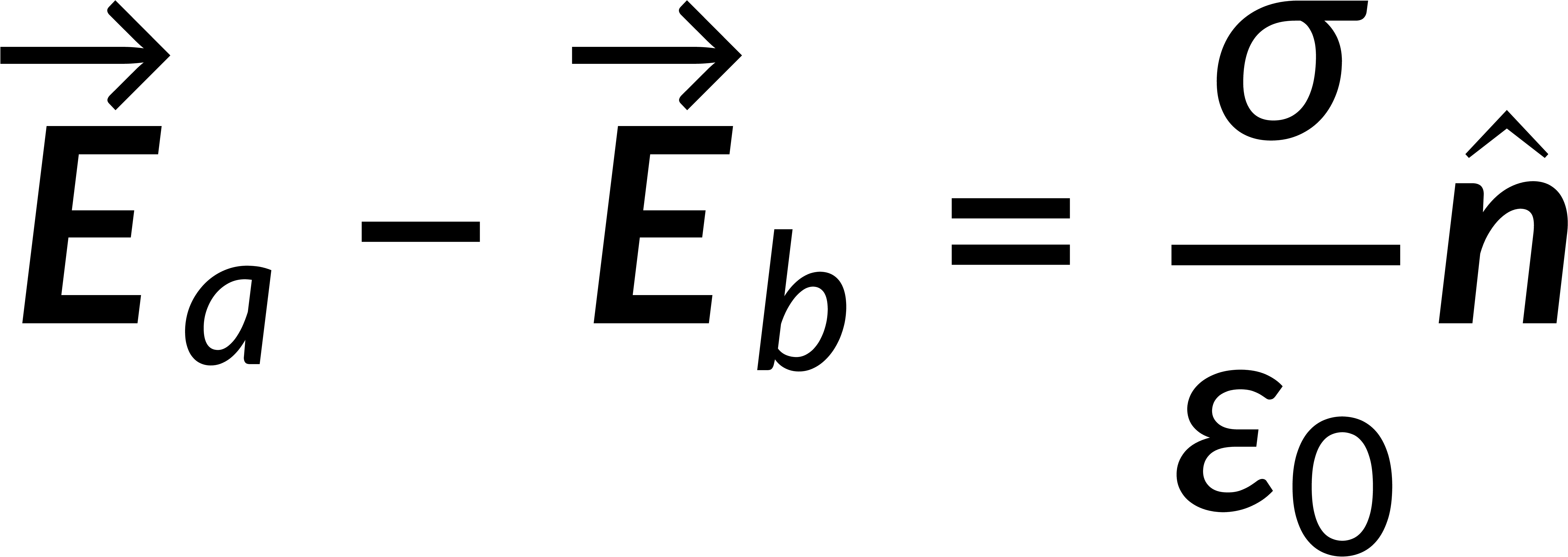
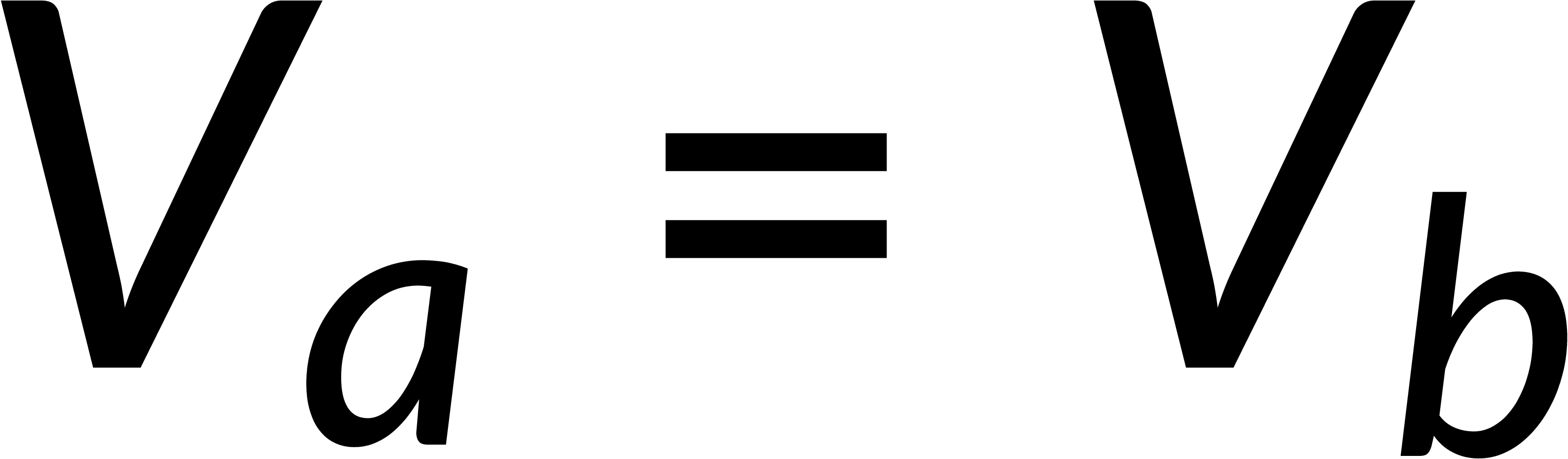
Bölümden 24:

Now Playing
24.14 : Electrostatic Boundary Conditions
Elektrik Potansiyeli
382 Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.1 : Elektrik Potansiyel Enerjisi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
5.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.2 : Düzgün bir elektrik alanında elektrik potansiyel enerjisi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
4.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.3 : İki Noktalı Yüklerin Elektrik Potansiyel Enerjisi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
4.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.4 : Elektrik Potansiyeli ve Potansiyel Farkı
Elektrik Potansiyeli
4.2K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.5 : Elektrik Alanından Elektrik Potansiyelinin Bulunması
Elektrik Potansiyeli
3.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.6 : Elektrik Potansiyeli Hesaplamaları I
Elektrik Potansiyeli
1.9K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.7 : Elektrik Potansiyeli Hesaplamaları II
Elektrik Potansiyeli
1.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.8 : Eşpotansiyel Yüzeyler ve Alan Çizgileri
Elektrik Potansiyeli
3.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.9 : Eşpotansiyel Yüzeyler ve İletkenler
Elektrik Potansiyeli
3.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.10 : Elektrik potansiyelinden elektrik alanının belirlenmesi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
4.3K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.11 : Poisson ve Laplace Denklemi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
2.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.12 : Van de Graaff Jeneratör
Elektrik Potansiyeli
1.6K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.13 : Bir yük dağılımıyla ilişkili enerji
Elektrik Potansiyeli
1.5K Görüntüleme Sayısı

24.15 : İkinci Teklik Teoremi
Elektrik Potansiyeli
943 Görüntüleme Sayısı
JoVE Hakkında
Telif Hakkı © 2020 MyJove Corporation. Tüm hakları saklıdır