Method Article
Bloodless Laparoscopic Partial Splenectomy Assisted by Bipolar Radiofrequency Excision Hemostatic Device
* These authors contributed equally
In This Article
Summary
The present protocol describes that bipolar radiofrequency device-assisted laparoscopic partial splenectomy (LPS) is safe and effective. A bipolar radiofrequency device in LPS can reduce intraoperative bleeding and achieve the clinical effect of a "bloodless spleen incision", which is worthy of clinical application.
Abstract
Among the lymphatic system in the human body, the spleen is the most extensive one and has hematopoietic, hemofiltration, blood storage, and immune functions. As a new method of preserving the spleen, laparoscopic partial splenectomy (LPS) has been increasingly applied in clinical practice with people's deeper insights into minimally invasive treatment and the development of technical equipment. Compared with conventional open splenectomy, LPS can preserve normal spleen tissue as much as possible, decrease the occurrence of complications after total splenectomy, and reduce postoperative hospital stay. The bipolar radiofrequency excision hemostatic device used for LPS can solidify the splenic tissue and close the small blood vessels, which reduces the hemorrhage of the spleen cross-section and clears the operative field, thus achieving the ideal effect of "bloodless partial splenectomy". Therefore, under the premise of strictly mastering the indications and fully understanding the vascular anatomy of the spleen, the application of the bipolar radiofrequency excision hemostatic device in LPS is worthy of clinical promotion.
Introduction
The spleen is the most extensive lymphatic system in the human body and has hematopoietic, hemofiltration, blood storage, and immune functions. Splenectomy is prone to complications such as thromboembolism, hemorrhagic, infectious, iatrogenic damage to adjacent organs, and overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI). Therefore, selective preservation of the spleen during the procedure has gradually attracted the attention of clinical surgeons1,2,3. Thus, sufficient splenic tissue must be preserved to maintain spleen function while ensuring complete resection of benign splenic tumors without recurrence. With the development of laparoscopic technology, laparoscopic partial splenectomy (LPS) has been gradually promoted in clinical practice, and its safety and effectiveness have been widely recognized4,5. LPS was first reported in 1995 by Poulin et al.6. Compared to total splenectomy, LPS has the advantage of reducing the incidence of postoperative complications and the length of the hospital stay.
The spleen is rich in blood supply. How to control and reduce bleeding in the process of resection is an urgent problem, especially in LPS. Therefore, various hemostatic energy devices have emerged and are applied to LPS, such as ultrasonic knife7, bipolar radiofrequency device8,9, bipolar electrocoagulation10, argon ion coagulation knife11, super suction knife11, and vascular closure device12. The high-frequency alternating current generated by the radio frequency electrodes is transmitted to the surrounding tissues. Bipolar radiofrequency excision hemostatic device has been widely used in hepatectomy because of its exact radiofrequency hemostatic effect but is rarely used in partial splenectomy13. Here, a method of bloodless laparoscopic partial splenectomy assisted by bipolar radiofrequency excision hemostatic device is described. The use of bipolar radiofrequency electrode-assisted LPS can effectively reduce intraoperative bleeding and improve the safety and effectiveness of surgery. The main objective of this method is to achieve the effect of partial splenectomy without blood by using a bipolar radiofrequency electrode, improve the safety and effectiveness of the operation, and facilitate clinical promotion. This procedure can be applied in most benign splenic diseases requiring partial splenectomy.
A 19-year-old male patient with no specific medical history was admitted to the hospital with a 2-week history of an occupying splenic lesion on physical examination. Physical examination showed no significant abnormalities. Laboratory tests such as routine blood, coagulation, and liver function were normal. A color Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen revealed a solid area of approximately 5.6 x 5.1 cm2 between the spleen and kidney, which was thought to originate from the left adrenal gland. Enhancement magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the upper abdomen showed a 5.1 x 4.6 cm2 hyperintense round occupying the upper pole of the spleen (Figure 1). The admission diagnosis revealed an occupying lesion in the spleen, likely a hemangioma. Upon admission, a preoperative evaluation was conducted. The patient had no contraindications to surgery. LPS was performed because of the patient's age, the many possible complications after total splenectomy, and the willingness of his family to undergo partial splenectomy.
Protocol
The present human surgery protocol is approved by and follows the ethical guidelines of the Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University (Guangzhou, China). Informed consent was obtained from the patient for the release of information and data related to his treatment.
1. Preoperative preparation
- Prohibit patient from eating for 8 h and drinking for 4 h before surgery.
- Use general anesthesia with tracheal intubation2. Treat patient with conventional sterilized skin and sterile towel sheets after adequate anesthesia is performed by an anesthesiologist.
NOTE: Disinfect the surgical area with iodophor three times.
2. Surgical technique
- Place the patient in supine position with legs divided, head high, and feet low, and the right side tilted at 15°.
- Establish the pneumoperitoneum by the pneumoperitoneum needle2 (see Table of Materials).
NOTE: The pneumoperitoneum pressure is set to 13 mmHg. - Make a 1 cm curved incision along the lower margin of the umbilical cord and puncture a 10 mm trocar, and then insert the laparoscope (see Table of Materials).
NOTE: Puncture trocar of 5, 12, 5, and 12 mm to the left under the xiphoid process, 4 cm below the rib cage in the right midclavicular line, intersect the left midclavicular line with the transverse umbilical line, and intersect the left anterior axillary line with the transverse umbilical line, respectively. - Perform abdominal exploration by entering the abdominal cavity to observe and evaluate the feasibility of LPS.
NOTE: Preliminary assessment content: the spleen size and degree of peripheral adhesion. - Free the greater omentum by lifting the greater omentum and transverse colon, and use an ultrasonic knife to free the greater omentum along the edge of the transverse colon toward the pylorus, starting in the middle of the greater curvature of the stomach.
- Open the gastrocolic ligament, and release the gastrosplenic ligament.
- Lift the stomach, separate, and expose the splenic artery through the back of the stomach at the superior margin of the pancreas. Separate the splenic artery and the superior pole branch of the splenic vein near the spleen (Figure 2).
- Turn the spleen to the right and the splenic diaphragmatic ligament and cut part of the splenorenal ligament with an ultrasonic knife (see Table of Materials) to expose the upper pole of the spleen fully.
- Clamp the superior pole branch of the splenic artery with a "Pug" vascular blocking forceps to block blood flow to the superior pole of the spleen and observe the ischemic line to confirm that the mass is within the limits of the ischemic splenic resection (Figure 3).
- Perform a secure ligation using non-absorbable polymer ligation clips (see Table of Materials) to disconnect the superior pole branches of the splenic artery and splenic vein.
NOTE: Separate, expose, clamp, and disconnect the lower pole branches of the splenic artery and splenic vein when performing partial resection of the lower pole of the spleen. - Place an 3.5 mm (10 Fr) disposable single-cavity rubber catheter (see Table of Materials) over the main trunk of the splenic artery at the site of dissection to serve as a vascular occlusion band to allow for blockage if necessary.
- Perform coagulation and ablation using a bipolar radiofrequency hemostatic device (see Table of Materials) along the ischemic line on the surface of the spleen (Figure 4).
NOTE: Preferences settings: LAP MODE, Power: 120 W. - After establishing coagulation of the necrotic area, dissect the spleen with an ultrasonic knife and observe no significant bleeding during dissection of the spleen (Figure 5) until the mass is removed along with the upper pole of the spleen.
- Place the specimen in a specimen bag, and enlarge the incision of trocar puncture at the intersection of the left midclavicular and transverse umbilical lines to 4-5 cm to remove the specimen altogether.
- Suture the incision with a 2-0 absorbable suture (see Table of Materials) and irrigate the abdominal cavity.
- After confirming that there was no active bleeding in the abdominal cavity, place absorbable hemostatic material (see Table of Materials) on the surgical wound, and then place the adhesive membrane.
- Place a laparoscopic drainage tube (see Table of Materials) at the medial edge of the splenic portion and exit from the left lower abdomen.
- Suture all 5 mm and 12 mm trocar holes layer by layer.
3. Postoperative care
- Closely observe and record vital signs in the first 24 h postoperatively by continuous real-time electrocardiograph (ECG, see Table of Materials) monitoring.
NOTE: Vital signs: heart rate, blood pressure, respirations, and pulse oximetry. - Administer an intravenous antibiotic (cefazolin sodium, 1.5 g with 100 mL of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 12 h) for 24 h postoperatively to prevent infection.
- Start liquid diet after 6 h postoperatively and ensure bed rest for 24 h.
- Remove the catheter 24 h postoperatively.
- Remove the drainage tube 48~72 h postoperatively.
Results
The patient was doing well after the surgery and was sent back to the ward. The operation lasted 120 min, with intraoperative blood loss of about 100 mL and about 2,600 mL of fluid replacement, without blood transfusion. Intraoperative urinary output was 600 mL. The patient recovered well with no postoperative complications and was discharged on the 6th postoperative day. Postoperative pathology showed a splenic capillary hemangioma with active cell growth and a size of 4.7 x 4.0 x 3.5 cm3. The spleen was dissected with an ultrasonic knife along the coagulation of the necrotic area, and no significant bleeding during dissection of the spleen. The spleen section showed coagulated necrotic tissue without obvious active hemorrhage (Figure 4, Table 1).
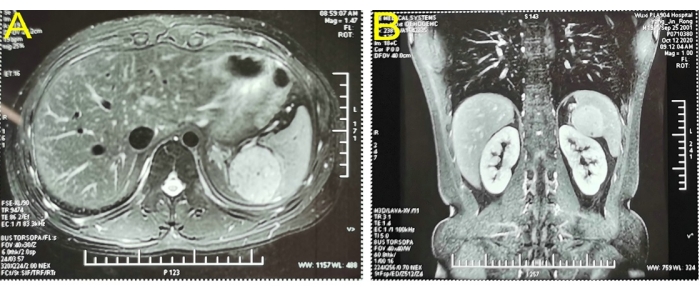
Figure 1: Enhancing magnetic resonance imaging confirmed a hyperintense round occupying the upper pole of the spleen. (A) Cross-sectional imaging. (B) Coronal view imaging. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
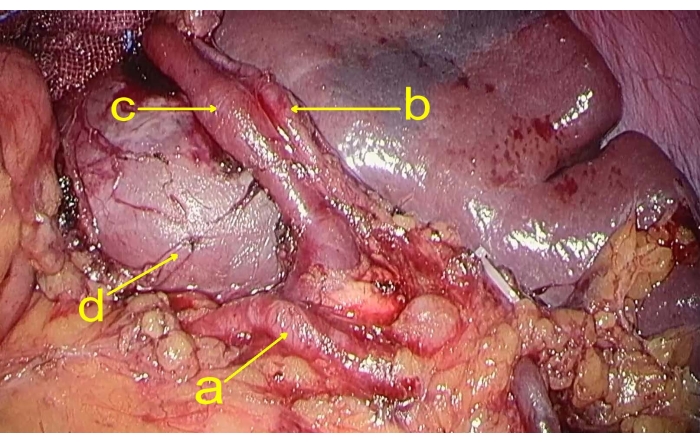
Figure 2: Vascular branches of the spleen. The figure shows (a) the splenic artery, (b) the superior pole branch of the splenic artery, (c) the superior pole branch of the splenic vein, and (d) the tumor. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
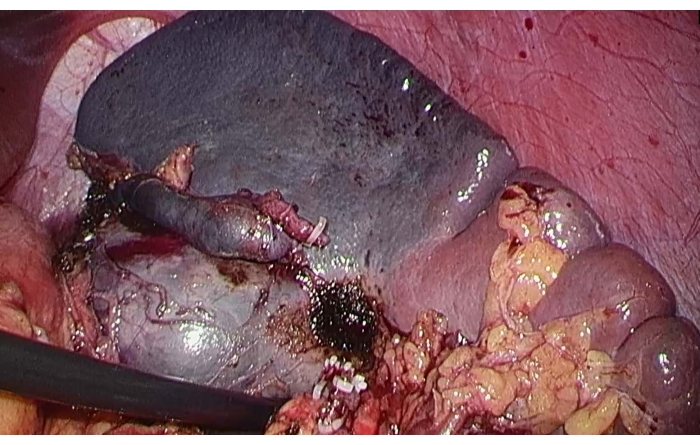
Figure 3: Ischemic line in the upper pole of the spleen. To block blood flow to the spleen's superior pole after clamping the splenic artery's superior pole branch, the ischemic line was observed. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
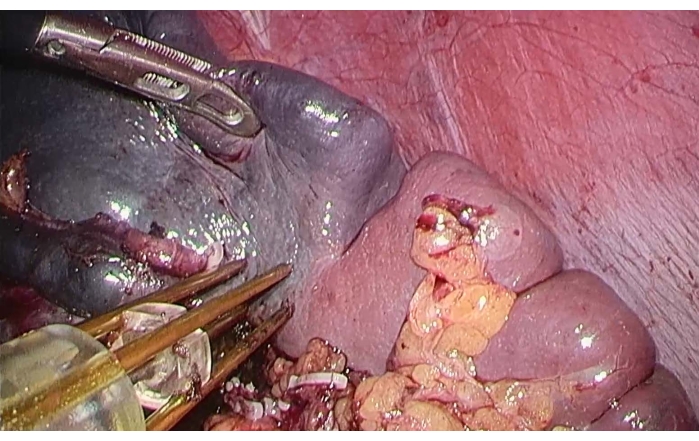
Figure 4: Bipolar radiofrequency ablation of the spleen. To lift the upper pole of the spleen with forceps, a bipolar radiofrequency hemostatic device was used along the ischemic line on the surface of the spleen to perform coagulation and ablation. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
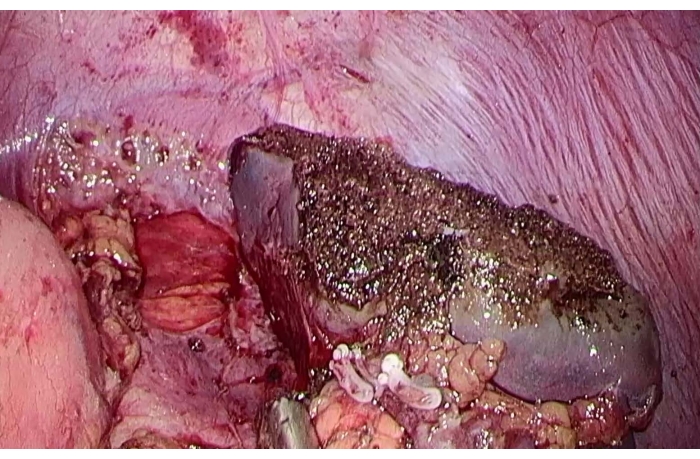
Figure 5: The residual spleen section after partial splenectomy. Please click here to view a larger version of this figure.
| Items | Results |
| OP time (min) | 120 |
| Operation ABL (mL) | 100 |
| Operation ABT (mL) | 0 |
| Fluid replacement (mL) | 2600 |
| Postop complications | None |
| Discharge time | The 6th postoperative day |
Table 1: Relevant outcomes of LPS. LPS, laparoscopic partial splenectomy; OP, operation time; ABL, amount of blood loss; ABT, Amount of blood transfusion.
Discussion
With the development of modern medicine, especially immunology, there is a better understanding of the anatomical structure and function of the spleen. In the past, many benign and malignant spleen diseases were treated by total splenectomy due to the limitations of knowledge and surgical techniques. In 1992, Delaitre et al. first reported laparoscopic splenectomy, and laparoscopic techniques began to be gradually applied to spleen surgery14. However, studies have shown complications such as thromboembolism, hemorrhage, infections, congenital damage to adjacent organs, and dangerous postoperative infections occur after total splenectomy2,3. Therefore, for patients with splenic diseases, the initial blind resection treatment has been gradually replaced by selective splenic preservation therapy, such as splenic repair suture, partial splenectomy, splenic artery embolization, and splenic transplantation. In 1995, Poulin et al. first reported LPS, which opened a new chapter in splenic surgery6. With a more comprehensive understanding of the function of the spleen, the anatomical relationship between the splenic lobules and segmental blood supply, and the application of various energy devices, LPS has been applied to patients in major centers15,16,17,18. LPS can preserve as much normal tissue of the spleen as possible while removing the diseased tissue, reducing various complications after total splenectomy. Compared with open partial splenectomy (OPS), LPS requires a longer time and more intraoperative bleeding. However, it does not increase the incidence of postoperative complications and delay postoperative recovery. On the contrary, studies have shown that LPS has a significantly lower postoperative complication rate and a significantly shorter postoperative hospital stay than OPS18,19,20.
The blood supply to each segment of the spleen is the anatomical basis of LPS. There are mainly two-lobe and four-segment types, i.e., the upper and lower segments of the spleen, the middle and upper segments of the spleen, the middle and lower segments of the spleen. It can also be divided into the splenic hilar, intermediate, and peripheral areas. The splenic artery divides into splenic lobular vessels at the splenic hilum, including 1, 2, 3, and multivessel types. The most common type is the 2- and 3-vessel type, in which the trunk of the splenic artery branches off 2 or 3 vessels of the splenic lobe and enters the spleen. In this regard, there are few arteriovenous anastomoses between adjacent splenic lobes (segments), forming an irregular plane with almost no vascular zone. This anatomical feature justifies the feasibility of partial splenic resection to a certain extent. Partial splenic separation can be performed in a relatively avascular zone to reduce the amount and rate of bleeding21,22. Surgeons can choose different types of partial spleen resections depending on specific conditions and the anatomy of the splenic blood supply. In this case, the tumor was in the spleen's upper part. After releasing and ligating the branch vessels in the upper part of the spleen, a clear ischemic line appeared on the surface of the spleen, based on where partial splenectomy is performed.
The spleen is rich in blood supply, and many blood vessels in the spleen parenchyma need to be dealt with during resection, which results in long operation time, heavy bleeding, and high risk. Therefore, various hemostatic energy devices have emerged and are applied to LPS7,8,9,10,11,12,23,24,25. A bipolar radiofrequency device is a bipolar radiofrequency electrode containing two pairs of 5 cm long reversed electrodes displayed in a rectangular array. The high-frequency alternating current generated by the radio frequency electrodes is transmitted to the surrounding tissues. After the alternating current passes through the tissue, molecules in the tissue rub against each other, generating heat along the current direction, resulting in ischemic necrosis of cells and forming a coagulated necrotic zone approximately 1 cm in width. In 2008, Professor Habib invented the Habib 4X bipolar radiofrequency cutting hemostatic electrode and used it in liver resection with promising results26. Subsequently, the bipolar radiofrequency device was gradually promoted for hepatectomy in major centers. Wang et al. used a bipolar radiofrequency device for LPS for the first time in China and achieved the therapeutic result of bloodless splenectomy27.
This patient underwent successful LPS using a bipolar radiofrequency device. Our experience is summarized as follows: (1) Strict indications, including trauma to the spleen, benign spleen tumors, splenic cysts, hematomas, and especially hematologic disorders of the splenic margins, required splenectomy. Partial splenectomy was contraindicated for tumors near the splenic gallbladder. In addition, some studies have shown that at least 25% to 30% of the residual spleen needs to be preserved to maintain normal spleen function17,18. (2) Preoperative CT and intraoperative ultrasonography were used to clarify the anatomical relationship between the lesion, the splenic artery, and its branches. After dissecting the splenic artery trunk, an disposable single-cavity rubber catheter was placed as a pre-blocking band to block the splenic pedicle and reduce bleeding on time when there was massive bleeding during surgery. The splenic pedicle could be fully exposed by pulling the catheter to protect important vessels and expose the bleeding site. (3) The splenic artery was dissected along the main splenic artery toward the splenic hilum to avoid injury to the pancreas. Attention was paid to identifying the direction of the branch vessels of the secondary splenic pedicle. The vessels in the splenic lobe to be resected were accurately clamped. The ischemic borders of the spleen were observed. Because some patients have anatomic variations in the branches of the splenic artery, careful identification of the anatomical relationship was required, and the vessels need to be carefully released. Only when the ischemia line has been found, the vessels must be severed. To ensure the viability of the spleen, a partial splenectomy could be performed after confirming the resection surface at approximately 1 cm on the blood supply side of the ischemic line. (4) Intraoperative operations were handled elaborately with moderate freedom, and the collateral blood vessels of the spleen were preserved to protect the secondary blood supply system of the spleen. When preserving the upper pole of the spleen, the upper part of the spleen and the gastric ligament must not be cut to avoid damaging the short gastric vessels and the blood supply to the upper pole of the spleen. When preserving the lower pole of the spleen, the lower part of the gastrosplenic ligament (splenic colonic ligament) needs to be protected to avoid damaging the left gastrointestinal vessels and the blood supply to the lower pole of the spleen. (5) The appropriate power for the bipolar radiofrequency device must be selected, and deep ablation and coagulation must be performed. After ablation disconnection, the broken end of the vessel was clamped using non-absorbable polymer locking clips, or a thicker tube was ligated and sutured to the splenic portion to merge the seal. This patient underwent the procedure successfully with no complications, validating the safety and feasibility of bipolar radiofrequency device-assisted LPS, but further exploration and validation in multicenter, large sample size is still needed.
This surgical method mainly applies to young patients with benign splenic tumors. It is not suitable for large benign tumors of the spleen, malignant tumors of the spleen, and the following situations: the residual spleen is too small to lose function after partial resection, and the branches of the spleen vessel are difficult to be exposed because of serious adhesion or vascular anomalies.
In conclusion, bipolar radiofrequency device-assisted LPS is safe and effective. Under the premise of strictly mastering the indications and fully understanding the vascular anatomy of the spleen, the application of a bipolar radiofrequency device in LPS can reduce intraoperative bleeding and achieve the clinical effect of "bloodless spleen incision", which is worthy of clinical application.
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82072627).
Materials
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| Absorbable hemostat | Ethicon, LLC | W1913T | |
| Absorbable medical film | Shanghai Divine Medical Technology Co., Ltd | 60007 | |
| Bipolar radiofrequency excision hemostatic device | Angio Dynamics, Inc | Rita1500X | Tools for spleen resection and coagulation of small vessels |
| pneumoperitoneum needle | Unimicro Medical Systems Co.,Ltd | 150mm | |
| Disposable spiral negative pressure drainage pipeline | Jiangsu Aiyuan Medical Technology Corp | 424280 | Drainage of abdominal residual fluid |
| Disposable trocar | Kangji Medical | 10004, 10006 | |
| Laparoscopic system | Olympus | WM-NP2 L-RECORDOR-01 | Laparoscopic camera system and supporting display screen |
| Non-absorbable polymer ligation clips (Hem-o-lok) | Teleflex Medical | 544230 | |
| Ultrasound knife | Johnson | GEN11 | Tools for spleen resection |
| Vicryl rapide | Ethicon, LLC | 2-0, VCP345H 90010 | Suture incision and Trocar hole |
| Disposable single-cavity rubber catheter | Yangzhou Huayue Technology Development Co., Ltd | 3.5mm (10Fr) | |
| Video system | Lenovo | GK309 | |
| Electrocardiographic monitor | Philips Goldway (SHENZHEN) Industrial, Inc | UT4000B | Postoperative ecg monitoring |
References
- Barmparas, G., et al. Postoperative infection risk after splenectomy: A prospective cohort study. International Journal of Surgery. 17, 10-14 (2015).
- De Pastena, M., et al. Laparoscopic hemi-splenectomy. Surgery Today. 48 (7), 735-738 (2018).
- Costi, R., et al. Spleen hydatidosis treated by hemi-splenectomy: A low-morbidity, cost-effective management by a recently improved surgical technique. International Journal of Surgery. 20, 41-45 (2015).
- Slater, B. J., Chan, F. P., Davis, K., Dutta, S. Institutional experience with laparoscopic partial splenectomy for hereditary spherocytosis. Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 45 (8), 1682-1686 (2010).
- Jiao, H. B. Experience and thinking of laparoscopic splenectomy. Chinese Journal of Clinical Physicians (Electronic Edition). 6 (21), 6660-6661 (2012).
- Poulin, E. C., Thibault, C., DesCôteaux, J. G., Côté, G. Partial laparoscopic splenectomy for trauma: technique and case report). Surgical Laparoscopy & Endoscopy. 5 (4), 306-310 (1995).
- Di Mauro, D., Fasano, A., Gelsomino, M., Manzelli, A. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using the harmonic scalpel for parenchymal transection: two case reports and review of the literature. Acta Biomedica. 92, 2021137(2021).
- Quesada, R., et al. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy for giant cyst using a radiofrequency-assisted device: a case report. Surgical Case Reports. 2 (1), 82(2016).
- Wang, W. D., et al. Partial splenectomy using a laparoscopic bipolar radiofrequency device: a case report. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 21 (11), 3420-3424 (2015).
- Cai, H., et al. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy: A preferred method for select patients. Journal of Laparoendoscopic & Advanced Surgical Techniques. 26 (12), 1010-1014 (2016).
- Godiris-Petit, G., Goasguen, N., Munoz-Bongrand, N., Cattan, P., Sarfati, E. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using the Harmonic Scalpel. Two case reports. Journal de Chirurgie (Paris). 144 (4), 339-341 (2007).
- Patrzyk, M., Glitsch, A., Hoene, A., von Bernstorff, W., Heidecke, C. D. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using a detachable clamp with and without partial splenic embolisation). Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery. 396 (3), 397-402 (2011).
- Ma, J., et al. Application value of Habib 4X in laparoscopic partial splenectomy. Chinese Journal of Hepatic Surgery (Electronic Edition). 9 (2), 181-185 (2020).
- Delaitre, B., Maignien, B., Icard, P. Laparoscopic splenectomy). British Journal of Surgery. 79 (12), 1334(1992).
- Poulin, E. C., Mamazza, J. Laparoscopic splenectomy: lessons from the learning curve. Canadian Journal of Surgery. 41 (1), 28-36 (1998).
- Corcione, F., et al. Technical standardization of laparoscopic splenectomy: experience with 105 cases. Surgical Endoscopy. 16 (6), 972-974 (2002).
- Breitenstein, S., Scholz, T., Schafer, M., Decurtins, M., Clavien, P. A. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 204 (1), 179-181 (2007).
- Lee, S. H., Lee, J. S., Yoon, Y. C., Hong, T. H. Role of laparoscopic partial splenectomy for tumorous lesions of the spleen. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery. 19 (6), 1052-1058 (2015).
- Liu, G., Fan, Y. Feasibility and safety of laparoscopic partial splenectomy: A systematic review. World Journal of Surgery. 43 (6), 1505-1518 (2019).
- Wang, L., et al. Partial splenectomy is superior to total splenectomy for selected patients with hemangiomas or cysts. World Journal of Surgery. 41 (5), 1281-1286 (2017).
- Ignjatovic, D., Stimec, B., Zivanovic, V. The basis for splenic segmental dearterialization: a post-mortem study. Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 27 (1), 15-18 (2005).
- Li, Y. B., Cai, Y. Q., Wang, X., Peng, B. Selective splenic pedicle occlusion in laparoscoic partial splenectomy. Chinese Journal of General Surgery. 32 (2), 122-125 (2017).
- Itamoto, T., Fukuda, S., Tashiro, H., Ohdan, H., Asahara, T. Radiofrequency-assisted partial splenectomy with a new and simple device. The American Journal of Surgery. 192 (2), 252-254 (2006).
- Zhang, Z. P., et al. Application value of secondary splenic pedicle separation technology through superior posterior approach of the pancreatic tail in laparoscopic partial splenectomy. Chinese Journal of Digestive Surgery. 17 (4), 405-409 (2018).
- Liu, L. G., et al. Laparoscopic partial splenectomy for splenic solid lesions. Chinese Journal of General Surgery. 33 (5), 398-400 (2018).
- Ayav, A., et al. Liver resection with a new multiprobe bipolar radiofrequency device. Archives of Surgery. 143 (4), 396-401 (2008).
- Wang, W. D., Chen, X. W., Ma, J., Liu, Q. B., Lin, J. Application of HabibTM4X laparoscopic partial splenectomy in the treatment of splenic lymphangioma. Chinese Journal of Surgery. 52 (8), 639-640 (2014).
Reprints and Permissions
Request permission to reuse the text or figures of this JoVE article
Request PermissionThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved