16.9 : טירציה של חומצה רב פרוטית
A polyprotic acid contains more than one ionizable hydrogen and undergoes a stepwise ionization process. If the acid dissociation constants of the ionizable protons differ sufficiently from each other, then the titration curve for such polyprotic acid generates a distinct equivalence point for each of its ionizable hydrogens. Therefore, titration of a diprotic acid results in the formation of two equivalence points, whereas the titration of a triprotic acid results in the formation of three equivalence points on the titration curve.
Carbonic acid, H2CO3, is an example of a weak diprotic acid. The first ionization of carbonic acid yields hydronium ions and bicarbonate ions in small amounts.
First ionization:
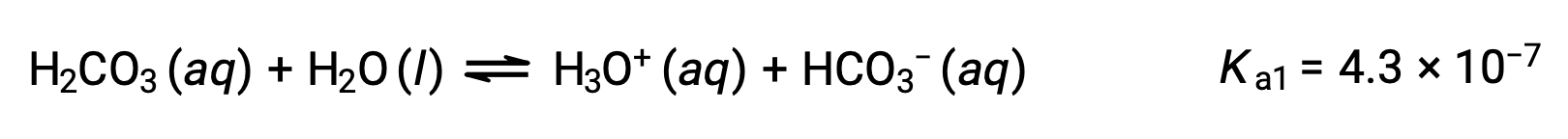
The bicarbonate ion can also act as an acid. It ionizes and forms hydronium ions and carbonate ions in even smaller quantities.
Second ionization:
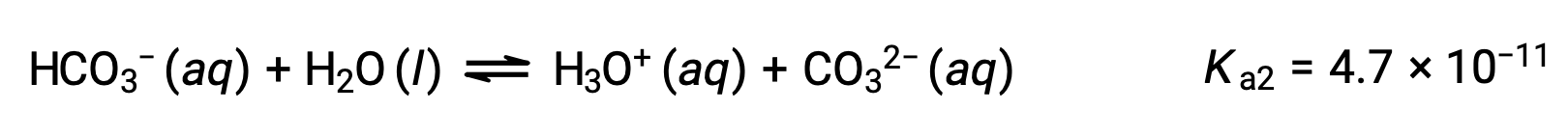
The Ka1 is larger than the Ka2 by a factor of 104. Therefore, when H2CO3 is titrated with a strong base like NaOH, it produces two distinct equivalence points for each ionizable hydrogen.
Phosphoric acid, a triprotic acid, ionizes in three steps:
First ionization:
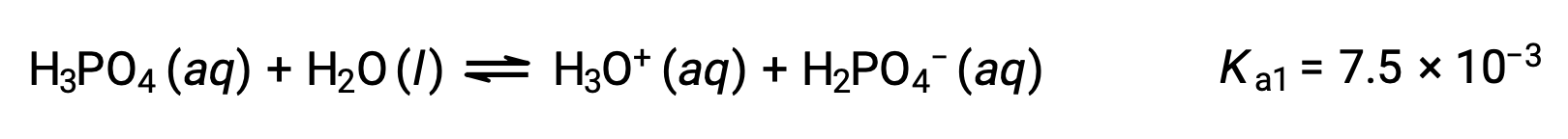
Second ionization:
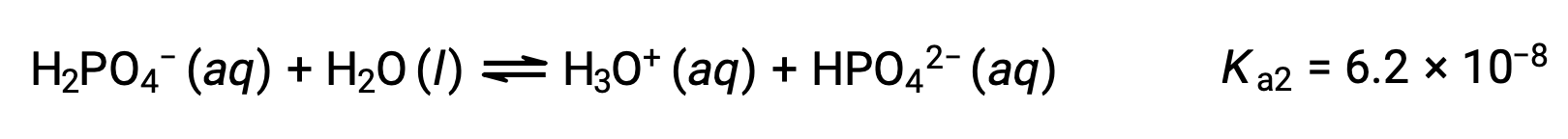
Third ionization:
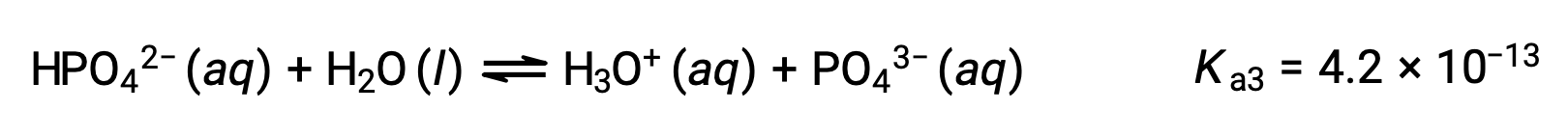
When H3PO4 is titrated with a strong base like KOH, it produces three equivalence points for each ionizable hydrogen. However, as HPO42− is a very weak acid, the third equivalence point is not easily discernible on the titration curve.
This text is adapted from Openstax, Chemistry 2e, Section 14.5: Polyprotic Acids.
From Chapter 16:

Now Playing
16.9 : טירציה של חומצה רב פרוטית
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
95.6K Views

16.1 : אפקט היון המשותף
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
40.8K Views

16.2 : בופרים
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
163.2K Views

16.3 : משואת הנדרסון-האסבלך
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
67.9K Views

16.4 : חישוב שינוייpH בתמיסת בופר
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
52.4K Views

16.5 : יעילות בופר
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
48.3K Views

16.6 : חישובי טיטרציה: חומצה חזקה- בסיס חזק
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
28.9K Views

16.7 : חישובי טיטרציה: חומצה חלשה- בסיס חלש
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
43.7K Views

16.8 : אינדיקטורים
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
47.7K Views

16.10 : שיווי משקל מסיסות
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
51.8K Views

16.11 : גורמים המשפיעים על מסיסות
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
32.9K Views

16.12 : יצירת יוני קומפלקס
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
23.0K Views

16.13 : שיקוע של יוני
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
27.4K Views

16.14 : אנליזה איכותית
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
20.0K Views

16.15 : עקומות טירציית חומצה-בסיס
Acid-base and Solubility Equilibria
126.1K Views
Copyright © 2025 MyJoVE Corporation. All rights reserved