Un abonnement à JoVE est nécessaire pour voir ce contenu. Connectez-vous ou commencez votre essai gratuit.
Method Article
Synthèse de structures organométalliques à base de Zr fonctionnalisées au triazole et au tétrazole par échange de ligands post-synthétiques
* Ces auteurs ont contribué à parts égales
Dans cet article
Résumé
L’échange de ligands post-synthétiques (PSE) est un outil polyvalent et puissant pour installer des groupes fonctionnels dans des structures organométalliques (MOF). L’exposition des MOF à des solutions contenant des ligands fonctionnalisés au triazole et au tétrazole peut incorporer ces fractions hétérocycliques dans les Zr-MOF par des procédés PSE.
Résumé
Les structures organométalliques (MOF) sont une classe de matériaux poreux formés par des liaisons de coordination entre des amas métalliques et des ligands organiques. Compte tenu de leur nature coordinatrice, les ligands organiques et le cadre de jambe de force peuvent être facilement retirés du MOF et/ou échangés avec d’autres molécules coordinatrices. En introduisant des ligands cibles dans des solutions contenant des MOF, des MOF fonctionnalisés peuvent être obtenus avec de nouvelles étiquettes chimiques via un processus appelé échange de ligands post-synthétique (PSE). PSE est une approche simple et pratique qui permet la préparation d’une large gamme de MOF avec de nouvelles étiquettes chimiques via un processus d’équilibre en solution solide. De plus, le PSE peut être effectué à température ambiante, ce qui permet l’incorporation de ligands thermiquement instables dans les MOF. Dans ce travail, nous démontrons l’aspect pratique de l’EPS en utilisant des ligands hétérocycliques contenant du triazole et du tétrazole pour fonctionnaliser un MOF à base de Zr (UiO-66; UiO = Université d’Oslo). Après digestion, les MOF fonctionnalisés sont caractérisés par diverses techniques, y compris la diffraction des rayons X en poudre et la spectroscopie par résonance magnétique nucléaire.
Introduction
Les structures organométalliques (MOF) sont des matériaux poreux tridimensionnels formés par des liaisons de coordination entre des amas métalliques et des ligands organiques multi-sujets. Les MOF ont attiré beaucoup d’attention en raison de leur porosité permanente, de leur faible densité et de leur capacité à associer des composants organiques et inorganiques, ce qui permet diverses applications 1,2. De plus, la vaste gamme de nœuds métalliques et de liants organiques à jambes de force offre aux MOF des combinaisons structurelles théoriquement illimitées. Même avec des structures de cadre identiques, les propriétés physiques et chimiques des MOF peuvent être modifiées par fonctionnalisation des ligands avec des étiquettes chimiques. Ce processus de modification offre une voie prometteuse pour adapter les propriétés des MOF à des applications spécifiques 3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
La pré-fonctionnalisation des ligands avant la synthèse MOF et la modification post-synthétique (PSM) des MOF ont été utilisées pour introduire et / ou modifier des groupes fonctionnels dans les ligands MOF10,11. En particulier, les MSP covalents ont fait l’objet d’études approfondies afin d’introduire de nouveaux groupes fonctionnels et de générer une gamme de MOF dotés de diverses fonctionnalités12,13,14. Par exemple, l’UiO-66-NH2 peut être converti en UiO-66-AM fonctionnalisés avec différentes longueurs de chaîne (allant de l’acétamide le plus court au plus long n-hexylamide) par des réactions d’acylation avec des halogénures d’acyle appropriés (tels que le chlorure d’acétyle ou le chlorure de n-hexanoyle)15,16. Cette approche démontre la polyvalence des MSP covalents pour introduire des groupes fonctionnels spécifiques sur les ligands MOF, ouvrant la voie à un large éventail d’applications.
En plus des MSP covalents, l’échange de ligands post-synthétique (ESP) est une stratégie prometteuse pour modifier les MOF (Figure 1). Étant donné que les MOF sont composés de liaisons de coordination entre les métaux et les ligands (tels que les carboxylates), ces liaisons de coordination peuvent être remplacées par des ligands externes à partir d’une solution. L’exposition des MOF à une solution contenant le ligand souhaité avec des étiquettes chimiques peut être incorporée dans les MOF via PSE 17,18,19,20,21,22. Étant donné que le processus PSE est accéléré par l’existence de solvants coordonnés, le phénomène est également appelé échange de ligand assisté par solvant (SALE)23,24. Cette approche offre une méthode flexible et facile pour fonctionnaliser les MOF avec une large gamme de ligands externes, permettant un large éventail d’applications 25,26,27,28,29.
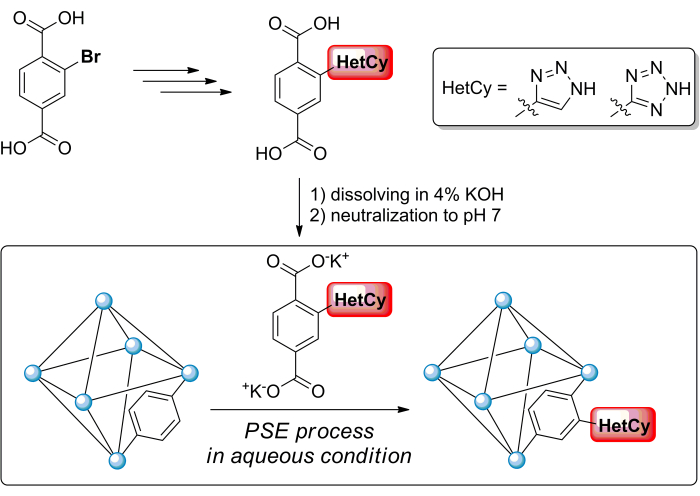
Figure 1 : Synthèse de ligands BDCH2fonctionnalisés au triazole et au tétrazole et préparation de MOF UiO-66 fonctionnalisés au triazole et au tétrazole par le biais de PSE. Veuillez cliquer ici pour voir une version agrandie de cette figure.
La progression du processus PSE peut être contrôlée en ajustant le rapport des ligands, la température d’échange et le temps. Notamment, le PSE à température ambiante peut être utilisé pour obtenir des MOF fonctionnalisés en échangeant des ligands d’une solution en solides MOF20. La stratégie PSE est particulièrement utile pour introduire à la fois des groupes fonctionnels thermiquement instables (tels que les groupes azido) et des groupes fonctionnels coordonnés (tels que les groupes phénol) dans les structures MOF18. En outre, la stratégie PSE a été appliquée à divers MOF présentant des variations de liaison métallique et de coordination. Cet échange est un processus universel dans la chimie des MOF30,31,32. Dans cette étude, nous présentons un protocole détaillé pour l’EPS afin d’obtenir des MOF fonctionnalisés à partir de MOF vierges et non fonctionnalisés, et nous fournissons une stratégie de caractérisation pour confirmer la fonctionnalisation réussie des MOF. Cette méthode démontre la polyvalence et la commodité de l’ESP pour modifier les MOF avec divers groupes fonctionnels.
L’acide benzène-1,4-dicarboxylique contenant du tétrazole (H2BDC-tétrazole)33 et l’acide benzène-1,4-dicarboxylique contenant du triazole (H2BDC-triazole) sont synthétisés comme ligands cibles et utilisés dans l’EPS des MOF UiO-66 pour obtenir de nouveaux MOF sans coordination contenant du triazole. Les triazoles et les tétrazoles possèdent tous deux des protons N-H acides sur leurs cycles hétérocycliques et peuvent se coordonner avec des cations métalliques, permettant ainsi leur utilisation dans la construction de MOF34,35. Cependant, il existe peu d’études sur l’incorporation de tétrazoles et de triazoles sans coordination dans les MOF et les structures connexes. Dans le cas des Zr-MOF fonctionnalisés au triazole, les MOF de type UiO-68 ont été étudiés aux propriétés photophysiques par synthèse solvothermique directe avec les fonctionnalités du benzotriazole36. Pour les Zr-MOF fonctionnalisés par tétrazole, la synthèse directe mixte a été utilisée33. Ces MOF fonctionnalisés à hétérocycles pourraient fournir des sites de coordination potentiels dans les pores MOF pour la catalyse, l’absorption moléculaire sélective par affinité de liaison et les applications liées à l’énergie, telles que la conduction de protons dans les piles à combustible.
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Protocole
Les réactifs nécessaires à la préparation des MOF et des ligands sont énumérés dans le tableau des matériaux.
1. Mise en place du processus d’échange de ligand post-synthétique (PSE)
- Sécher complètement les MOF UiO-66 présynthétisés sous vide pour éliminer tous les sels métalliques et ligands n’ayant pas réagi dans les pores, ainsi que les résidus de solvants restants pendant la nuit.
NOTE: Voir le dossier supplémentaire 1 pour la procédure de synthèse des MOF UiO-66. - Préparer des ligands fonctionnalisés, H 2 BDC-Triazole, etH2BDC-Tétrazole (voir le dossier supplémentaire 1 pour le processus de préparation; Figure supplémentaire 1 et Figure supplémentaire 2 pour caractérisation) à l’état isolé et complètement sèche sous vide pendant la nuit.
- Préparer une solution aqueuse d’hydroxyde de potassium (KOH) à 4 % en dissolvant l’hydroxyde de potassium dans de l’eau désionisée.
- Effectuer le procédé PSE dans des flacons à scintillation de 20 mL munis de bouchons en polypropylène (PP) (voir le tableau des matériaux).
- Mesurer le BDC-Triazole H 2 (23,3 mg, 0,1 mmole) ou H2BDC-Tétrazole (23,4 mg, 0,1 mmole) et placer dans le flacon de scintillation.
- Dissoudre le ligandH2BDCen solution aqueuse. Utilisez une pipette en verre pour transférer 1,0 mL de la solution aqueuse à 4 % de KOH dans le flacon à scintillation contenant du BDC-Triazole ou du BDC-Tétrazole.
ATTENTION : La solution aqueuse à 4% KOH est très basique. Évitez toute forme de contact et portez un équipement de protection individuelle. - Sonifier le mélange jusqu’à ce que tous les solides soient complètement dissous.
- Neutraliser la solution à pH 7. Utiliser une pipette en verre pour transférer la solution aqueuse d’acide chlorhydrique 1 M (HCl) sous agitation dans le flacon à scintillation contenant du dicarboxylate jusqu’à ce que le pH 7 soit atteint. Mesurez le pH soit par du papier pH (et sa couleur) ou un pH-mètre.
NOTE: Il est crucial de maintenir un pH de 7 pendant le processus d’échange, car les MOF sont généralement instables dans des conditions de base (>pH 7) et le ligand BDC n’est pas soluble dans des conditions acides (pH <7). Environ 1,5 mL de solution aqueuse HCl 1 M est nécessaire pour neutraliser la solution contenant du BDC-Triazole ou du BDC-Tétrazole. - Ajouter les MOF à la solution de dicarboxylate et incuber. Ajouter UiO-66 MOF (33 mg, 0,02 mmole) au flacon de scintillation contenant une solution de pH 7.
NOTE: À pH 7, les particules d’UiO-66 MOF ne sont pas solubles dans l’eau, ce qui entraîne leur suspension dans l’eau. - Incuber le flacon de scintillation contenant le MOF et le ligand dans un agitateur à 120 rpm et à température ambiante pendant 24 h.
NOTE: L’agitation peut être utilisée comme alternative à l’incubation par agitateur pour le procédé PSE. Cependant, il faut faire preuve de prudence, car le contact physique entre la barre d’agitation magnétique et les MOF peut entraîner la fissuration ou la rupture des particules MOF.
2. Isoler le MOF échangé et le processus de lavage
- Après incubation, isoler le MOF solide du mélange par centrifugation (1 166 x g, 5 min, température ambiante).
- Ajouter du méthanol frais (10 mL) au MOF solide obtenu et agiter le mélange pour former un mélange hétérogène afin de dissoudre les ligands BDC restants non échangés.
- Isoler le solide qui a été isolé par centrifugation (1 166 x g, 5 min, température ambiante).
- Répétez les étapes 2.2-2.3 deux fois de plus pour un total de trois cycles de lavage.
- Sécher complètement le solide MOF échangé sous vide pendant la nuit après le dernier lavage.
3. Caractérisation du MOF par diffraction des rayons X en poudre (PXRD)
- Transférer environ 10 mg du solide MOF échangé dans un porte-échantillon PXRD (voir le tableau des matériaux).
- Placez le porte-échantillon dans le diffractomètre.
- Collectez le motif PXRD (Figure 2) dans la plage 2θ comprise entre 5° et 30°.
- Comparez les données obtenues au MOF UiO-66 parent et au modèle simulé.
4. Caractérisation du MOF par résonance magnétique nucléaire (RMN) après digestion
- Transférer environ 30 mg du solide MOF échangé dans un flacon frais de 4 mL.
- Utiliser une micropipette pour transférer 400 μL de DMSO-d 6 dans l’échantillon MOF.
- Utiliser une micropipette pour transférer 200 μL de solution de 4,14 M NH4F/D2O à une suspension DMSO-d 6 de poudre MOF.
NOTE: Une solution aqueuse d’environ 40% HF peut être utilisée à la place de la solution NH4F/D2O. Dans ce cas, un pic significatif deH2Oest observé dans la RMN. Cependant, une digestion plus claire est possible dans le cas de la digestion HF.
ATTENTION : L’IC est hautement toxique pour l’organisme et le système nerveux central. Toute forme de contact doit être évitée, le travail doit être effectué dans une hotte et un équipement de protection individuelle doit être porté. - Sonifier le mélange hétérogène pendant 30 min jusqu’à ce que le MOF soit dissous dans le solvant mixte diméthylsulfoxyde (DMSO)-D2Oaprès digestion.
- Éliminer tout solide insoluble restant en filtrant la solution à travers un filtre à seringue en polyfluorure de vinylidène (PVDF) (Φ 13 mm, pores de 0,45 μm; voir le tableau des matériaux) tout en la transférant du flacon de 4 mL à un tube RMN.
- Placez le tube RMN dans l’appareil RMN. Recueillir les données RMN (Figure 3).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Résultats
La synthèse réussie de MOFs UiO-66 échangés, d’UiO-66-Triazole et d’UiO-66-Tetrazole a produit des solides microcristallins incolores. Les ligands H 2 BDC-Triazoleet H2BDC-Tétrazole présentaient également un état solide incolore. La méthode standard utilisée pour déterminer le succès de l’échange consistait à mesurer les modèles PXRD et à comparer la cristallinité de l’échantillon avec le MOF UiO-66 immaculé. La figure 2 montre les modèles PX...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Discussion
Le processus PSE avec des ligands BDC fonctionnalisés vers des MOF UiO-66 à base de Zr est une méthode simple et polyvalente pour obtenir des MOF avec des étiquettes chimiques. Le processus PSE est mieux conduit en milieu aqueux, nécessitant l’étape initiale de solvatation du ligand dans un milieu aqueux. Lors de l’utilisation de BDC présynthétisé avec des groupes fonctionnels, une dissolution directe dans un solvant basique, tel qu’une solution aqueuse à 4% KOH, est recommandée. Alternativement, le sel ...
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Déclarations de divulgation
Les auteurs n’ont rien à divulguer.
Remerciements
Cette recherche a été soutenue par le Programme de recherche scientifique fondamentale par l’intermédiaire de la Fondation nationale de recherche de Corée (NRF) financée par le ministère des Sciences et des TIC (NRF-2022R1A2C1009706).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
matériels
| Name | Company | Catalog Number | Comments |
| 2-Bromoterephthalic acid | BLD Pharm | BD5695 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Azidotrimethylsilane | Simga Aldrich | 155071 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) dichloride | TCI | B1667 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Copper(I) cyanide | Alfa-Aesar | 12135 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| Copper(I) iodide | Acros organics | 20150 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Digital Orbital Shaker | Daihan Scientific | SHO-1D | PSE |
| Formic Acid | Daejung chemical | F0195 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| Hybrid LC/Q-TOF system | Bruker BioSciences | maXis 4G | HR-MS |
| Lithum hydroxide monohydrate | Daejung chemical | 5087-4405 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Magnesium sulfate | Samchun chemical | M1807 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Methyl alcohol | Daejung chemical | M0584 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | Daejung chemical | D0552 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer-500 MHz | Bruker | AVANCE 500MHz | NMR |
| Polypropylene cap (22 mm, Cork-Backed Foil Lined) | Sungho Korea | 22-200 | material for digestion |
| Potassium cyanide | Alfa-Aesar | L13273 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| PVDF Synringe filter (13 mm, 0.45 µm) | LK Lab Korea | F14-61-363 | material for digestion |
| Scintillation vial (20 mL, borosilicate glass) | Sungho Korea | 74504-20 | material for digestion |
| Sodium azide | TCI | S0489 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Samchun chemical | S0343 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (1 M THF solution) | Acros organics | 20195 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Triethylamine | TCI | T0424 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Triethylamine hydrochloride | Daejung chemical | 8628-4405 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
| Trimethylsilyl-acetylene | Alfa-Aesar | A12856 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| Triphenylphosphine | TCI | T0519 | reagent for BDC-Triazole |
| X RAY DIFFRACTOMETER SYSTEM | Rigaku | MiniFlex 600 | PXRD |
| Zirconium(IV) chloride | Alfa-Aesar | 12104 | reagent for BDC-Tetrazole |
Références
- Zhou, H. -C., Long, J. R., Yaghi, O. M. Introduction to metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Reviews. 112 (2), 673-674 (2012).
- Furukawa, H., Cordova, K. E., O'Keefe, M., Yaghi, O. M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science. 341 (6149), 1230444(2013).
- Razavi, S. A. A., Morsali, A. Linker functionalized metal-organic frameworks. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 399, 213023(2019).
- Kim, D., Kang, M., Ha, H., Hong, C. S., Kim, M. Multiple functional groups in metal-organic frameworks and their positional regioisomerism. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 438, 213892(2021).
- Lu, W., et al. Tuning the structure and function of metal-organic frameworks via linker design. Chemical Society Reviews. 43 (16), 5561-5593 (2014).
- Xie, L. -H., Liu, X. -M., He, T., Li, J. -R. Metal-organic frameworks for the capture of trace aromatic volatile organic compounds. Chem. 4 (8), 1911-1927 (2018).
- Lv, X. -L., et al. Ligand rigidification for enhancing the stability of metal-organic frameworks. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 141 (26), 10283-10293 (2019).
- Robison, L., et al. Transient catenation in a zirconium-based metal-organic framework and its effect on mechanical stability and sorption properties. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 143 (3), 1503-1512 (2021).
- He, T., Kong, X. -J., Li, J. -R. Chemically stable metal-organic frameworks: rational construction and application expansion. Accounts of Chemical Research. 54 (15), 3083-3094 (2021).
- Kalaj, M., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic modification: an enabling technology for the advancement of metal-organic frameworks. ACS Central Science. 6 (7), 1046-1057 (2020).
- Mandal, S., Natarajan, S., Mani, P., Pankajakshan, A. Post-synthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks toward applications. Advanced Functional Materials. 31 (4), 2006291(2021).
- Wang, Z., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Society Reviews. 38 (5), 1315-1329 (2009).
- Tanabe, K. K., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks-a progress report. Chemical Society Reviews. 40 (2), 498-519 (2011).
- Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic methods for the functionalization of metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Reviews. 112 (2), 970-1000 (2012).
- Wang, Z., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic covalent modification of a neutral metal−organic framework. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 129 (41), 12368-12369 (2007).
- Garibay, S. J., Cohen, S. M. Isoreticular synthesis and modification of frameworks with the UiO-66 topology. Chemical Communications. 46 (41), 7700-7702 (2010).
- Kim, M., Cahill, J. F., Fei, H., Prather, K. A., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic ligand and cation exchange in robust metal-organic frameworks. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 134 (43), 18082-18088 (2012).
- Kim, M., Cahill, J. F., Su, Y., Prather, K. A., Cohen, S. M. Postsynthetic ligand exchange as a route to functionalization of 'inert' metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Science. 3 (1), 126-130 (2012).
- Taddei, M., Wakeham, R. J., Koutsianos, A., Andreoli, E., Barron, A. R. Post-synthetic ligand exchange in zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks: beware of the defects. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 57 (36), 11706-11710 (2018).
- Park, H., et al. Defect engineering into metal-organic frameworks for the rapid and sequential installation of functionalities. Inorganic Chemistry. 57 (3), 1040-1047 (2018).
- Kim, S., Lee, J., Jeoung, S., Moon, H. R., Kim, M. Surface-deactivated core-shell metal-organic framework by simple ligand exchange for enhanced size discrimination in aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Chemistry-A European Journal. 26 (34), 7568-7572 (2020).
- Lee, J., et al. Pore engineering of covalently connected metal-organic framework nanoparticle-mixed-matrix membrane composites for molecular separation. ACS Applied Nano Materials. 3 (9), 9356-9362 (2020).
- Karagiaridi, O., Bury, W., Mondloch, J. E., Hupp, J. T., Farha, O. K. Solvent-assisted linker exchange: an alternative to the de synthesis of unattainable metal-organic frameworks. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 53 (18), 4530-4540 (2014).
- Yu, D., et al. A solvent-assisted ligand exchange approach enables metal-organic frameworks with diverse and complex architectures. Nature Communications. 11, 927(2020).
- Lee, S. Y., et al. Design of ultra-thin nanosheet bimetallic NiCo MOF with binary ligand via solvent-assisted ligand exchange (SALE) reaction for high performance supercapacitors. Electrochimica Acta. 451, 142291(2023).
- Liao, W. -M., et al. Post-synthetic exchange (PSE) of UiO-67 frameworks with Ru/Rh half-sandwich units for visible-light-driven H2 evolution and CO2 reduction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 6 (24), 11337-11345 (2018).
- Islamoglu, T., et al. Postsynthetic tuning of metal-organic frameworks for targeted applications. Accounts of Chemical Research. 50 (4), 805-813 (2017).
- Lee, J., et al. Strategies in metal-organic framework-based catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols and recent progress. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society. 42 (3), 359-368 (2021).
- Kalaj, M., Prosser, K. E., Cohen, S. M. Room temperature aqueous synthesis of UiO-66 derivatives via postsynthetic exchange. Dalton Transactions. 49 (26), 8841-8845 (2020).
- Deria, P., et al. Beyond post-synthesis modification: evolution of metal-organic frameworks via building block replacement. Chemical Society Reviews. 43 (16), 5896-5912 (2014).
- Han, Y., Li, J. -R., Xie, Y., Guo, G. Substitution reactions in metal-organic frameworks and metal-organic polyhedral. Chemical Society Reviews. 43 (16), 5952-5981 (2014).
- Xu, M. -M., Chen, Q., Xie, L. -H., Li, J. -R. Exchange reactions in metal-organic frameworks: New advances. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 421, 213421(2020).
- Lee, D., et al. Uncoordinated tetrazole ligands in metal-organic frameworks for proton-conductivity studies. Bulletin of the Korean Chemical Society. 43 (7), 912-917 (2022).
- Han, B. -X., Jiang, Y. -F., Sun, X. -R., Li, Z. -F., Li, G. Proton conductive N-heterocyclic metal-organic frameworks. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 432, 213754(2021).
- Han, Z., Zhao, Y., Peng, J., Gómez-García, C. J. Unusual oxidation of an N-heterocycle ligand in a metal−organic framework. Inorganic Chemistry. 46 (14), 5453-5455 (2007).
- Wu, S., et al. Linker engineering toward full-color emission of UiO-68 type metal-organic frameworks. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 143 (28), 10547-10552 (2021).
- Hamzah, H. A., et al. Post-synthetic mannich chemistry on metal-organic frameworks: system-specific reactivity and functionality-triggered dissolution. Chemistry-A European Journal. 24 (43), 11094-11102 (2018).
- Oozeerally, R., et al. Systematic modification of UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks for glucose conversion into 5-hydroxymethyl furfural in water. ChemCatChem. 13 (10), 2517-2529 (2021).
- Hamzah, H. A., Crickmore, T. S., Rixason, D., Burrows, A. D. Post-synthetic modification of zirconium metal-organic frameworks by catalyst-free aza-Michael additions. Dalton Transactions. 47 (41), 14491-14496 (2018).
Access restricted. Please log in or start a trial to view this content.
Réimpressions et Autorisations
Demande d’autorisation pour utiliser le texte ou les figures de cet article JoVE
Demande d’autorisationThis article has been published
Video Coming Soon